-
黑马C++ 01 基础 —— 数据类型、运算符、循环
01 变量
- 变量存在的意义:方便管理内存空间
- 语法:数据类型 变量名 = 变量初始值 int a = 10
#includeusing namespace std; //变量存在的意义:方便管理内存空间 //语法:数据类型 变量名 = 变量初始值 int main() { int a = 10; cout << "a=" << a << endl; system("pause"); return 0; } - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
02 常量
-
#define 宏常量:
#define 常量名 常量值- 通常在文件上方定义,表示一个常量
-
const 修饰的变量
const 数据类型 常量名 = 常量值- 通常在变量定义前加关键字const,修饰该变量为常量,不可修改
#includeusing namespace std; //常量定义方式 //1、 #define 宏常量 //2、 const 修饰的变量 //1、#define 宏常量 #define Day 7 int main() { //Day = 14;//报错,Day是常量,一旦修改就报错 cout << "一周总共有:" << Day << " 天" << endl; //2、const 修饰的变量 const int month = 12; // month = 24;//报错,const修饰的变量成为常量 cout << "一年总共有:" << month << " 月" << endl; system("pause"); return 0; } - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
03 标识符命名
标识符命名规则
-
不可以是关键字
-
由首字母、数字、下划线构成
-
第一个字符只能是字母或者下划线
-
标识符区分大小写
建议:给变量取名的时候,最好能够做到见名知意
04 数据类型
整型

数据类型 占用空间 取值范围 short(短整型) 2字节 (-2^15 ~ 2^15-1) int(整型) 4字节 (-2^31 ~ 2^31-1) long(长整形) Windows为4字节,Linux为4字节(32位),8字节(64位) (-2^31 ~ 2^31-1) long long(长长整形) 8字节 (-2^63 ~ 2^63-1) sizeof关键字
- 利用sizeof求出数据类型占用内存大小
- 语法:sizeof(数据类型/变量)
- 整型:short(2) int(4) long(4) long long (8)
#includeusing namespace std; int main() { //整型:short(2) int(4) long(4) long long (8) //利用sizeof求出数据类型占用内存大小 //语法:sizeof(数据类型 / 变量) short num1 = 10; cout << "num1 占用的内存空间: " << sizeof(num1) << endl; cout << "short 占用的内存空间: " << sizeof(short) << endl; //写成sizeof(short)也可以 int num2 = 10; cout << "int 占用的内存空间: " << sizeof(int) << endl; long num3 = 10; cout << "long 占用的内存空间: " << sizeof(long) << endl; long long num4 = 10; cout << "long long 占用的内存空间: " << sizeof(long long) << endl; system("pause"); return 0; } - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
实型(浮点型)
浮点型变量分为两种:
- 单精度 float 4字节
- 双精度 double 8字节
- 默认情况下 输出一个小数,会显示出6位有效数字
数据类型 占用空间 有效数字范围 float 4字节 7位有效数字 double 8字节 15~16位有效数字 int main() { float f1 = 3.14f; double d1 = 3.14; cout << f1 << endl; cout << d1<< endl; cout << "float sizeof = " << sizeof(f1) << endl;// 4个字节 cout << "double sizeof = " << sizeof(d1) << endl;// 8个字节 //科学计数法 float f2 = 3e2; // 3 * 10 ^ 2 cout << "f2 = " << f2 << endl; float f3 = 3e-2; // 3 * 0.1 ^ 2 cout << "f3 = " << f3 << endl; system("pause"); return 0; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
字符型
大小为1个字节
字符型变量用于显示单个字符:char ch = ‘a’;`注意1:在显示字符型变量时,用单引号将字符括起来,不要用双引号
注意2:单引号内只能有一个字符,不可以是字符串- C和C++中字符型变量只占用1个字节。
- 字符型变量不是把字符本身放到内存中存储,而是将对应的ASCII编码放入到存储单元
- a —— 97 A —— 65
#includeusing namespace std; int main() { //1、字符型变量创建方式 char ch = 'a'; cout << ch << endl; //2、字符型变量所占内存大小 cout << sizeof(char) << endl; //3、字符型变量常见错误 //ch = "abcde"; //错误,不可以用双引号,创建字符型变量时,要用单引号 //ch = 'abcde'; //错误,单引号内只能引用一个字符 //4、字符型变量对应的ASCII编码 // a —— 97 A —— 65 cout << (int)ch << endl; //查看字符a对应的ASCII码,97 ch = 97; //可以直接用ASCII给字符型变量赋值 cout << ch << endl; // a system("pause"); return 0; } - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
转义字符
转义字符 含义 ASCII码值(十进制) \a 警报 007 \b 退格(BS) ,将当前位置移到前一列 008 \f 换页(FF),将当前位置移到下页开头 012 \n 换行(LF) ,将当前位置移到下一行开头 010 \r 回车(CR) ,将当前位置移到本行开头 013 \t 水平制表(HT) (跳到下一个TAB位置) 009 \v 垂直制表(VT) 011 \\ 代表一个反斜线字符"" 092 ’ 代表一个单引号(撇号)字符 039 " 代表一个双引号字符 034 ? 代表一个问号 063 \0 数字0 000 \ddd 8进制转义字符,d范围0~7 3位8进制 \xhh 16进制转义字符,h范围09,af,A~F 3位16进制 - 换行符 \n:起到换行的作用
- 反斜杠 \ :两个反斜杠输出一个反斜杠
- 水平制表符 \t :整齐输出数据,数值和\t加起来有8个空格
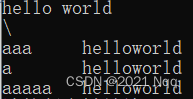
#includeusing namespace std; int main() { //转义字符 //换行符 \n cout << "hello world\n"; //反斜杠 \\ cout << "\\" << endl;//两个反斜杠输出一个反斜杠 //水平制表符 \t 整齐输出数据 cout << "aaa\thelloworld" << endl; cout << "a\thelloworld" << endl; cout << "aaaaa\thelloworld" << endl; system("pause"); return 0; } - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
结果
字符串型(两种风格)
C风格字符串:
char 变量名[] = "字符串值"- C风格的字符串要用双引号括起来
char str[] = "hello world"; cout << str << endl;- 1
- 2
C++风格字符串:
string 变量名 = "字符串值"- C++风格字符串,需要加入头文件 #include
string str2 = "hello world"; cout << str2 << endl;- 1
- 2
#include#include //C++风格的字符串要包含头文件 using namespace std; int main() { //1.C风格字符串 //注意:char字符串名[];等号后用双引号包含字符串; //注意事项1 char 字符串名[] //注意事项2 等号后面 要用双引号 包含起来字符串 char str[] = "hello world"; cout << str << endl; //2.C++风格字符串 //包含头文件#include string str2 = "hello world"; cout << str2 << endl; system("pause"); return 0; } - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
bool类型
bool类型占1个字节大小
#includeusing namespace std; int main() { //1.创建bool数据类型 bool flag = true;// true 代表真 cout << flag << endl; // 1 flag = false;// false 代表假 cout << flag << endl; // 0 //本质上 1代表真,0代表假 //2.查看bool类型所占内存空间 cout << "size of bool = " << sizeof(bool) << endl; //1 system("pause"); return 0; } - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
数据输入
从键盘获取数据
cin >> 变量#include#include // C++ string头文件 using namespace std; int main() { //1.整型输入 int a = 0; cout << "请输入整型变量:" << endl; cin >> a; cout << "整型变量a = " << a << endl; //2.浮点型输入 float f = 3.14f; cout << "请输入浮点型变量:" << endl; cin >> f; cout << "浮点型变量f = " << f << endl; //3.字符型输入 char ch = 0; cout << "请输入字符型变量:" << endl; cin >> ch; cout << "字符型变量ch = " << ch << endl; //4.字符串型输入 string str; cout << "请输入字符串型变量:" << endl; cin >> str; cout << "字符串变量str = " << str << endl; //5.布尔类型输入 bool flag = true; cout << "请输入布尔型变量:" << endl; cin >> flag;//bool类型,只要是非0的值都代表了真 cout << "布尔型变量flag = " << flag << endl; system("pause"); return 0; } - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
05 运算符
运算符类型 作用 算术运算符 用于处理四则运算 赋值运算符 用于将表达式的值赋给变量 比较运算符 用于表达式的比较,并返回一个真值或假值 逻辑运算符 用于根据表达式的值返回真值或假值 算术运算符
运算符 术语 示例 结果 + 正号 +3 3 - 负号 -3 -3 + 加 10 + 5 15 - 减 10 - 5 5 * 乘 10 * 5 50 / 除 10 / 5 2 % 取模(取余) 10 % 3 1 ++ 前置递增 a=2; b=++a; a=3; b=3; ++ 后置递增 a=2; b=a++; a=3; b=2; – 前置递减 a=2; b=–a; a=1; b=1; – 后置递减 a=2; b=a–; a=1; b=2; 加减乘除
- 在除法运算中,除数不能为0
//加减乘除 int main() { int a1 = 10; int b1 = 3; cout << a1 + b1 << endl; cout << a1 - b1 << endl; cout << a1 * b1 << endl; cout << a1 / b1 << endl; //两个整数相除结果依然是整数 int a2 = 10; int b2 = 20; cout << a2 / b2 << endl; int a3 = 10; int b3 = 0; //cout << a3 / b3 << endl; //报错,除数不可以为0 //两个小数可以相除 double d1 = 0.5; double d2 = 0.25; cout << d1 / d2 << endl; system("pause"); return 0; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
取模

- 只有整数有取模运算
- 取模运算本质就是求余数
//取模 int main() { int a1 = 10; int b1 = 3; cout << 10 % 3 << endl; int a2 = 10; int b2 = 20; cout << a2 % b2 << endl; int a3 = 10; int b3 = 0; //cout << a3 % b3 << endl; //取模运算时,除数也不能为0 //两个小数不可以取模 double d1 = 3.14; double d2 = 1.1; //cout << d1 % d2 << endl; system("pause"); return 0; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
自加自减
- 前置递增先对变量进行++,再计算表达式,后置递增相反
#includeusing namespace std; int main() { //后置递增 int a = 10; a++; //等价于a = a + 1 cout << a << endl; // 11 //前置递增 int b = 10; ++b; cout << b << endl; // 11 //区别 //前置递增:先对变量进行++,再计算表达式 int a2 = 10; int b2 = ++a2 * 10; cout << "a2 = " << a2 << endl;// 11 cout << "b2 = " << b2 << endl;// 110 //后置递增:先计算表达式,后对变量进行++ int a3 = 10; int b3 = a3++ * 10; cout << "a3 = " << a3 << endl;// 11 cout << "b3 = " << b3 << endl;// 100 system("pause"); return 0; } - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
赋值运算符
运算符 术语 示例 结果 = 赋值 a=2; b=3; a=2; b=3; += 加等于 a=0; a+=2; a=2; -= 减等于 a=5; a-=3; a=2; *= 乘等于 a=2; a*=2; a=4; /= 除等于 a=4; a/=2; a=2; %= 模等于 a=3; a%2; a=1; int main() { //赋值运算符 // = int a = 10; a = 100; cout << "a = " << a << endl; // += a = 10; a += 2; // a = a + 2; cout << "a = " << a << endl; // -= a = 10; a -= 2; // a = a - 2 cout << "a = " << a << endl; // *= a = 10; a *= 2; // a = a * 2 cout << "a = " << a << endl; // /= a = 10; a /= 2; // a = a / 2; cout << "a = " << a << endl; // %= a = 10; a %= 2; // a = a % 2; cout << "a = " << a << endl; system("pause"); return 0; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
比较运算符
- 用于表达式的比较,并返回一个真值或假值
运算符 术语 示例 结果 == 相等于 4 == 3 0 != 不等于 4 != 3 1 < 小于 4 < 3 0 > 大于 4 > 3 1 <= 小于等于 4 <= 3 0 >= 大于等于 4 >= 1 1 #includeusing namespace std; int main() { int a = 10; int b = 20; // == cout << (a == b) << endl; // 0 // != cout << (a != b) << endl; // 1 // > cout << (a > b) << endl; // 0 // < cout << (a < b) << endl; // 1 // >= cout << (a >= b) << endl; // 0 // <= cout << (a <= b) << endl; // 1 system("pause"); return 0; } - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
逻辑运算符
运算符 术语 示例 结果 ! 非 !a 如果a为假,则!a为真; 如果a为真,则!a为假。 && 与 a && b 如果a和b都为真,则结果为真,否则为假。 || 或 a || b 如果a和b有一个为真,则结果为真,二者都为假时,结果为假。 - 逻辑 —— 非
//逻辑运算符 --- 非 int main() { int a = 10; cout << !a << endl; // 0 cout << !!a << endl; // 1 system("pause"); return 0; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 逻辑 —— 与

//逻辑运算符 --- 与 int main() { int a = 10; int b = 10; cout << (a && b) << endl;// 1 a = 10; b = 0; cout << (a && b) << endl;// 0 a = 0; b = 0; cout << (a && b) << endl;// 0 system("pause"); return 0; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 逻辑 —— 或

//逻辑运算符 --- 或 int main() { int a = 10; int b = 10; cout << (a || b) << endl;// 1 a = 10; b = 0; cout << (a || b) << endl;// 1 a = 0; b = 0; cout << (a || b) << endl;// 0 system("pause"); return 0; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
06 程序结构
选择结构
- 依据条件是否满足,有选择的执行相应功能
多行if语句
#includeusing namespace std; int main() { int score = 0; cout << "请输入考试分数:" << endl; cin >> score; if (score > 600) { cout << "我考上了一本大学" << endl; } else { cout << "我未考上一本大学" << endl; } system("pause"); return 0; } - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
嵌套if语句
#includeusing namespace std; int main() { //提示用户输入一个高考考试分数,根据分数做如下判断 //如果大于600分视为考上一本,大于500分考上二本,大于400考上三本,其余视为未考上本科; //在一本分数中,如果大于700分,考入北大,大于650分,考入清华,大于600考入人大。 int score = 0; cout << "请输入高考分数:" << endl; cin >> score; cout << "输入的分数为:" << score << endl; if (score > 600) { cout << "考入一本" << endl; if (score > 700) { cout << "考入北大" << endl; } else if (score > 650) { cout << "考入清华" << endl; } else { cout << "考入人大" << endl; } } else if (score > 500) { cout << "考入二本" << endl; } else if (score > 400) { cout << "考入三本" << endl; } else { cout << "未考上" << endl; } system("pause"); return 0; } - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
练习:三只小猪称重
有三只小猪ABC,请分别输入三只小猪的体重,并且判断哪只小猪最重?
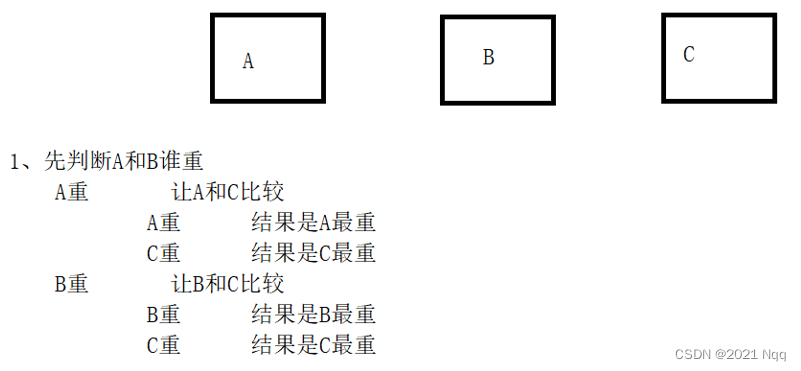
#includeusing namespace std; int main() { //有三只小猪ABC,请分别输入三只小猪的体重,并且判断哪只小猪最重 //1.创建3只小猪的体重变量 int num1 = 0; int num2 = 0; int num3 = 0; //2.让用户输入三只小猪的重量 cout << "请输入小猪A的体重" << endl; cin >> num1; cout << "请输入小猪B的体重" << endl; cin >> num2; cout << "请输入小猪C的体重" << endl; cin >> num3; cout << "小猪A的体重为:" << num1 << endl; cout << "小猪B的体重为:" << num2 << endl; cout << "小猪C的体重为:" << num3 << endl; //3.判断哪只最重 //先判断A和B的重量 if (num1 > num2) //A比B重 { if (num1 > num3) //A比C重 { cout << "小猪A最重" << endl; } else //C比A重 { cout << "小猪C最重" << endl; } } else //B比A重 { if (num2 > num3) //B比C重 { cout << "小猪B最重" << endl; } else //C比B重 { cout << "小猪C最重" << endl; } } system("pause"); return 0; } - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
三目运算
表达式1 ? 表达式2 :表达式3
如果表达式1的值为真,执行表达式2,并返回表达式2的结果;
如果表达式1的值为假,执行表达式3,并返回表达式3的结果。#includeusing namespace std; int main() { //三目运算符 //创建a,b,c,将变量大的值赋值给变量c //将a和b作比较,将变量大的值赋值给变量c int a = 10; int b = 20; int c = 0; c = a > b ? a : b; cout << "c = " << c << endl;// c = b 为20 //C++中三目运算符返回的是变量,可以继续赋值 (a > b ? a : b) = 100; cout << "a = " << a << endl;// 10 cout << "b = " << b << endl;// 100 cout << "c = " << c << endl;// 20 cout << "hello world" << endl; system("pause"); return 0; } - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
switch语句
表达式
switch(表达式) { case 结果1:执行语句;break; case 结果2:执行语句;break; ... default:执行语句;break; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
if和switch的区别
- switch的缺点:判断时候只能是整型或者字符型,不可以是一个区间
- switch的优点:结构清晰,执行效率高
#includeusing namespace std; int main() { //请给电影评分 //10 ~ 9 经典 // 8 ~ 7 非常好 // 6 ~ 5 一般 // 5分以下 烂片 //1.提示用户给电影打分 cout << "请给电影打分" << endl; //2.用户开始进行打分 int score = 0; cin >> score; cout << "您打的分数为:" << score << endl; //3.根据用户输入的分数提示用户最后的结果 switch (score) { case 10: case 9: cout << "经典" << endl; break;// 退出当前分支 case 8: cout << "非常好" << endl; break; case 7: case 6: cout << "一般" << endl; break; default://以上这些选择都没有选到 cout << "烂片" << endl; break; } //if和switch的区别 //switch的缺点:判断时候只能是整型或者字符型,不可以是一个区间 //switch的优点:结构清晰,执行效率高 system("pause"); return 0; } - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
循环结构
while循环
#includeusing namespace std; int main() { //while循环 //屏幕中打印0~9打印 int num = 0; while (num < 10) { cout << "num = " << num << endl; num++; } system("pause"); return 0; } - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
while循环练习:猜数字

添加随机数种子
//time系统时间文件的包含 #include//添加随机数种子,作用:利用当前系统时间生成随机数,防止每次随机数都一样 srand((unsigned int)time(NULL)); //1.系统生成随机数,rand()%100——生成0~99的随机数 int num = rand() % 100 + 1; //rand()%100+1 生成 1~100 的随机数 - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
while猜测
#includeusing namespace std; //time系统时间文件的包含 #include int main() { //添加随机数种子,作用:利用当前系统时间生成随机数,防止每次随机数都一样 srand((unsigned int)time(NULL)); //1.系统生成随机数,rand()%100——生成0~99的随机数 int num = rand() % 100 + 1; //rand()%100+1 生成 1~100 的随机数 //cout << num << endl; //2.玩家进行猜测 int val = 0; //玩家输入的数据 while (1) { cin >> val; //3.判断玩家的猜测 if (val > num) { cout << "猜测过大" << endl; } else if (val < num) { cout << "猜测过小" << endl; } else { cout << "猜对了" << endl; //猜对 退出游戏 break; //break可以利用当前关键字退出当前循环 } } //猜错 提示猜的结果 过大或者过小 重新返回第2步 system("pause"); return 0; } - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
do while循环
- 与while循环区别在于,do…while先执行一次循环语句,再判断循环条件
#includeusing namespace std; int main() { //do while 语句 int num = 0; do { cout << "num = " << num << endl; num++; } while (num < 10); //do while和while的区别是在于do while 会先执行一次循环 system("pause"); return 0; } - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
do while循环练习:水仙花数
案例描述:水仙花数是指一个 3 位数,它的每个位上的数字的 3次幂之和等于它本身
例如:1^3 + 5^3+ 3^3 = 153
请利用do…while语句,求出所有3位数中的水仙花数
for循环
- for循环中的表达式,要用分号进行分隔
for(起始表达式;条件表达式;末尾循环体) { 循环语句; }
#includeusing namespace std; int main() { //for循环 //数字0打印到数字9 int i = 0; for (; ;) { if (i >= 10) { break; } cout << i << endl; i++; } system("pause"); return 0; } - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
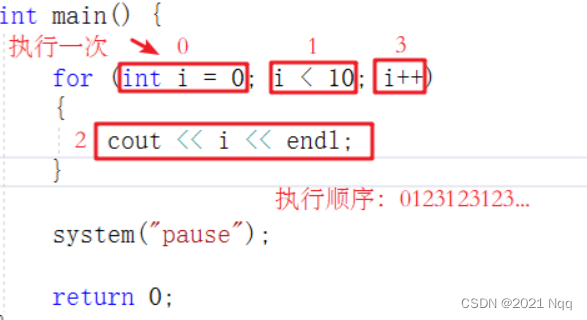
#includeusing namespace std; int main() { //for循环 //数字0打印到数字9 for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { cout << i << endl; } system("pause"); return 0; } - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 详解
for循环练习:敲桌子
案例描述:从1开始数到数字100, 如果数字个位含有7,或者数字十位含有7,或者该数字是7的倍数,我们打印敲桌子,其余数字直接打印输出。
- 分析

#includeusing namespace std; int main() { //敲桌子 //1、输出1~100数字 for (int i = 1; i <= 100; i++) { //2、从100个数字中找到特殊数字,打印“敲桌子” //如果是7的倍数、个位有7、或者十位有7,打印敲桌子 if (i % 7 == 0 || i % 10 == 7 || i / 10 == 7) // 如果是特殊数字,打印敲桌子 { cout << "敲桌子" << endl; } else // 如果不是特殊数字,打印数字 { cout << i << endl; } } } - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
嵌套循环
- 在循环体中再嵌套一层循环
- 在屏幕中打印如下图片,就需要利用嵌套循环

#includeusing namespace std; int main() { //利用嵌套循环实现星图 //打印一行星图 for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) //做10次操作下面的操作 { for (int j = 0; j < 10; j++) { cout << "* "; } cout << endl;//做换行处理 } system("pause"); return 0; } - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
嵌套循环练习:乘法口诀表
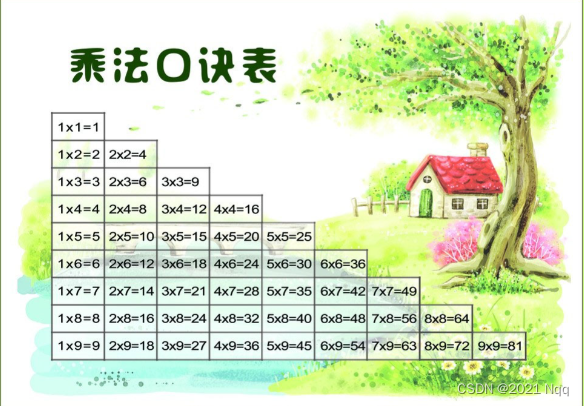
- 分析

#includeusing namespace std; //列数<=当前行数 int main() { //乘法口诀表 列数*行数=结果 列数<=当前行数 //打印行数 for (int i = 1; i <= 9; i++) //行数 { //cout << i << endl; for (int j = 1; j <= i; j++) //列数 { cout << j << " * " << i << " = " << j * i << "\t"; } cout << endl; } } - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
跳转语句
break语句
break使用的时机:
- 出现在switch条件语句中,作用是终止case并跳出switch
- 出现在循环语句中,作用是跳出当前的循环语句
- 出现在嵌套循环中,跳出最近的内层循环语句
#includeusing namespace std; int main() { //出现在switch条件语句中,作用是终止case并跳出switch //出现在循环语句中,作用是跳出当前的循环语句 //出现在嵌套循环中,跳出最近的内层循环语句 //1.出现在switch中 cout << "请选择副本难度" << endl; cout << "1.普通" << endl; cout << "2.中等" << endl; cout << "3.困难" << endl; int select = 0; //创建选择结果的变量 cin >> select; //等待用户的输入 switch (select) { case 1: cout << "您选择的是普通难度" << endl; break; case 2: cout << "您选择的是中等难度" << endl; break; case 3: cout << "您选择的是困难难度" << endl; break; default: //默认情况下输入 break; } //2.出现在循环语句 for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { //如果i等于5,退出循环,不再打印 if (i == 5) { break; //退出循环 } cout << i << endl; } //3.出现在嵌套循环语句中 for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) //做10次操作下面的操作 { for (int j = 0; j < 10; j++) { if (j == 5) { break; //退出内层循环,即影响j } cout << "* "; } cout << endl;//做换行处理 } system("pause"); return 0; } - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
continue语句

- 在循环语句中,跳过本次循环中余下尚未执行的语句,继续执行下一次循环
#includeusing namespace std; //continue:执行到本行,就不再执行后面的代码,而执行下一次循环 int main() { //continue语句 for (int i = 0; i <= 100; i++) { //奇数输出,偶数不输出 if (i % 2 == 0) { continue; //筛选条件,执行到此就不再向下执行,执行下一次循环 //break会退出循环,continue不会 } cout << i << endl; } system("pause"); return 0; } - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
-
相关阅读:
Linux Debian12使用podman安装pikachu靶场环境
【ML】李宏毅三:梯度下降&分类(高斯分布)
【Linux】多线程
多维时序 | MATLAB实现SSA-CNN-BiLSTM-Attention多变量时间序列预测(SE注意力机制)
简单了解一下:NodeJS的fs文件系统
Less教程及常用的操作
「高效程序员的修炼」代码版本管理工具 Git 用起来 01 Git 基础
UDP的可靠性传输2
精品基于PHP实现的好物优购商城|电商小程序
如何找到合适代理类型?为您多角度剖析!
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_42731062/article/details/126275676