-
NLP之无监督方式构建词库
一、数据介绍及处理
本文以电商领域的商品名称为语料进行实验,来寻找未登录词。
首先,将json格式的数据,提取其goods_name列,写入到txt文件中。import pandas as pd """ 将数据中的goods_name列与search_value列进行去重后再分别写入到txt """ class DataConvert(object): def __init__(self, file_input_name, file_corpus, file_searchValue): self.file_input_name = file_input_name self.file_corpus = file_corpus self.file_searchValue = file_searchValue def run(self): # 读取原始数据 # lines=True:文件的每一行为一个完整的字典,默认是一个列表中包含很多字典 input_file = pd.read_json(self.file_input_name, lines=True) # 选定需要操作的两列,并进行去重 goods_names = input_file.loc[:, 'goods_name'].dropna().drop_duplicates().tolist() search_values = input_file.loc[:, 'search_value'].dropna().drop_duplicates().tolist() # 将这两列写入到输出文件中 with open(self.file_corpus, "w", encoding="utf-8") as f1: for goods_name in goods_names: try: f1.write(goods_name) f1.write("\n") except: print(goods_name) f1.close() with open(self.file_searchValue, "w", encoding="utf-8") as f2: for search_value in search_values: f2.write(search_value) f2.write("\n") f2.close()- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
得到的file_corpus格式如下:

二、寻找未登录词
1.统计语料库中的词信息
统计语料库中出现单字,双字的频率,前后链接的字相关信息;
#!usr/bin/env python # -*- coding:utf-8 -*- """ 统计语料库中出现单字,双字的频率,前后链接的字相关信息; """ import re import codecs import json import os # \u4E00-\u9FD5表示所有汉字 # a-zA-Z0-9表示26个英文字母与数字 # -+#&\._/ \(\) \~\'表示常用符号 # \u03bc\u3001 \uff08\uff09 \u2019:表示特殊字符,一些程式码 re_han = re.compile("([\u4E00-\u9FD5a-zA-Z0-9-+#&\._/\u03bc\u3001\(\)\uff08\uff09\~\'\u2019]+)", re.U) class Finding(object): def __init__(self, file_corpus, file_count, count): self.file_corpus = file_corpus self.file_count = file_count self.count = count def split_text(self, sentence): """ 找到每个商品名称中符合正则表达式的子串,以列表形式返回 :param sentence: :return: """ # re.findall():在字符串中找到正则表达式所匹配的所有子串,并返回一个列表 seglist = re_han.findall(sentence) return seglist def count_word(self, seglist, k): """ 遍历每个子串,返回窗口对应的词与前后各一个词 :param seglist: 商品名称的子串列表 :param k: 窗口大小 :return: """ for words in seglist: ln = len(words) i = 0 j = 0 if words: while 1: j = i + k if j <= ln: word = words[i:j] if i == 0: lword = 'S' else: lword = words[i - 1:i] if j == ln: rword = 'E' else: rword = words[j:j + 1] i += 1 yield word, lword, rword else: break def find_word(self): """ :return: """ # 读取语料数据 input_data = codecs.open(self.file_corpus, 'r', encoding='utf-8') dataset = {} # enumerate将可迭代对象转化为索引与数据的格式,起始下标为1 for lineno, line in enumerate(input_data, 1): try: line = line.strip() # 找到每个商品名称中符合正则表达式的子串,以列表形式返回 seglist = self.split_text(line) # count_word:遍历每个子串,返回窗口对应的词与前后各一个词 # 遍历这三个词,[[], {}, {}]分别记录窗口对应的词出现的个数,前一个词及出现个数,后一个词及出现个数 for w, lw, rw in self.count_word(seglist, self.count): if w not in dataset: dataset.setdefault(w, [[], {}, {}]) dataset[w][0] = 1 else: dataset[w][0] += 1 if lw: dataset[w][1][lw] = dataset[w][1].get(lw, 0) + 1 if rw: dataset[w][2][rw] = dataset[w][2].get(rw, 0) + 1 except: pass self.write_data(dataset) def write_data(self, dataset): """ 将统计结果写入到字典中 :param dataset: :return: """ output_data = codecs.open(self.file_count, 'w', encoding='utf-8') for word in dataset: output_data.write(word + '\t' + json.dumps(dataset[word], ensure_ascii=False, sort_keys=False) + '\n') output_data.close()- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
这一步会生成两个文件,分别是
count_one.txt

count_two.txt文件。

2.利用互信息熵得到初始化词库
对统计出的单字和双字的结果,使用互信熵,选择大于阈值K=的词加入词库,作为初始词库。在计算机领域,更常用的是点间互信息,点间互信息计算了两个具体事件之间的互信息。 点间互信息的定义如下:
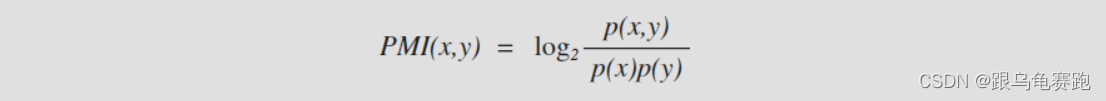
本文操作时,选择以e为底。#!usr/bin/env python # -*- coding:utf-8 -*- """ 对统计出的单字和双字的结果,使用互信熵,选择大于阈值K=的词加入词库,作为初始词库; """ import codecs import json import math def load_data(file_count_one): """ 加载单字文件:{one_word,[[], {}, {}]},并返回总词数与单字字典:{one_word:one_word_freq} :param file_count_one:文件名 :return: """ count_one_data = codecs.open(file_count_one, 'r', encoding='utf-8') count_one_param = {} N = 0 # 遍历每一行,返回总词数与单字字典:{one_word:one_word_freq} for line in count_one_data.readlines(): line = line.strip() line = line.split('\t') try: word = line[0] value = json.loads(line[1]) N += value[0] count_one_param[word] = int(value[0]) except: pass count_one_data.close() return N, count_one_param def select(file_count_one, file_count_two, file_dict, K=10.8): """ 遍历每一行,利用互信息熵计算每个词的成词概率PMI,利用阈值K来筛选一部分词,将结果保存到file_dict字典中 :param file_count_one: 窗口为1的文件 :param file_count_two: 窗口为2的文件 :param file_dict: 字典文件 :param K: 稳定词的阈值 :return: """ count_two_data = codecs.open(file_count_two, 'r', encoding='utf-8') # 总词数与单字字典 N, count_one_param = load_data(file_count_one) count_two_param = {} # 遍历每一行,利用互信息熵计算每个词的成词概率PMI for line in count_two_data.readlines(): line = line.strip() line = line.split('\t') try: word = line[0] value = json.loads(line[1]) # 双字出现的词频 / 总的字数 P_w = 1.0 * value[0] / N # 双字的第一个字出现的词频 / 总的字数 P_w1 = 1.0 * count_one_param.get(word[0], 1) / N # 双字的第二个字出现的词频 / 总的字数 P_w2 = 1.0 * count_one_param.get(word[1], 1) / N # 计算点间互信息PMI的计算公式,两个字的成词概率越大,则PMI值越大;如果两个子不相关,则PMI=0 mi = math.log(P_w / (P_w1 * P_w2)) count_two_param[word] = mi except: pass select_two_param = [] for w in count_two_param: mi = count_two_param[w] if mi > K: select_two_param.append(w) with codecs.open(file_dict, 'a', encoding='utf-8') as f: for w in select_two_param: f.write(w + '\t' + 'org' + '\n') count_two_data.close()- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
这一步会生成初始词库文件
dict.txt,后续发现的新词也会追加到这个文件中,构成新的词库文件。

这里我从业务端获得了几万条初始手工添加的词。考虑到初始已经有许多词,所以,互信息熵的阈值K设置的可以大一点。如果没有的话,K会对最后结果起决定作用。所使用的材料是长文本还是短文本也会对K有影响。可以尝试初始设置为K=8来运行程序。3.对语料库进行切分
有了初始词库,使用正向最大匹配,对语料库进行切分,对切分出来的字串按频率排序输出并记下数量
seg_num。""" 有了初始词库,使用正向最大匹配,对语料库进行切分,对切分出来的字串按频率排序输出并记下数量seg_num """ from __future__ import unicode_literals import codecs import re # 匹配所有汉字与规定符号 re_han_cut = re.compile("([\u4E00-\u9FD5a-zA-Z0-9-+#&\._/\u03bc\u3001\(\)\uff08\uff09\~\'\u2019]+)", re.U) # 匹配所有汉字 re_han = re.compile("([\u4E00-\u9FD5]+)", re.U) class Cuting(object): def __init__(self, file_corpus, file_dict, file_segment): self.file_corpus = file_corpus self.file_dict = file_dict self.file_segment = file_segment self.wdict = {} self.get_dict() def get_dict(self): """ 遍历初始字典文件,初始化wdict字典 => {one_word:[many two world]} :return: """ f = codecs.open(self.file_dict, 'r', encoding='utf-8') # 遍历每一行数据 for lineno, line in enumerate(f, 1): line = line.strip() line = line.split('\t') w = line[0] if w: if w[0] in self.wdict: value = self.wdict[w[0]] value.append(w) self.wdict[w[0]] = value else: self.wdict[w[0]] = [w] def fmm(self, sentence): """ 将子串中在wdict中two_word保存到result表中 :param sentence: 字符子串 :return: """ N = len(sentence) k = 0 result = [] while k < N: w = sentence[k] maxlen = 1 # 如果这个字在初始化字典wdict中 if w in self.wdict: # 初始化字典中的value,是一个列表,里面有许多上一步找到的two_word words = self.wdict[w] t = '' for item in words: itemlen = len(item) if sentence[k:k + itemlen] == item and itemlen >= maxlen: t = item maxlen = itemlen if t and t not in result: result.append(t) k = k + maxlen return result def judge(self, words): """ 判断这个子串是否只有汉字 :param words: :return: """ flag = False n = len(''.join(re_han.findall(words))) if n == len(words): flag = True return flag def cut(self, sentence): """ :param sentence: :return: """ buf = [] # 在商品名称中找到正则表达式所匹配的所有子串,并返回一个列表 blocks = re_han_cut.findall(sentence) # 遍历每一个子串 for blk in blocks: if blk: # 将子串中在wdict中的two_word返回 fm = self.fmm(blk) if fm: try: # 如果返回值不为空,则将这些词以“|”进行拼接,并以此构建正则表达式 re_split = re.compile('|'.join(fm)) # split方法按照能够匹配的子串将字符串分割后返回列表 for s in re_split.split(blk): # 如果这个子串只有汉字,则将该子串添加到列表中,最终返回该列表 if s and self.judge(s): buf.append(s) except: pass return buf def find(self): """ :return: """ input_data = codecs.open(self.file_corpus, 'r', encoding='utf-8') output_data = codecs.open(self.file_segment, 'w', encoding='utf-8') dataset = {} # 遍历每一个语料文件 for lineno, line in enumerate(input_data, 1): line = line.strip() # 遍历基于正则切割的字符串列表 for w in self.cut(line): if len(w) >= 2: dataset[w] = dataset.get(w, 0) + 1 # 基于词频进行排序 data_two = sorted(dataset.items(), key=lambda d: d[1], reverse=True) seg_num = len(data_two) for key in data_two: output_data.write(key[0] + '\t' + str(key[1]) + '\n') print('Having segment %d words' % seg_num) input_data.close() output_data.close() return seg_num- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
这一步会生成片段语料文件
file_segment.txt
片段语料文件会根据初始词库的迭代更新而变化。4.利用搜索引擎判断新词
对切分产生的字串按频率排序,前H=2000的字串进行搜索引擎(百度)。若字串是“百度百科”收录词条,将该字串作为词加入词库;或者在搜索页面的文本中出现的次数超过60,也将该字串作为词加入词库;
#!usr/bin/env python # -*- coding:utf-8 -*- """ 对切分产生的字串按频率排序,前H=2000的字串进行搜索引擎(百度), 若字串是“百度百科”收录词条,将该字串作为词加入词库, 或者在搜索页面的文本中出现的次数超过60,也将该字串作为词加入词库; """ import requests from lxml import etree import codecs import re def search(file_segment, file_dict, H, R, iternum): # headers,从网站的检查中获取 headers = {'Accept': 'text/html,application/xhtml+xml,application/xml;q=0.9,image/webp,*/*;q=0.8', 'Accept-Encoding': 'gzip, deflate, sdch, b', 'Accept-Language': 'zh-CN,zh;q=0.8', 'Cache-Control': 'max-age=0', 'Connection': 'keep-alive', 'User-Agent': 'Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; WOW64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/57.0.2987.133 Safari/537.' } # 加载切分出来的子符串 input_data = codecs.open(file_segment, 'r', encoding='utf-8') read_data = input_data.readlines() N = len(read_data) if H > N: H = N output_data = codecs.open(file_dict, 'a', encoding='utf-8') n = 0 m = 1 # 遍历切分出的子符串 for line in read_data[:H]: line = line.rstrip() line = line.split('\t') # 字符串 word = line[0] try: # 访问百度百科词条 urlbase = 'https://www.baidu.com/s?wd=' + word dom = requests.get(urlbase, headers=headers) ct = dom.text # 在搜索页面的文本中出现的次数 num = ct.count(word) html = dom.content selector = etree.HTML(html) flag = False # 若字串是“百度百科”收录词条,将该字串作为词加入词库 if selector.xpath('//h3[@class="t c-gap-bottom-small"]'): ct = ''.join(selector.xpath('//h3[@class="t c-gap-bottom-small"]//text()')) lable = re.findall(u'(.*)_百度百科', ct) for w in lable: w = w.strip() if w == word: flag = True if flag: output_data.write(word + '\titer_' + str(iternum) + '\n') n += 1 # 在搜索页面的文本中出现的次数超过阈值R=60,也将该字串作为词加入词库 else: if num >= R: output_data.write(word + '\titer_' + str(iternum) + '\n') n += 1 m += 1 if m % 100 == 0: print('having crawl %dth word\n' % m) except: pass print('Having add %d words to file_dict at iter_%d' % (n, iternum)) input_data.close() output_data.close() return n- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
这一步会将发现的新词添加到
dict.txt文件中。5.迭代寻找新词
更新词库后,重复step3,step4进行迭代。当searh_num=0时,结束迭代;当seg_num小于设定的Y=3000,进行最后一次step4,并H设定为H=seg_num,执行完后结束迭代,最后词库就是本程序所找的词。
#!usr/bin/env python # -*- coding:utf-8 -*- """ 算法步骤: 1.统计语料库中出现单字,双字的频率,前后链接的字相关信息; 2.对统计出的单字和双字的结果,使用互信熵,选择大于阈值K=的词加入词库,作为初始词库; 3.有了初始词库,使用正向最大匹配,对语料库进行切分,对切分出来的字串按频率排序输出并记下数量seg_num 4.对切分产生的字串按频率排序,前H=5000的字串进行搜索引擎(百度), 若字串是“百度百科”收录词条,将该字串作为词加入词库, 或者在搜索页面的文本中出现的次数超过60,也将该字串作为词加入词库; 5.更新词库后,重复step3,step4进行迭代,,当searh_num=0时,结束迭代; 当seg_num小于设定的Y=1000,进行最后一次step4,并H设定为H=seg_num,执行完后结束迭代, 最后词库就是本程序所找的词 """ from __future__ import absolute_import __version__ = '1.0' __license__ = 'MIT' import os import logging import time import codecs import sys from module.corpus_count import * from module.corpus_segment import * from module.select_model import * from module.words_search import * # 获取当前路径 medfw_path = os.getcwd() file_corpus = medfw_path + '/data_org/file_corpus.txt' file_dict = medfw_path + '/data_org/dict.txt' file_count_one = medfw_path + '/data_org/count_one.txt' file_count_two = medfw_path + '/data_org/count_two.txt' file_segment = medfw_path + '/data_org/file_segment.txt' # 日志设置 log_console = logging.StreamHandler(sys.stderr) default_logger = logging.getLogger(__name__) default_logger.setLevel(logging.DEBUG) default_logger.addHandler(log_console) def setLogLevel(log_level): global logger default_logger.setLevel(log_level) class MedFW(object): def __init__(self, K=10, H=2000, R=60, Y=5000): self.K = K # 互信息熵的阈值 self.H = H # 取file_segment.txt前多少个 self.R = R # 片段单词在搜索引擎出现的阈值 self.Y = Y # 迭代结束结束条件参数 self.seg_num = 0 # 片段语料库的数量 self.search_num = 0 # 搜索引擎向 file_dict 添加单词的数量 # step1: 统计语料库中出现单字,双字的频率,前后链接的字相关信息; def medfw_s1(self): for i in range(1, 3): if i == 1: file_count = file_count_one else: file_count = file_count_two default_logger.debug("Counting courpus to get %s...\n" % (file_count)) t1 = time.time() cc = Finding(file_corpus, file_count, i) cc.find_word() default_logger.debug("Getting %s cost %.3f seconds...\n" % (file_count, time.time() - t1)) # step2: 对统计出的单字和双字的结果,使用互信熵,选择大于阈值K=的词加入词库,作为初始词库; def medfw_s2(self): default_logger.debug("Select stable words and generate initial vocabulary... \n") select(file_count_one, file_count_two, file_dict, self.K) # step3: 有了初始词库,使用正向最大匹配,对语料库进行切分,对切分出来的字串按频率排序输出并记下数量seg_num def medfw_s3(self): t1 = time.time() sc = Cuting(file_corpus, file_dict, file_segment) self.seg_num = sc.find() default_logger.debug("Segment corpuscost %.3f seconds...\n" % (time.time() - t1)) # step4:对片段语料中的单词使用搜索引擎进行搜索 def medfw_s4(self, H, R, iternum): t1 = time.time() self.search_num = search(file_segment, file_dict, H, R, iternum) default_logger.debug("Select words cost %.3f seconds...\n" % (time.time() - t1)) # 主程序 def medfw(self): # default_logger.debug("Starting to find words and do step1...\n" ) print('-----------------------------------') print('step1:count corpus') self.medfw_s1() print('-----------------------------------') print('step2:select stable words and generate initial vocabulary') self.medfw_s2() print('-----------------------------------') print('step3:use initial vocabulary to segment corpus') self.medfw_s3() print('-----------------------------------') print('step4:use search engine to select words of segment corpus') self.medfw_s4(H=self.H, R=self.R, iternum=0) print('-----------------------------------') print('step5:cycling iteration') iter_num = 1 while True: if self.search_num: default_logger.debug("Itering %d...\n" % (iter_num)) t1 = time.time() self.medfw_s3() print("---------------------- seg_num:%s -----------------------" % self.seg_num) if self.seg_num <= self.Y: self.H = self.seg_num self.medfw_s4(H=self.H, R=self.R, iternum=iter_num) default_logger.debug("Ending the iteration ...\n") break else: self.medfw_s4(H=self.H, R=self.R, iternum=iter_num) iter_num += 1 default_logger.debug("Itering %d cost %.3f seconds...\n " % ((iter_num - 1), time.time() - t1)) else: break with codecs.open(file_dict, 'r', encoding='utf-8') as f: total_num = len(f.readlines()) print('Having succcessfuly find %d words from corpus ' % total_num) if __name__ == '__main__': md = MedFW(K=10, H=3000, R=50, Y=3000) md.medfw()- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
- 134
- 135
- 136
- 137
- 138
这一步会多轮迭代寻找新词。
6.方法总结
实践表明:这种思路获得的结果有一定用处,获得的结果需要人工来甄别。缺点的话也很明显,比如一个长的品牌名或者商品名,如果其中几个连续的词的词频很高,并且本身也能成词,就会将这个品牌名或者商品名切散!还有待继续研究!
-
相关阅读:
C++ vector类模拟实现
Linux 进程概念 —— 初识操作系统(OS)
无涯教程-JavaScript - ERFC.PRECISE函数
用GAN网络生成彩票号码
线上教育培训办公系统系统的设计
[蓝桥杯复盘] 第 3 场双周赛20231111
自定义GPT已经出现,并将影响人工智能的一切,做好被挑战的准备了吗?
SpringBoot项目文件上传校验(注解版)
【OS】AUTOSAR架构下MCAL Modules软件分区问题分析
深度学习的历史
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/liujiesxs/article/details/126173350
