-
acwing 802. 区间和-java详细解析版
题目所属分类
离散化的知识
原题链接
假定有一个无限长的数轴,数轴上每个坐标上的数都是 0
现在,我们首先进行 n次操作,每次操作将某一位置 x 上的数加 c接下来,进行 m次询问,每个询问包含两个整数 l 和 r,你需要求出在区间 [l,r]之间的所有数的和。
- 输入格式
第一行包含两个整数 n和 m
接下来 n行,每行包含两个整数 x 和 c
再接下来 m行,每行包含两个整数 l 和 r - 输出格式共 m行,每行输出一个询问中所求的区间内数字和。
代码案例:

题解
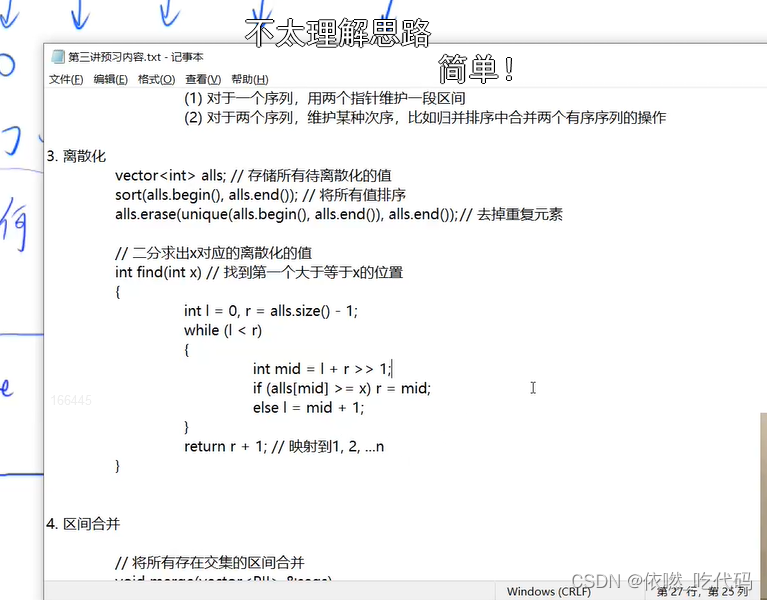
主要分为5大步:
1.读输入。将每次读入的x c 以Pair这样的形式add到adds中,将每次读入的位置x add到alls中,将每次读入的l r add到query中 同时也add到alls。
2.排序、去重。去重使用的是hashSet
3.通过遍历adds,完成对应的离散化的数组映射到的a数组 进而形成遍历alls中的s[i] 然后遍历query查找到对应的l和r (用到find函数——返回的是输入的坐标的离散化下标)
4.初始化s数组。
5.通过遍历query,完成求区间[l,r]的和,并输出结果。
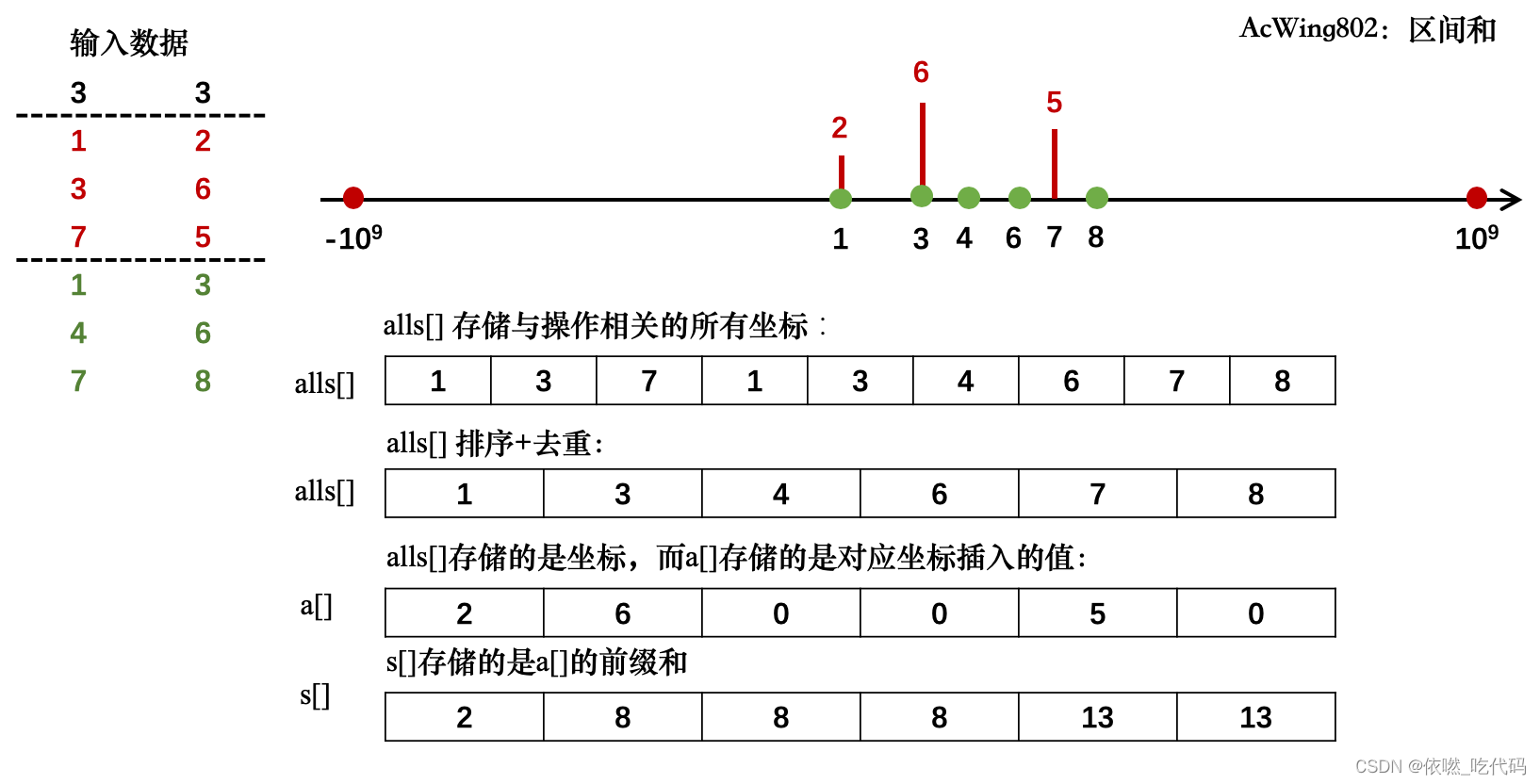
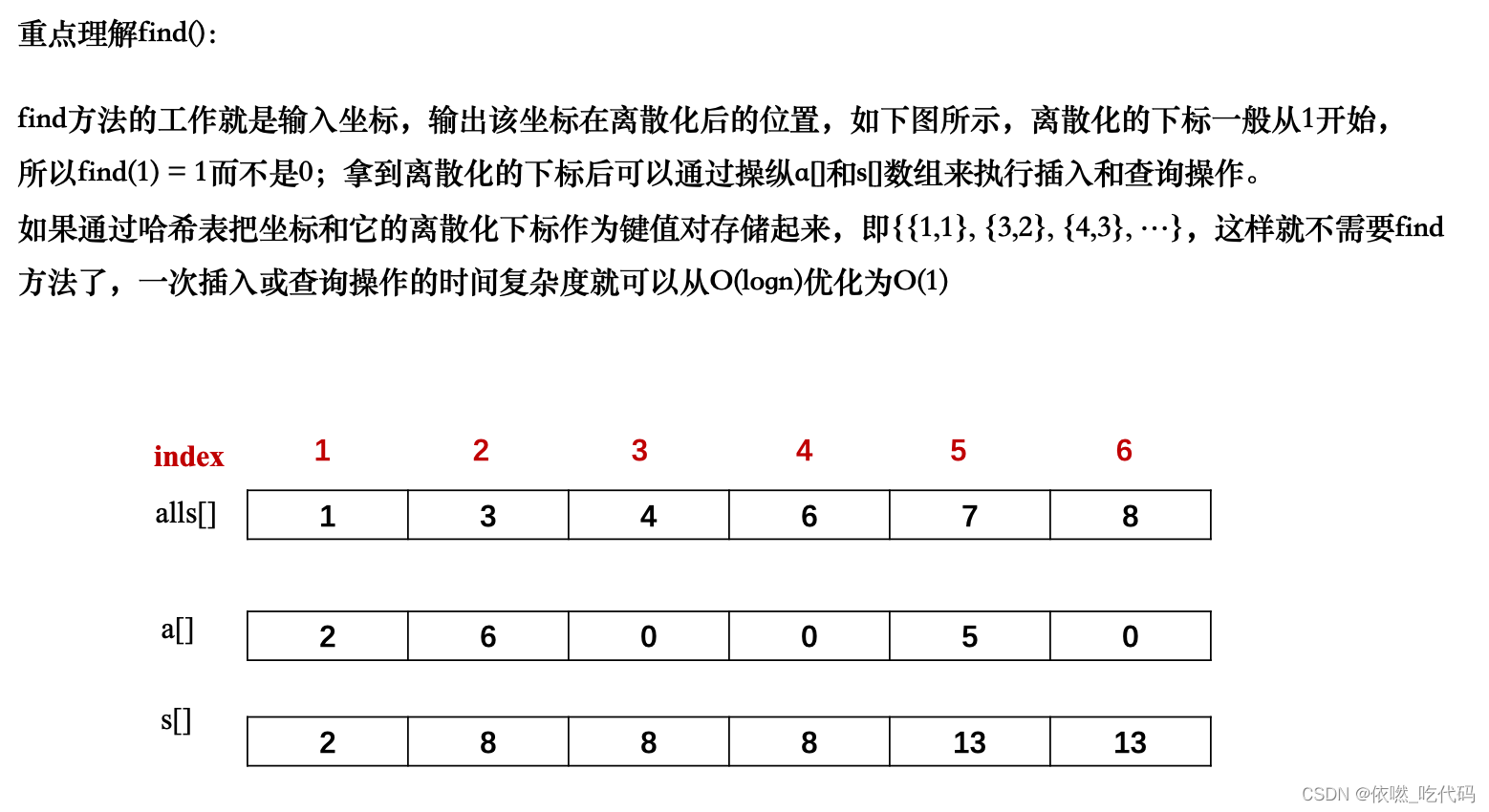
关于为什么要去重?
因为所有的坐标都是公用的,将重复的去掉之后,两个list所存的操作,List<Pair> add = new ArrayList<>();//用来存n次操作 List<Pair> query = new ArrayList<>();//用来存m次询问- 1
- 2
映射是一 一对应,去掉重复的点之后,然后将之前存的这两个list里面的操作出来寻找,如果不是一 一对应的话,你就不能操作
自己Java版本的写法
关于去重 排序 用的是Hashset方法去重 也可以用下面的unique函数去重
import java.util.*; public class Main { static int N = 300010;//一个N +两个M 所以要开30万 static List<Integer> alls = new ArrayList<>();//存放的是离散化后的list 实际上就是用来存所有的下标x,l,r; static List<Pair> query = new ArrayList<>(), adds = new ArrayList<Pair>();//用来存n次操作 和 m次查询 static int a[] = new int[N], s[] = new int[N];//a是存放的数值数组 s是前缀和的数组 public static void main(String[] args){ Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in); int n = scan.nextInt();//n次操作 int m = scan.nextInt();//m次询问 //输入n次操作,每次操作存入add集合中,然后将下标x存入alls集合中 for(int i = 0 ; i < n ; i++){ int x = scan.nextInt(); int c = scan.nextInt(); alls.add(x); adds.add(new Pair(x, c)); } //输入m次询问,每次询问存入query集合中,因为l,r是求和的下标区间和,所以l,r都存入alls集合中。 for(int i = 0 ; i < m ; i ++ ){ int l = scan.nextInt(); int r = scan.nextInt(); query.add(new Pair(l,r)); alls.add(l); alls.add(r); } // Java的离散化操作 alls = new ArrayList<>(new HashSet<>(alls));//通过hashset去重 Collections.sort(alls); //排序,现在alls集合中存的是x,l,r所有值 //增强for循环 for(元素类型 变量名 : 数组或者集合) 缺点:无下标,简单。 for(Pair item : adds){ int index = find(item.first);// a[index] += item.second;// } for(int i = 1 ; i <= alls.size() ; i ++ ) s[i] = s[i-1] + a[i]; //这是前缀和公式代码 for(Pair item : query){ int l = find(item.first); // int r = find(item.second); // System.out.println(s[r] - s[l-1]); // } } //二分查找(find函数中是使用了二分来查找x在alls中的下标+1,因为需要符合我们要用的前缀和公式, //要让下标不是从0输出,最低的下标是1,符合前缀和的从1开始,所以输出的值加1) static int find(int x) {//寻找第一个大于等于x的数 ||第一个小于等于x的数 int l = 0, r = alls.size() - 1; while(l < r) { int mid = l + r + 1 >> 1; if(alls.get(mid) <= x) l = mid; else r = mid - 1; } return l + 1; } } //这是一个Pair类,用来存操作的类 class Pair{ int first; int second; public Pair(int x,int c){ this.first = x; this.second = c; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
关于Pair类的写法 还是简便一点好
static class CII { int x1, x2; public CII(int a, int b) { x1 = a; x2 = b; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
中规中矩的写法 符合y总的C++代码

- 为什么unique 函数返回的是 return a.begin() + j;
从数组a的开头往后数j个数,都是去重后的数 - subList() 方法用于截取并返回动态数组中的一部分。
subList() 方法的语法为:
arraylist.subList(int fromIndex, int toIndex)
和subString一样 只不过这个是动态数组中的截取 也是左闭右开区间import java.util.*; public class Main{ public static void main(String[] args){ Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in); int n = scan.nextInt();//n次操作 int m = scan.nextInt();//m次询问 int N = 300010;//表示需要用到的下标数量,因为一开始可能重复,所以按照最大可能开最大的数组; int[] a = new int[N]; //用来存值,从一开始的值,因为要用到前缀和,所以0不操作; int[] s = new int[N];//用来存前缀和,从一开始进行记录a数组; List<Integer> alls = new ArrayList<>();//用来存所有的下标,x,l,r; //因为可能会重复乱序,所以需要进行去重,排序; List<Pair> add = new ArrayList<>();//用来存n次操作 List<Pair> query = new ArrayList<>();//用来存m次询问 //输入n次操作,每次操作存入add集合中,然后将下标x存入alls集合中 for(int i = 0 ; i < n ; i ++ ){ int x = scan.nextInt(); int c = scan.nextInt(); add.add(new Pair(x,c)); alls.add(x); } //输入m次询问,每次询问存入query集合中,因为l,r是求和的下标区间和,所以l,r都存入alls集合中。 for(int i = 0 ; i < m ; i ++ ){ int l = scan.nextInt(); int r = scan.nextInt(); query.add(new Pair(l,r)); alls.add(l); alls.add(r); } Collections.sort(alls); //排序,现在alls集合中存的是x,l,r所有值 int unique = unique(alls); //这一步是去重,因为l,x,r中可能有重复的数; alls = alls.subList(0,unique); //将去重之后的alls的长度范围中的值重新赋值给alls集合中。 //增强for循环 for(元素类型 变量名 : 数组或者集合) 缺点:无下标,简单。 for(Pair item : add){ int index = find(item.first,alls);// a[index] += item.second;// } for(int i = 1 ; i <= alls.size() ; i ++ ) s[i] = s[i-1] + a[i]; //这是前缀和公式代码 for(Pair item : query){ int l = find(item.first,alls); // int r = find(item.second,alls); // System.out.println(s[r] - s[l-1]); // } } //去重(只要符合是第一个数或者后面一个数不等于前面一个数就是不重复的数) public static int unique(List<Integer> list){ int j = 0; for(int i = 0 ; i <= list.size() - 1; i ++ ){ if(i == 0 || list.get(i) != list.get(i-1)){ list.set(j,list.get(i)); //将不重复之后的数一个一个重新存入list中。 j ++ ; } } return j; } //二分查找(在集合中查找你现在的下标是在什么位置,因为需要符合我们要用的前缀和公式,要让下标不是从0输出,最低的下标是1,符合前缀和的从1开始,所以输出的值加1) public static int find(int x ,List<Integer> list){ int l = 0; int r = list.size() - 1; while(l < r){ int mid = ( l + r )/ 2; if(list.get(mid) >= x) r = mid; else l = mid + 1; } return l + 1; } } //这是一个Pair类,用来存操作的类 class Pair{ int first; int second; public Pair(int x,int c){ this.first = x; this.second = c; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
总结
- 输入格式
-
相关阅读:
OpenCV(三十):图像膨胀
* 论文笔记 【OffDQ: An Offline Deep Learning Framework for QoS Prediction】
Java面向对象基础 笔记记录
SVG—初识1
C++数据传输
谁来看看这个算法解答这个问题的解题过程!
Web自动化测试工具哪家强? Selenium与Cypress的比较
shell排序算法
【JAVA】HTTP协议
雷达电子战实例及经验教训 (03)
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_41810415/article/details/126251195
