-
初见物理引擎库Cannon.js(2)
0 前言
本文是“初见物理引擎库Cannon.js”系列的第二篇文章,在本文中主要讲解
dat.gui的使用。1
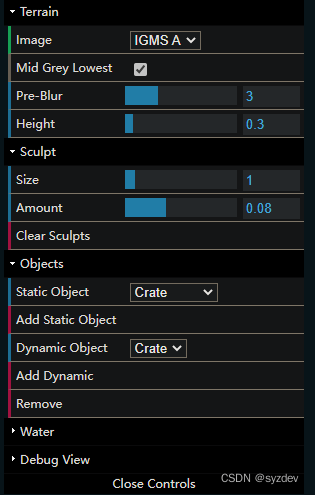
dat.gui简介熟悉Three.js的读者肯定对
dat.gui不陌生,通过该工具能够创建一个小型的菜单,如下图,在菜单中能够实时的修改一些变量或执行一些操作:
在Three.js官方案例中,也大量的使用了此类工具,如webgl_clipping_stencil,如下图:
只不过官方使用的是lil-gui,而不是dat.gui,两者实现的功能和使用方式类似,本文仅讲解dat.gui。2 在线地址
[ Live Demo ]:Cannon.js - datgui (syzdev.cn)
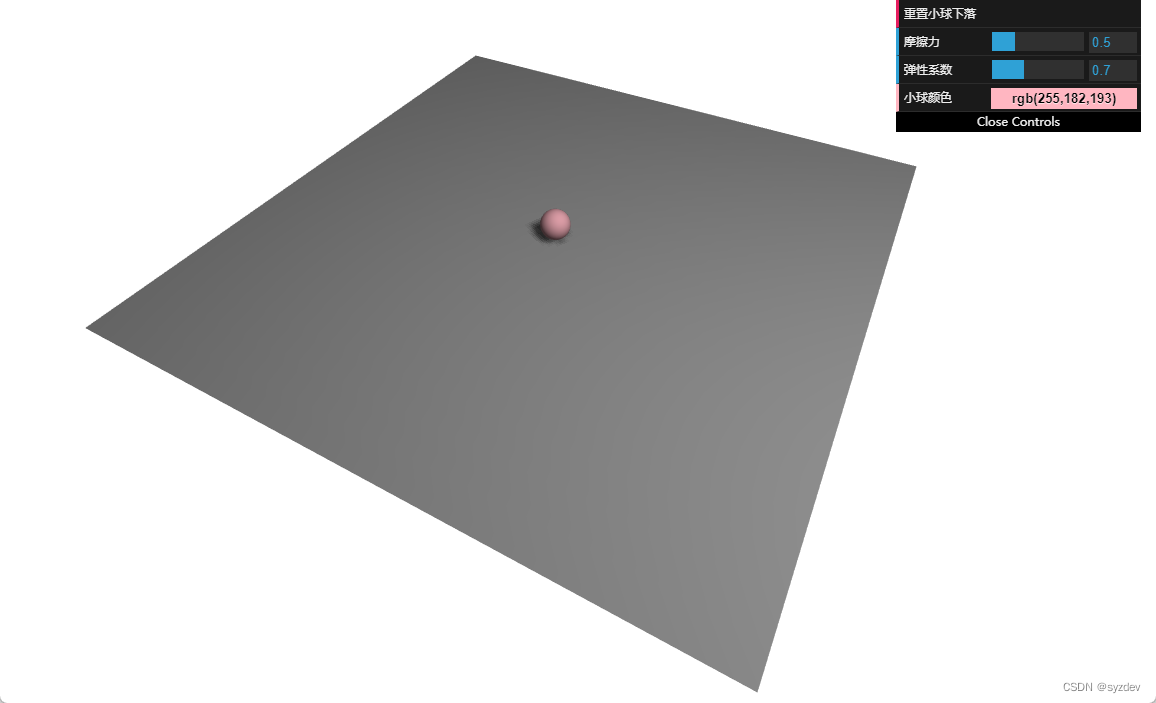
本文沿用“初见物理引擎库Cannon.js(1)”中的示例,并在此基础上实现如下功能:
- 重置小球下落;
- 修改摩擦力;
- 修改弹性系数;
- 修改小球颜色。
3
dat.gui的使用方法3.1引入
dat.gui.min.js3.1.1 CDN引入
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/dat.gui@0.7.9/build/dat.gui.min.js">script>- 1
3.1.2 NPM引入
npm install dat.gui- 1
3.2 初始化
首先要初始化一个
gui对象,该变量表示菜单对象,对菜单的操作都是基于该对象完成的。let gui = new dat.GUI()- 1
接下来要初始化菜单的数据对象
controls,即菜单中要修改哪些变量或执行哪些操作,除此之外还要为这些变量提供默认值或给这些操作提供按钮点击事件。不难发现,要实现上述的4个功能,需要修改3个变量:
- 关联材质
cannonDefaultCantactMaterial:用于修改摩擦力和弹性系数; - 小球
cannonSphereBody:用于重置小球下落; - 小球材质
threeSphereMaterial:用于修改小球的颜色。
注:上述3个变量,在初始化菜单的数据对象
controls和创建实体时都要使用,因此要保证三者在同一个作用域下,最简单的办法是将上述三个变量定义为全局变量。而重置小球下落是一个按钮,点击后将触发一个事件
resetBall,因此在数据对象中controls,该变量为一个函数,函数中要重置小球的位置、重置小球的速度,修改摩擦力和弹性系数。综上所述,完整的数据对象
controls如下:let controls = { resetBall: () => { cannonSphereBody.position.set(0, 10, 0) // 重置小球位置 cannonSphereBody.velocity.set(0, 0, 0) // 重置小球速度 cannonDefaultCantactMaterial.friction = friction // 修改摩擦力 cannonDefaultCantactMaterial.restitution = restitution // 修改弹性系数 }, friction: 0.5, // 摩擦力,默认值为0.5 restitution: 0.7, // 弹性系数,默认值为0.7 color: threeSphereMaterial.color.getStyle() // 小球的颜色,默认值为初始化时的材质颜色 }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
3.3 添加菜单项
完成了1.3节中的初始化工作,确定了要修改的变量和要执行的操作,接下来的工作就是将其添加到菜单对象
gui上,上述4个功能在菜单项上可以分为3类:- 按钮类型:重置小球下落;
- 数字输入类型:修改摩擦力和弹性系数;
- 颜色选取类型:修改小球的颜色。
之所以要对菜单项进行分类,是因为在添加菜单项时,对不同类型的菜单项要使用不同的添加方法或参数。
3.3.1 添加按钮类型菜单项
当菜单项类型为按钮时,使用的是
add方法,在方法中提供数据对象controls和要执行的操作方法resetBall。以重置小球下落的按钮为例,添加方法如下:gui.add(controls, 'resetBall')- 1
3.3.2 添加数字输入类型菜单项
当菜单项类型为数字输入类型时,使用的也是
add方法,但参数有所不同,以修改摩擦力为例,除了提供数据对象controls和操作变量friction之外,还可以提供可选的参数最小值、最大值和步长,最后在回调函数onChange中执行对应的修改即可,代码如下(参数中省略了步长):// 摩擦力 gui.add(controls, 'friction', 0, 2).onChange((e) => { friction = e }) // 同理:弹性系数 gui.add(controls, 'restitution', 0, 2).onChange((e) => { restitution = e })- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
按钮类型的菜单不需要提供回调函数,这是因为按钮类型本身就触发了一个方法,在方法中执行了所需的操作。
3.3.3 添加颜色选取类型菜单项
当菜单项类型为颜色选取类型时,使用的是
addColor方法,在方法中提供数据对象controls和要修改的颜色值color,最后在回调函数onChange中执行对应的修改即可,代码如下:gui.addColor(controls, 'color').onChange((e) => { threeSphereMaterial.color.setStyle(e) })- 1
- 2
- 3
3.4 在菜单项中使用中文
完成上述操作后,如下图所示:
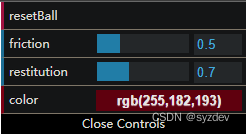
不难发现,菜单项中的名称默认使用的是数据对象controls中的变量名,在实践中往往需要将菜单项的文字修改为中文,虽然JavaScript已经支持了ASCII扩展字符和Unicode字符的标识符,但依然不建议这么做,在dat.gui中,可以使用name方法,给菜单项的文字取个别名,代码如下:gui.add(controls, 'resetBall').name('重置小球下落') // 类似的 gui.add(controls, 'friction', 0, 2).name('摩擦力').onChange((e) => { friction = e }) gui.add(controls, 'restitution', 0, 2).name('弹性系数').onChange((e) => { restitution = e }) gui.addColor(controls, 'color').name('小球颜色').onChange((e) => { threeSphereMaterial.color.setStyle(e)- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
这样,菜单项中的文字就修改为了中文,如下图所示:
4 实现代码
/** * MeshBodyToUpdate为一个对象数组 * 数组中的每一个对象为Three中的Mesh和Cannon中的Body * 添加的形式如下 * MeshBodyToUpdate.push({ * mesh: mesh, * body: body, * }) * 在render函数中遍历该数组,将Three中的Mesh的位置和旋转更新为Cannon中的Body的位置和旋转 */ const MeshBodyToUpdate = [] /** * 声明默认材质 * 用于初始化Cannon时创建关联材质 */ const cannonDefaultMaterial = new CANNON.Material() /** * 初始化Three的参数,为了将Three和Cannon分离 * 用three对象来保存Three中的场景scene、相机camera和渲染器renderer */ let three = { scene: null, camera: null, renderer: null, } /** * 初始化Cannon参数 */ let cannon = { world: null, } /** * dat.gui控制的变量 */ let cannonDefaultCantactMaterial = null // 关联材质 let cannonSphereBody = null // 小球 let threeSphereMaterial = null // 小球材质 /** * @description: 初始化dat.gui */ const initDatGui = () => { let gui = new dat.GUI() let controls = { resetBall: () => { cannonSphereBody.position.set(0, 10, 0) // 重置小球位置 cannonSphereBody.velocity.set(0, 0, 0) // 重置小球速度 cannonDefaultCantactMaterial.friction = friction // 修改摩擦力 cannonDefaultCantactMaterial.restitution = restitution // 修改弹性系数 }, friction: 0.5, restitution: 0.7, color: threeSphereMaterial.color.getStyle() } gui.add(controls, 'resetBall').name('重置小球下落') gui.add(controls, 'friction', 0, 2).name('摩擦力').onChange((e) => { friction = e }) gui.add(controls, 'restitution', 0, 2).name('弹性系数').onChange((e) => { restitution = e }) gui.addColor(controls, 'color').name('小球颜色').onChange((e) => { threeSphereMaterial.color.setStyle(e) }) } /** * @description: 初始化Three场景 */ const initThree = () => { // 1 初始化Three场景 three.scene = new THREE.Scene() // 2 初始化Three相机 /** * THREE.PerspectiveCamera 初始化一个Three透视相机 * fov:摄像机视锥体垂直视野角度 * aspect:相机场景长宽比 * near:摄像机视锥体近端面 * far:摄像机视锥体远端面 */ three.camera = new THREE.PerspectiveCamera( 60, window.innerWidth / window.innerHeight, 0.1, 1000 ) three.camera.position.set(20, 20, 20) // 设置相机位置 three.camera.lookAt(three.scene.position) // 设置相机视角朝向Three场景scene // three.scene.add(new THREE.AxesHelper(20)) // 添加场景坐标轴 // 3 初始化Three渲染器 three.renderer = new THREE.WebGLRenderer({ antialias: true }) // 初始化Three渲染器 // three.renderer = new THREE.WebGLRenderer() // 初始化Three渲染器 three.renderer.setClearColor(0xffffff, 1.0) // 设置渲染背景色 three.renderer.shadowMap.enabled = true // 开启场景光照阴影效果 three.renderer.setSize(window.innerWidth, window.innerHeight) // 设置渲染范围大小 // 4 初始化光源 three.scene.add(new THREE.AmbientLight(0x404040)) // 初始化坏境光 // 初始化聚光源 let spotLight = new THREE.SpotLight(0x999999) spotLight.position.set(-10, 30, 20) // 设置聚光源的位置 spotLight.castShadow = true // 开启聚光源投射阴影 // spotLight.distance = 1000000000 three.scene.add(spotLight) // 5 添加Three到DOM下 document .getElementById('threeContainer') .appendChild(three.renderer.domElement) // OrbitControls轨道控制器 let controls = new THREE.OrbitControls(three.camera, three.renderer.domElement) } /** * @description: 初始化Cannon物理场景 */ const initCannon = () => { // 1 初始化Cannon中的物理世界World cannon.world = new CANNON.World() // 2 设置物理世界中的重力,设置为y轴负方向的-9.8 m/s²,模拟真实世界 cannon.world.gravity.set(0, -9.8, 0) // 3 设置物理世界中的碰撞检测模式 cannon.world.broadphase = new CANNON.NaiveBroadphase() // 4 设置物理世界中的联系材质,用于判断物体之间的接触关系 // 4.1 声明混泥土材质 // const cannonConcreteMaterial = new CANNON.Material('concrete') // 4.2 声明塑料材质 // const cannonPlasticMaterial = new CANNON.Material('plastic') // 4.3 声明默认材质 // const cannonDefaultMaterial = new CANNON.Material() // 4.4 创建两个默认材质的关联材质 cannonDefaultCantactMaterial = new CANNON.ContactMaterial( cannonDefaultMaterial, cannonDefaultMaterial, { friction: 0.5, restitution: 0.7, } ) // 4.5 将两个默认材质添加到物理世界world中 cannon.world.addContactMaterial(cannonDefaultCantactMaterial) } /** * @description: 创建地板 * 由于Plane不需要改变位置,所以不需要添加至MeshBodyToUpdate进行位置旋转同步 */ const createPlane = () => { // 1 创建Cannon中的地板刚体 // 1.0 创建地板刚体形状 let cannonPlaneShape = new CANNON.Plane() // 1.1 创建地板刚体的材质,默认材质 // let cannonPlaneMaterial = new CANNON.Material() let cannonPlaneMaterial = cannonDefaultMaterial // 1.2 创建地板刚体的质量mass,质量为0的物体为静止的物体 let cannonPlaneMass = 0 // 1.3 创建地板刚体的位置position,坐标原点 let cannonPlanePosition = new CANNON.Vec3(0, 0, 0) // 1.4 创建地板刚体的Body let cannonPlaneBody = new CANNON.Body({ mass: cannonPlaneMass, position: cannonPlanePosition, shape: cannonPlaneShape, material: cannonPlaneMaterial, }) // 1.5 旋转地板刚体Body,使其垂直与y轴 // setFromAxisAngle方法第一个参数是旋转轴,第二个参数是角度 cannonPlaneBody.quaternion.setFromAxisAngle( new CANNON.Vec3(1, 0, 0), -Math.PI / 2 ) // 1.6 将cannonPlaneBody添加到物理场景world中 cannon.world.addBody(cannonPlaneBody) // 2 创建Three中的地板网格 // 2.0 创建Three中的地板网格形状 let threePlaneGeometry = new THREE.PlaneGeometry(20, 20, 20) // 2.1 创建地板网格的材质 let threePlaneMaterial = new THREE.MeshLambertMaterial({ color: 0xa5a5a5, side: THREE.DoubleSide, }) // 2.2 创建地板网格的mesh let threePlaneMesh = new THREE.Mesh( threePlaneGeometry, threePlaneMaterial ) // 2.3 设置地板网格的旋转 threePlaneMesh.rotation.x = -Math.PI / 2 // 2.4 开启地表网格接收光照阴影 threePlaneMesh.receiveShadow = true // 2.5 设置地板网格的位置,坐标原点 threePlaneMesh.position.set(0, 0, 0) // 2.6 设置地板网格的大小缩放 threePlaneMesh.scale.set(2, 2, 2) // 2.7 将threePlaneMesh添加到Three场景scene中 three.scene.add(threePlaneMesh) } /** * @description: 创建球体 * 球体是含有质量mass的,所以需要添加至MeshBodyToUpdate进行位置旋转同步 */ const createSphere = () => { // 1 创建Cannon中的球体刚体 // 1.1 创建球体刚体形状,参数为球体的半径 let cannonSphereShape = new CANNON.Sphere(1) // 1.2 创建球体刚体的材质,默认材质 // let cannonSphereMaterial = new CANNON.Material() let cannonSphereMaterial = cannonDefaultMaterial // 1.3 创建球体刚体的质量mass,单位为kg let cannonSphereMass = 5 // 1.4 创建球体刚体的位置position let cannonSpherePosition = new CANNON.Vec3(0, 10, 0) // 1.5 创建球体刚体的Body cannonSphereBody = new CANNON.Body({ mass: cannonSphereMass, shape: cannonSphereShape, position: cannonSpherePosition, material: cannonSphereMaterial, }) // 1.6 将cannonSphereBody添加到物理场景world中 cannon.world.addBody(cannonSphereBody) // 2 创建Three中的球体网格 // 2.1 创建球体网格的形状 let threeSphereGeometry = new THREE.SphereGeometry(1, 32, 32) // 2.2 创建球体网格的材质 threeSphereMaterial = new THREE.MeshStandardMaterial({ color: 0xFFB6C1, }) // 2.3 创建球体网格的Mesh let threeSphereMesh = new THREE.Mesh( threeSphereGeometry, threeSphereMaterial ) // 2.4 设置球体网格投射光照阴影 threeSphereMesh.castShadow = true // 2.5 将threeSphereMesh添加到Three场景的scene中 three.scene.add(threeSphereMesh) // 3 将cannonSphereBody和threeSphereMesh添加到MeshBodyToUpdate中 MeshBodyToUpdate.push({ body: cannonSphereBody, mesh: threeSphereMesh, }) } /** * @description: 循环渲染场景 */ const render = () => { /** * 设置更新物理世界world的步长timestep * 这里选用60Hz的速度,即1.0 / 60.0 */ cannon.world.step(1.0 / 60.0) // 更新MeshBodyToUpdate中的Mesh和Body,使其位置和旋转同步 for (const object of MeshBodyToUpdate) { object.mesh.position.copy(object.body.position) object.mesh.quaternion.copy(object.body.quaternion) } requestAnimationFrame(render) three.renderer.render(three.scene, three.camera) } initThree() initCannon() createPlane() createSphere() initDatGui() render() // 改变窗口大小重新渲染场景 window.addEventListener('resize', () => { three.camera.aspect = window.innerWidth / window.innerHeight three.camera.updateProjectionMatrix() three.renderer.setSize(window.innerWidth, window.innerHeight) })- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
- 134
- 135
- 136
- 137
- 138
- 139
- 140
- 141
- 142
- 143
- 144
- 145
- 146
- 147
- 148
- 149
- 150
- 151
- 152
- 153
- 154
- 155
- 156
- 157
- 158
- 159
- 160
- 161
- 162
- 163
- 164
- 165
- 166
- 167
- 168
- 169
- 170
- 171
- 172
- 173
- 174
- 175
- 176
- 177
- 178
- 179
- 180
- 181
- 182
- 183
- 184
- 185
- 186
- 187
- 188
- 189
- 190
- 191
- 192
- 193
- 194
- 195
- 196
- 197
- 198
- 199
- 200
- 201
- 202
- 203
- 204
- 205
- 206
- 207
- 208
- 209
- 210
- 211
- 212
- 213
- 214
- 215
- 216
- 217
- 218
- 219
- 220
- 221
- 222
- 223
- 224
- 225
- 226
- 227
- 228
- 229
- 230
- 231
- 232
- 233
- 234
- 235
- 236
- 237
- 238
- 239
- 240
- 241
- 242
- 243
- 244
- 245
- 246
- 247
- 248
- 249
- 250
- 251
- 252
- 253
- 254
- 255
- 256
- 257
- 258
- 259
- 260
- 261
- 262
- 263
- 264
- 265
- 266
- 267
- 268
- 269
- 270
- 271
- 272
- 273
- 274
- 275
- 276
- 277
- 278
- 279
- 280
- 281
- 282
- 283
- 284
- 285
- 286
- 287
- 288
- 289
- 290
- 291
- 292
- 293
- 294
- 295
- 296
-
相关阅读:
LeetCode - Medium - 63. Unique Paths II
linux挖矿病毒kthreaddk横行,如何灭掉它?
Spring Data JPA
Windows10 MySQL(8.0.37)安装与配置
NM DEV Mathematics for Java 【suanshu.net免费】
李沐推荐的算法入门书分享,有动画图解、能运行、可讨论
【Unity3D】游戏物体操作 ④ ( 选中多个游戏物体操作 | 复制选中物体 | 聚焦选中物体 | 激活、禁用选中物体 | 对齐选中物体 )
JavaScript 垃圾回收机制
优化你的计算机性能:如何根据 CPU 占用率决定硬件升级
Spring(三)- Spring中Bean的配置
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/syzdev/article/details/126245246
