-
LinkedList与链表
引入链表
顺序表的引入带给了我们许多便利,比如在随机访问元素时,可以做到简单快捷;可是我们也不难发现,对顺序表进行插入删除的操作时,就显得较为繁琐,因此我们引入了链表结构,帮助我们快速的进行插入删除等操作;
链表的结构
线性表的链式存储结构就是用一组任意的存储单元来存放线性表的数据元素,其中每个数据元素存储的信息包括2个部分:即存储数据本身信息的数值域和存储下一个数据元素地址的next域,这个数据元素就被称为结点;
这组存储单元可以是连续的,也可以是不连续的,由于使用链式结构时,因为我们可以得知后一个元素的地址,因此通过这个地址就可以找到下一个元素;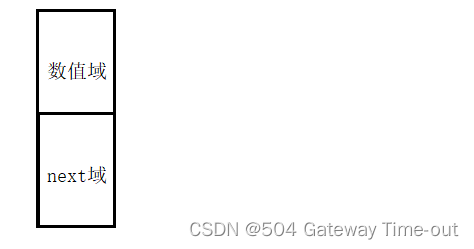 单链表的结构我们就可以简单理解为这样:
单链表的结构我们就可以简单理解为这样: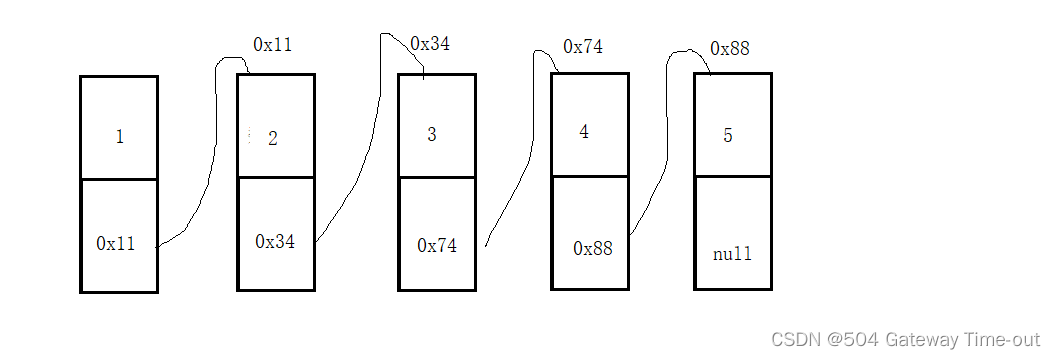
单链表操作的模拟实现
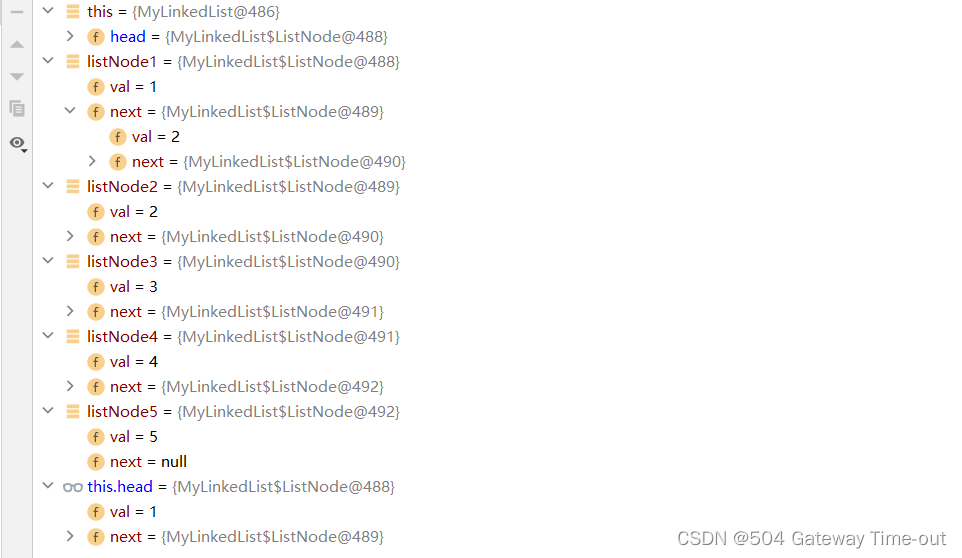
为了更加深入了解单链表的结构,同时对后续代码进行检验,我们先手动创建一个单链表:
public class MyLinkedList { static class ListNode{ public int val; //数值域 public ListNode next; //下一个结点的地址 public ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; } } public ListNode head; //链表的头结点 public void create(){ ListNode listNode1=new ListNode(1); ListNode listNode2=new ListNode(2); ListNode listNode3=new ListNode(3); ListNode listNode4=new ListNode(4); ListNode listNode5=new ListNode(5); listNode1.next=listNode2; listNode2.next=listNode3; listNode3.next=listNode4; listNode4.next=listNode5; this.head=listNode1; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
这样一个简单的单链表就创建完成了
- 单链表的遍历;
大体思路:遍历就是要访问到链表的每一个结点,我们可以首先创建一个结点head,指向当前链表的第一个结点,如果结点head不为空,我们就可以打印该结点的值,然后结点head向后走,指向它的下一个结点,循环访问,循环打印;
//遍历单链表 public void display(){ ListNode head=this.head; while(head!=null){ System.out.print(head.val+" "); head=head.next; } System.out.println(); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 打印链表的长度;
大体思路:打印链表的长度,其本质其实也是遍历链表,可以创建一个临时变量来记录,如果当前的结点不为空,临时变量+1,即可;
//得到单链表的长度 public int size(){ ListNode head=this.head; int count=0; while (head!=null){ count++; head=head.next; } return count; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 查找链表中是否包含了关键字key;
大体思路:代码的核心依然是进行遍历,如果在遍历的过程中找到了与关键字相同的结点,返回true即可;
//查找是否包含关键字key是否在单链表当中 public boolean contains(int key){ ListNode cur=this.head; //这里的循环判断条件不能为cur.next!=null //否则如果是查找的值恰好为最后一个结点,不能进入循环,判断就会错误; while(cur!=null){ if(cur.val!=key){ cur=cur.next; }else{ return true; } } return false; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 头插法
大体思路:头插法是在原链表的第一个结点前面插入新的结点,因此关键点就是让新结点的next指向原链表的第一个结点,然后更新插入之后的头结点;
//头插法 public void addFirst(int data) { ListNode node=new ListNode(data); //如果第一个结点为空,就是node的下一个结点为空,因此可以不用特殊考虑 /* if(this.head==null){ this.head=node; }*/ node.next=this.head; this.head=node; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 尾插法
大体思路:尾插法是在链表的最后一个结点后面插入新的结点,因此找到链表的最后一个结点就是关键;因为链表的最后一个结点的next域为null,因次利用这个特性就可以找到链表的最后一个结点;另外,尾插法我们需要考虑头结点为空的情况,因为当头结点为空时,我们访问一个空节点势必就会出现空指针异常;
//尾插法 public void addLast(int data) { ListNode cur=this.head; ListNode node=new ListNode(data); //头结点为空时 if(this.head==null){ head=node; }else{ while (cur.next!=null){ cur=cur.next; } cur.next=node; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 任意位置插入,第一个数据节点为0号下标;
大体思路:在任意位置插入,可以分为3种情况:插入到链表的最前面,可以直接使用头插法;插入到链表的最后,直接使用尾插法;在链表的任意中间位置插入,需要考虑插入位置的前一个元素和后一个元素,要去到后一个元素,就需要移动下标 -1次;
//任意位置插入,第一个数据节点为0号下标 public void addIndex(int index,int data) { ListNode cur=this.head; ListNode pre=this.head; ListNode node=new ListNode(data); //如果需要插入到整个链表的最前面,直接使用头插法 if (index==0){ addFirst(data); return; } //插入到最后,直接使用尾插法 if (index==size()){ addLast(data); return; } while (index-1!=0){ cur=cur.next; index--; } pre=cur; cur=cur.next; pre.next=node; node.next=cur; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 清空链表
大体思路:很容易想到的清空方式就是直接将头结点置为空,由于链式结构的特点,后续的结点也会依次被清空,但这种做法显得粗暴;可以换一种方式一 一置空:
public void clear(){ ListNode cur=this.head; ListNode curNext=null; while (cur!=null){ curNext=cur.next; cur.next=null; cur=curNext; } this.head=null; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 删除第一次出现关键字为key的节点;
大体思路:删除该结点,其实就是让该结点的上一个结点直接指向该结点的下一个结点,此时该结点不指向任何结点,也不被任何结点指向,相当于删除;
//删除第一次出现关键字为key的节点 public void remove(int key){ ListNode cur=this.head; ListNode pre=cur; if (this.head==null){ System.out.println("链表为空,无法删除"); } if (this.head.val==key){ this.head=this.head.next; } while (cur!=null){ if(cur.val==key){ pre.next=cur.next; return; }else{ pre=cur; cur=cur.next; } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 删除所有值为key的节点;
大体思路:删除所有值为key的结点实际上是对删除第一次出现的关键字key的结点的一个拓展,与只删除一次大体类似,只需要在删完第一个以后继续向后遍历即可;
//删除所有值为key的节点 public void removeAllKey(int key){ if (this.head==null){ System.out.println("链表为空,无法删除"); } ListNode cur=this.head; ListNode pre=cur; while (cur!=null){ if(cur.val==key){ pre.next=cur.next; cur=cur.next; //return; }else{ pre=cur; cur=cur.next; } } if (this.head.val==key){ this.head=this.head.next; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
LinkedList
Java中的链表LinkedList其底层就是一个双向链表,所谓双向链表,与单链表相比,其实就是一个结点增加个一个前驱,即一个双向链表的每个结点由3部分组成,即数值,前驱,后继;
LinkedList的模拟实现
双向链表的实现与单链表较为相似:
public class MyLinkedList { static class LinkNode { public int val; //数值域 public LinkNode prev; //前驱 public LinkNode next; //后继 public LinkNode(int val){ this.val=val; } } public LinkNode head; //链表的头结点 public LinkNode last; //链表的尾巴结点 //头插法 public void addFirst(int data) { LinkNode node=new LinkNode(data); //如果当前链表为空,判断,防止出现空指针异常 if(head==null){ head=node; last=node; }else{ node.next=head; head.prev=node; head=node; } } //尾插法 public void addLast(int data){ LinkNode node=new LinkNode(data); if (head==null){ head=node; last=node; } last.next=node; node.prev=last; node.next=null; last=node; } //任意位置插入,第一个数据节点为0号下标 public void addIndex(int index,int data){ LinkNode node=new LinkNode(data); LinkNode cur=head; if(index<0||index>size()){ System.out.println("插入位置不合法"); return; } //插入位置为0,头插法 if (index==0){ addFirst(data); return; //这里一定要注意返回 } if (index==size()){ addLast(data); return; } //在中间位置插入,首先让cur移动到要插入的位置 while (index!=0){ cur=cur.next; index--; } cur.prev.next=node; node.prev=cur.prev; node.next=cur; cur.prev=node; } //查找是否包含关键字key是否在单链表当中 public boolean contains(int key) { if(head==null){ return false; } LinkNode cur=head; while (cur!=null){ if(cur.val==key){ return true; } cur=cur.next; } return false; } //删除第一次出现关键字为key的节点 public void remove(int key){ LinkNode cur=head; if(head==null){ return; } if(head.val==key){ head=head.next; return; } if (last.val==key){ last=last.prev; last.next=null; return; } while (cur!=null){ if(cur.val==key){ cur.prev.next=cur.next; cur.next.prev=cur.prev; } cur=cur.next; } } //删除所有值为key的节点 public void removeAllKey(int key){ LinkNode cur=head; while (cur!=null){ //表示还没有遍历结束 if(cur.val==key){ if(cur==head){ //如果头结点正好需要删除 head=head.next; if(head!=null){ head.prev=null; } }else{ cur.prev.next=cur.next; if(cur.next!=null){ cur.next.prev=cur.prev; } } cur=cur.next; }else{ cur=cur.next; } } } //得到单链表的长度 public int size(){ int count=0; LinkNode cur=head; while (cur!=null){ count++; cur=cur.next; } return count; } public void display(){ LinkNode cur=head; while (cur!=null){ System.out.print(cur.val+" "); cur=cur.next; } System.out.println(); } public void clear(){ LinkNode cur = head; //遍历链表删除 while (cur != null) { //需要记录下当前值为空的下一个结点 LinkNode curNext = cur.next; ///cur.val = null; //如果数组域是引用类型,需要手动置为null cur.prev = null; cur.next = null; cur = curNext; } head = null; last = null; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
- 134
- 135
- 136
- 137
- 138
- 139
- 140
- 141
- 142
- 143
- 144
- 145
- 146
- 147
- 148
- 149
- 150
- 151
- 152
- 153
- 154
- 155
- 156
- 157
- 158
- 159
- 160
- 161
- 162
- 163
- 164
- 165
- 166
- 167
- 168
- 169
- 170
- 171
- 172
- 173
- 174
- 175
- 176
- 177
- 178
- 179
- 180
- 181
- 182
- 183
- 184
- 185
- 186
- 187
- 188
- 189
- 190
- 191
- 192
- 193
- 194
LinkedList的具体使用
- LinkedList的构造;
public static void main(String[] args) { //没有参数的构造 List<Integer> list1 = new LinkedList<>(); list1.add(1); list1.add(2); list1.add(3); // 使用其他集合容器(list1)中的元素构造list3 List<Integer> list3 = new LinkedList<>(list1); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- LinkedList的一些常用方法;
public static void main(String[] args) { LinkedList<Integer> linkedList=new LinkedList<>(); //插入,默认尾插 linkedList.add(1); linkedList.add(2); linkedList.add(3); linkedList.add(4); linkedList.add(5); //System.out.println(linkedList); // [1, 2, 3, 4, 5] //指定位置插入元素 linkedList.add(2,9); //将9插入到链表的2号位置 //System.out.println(linkedList); // [1, 2, 9, 3, 4, 5] //删除指定位置的元素 linkedList.remove(1); //默认第一个下标为0,删除下标为1位置的元素 //System.out.println(linkedList); // [1, 9, 3, 4, 5] //获取下标位置的元素 int ret=linkedList.get(2); //System.out.println(ret); // 3 //根据下标设置元素值 linkedList.set(3,8); //System.out.println(linkedList); // [1, 9, 3, 8, 5] //判断链表中是否包含了某元素 boolean b=linkedList.contains(9); //System.out.println(b); //true //返回元素的下标,第一个 int r=linkedList.indexOf(5); //System.out.println(r); // 4 //返回元素的下标,最后一个 linkedList.add(3); int r1=linkedList.lastIndexOf(3); System.out.println(r1); //5 //截取链表的部分,以下标截取 List list=linkedList.subList(2,5); System.out.println(list); // [3, 8, 5] //清空链表 linkedList.clear(); //链表的长度 int len=linkedList.size(); System.out.println(len); // 0 }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
public static void main(String[] args) { //没有参数的构造 List<Integer> list1 = new LinkedList<>(); LinkedList<Integer> linkedList=new LinkedList<>(); list1.add(1); list1.add(2); list1.add(3); // 使用其他集合容器(list1)中的元素构造list3 List<Integer> list3 = new LinkedList<>(list1); //尾插入list1中的所有元素 linkedList.addAll(list1); System.out.println(linkedList); //[1, 2, 3] }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
LinkedList的遍历
public static void main(String[] args) { LinkedList<Integer> linkedList1=new LinkedList<>(); //插入,默认尾插 linkedList1.add(1); linkedList1.add(2); linkedList1.add(3); linkedList1.add(4); linkedList1.add(5); //for-each循环 for (int t:linkedList1) { System.out.print(t+" "); // 1 2 3 4 5 } System.out.println(); //for循环 for (int i = 0; i <linkedList1.size() ; i++) { System.out.print(linkedList1.get(i)+" "); // 1 2 3 4 5 } System.out.println(); //使用迭代器遍历---正向遍历 ListIterator<Integer> iterator=linkedList1.listIterator(); while (iterator.hasNext()){ System.out.print(iterator.next()+" "); // 1 2 3 4 5 } System.out.println(); //使用反向迭代器---反向遍历 ListIterator<Integer> iterator1=linkedList1.listIterator(linkedList1.size()); while (iterator1.hasPrevious()){ System.out.print(iterator1.previous()+" "); // 5 4 3 2 1 } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
ArraysList与LinkedList的区别(!)
- ArraysList在物理和逻辑上都是连续的;LinkedList在物理上不连续,在逻辑上连续;
- ArraysList基于数组实现;LinkedList基于双向链表实现;
- ArraysList随机访问的时间复杂度O(1);LinkedList随机访问,时间复杂度为O(n),因此随机访问时前者优于后者;
- ArraysList对于随机访问更加高效;LinkedList对于插入和删除元素更加高效;
-
相关阅读:
基于java冰球馆管理系统计算机毕业设计源码+系统+lw文档+mysql数据库+调试部署
2022暑期复习-Day6
springboot使用MongoTemplate根据正则表达式查询日期数据
SpringBoot集成Thymeleaf——关闭页面缓存——设置热部署
NLP-D31-ARIMA&《人类语言处理》开课&考试&放松
npm、cnpm、pnpm使用详细
【python】奥数题
App基本框架搭建丨日志管理 - KLog
CSS基础
《DevOps 精要:业务视角》- 读书笔记(七)
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_54175406/article/details/126212350
