-
LeetCode-104. Maximum Depth of Binary Tree [C++][Java]
Given the
rootof a binary tree and an integertargetSum, return the number of paths where the sum of the values along the path equalstargetSum.The path does not need to start or end at the root or a leaf, but it must go downwards (i.e., traveling only from parent nodes to child nodes).
Example 1:
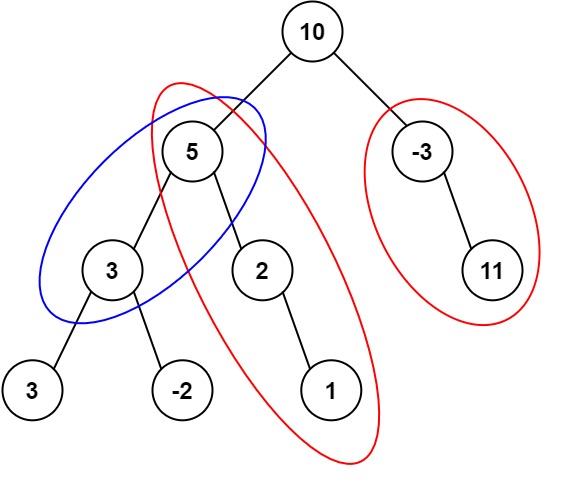
Input: root = [10,5,-3,3,2,null,11,3,-2,null,1], targetSum = 8 Output: 3 Explanation: The paths that sum to 8 are shown.
Example 2:
Input: root = [5,4,8,11,null,13,4,7,2,null,null,5,1], targetSum = 22 Output: 3
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[0, 1000]. -10^9 <= Node.val <= 10^9-1000 <= targetSum <= 1000
【C++】
- /**
- * Definition for a binary tree node.
- * struct TreeNode {
- * int val;
- * TreeNode *left;
- * TreeNode *right;
- * TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
- * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
- * TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
- * };
- */
1. 双递归
小心数据溢出
- class Solution {
- public:
- int pathSum(TreeNode* root, int targetSum) {
- if (root == nullptr) {return 0;}
- return pathSumStartWithRoot(root, targetSum)
- + pathSum(root->left, targetSum)
- + pathSum(root->right, targetSum);
- }
- int pathSumStartWithRoot(TreeNode* root, int sum) {
- if (!root) {return 0;}
- int count = root->val == sum? 1: 0;
- if (double(sum) - double(root->val) < INT_MIN) {return 0;}
- int remaingSum = sum - root->val;
- count += pathSumStartWithRoot(root->left, remaingSum);
- count += pathSumStartWithRoot(root->right, remaingSum);
- return count;
- }
- };
2.递归+回溯
- class Solution {
- public:
- int pathSum(TreeNode* root, int targetSum) {
- int pathCount = 0;
- vector<int> currentPath;
- pathSumHelper(root, targetSum, currentPath, pathCount);
- return pathCount;
- }
- void pathSumHelper(TreeNode *root,
- int sum ,
- vector<int> ¤tPath,
- int &pathCount) {
- if(!root) return;
- currentPath.push_back(root->val);
- double currentSum = 0;
- for(int j=currentPath.size()-1; j>=0; j--) {
- currentSum += (double)currentPath[j];
- if(currentSum == sum) pathCount++;
- }
- pathSumHelper(root->left, sum, currentPath, pathCount);
- pathSumHelper(root->right, sum, currentPath, pathCount);
- currentPath.pop_back();
- }
- };
【Java】
- /**
- * Definition for a binary tree node.
- * public class TreeNode {
- * int val;
- * TreeNode left;
- * TreeNode right;
- * TreeNode() {}
- * TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
- * TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
- * this.val = val;
- * this.left = left;
- * this.right = right;
- * }
- * }
- */
1. 双循环
- class Solution {
- public int pathSum(TreeNode root, int targetSum) {
- if (root == null) {return 0;}
- return pathSumHelper(root, targetSum)
- + pathSum(root.left, targetSum)
- + pathSum(root.right, targetSum);
- }
- public int pathSumHelper(TreeNode root, int sum) {
- if (root == null) {return 0;}
- int count = sum == root.val ? 1 : 0;
- if (Double.valueOf(sum)
- - Double.valueOf(root.val)
- < Integer.MIN_VALUE) {
- return 0;
- }
- int remaining = sum - root.val;
- return count
- + pathSumHelper(root.left, remaining)
- + pathSumHelper(root.right, remaining);
- }
- }
参考文献
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
-
相关阅读:
nodejs+vue 大学生就业管理系统
【Linux常用命令14】Linux系统监控常用命令
Windows 根据dll生成 lib文件
Spring In Action 5 学习笔记 chapter1 拓展
Ubuntu部署OpenStack踩坑指南:还要看系统版本?
window10 mysql zip 安装
Mac安装telnet
Vue3修改Element-plus语言与项目国际化
R语言ggplot2可视化:使用ggplot2可视化散点图、使用labs参数自定义X轴的轴标签文本(customize X axis labels)
内衣洗衣机和手洗哪个干净?迷你洗衣机品牌推荐
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_15711195/article/details/126239920
 https://leetcode.com/problems/maximum-depth-of-binary-tree/
https://leetcode.com/problems/maximum-depth-of-binary-tree/