-
解题-->在线OJ(十九)
1.单词长度的最大乘积

解题思路:
双层for循环,判断两个字符串是否含有相同的字符,如果不包含,计算这两个字符串的乘积,同时,更新ret的值。class Solution { public static int maxProduct(String[] words) { int ret=0; for(int i=0;i<words.length;i++){ for(int j=i+1;j<words.length;j++){ //如果两个字符串不包含相同的字符 if(isNotContains(words[i],words[j])){ //计算两个字符串长度的乘积 int product=words[i].length() * words[j].length(); ret=Math.max(ret,product); } } } return ret; } //判断两个字符串中是否包含相同的字符 public static boolean isNotContains(String s1,String s2){ HashSet set=new HashSet(); for(int i=0;i<s1.length();i++){ set.add(s1.charAt(i)); } for(int i=0;i<s2.length();i++){ if(set.contains(s2.charAt(i))){ return false; } } return true; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
2.每日温度
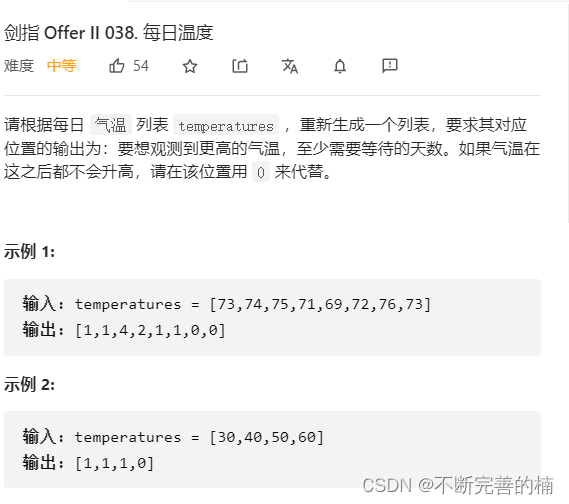
class Solution { public static int[] dailyTemperatures(int[] temperatures) { int[] result=new int[temperatures.length]; for(int i=0;i<temperatures.length;i++){ int count=0; for(int j=i+1;j<temperatures.length;j++){ if(temperatures[j]>temperatures[i]){ count++; result[i]=count; break; }else{ count++; } } } result[result.length-1]=0; return result; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
3.最小时间差
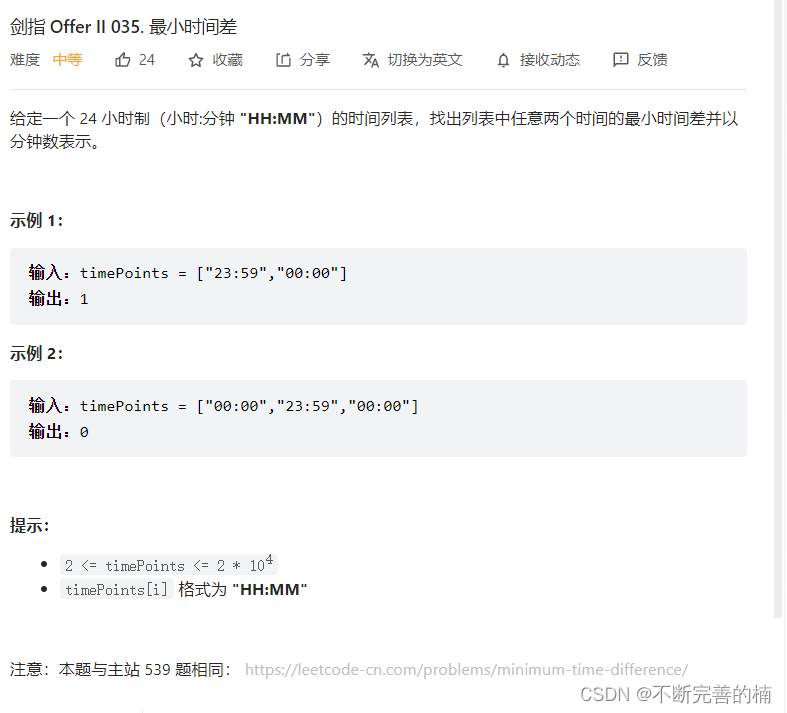
class Solution { public static int findMinDifference(List<String> timePoints) { int[] temp=new int[timePoints.size()]; int num=0; for(String s:timePoints){ temp[num]=(60*((s.charAt(0)-'0')*10+(s.charAt(1)-'0'))+((s.charAt(3)-'0')*10+(s.charAt(4))-'0')); num++; } Arrays.sort(temp); int min=24*60-temp[temp.length-1]+temp[0]; for(int i=0;i<temp.length-1;i++){ min=Math.min(min,temp[i+1]-temp[i]); } return min; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
4.最长连续序列
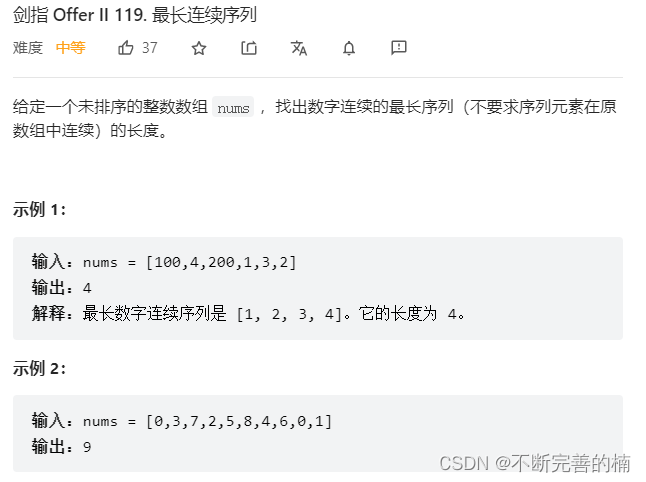
class Solution { public static int longestConsecutive(int[] nums) { //如果数组长度是0,直接返回0 if(nums.length==0){ return 0; } //将数组进行排序 Arrays.sort(nums); int result=1; int count=1; //for循环数组 for(int i=0;i<nums.length-1;i++){ //如果前后两个数之差等于1,count++,如果两数之差等于0,continue,否则,就把count重新赋值给1 if(Math.abs(nums[i+1]-nums[i])==1){ count++; }else if(Math.abs(nums[i+1]-nums[i])==0){ continue; }else{ count=1; } //result时时更新 result=Math.max(result,count); } return result; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
5.0和1个数相同的子数组

解题思路:

class Solution { public static int findMaxLength(int[] nums) { int max=0; HashMap<Integer,Integer> hashMap=new HashMap<>(); int sum=0; //首先,给hashMap里面存入(0,-1) hashMap.put(0,-1); for(int i=0;i<nums.length;i++){ //如果nums[i]等于1,就赋值给1,否则,就赋值给-1 sum+=(nums[i]==1?1:-1); //判断hashMap里面是否包含sum.如果包含,下标i-hashMap.get(sum)的区间范围内都是0和1个数相同的子数组 if(hashMap.containsKey(sum)){ max=Math.max(max,i-hashMap.get(sum)); }else{ //如果hashMap当中不包含sum,hashMap里面直接put数据即可 hashMap.put(sum,i); } } return max; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
6.不含重复字符的最长子字符串
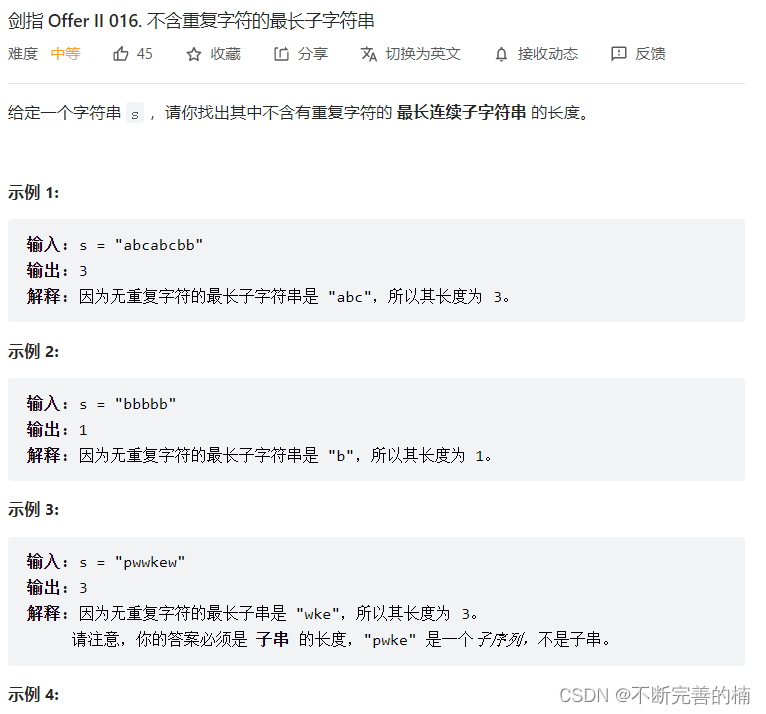
1.定义两个下标,i负责头,j负责尾
2.如果hashMap当中不包含s.charAt(j),那么就更新最大值,并且,往hashMap当中,存入此值;
3.如果hashMap当中包含s.charAt(j),那么更新i的值,i=Math.max(i,hashMap.get(s.charAt(j))),从hashMap当中取到s.charAt(j),与i进行比较,取较大值。
4.更新完i下标之后,再更新最大值和map当中s.charAt(j)的下标。class Solution { public static int lengthOfLongestSubstring(String s) { if(s==""){ return 0; } int max=0; HashMap<Character,Integer> hashMap=new HashMap<>(); int i=0; int j=0; for(;j<s.length();j++){ if(hashMap.containsKey(s.charAt(j))){ i=Math.max(hashMap.get(s.charAt(j)),i); } max=Math.max(max,j-i+1); hashMap.put(s.charAt(j),j+1); } return max; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
7.链表中的两数相加

解题思路:
1.先计算出两个链表的长度;
2.如果两个链表长度均为1的话,进行求和,并且判断和是否大于等于10,从而决定返回的节点个数是一个还是两个;
3.如果其中一个链表长度大于1或者两个链表长度都大于1的话,就进行翻转链表,比如,将,7->2->4->3翻转成3->4->2->7;
4.翻转链表之和,再进行链表,两两节点求和,在求和的过程中,需要注意:两个节点之和是否大于9,如果大于,需要给进位值赋值。
5.对求和之后的链表再进行翻转,最后,返回head即可。class Solution { public static ListNode addTwoNumbers(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) { //首先记录下两个链表的长度 ListNode le=l1; int length1=0; while(le!=null){ length1++; le=le.next; } ListNode le2=l2; int length2=0; while(le2!=null){ length2++; le2=le2.next; } //如果两个链表长度都为1的话,且两值相加小于10的话,直接返回一个节点,值是两个节点的和 if(length1==1 && length2==1){ int temp=l1.val+l2.val; //如果两个节点的值之和大于等于10的话,就需要多一个节点,来保存进位值 if(temp>=10){ int t1=temp; ListNode node=new ListNode(temp%10); ListNode node2=new ListNode(t1/10); node2.next=node; node.next=null; return node2; }else{ return new ListNode(l1.val+l2.val); } } ListNode head = new ListNode(-1); ListNode move=head; //只有链表长度大于1的时候,才需要反转链表 if(length1>1){ l1 = reverseList(l1); } if(length2>1){ l2=reverseList(l2); } //对反转之后的两个链表,进行求和 int ret=0; while(l1!=null && l2!=null){ int temp=0; temp+=l1.val; temp+=l2.val; int count=temp; ListNode node=new ListNode((ret+temp)%10); move.next=node; move=move.next; ret=(ret+temp)/10; l1=l1.next; l2=l2.next; } //当链表1不为空,链表2 为空的时候 while (l1!=null){ int temp=0; temp+=l1.val; ListNode node=new ListNode((ret+temp)%10); move.next=node; move=move.next; ret=(ret+temp)/10; l1=l1.next; } //当链表1为空,链表2不为空的时候 while (l2!=null){ int temp=0; temp+=l2.val; ListNode node=new ListNode((ret+temp)%10); move.next=node; move=move.next; ret=(ret+temp)/10; l2=l2.next; } //当进位值不等于0的时候,需要再创建一个节点来保存这个进位值 if(ret!=0){ ListNode node=new ListNode(ret); move.next=node; move=move.next; } move.next=null; //在所有节点求和之和,再反转链表 head=reverseList(head.next); return head; } //这个方法是控制反转链表的 public static ListNode reverseList(ListNode l1){ ListNode pre=l1; ListNode node=l1.next; pre.next=null; while(node!=null && node.next!=null){ ListNode nodeNext=node.next; node.next=pre; pre=node; node=nodeNext; } node.next=pre; return node; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
8.删除链表的倒数第n个节点

class Solution { public static ListNode removeNthFromEnd(ListNode head, int n) { ListNode temp=head; int length=0; //计算链表长度 while(temp!=null){ length++; temp=temp.next; } //如果有5个节点,删除倒数第2个节点,也就相当于是删除正数的第4个节点 int ret=length-n+1; //如果链表长度大于等于1,要删除第一个节点,直接返回head.next即可 if(length>=1 && ret==1){ return head.next; } ListNode pre=head; ListNode node=head.next; //走到这一步,就证明删除的不是第一个节点,count就赋值于2 //定义三个变量,pre,node,nodeNext //如果node不是待删除节点,pre.next=node //如果node是待删除节点,pre.next=nodeNext int count=2; while(node!=null){ ListNode nodeNext=node.next; //此时,node就是待删除节点 if(count==ret){ pre.next=nodeNext; node=nodeNext; count++; continue; } //node不是待删除节点 pre.next=node; pre=node; node=nodeNext; count++; } //返回头节点即可 return head; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
9.重排链表

1.计算链表长度,链表长度<=2的,直接返回
2.找到链表的中间节点,将链表一分为二,将后半部分的链表进行反转。
3.定义一个新的节点,依次往新的节点后面添加数据,规律是,添加一个前半部分的节点,再添加一个反转后的后半部分的节点
4.再将剩余的节点添加到newNode节点之后class Solution { public static void reorderList(ListNode head) { int leng=0; ListNode temp=head; //计算链表的长度 while (temp!=null){ leng++; temp=temp.next; } //如果链表长度<=2直接返回 if(leng==1||leng==2){ return; } //找到链表的中间节点 ListNode fast=head; ListNode slow=head; ListNode pslow=new ListNode(-1); while(fast!=null && fast.next!=null){ pslow=slow; slow=slow.next; fast=fast.next.next; } ListNode newList1=head; pslow.next=null; //以slow为分界线,将链表分为两部分,后半部分进行反转 ListNode newList2=reverseList(slow); //定义一个新的节点,用于合成两个链表 ListNode newNode=new ListNode(-1); //往新链表后面添加数据 while(newList1!=null && newList2!=null){ newNode.next=newList1; newNode=newNode.next; newList1=newList1.next; newNode.next=newList2; newNode=newNode.next; newList2=newList2.next; } //如果前半部分链表不为空,就直接将剩余的加上去 if(newList1!=null){ newNode.next=newList1; } //如果前半部分链表不为空,就直接将剩余的加上去 if(newList2!=null){ newNode.next=newList2; } } //反转链表 public static ListNode reverseList(ListNode head){ ListNode pre=head; ListNode node=head.next; pre.next=null; while(node!=null){ ListNode nodeNext=node.next; node.next=pre; pre=node; node=nodeNext; } return pre; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
10.链表中环的入口节点
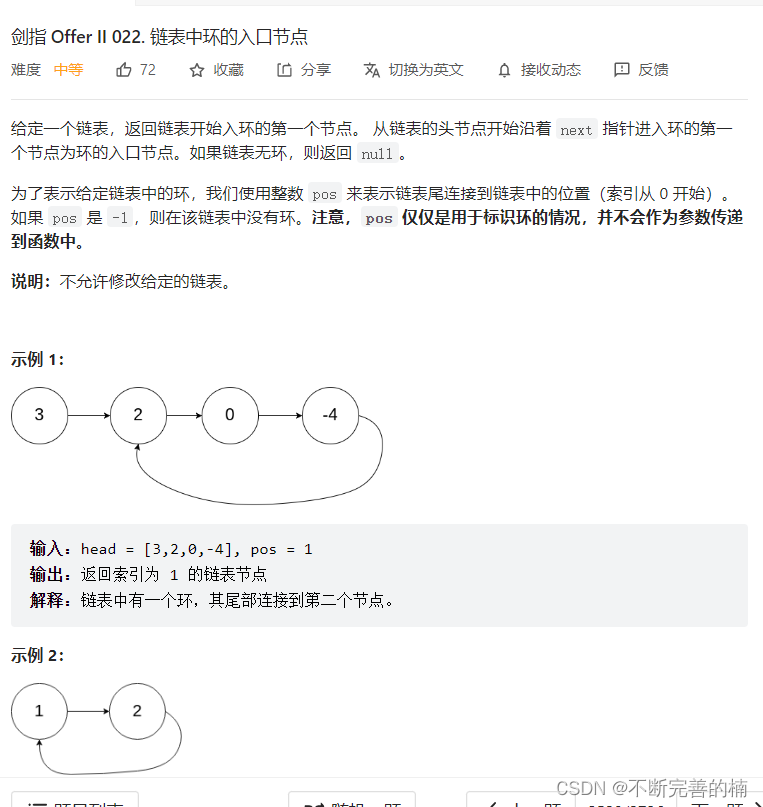
public class Solution { public static ListNode detectCycle(ListNode head) { ListNode slow=head; ListNode fast=head; //先找到相遇节点 while(fast!=null && fast.next!=null){ slow=slow.next; fast=fast.next.next; //找到相遇节点之后,fast=head //然后fast=fast.next;slow=slow.next //当再次相遇的时候,此时,相遇节点就是循环链表中环的入口节点 if(fast==slow){ fast=head; while(fast!=slow){ fast=fast.next; slow=slow.next; } return slow; } } return null; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
-
相关阅读:
谷歌插件将网页转图片
GoLand GC(垃圾回收机制)简介及调优
Ribbon框架原理及解析
X-Frame-Options(点击劫持) 网页劫持漏洞
SpringBoot整合任务系统(quartz和SpringTask)
【Git技巧】第七篇 git分区原理(超级详细)
Axure 9 使用 font awesome 字体发布原型
Verilog 代码题练手 (2-1)
应对广告虚假流量,app广告变现该如何风控?
md-editor-v3拓展工具栏失效的问题
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_51062428/article/details/126133859
