-
反转链表的几种方式(兼顾每日刷题Day15)
题目1概览
法1题解
采用头插法进行链表的反转,头插法是指在原有链表的基础上,依次将位于链表头部的节点摘下,然后采用从头部插入的方式生成一个新链表,则此链表即为原链表的反转版。
法1Code
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * struct ListNode { * int val; * ListNode *next; * ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: ListNode* reverseList(ListNode* head) { ListNode* new_head = NULL; ListNode* temp = NULL; if (head == nullptr || head->next == nullptr) { return head; } while(head!=NULL) { temp = head; head = head->next; temp->next = new_head; new_head = temp; } return new_head; } };- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
因为最后new_head总是会等于temp的值,所以new_head总是会保持第一个的位置,最后直接返回即可。
法1结果

法2题解
采用就地逆转法。
就地逆置法和头插法的实现思想类似,唯一的区别在于,头插法是通过建立一个新链表实现的,而就地逆置法则是直接对原链表做修改,从而实现将原链表反转。值得一提的是,在原链表的基础上做修改,需要额外借助 2 个指针(假设分别为 beg 和 end)。
法2Code
link * reverse(link * head) { link * beg = NULL; link * end = NULL; if (head == NULL || head->next == NULL) { return head; } beg = head; end = head->next; while (end != NULL) { //先将end节点的下一节点接上beg节点,将 end 从链表中摘除 beg->next = end->next; //将 end 移动至链表头 end->next = head; head = end; //调整 end 的指向,另其指向 beg 后的一个节点,为反转下一个节点做准备 end = beg->next; } return head; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
题目2概览
法1题解
由于初始状态合并链表中无节点,因此循环第一轮时无法将节点添加到合并链表中。解决方案:初始化一个辅助节点 d u m dum dum作为合并链表的伪头节点,将各节点添加至 d u m dum dum之后的节点。同时cur用来添加,dum保持不变,cur一开始指向dum。
循环跳出的条件为:l1或者l2有一个为空就跳出,对应的代码就是while(l1 != null && l2 != null),当有一个为null,就跳出while。
比较的条件就是if (l1->val < l2->val) { cur->next = l1; l1 = l1->next; } else { cur->next = l2; l2 = l2->next; }
把小的加入到cur之后,同时更改l1和l2的走向即可。最后判断l1和l2哪一个是非空,把非空的加进cur之后。最后返回dum->next即可。法1Code
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * struct ListNode { * int val; * ListNode *next; * ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: ListNode* mergeTwoLists(ListNode* l1, ListNode* l2) { ListNode *dum = new ListNode(0);//初始化伪头结点dum ListNode *cur = new ListNode(0);//一开始cur指向dum cur = dum; while ((l1 != NULL) && (l2 != NULL)) { if (l1->val < l2->val) { cur->next = l1; l1 = l1->next; } else { cur->next = l2; l2 = l2->next; } cur = cur->next; } if (l1 != NULL) { cur->next = l1; } if (l2 != NULL) { cur->next = l2; } return dum->next; } };- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
法1结果

法2题解
采用递归的方法进行。
法2Code
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * struct ListNode { * int val; * ListNode *next; * ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: ListNode* mergeTwoLists(ListNode* l1, ListNode* l2) { if (l1 == NULL) { return l2; } if (l2 == NULL) { return l1; } if (l1->val < l2->val) { l1->next = mergeTwoLists(l1->next, l2); return l1; } else { l2->next = mergeTwoLists(l1, l2->next); return l2; } } };- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
当
l1->val < l2->val,就把l1的头结点放入第一位,之后要寻找接上这个的下一个结点,怎么寻找呢?采用递归调用,看l1->next和l2哪个更大,然后一直寻找,最后一层一层递归返回;else部分同理。法2结果

题目3概览

题解
把链表压入栈中,然后再一个个pop进行返回,因为已知出栈的个数k,返回最后一个出栈的节点即可。
Code
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * struct ListNode { * int val; * ListNode *next; * ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: ListNode* getKthFromEnd(ListNode* head, int k) { stack<ListNode*>st; while(head!=NULL) { st.push(head); head = head->next; } ListNode* res = NULL; for (int i = 0; i < k; ++i) { res = st.top(); st.pop(); } return res; } };- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
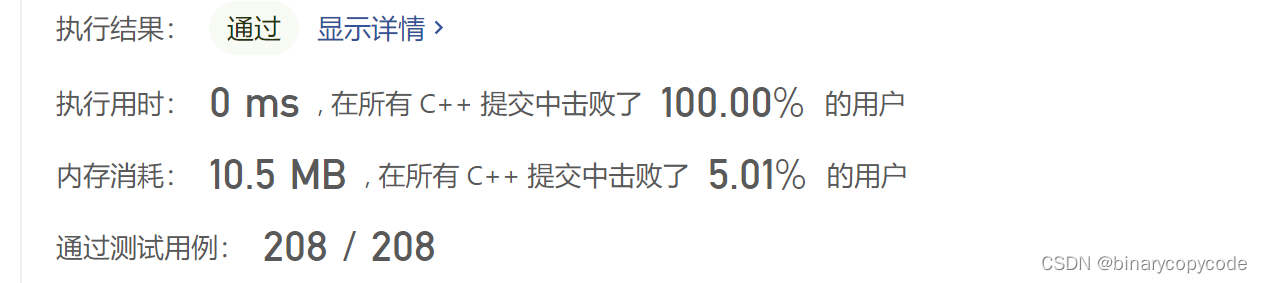
结果
-
相关阅读:
centos7搭建DNS服务完整版
【毕业设计】水果图像识别系统 - 深度学习 OpenCV python
度量方法总结
Python面向对象编程
算法通过村第十一关黄金挑战——位运算如何实现压缩储存
38.企业快速开发平台Spring Cloud+Spring Boot+Mybatis之Highcharts 使用百分比的堆叠柱形图
pnpm新建vite+vue3项目
震惊--Nginx的map指令还能这样用
【LeetCode每日一题】【单调栈】2022-10-21 901. 股票价格跨度 Java实现
MySQL学习(三)——多表连接查询
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_44673253/article/details/126222109