-
多线程(一)
线程的认识
基本概念
线程:
一个顺序的单一程序执行流就是一个线程,代码一句一句的有先后顺序的执行
多线程:
多个单一顺序执行的流程并发允许,造成"感官上同时运行"的效果.
并发
多个线程实际运行是走走停停的。线程调度程序会将CPU运行时间划分为若干个时间片段并尽可能的分配给每个线程,拿到时间片的线程被CPU执行这段时间。
当超时后线程调度程序会再次分配一个时间片给一个线程使得CPU执行它,如此反复。
由于CPU执行时间在纳秒级别,我们感觉不到切换线程运行的过程,所以微观上走走停停,宏观上感觉一起运行的现象称为并发运行!
用途- 当出现多个代码片段执行顺序有冲突时,希望它们各干各的时就应该当放在不同线程上"同时"运行
- 一个线程可以运行,但是多个线程可以更快时,可以使用多个线程运行
线程的声明周期
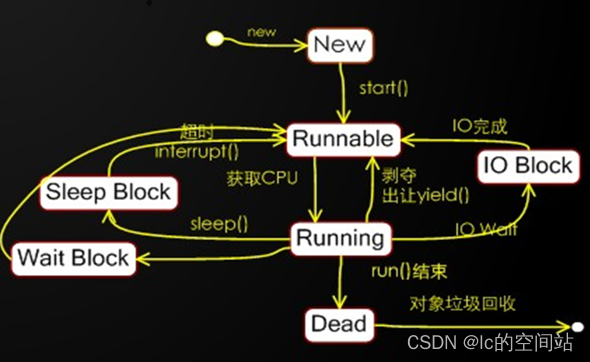
创建线程有两种方式
方式一:继承Thread并重写run()方法
定义一个线程类,重写run方法,在其中定义线程要执行的任务(希望和其他线程并发执行的任务)
注:启动该线程要调用该线程的start方法,而不是run方法!!!
优点
结构简单,利于匿名内部类形式创建
缺点
1:由于java是单继承的,这会导致继承了Thread就无法再继承其他类去服用方法
2:定义线程的同时重写了run方法,这就等于将线程的任务定义在了这个线程中导致线程只能干这件事,重用性很低package thread; public class ThreadDemo1 extends Thread{ public static void main(String[] args) { Thread t1=new MyThread1(); Thread t2=new MyThread2(); t1.start(); t2.start(); } } class MyThread1 extends Thread{ @Override public void run() { for (int i=0;i<1000;i++){ System.out.println("hello 姐"); } } } class MyThread2 extends Thread{ @Override public void run() { for (int i=0;i<1000;i++){ System.out.println("来啦~老弟"); } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
方式二:实现Runnable接口单独定义线程任务
package thread; public class ThreadDemo2 { public static void main(String[] args) { //实例化任务 Runnable r1 = new MyRunnable1(); Runnable r2 = new MyRunnable1(); //创建线程并指派任务 Thread t1=new Thread(r1); Thread t2=new Thread(r2); t1.start(); t2.start(); } } class MyRunnable1 implements Runnable{ @Override public void run() { for (int i=0;i<1000;i++){ System.out.println("你是谁啊?"); } } } class MyRunnable2 implements Runnable{ @Override public void run() { for (int i=0;i<1000;i++){ System.out.println("开门!查水表的!"); } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
匿名内部类形式完成线程的两种创建
package thread; public class ThreadDemo3 { public static void main(String[] args) { Thread t1=new Thread(){ @Override public void run() { for (int i=0;i<1000;i++){ System.out.println("你是谁啊?"); } } }; Runnable r2=new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { for (int i=0;i<1000;i++){ System.out.println("查水表的!"); } } }; Thread t2=new Thread(r2); t1.start(); t2.start(); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
static Thread currentThread()
该方法可以获取运行这个方法的线程
java中的代码都是依靠线程运行的,执行main方法的线程称为主线程
方法,该线程的名字叫做"main",所以通常称它为"主线程"
我们自己定义的线程在不指定名字的情况下系统会分配一个名字
格式为"thread-x"(x是一个数)
后期会学习一个很重要的API:ThreadLocal,它可以使得我们在一个线程上跨越多个方法共享数据使用,其内部要用到currentThread方法来辨别线程,如spring的事务控制就是依靠ThreadLocal实现的。package thread; public class CurrentThreadDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { Thread main = Thread.currentThread(); System.out.println("线程:"+main); dosome(); } public static void dosome(){ Thread t = Thread.currentThread(); System.out.println("执行dosome方法的线程是:"+t); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
运行结果

线程API
获取线程相关信息的方法
package thread; public class ThreadInfoDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { Thread main = Thread.currentThread();//获取主线程 String name=main.getName();//获取线程的名字 System.out.println("名字"+name); long id = main.getId();//获取该线程的唯一标识 System.out.println("id:"+id); int priority = main.getPriority(); System.out.println("优先级:"+priority); boolean isAlive = main.isAlive();//该线程是否活着 System.out.println("是否或者:"+isAlive); boolean isDaemon = main.isDaemon(); System.out.println("是否为守护线程:"+isDaemon); boolean isInterrupted = main.isInterrupted(); System.out.println("是否被中断了"+isInterrupted); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
线程优先级
线程start后会纳入到线程调度器中统一管理,线程只能被动的被分配时间片并发运行,而无法主动索取时间片,线程调度器尽可能均匀的将时间片分配给每个线程。
线程有10个优先级,使用整数1-10表示- 1为最小优先级,10为最高优先级,5为默认值
- 调整线程的优先级可能最大程度的干涉获取时间片的几率,优先级越高的线程获取时间片的次数越多,反之则越少
package thread; public class PriorityDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { Thread max=new Thread(){ @Override public void run() { for (int i=0;i<1000;i++){ System.out.println("max"); } } }; Thread min=new Thread(){ @Override public void run() { for (int i=0;i<1000;i++){ System.out.println("min"); } } }; Thread norm=new Thread(){ @Override public void run() { for (int i=0;i<1000;i++){ System.out.println("norm"); } } }; min.setPriority(Thread.MIN_PRIORITY); max.setPriority(Thread.MAX_PRIORITY); min.start(); norm.start(); max.start(); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
-
相关阅读:
企业电子招标采购系统源码Spring Boot + Mybatis + Redis + Layui + 前后端分离 构建企业电子招采平台之立项流程图
数据结构与算法 | 第一章:概论
电脑上怎么把mov转换成mp4?
【计算机EI检索】2022年第六届视觉,图像与信号处理国际会议(ICVISP 2022)
Pytorch学习:卷积神经网络—nn.Conv2d、nn.MaxPool2d、nn.ReLU、nn.Linear和nn.Dropout
大数据分布式处理框架Hadoop
深入了解Java位运算符
10-QNX与Android双系统通讯之FDBUS(1)
Jest单元测试(一)
数据结构期末复习(十套试卷)库题
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/longgetaotao_06/article/details/126206196
