-
刷题数据结构实现类
- 链表的实现类(ListNode)
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * public class ListNode { * int val; * ListNode next; * ListNode() {} * ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; } * ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; } * } */- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
public class ListNode { public int val; public ListNode next; public ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; } public ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; } public ListNode(int v0, int... values) { this.val = v0; ListNode temp = this; for (int value : values) { temp.next = new ListNode(value); temp = temp.next; } } @Override public String toString() { return String.format("%d -> %s", this.val, this.next); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 二叉树实现类。
import java.util.LinkedList; public class TreeNode { public int val; public TreeNode left; public TreeNode right; public TreeNode() { } public TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; } public TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) { this.val = val; this.left = left; this.right = right; } public TreeNode(int v0, Integer... values) { this.val = v0; LinkedList<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>(); int index = 0; queue.addLast(this); while (index < values.length) { int size = queue.size(); for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) { TreeNode node = queue.removeFirst(); if (index < values.length && values[index] != null) { node.left = new TreeNode(values[index]); queue.addLast(node.left); } index++; if (index < values.length && values[index] != null) { node.right = new TreeNode(values[index]); queue.addLast(node.right); } index++; } } } @Override public String toString() { LinkedList<Integer> arr = new LinkedList<>(); LinkedList<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>(); queue.addLast(this); while (!queue.isEmpty()) { int size = queue.size(); for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) { TreeNode node = queue.removeFirst(); if (node != null) { arr.addLast(node.val); queue.addLast(node.left); queue.addLast(node.right); } else { arr.addLast(null); } } } while (arr.peekLast() == null) { arr.removeLast(); } return arr.toString(); } public static void main(String[] args) { TreeNode root = new TreeNode(1, null, 2, 3, 4, 5); System.out.println(root); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 二叉搜索树实现类
其实二叉树的实现类有两种模型,一种是单独的value值模型,一种是key-value模型。在我们的leetcode中,我们一般使用单独的value值模型,因为我们一般在其中保存的是int类型的数据。
import java.util.LinkedList; public class Tree{ private TreeNode root; private class TreeNode{ private int val; private TreeNode left; private TreeNode right; public TreeNode(int val,TreeNode left,TreeNode right) { this.val=val; this.left=left; this.right=right; } public TreeNode(int v0, Integer... values) { this.val = v0; LinkedList<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>(); int index = 0; queue.addLast(this); while (index < values.length) { int size = queue.size(); for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) { TreeNode node = queue.removeFirst(); if (index < values.length && values[index] != null) { node.left = new TreeNode(values[index]); queue.addLast(node.left); } index++; if (index < values.length && values[index] != null) { node.right = new TreeNode(values[index]); queue.addLast(node.right); } index++; } } } @Override public String toString() { LinkedList<Integer> arr = new LinkedList<>(); LinkedList<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>(); queue.addLast(this); while (!queue.isEmpty()) { int size = queue.size(); for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) { TreeNode node = queue.removeFirst(); if (node != null) { arr.addLast(node.val); queue.addLast(node.left); queue.addLast(node.right); } else { arr.addLast(null); } } } while (arr.peekLast() == null) { arr.removeLast(); } return arr.toString(); } } public Tree() { this.root=null; } public void insert(int x) { root=insert(this.root,x); } public TreeNode get(int x) { return get(root,x); } public void delete(int x) { root=delete(this.root,x); } public TreeNode insert(TreeNode root,int x) { if(root==null) { return new TreeNode(x,null,null); } if(x<root.val) { root.left=insert(root.left,x); } else if(x>root.val) { root.right=insert(root.right,x); } else{ root.val=x; } return root; } //注意两者递归的不同,对于上面的递归来说,他最终返回的是根节点,是整个树,而他自己是树上插入的一个节点 //而下面的这个是有值就行,我抓住这个节点就直接返回 public TreeNode get(TreeNode root,int x) { if(root==null) { return null; } if(x<root.val) { return get(root.left,x); } else if(x>root.val) { return get(root.right,x); } else { return root; } } public TreeNode delete(TreeNode root,int x) { if(root==null) { return null; } if(root.val<x) { root.right=delete(root.right,x); } else if(root.val>x) { root.left=delete(root.left,x); } else{ //找到右子树中最小的结点 if(root.right==null){ return root.left; } if(root.left==null){ return root.right; } TreeNode minnode=root.right; while(minnode.left!=null) { minnode=minnode.left; } TreeNode temp=root.right; // while(temp.left!=null) // { // if(temp.left.left==null) // { // temp.left=null; // } // else{ // temp=temp.left; // } // } root.right=delete(root.right,minnode.val); minnode.left=root.left; minnode.right=root.right; root=minnode; } return root; } public void show() { System.out.println(root.toString()); } public static void main(String[] args) { Tree tree = new Tree(); // tree.insert(1); // tree.insert(0); // tree.insert(10); // tree.insert(3); // tree.insert(6); tree.insert(5); tree.insert(3); tree.insert(6); tree.insert(2); tree.insert(4); tree.insert(7); tree.show(); tree.delete(3); tree.show(); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
- 134
- 135
- 136
- 137
- 138
- 139
- 140
- 141
- 142
- 143
- 144
- 145
- 146
- 147
- 148
- 149
- 150
- 151
- 152
- 153
- 154
- 155
- 156
- 157
- 158
- 159
- 160
- 161
- 162
- 163
- 164
- 165
- 166
- 167
- 168
- 169
- 170
- 171
- 172
- 173
- 174
- 175
- 176
- 177
- 178
- 179
- 180
- 181
- 182
- 183
- 184
- 185
- 186
- 187
- 188
- 189
由于对于二叉搜索树来说,有一定的限制不用于一般的二叉树,必须满足:
一棵空树或者具有下列性质的二叉树:- 若任意节点的左子树不空,则左子树上所有结点的值均小于它的根结点的值;
- 若任意节点的右子树不空,则右子树上所有结点的值均大于它的根结点的值;
- 任意节点的左、右子树也分别为二叉查找树。
- 没有键值相等的节点(no duplicate nodes)。
所以我们在对二叉搜索树进行初始化的时候,需要考虑这样的限制,所以我们提供了相应的单值插入方法、删除方法以及查找方法。需要注意的是如果我们最终希望返回的是整个的树对象,我们就要在每一步的递归中用相应的节点去接受递归方法的返回值,使得整个树节点连接起来。
删除节点时可以分为三种情况:
被删除的节点没有任何任何子节点,直接该节点的父节点的link置为null。
被删除的节点没有有左子树或者右子树,则直接返回其左子树或右子树
被删除的节点既有左子树又有右子树,这个时候有两种选择:
选择1:
找到被删除的节点t
找到t的右子树中最小的节点,保存到局部变量minnode中
删除t的右子树中的最小节点,并让minnode的右子树等于已经删除掉最小节点的右子树
将minnode的左节点设置为t的左节点选择2:
找到被删除的节点t
找到t的左子树中最大的节点,保存到局部变量maxnode中
删除t的左子树中的最大节点,并让maxnode的左子树等于已经删除掉最大节点的左子树
将maxnode的右节点设置为t的右节点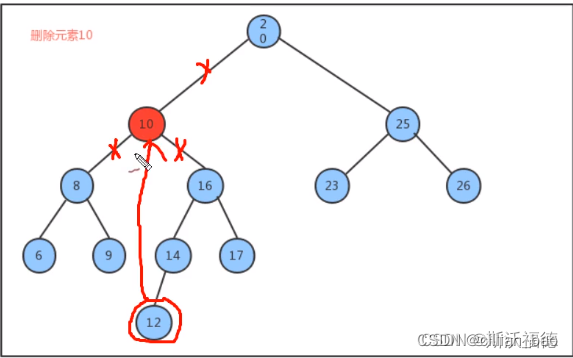
-
相关阅读:
Linux中“EXT 类型文件恢复与xfs 类型文件备份和恢复”
FineBI 无法将聚合和非聚合参数混用(或条件求和)
VMWARE 服务器整合为战提供的解决方案
微信公众号开发接入
为什么资源管理对现代企业很重要?
Eigen矩阵运算库快速上手
并行计算的量化模型及其在深度学习引擎里的应用
区间预测 | Matlab实现QRCNN-BiGRU-Attention分位数回归卷积双向门控循环单元注意力机制时序区间预测
新建一个flask项目
大厂必备的6款React UI框架
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/cillian_bao/article/details/126065034
