-
剑指Offer面试题解总结21-30
剑指Offer(21~30)
调整数组顺序使奇数位于偶数前面
题链
题解:利用两个指针分别指向数组的首元素和尾元素,尾指针向前遍历遇到奇数停止,并将尾指针指向的奇数赋值给头指针指向的元素;头指针向后遍历遇到偶数停止,并将头指针指向的偶数赋值给尾指针指向的元素,重复这个过程.整个过程类似于一趟快排public int[] exchange(int[] nums) { if(nums == null || nums.length == 0){ return nums; } int n = nums.length; int l = 0,r = n-1; int key = nums[0]; while(l < r){ while(r > l && nums[r] % 2 == 0){ r--; } nums[l] = nums[r]; while(l < r && nums[l] % 2 == 1){ l++; } nums[r] = nums[l]; } nums[l] = key; return nums; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
链表中倒数第k个节点
题链
题解:经典的链表题.首先定义cur指向头节点然后向cur沿链表方向移动k步,之后定义res节点指向头结点,同时移动cur和res,当res指向null时res指向的节点就是链表中倒数第k个节点public ListNode getKthFromEnd(ListNode head, int k) { ListNode fast = head; while(k-- > 0){ fast = fast.next; } ListNode slow = head; while(fast != null){ slow = slow.next; fast = fast.next; } return slow; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
反转链表
题链
题解:经典链表题.定义两个指针pre,cur分别指向链表头元素和头元素的下一个节点.之后每次翻转两个元素的指向,然后向后移动知道cur指向null.需要注意的是在遍历的过程中需要事先保存好cur的下一个节点.public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) { //当链表中有0或1个元素时直接返回即可 if(head == null || head.next == null){ return head; } ListNode pre = head,cur = head.next; while(cur != null){ ListNode newCur = cur.next; cur.next = pre; if(pre == head){ pre.next = null; } pre = cur; cur = newCur; } return pre; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
合并两个有序的链表
题链
题解:经典链表题.定义一个虚拟节点dummy和cur并令cur指向dummy,然后分别遍历两个有序链表的元素,然后比较两个节点值的大小将较小的节点的值赋给一个新的节点,然后令cur的下一个节点指向新节点并同时将指针更新到下一个节点.当两个链表中有一个链表遍历结束后直接将cur指向另一个没有遍历完链表的指针上.最终返回dummy的下一个节点public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) { ListNode yummy = new ListNode(-1); ListNode cur = yummy; ListNode cur1 = l1, cur2 = l2; while(cur1 != null && cur2 != null){ if(cur1.val < cur2.val){ cur.next = cur1; cur = cur1; cur1 = cur1.next; }else{ cur.next = cur2; cur = cur2; cur2 = cur2.next; } } cur.next = cur1 == null ? cur2 : cur1; return yummy.next; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
树的子结构
题链
题解:经典二叉树题.首先构造辅助函数来比较两个二叉树是否完全相同.然后顺序遍历A的所有子树中是否存在和B结构相同的二叉树,如果有则直接返回true,否则返回false.public boolean isSubStructure(TreeNode A, TreeNode B) { if(A == null && B == null){ return true; }else if((A == null || B == null)){ return false; } if(isSameTree(A,B)){ return true; } return isSubStructure(A.left,B) || isSubStructure(A.right,B); } public boolean isSameTree(TreeNode A,TreeNode B){ if(B == null){ return true; }else if((A == null || B == null)){ return false; } if(A.val != B.val){ return false; } return isSameTree(A.left,B.left) && isSameTree(A.right,B.right); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
二叉树的镜像
题链
题解:经典二叉树题.直接递归每个子树的左右节点即可.public TreeNode mirrorTree(TreeNode root) { if(root == null){ return null; } TreeNode r = new TreeNode(root.val); r.left = mirrorTree(root.right); r.right = mirrorTree(root.left); return r; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
对称的二叉树
题链
题解:经典的二叉树题.递归判断每个子树是否对称.首先遍历根的左右子节点的值是否相同,如果不相同则直接返回false,然后比较root.left.right和root.right.left以及root.left.left和root.right.right.全部遍历完如果都对称则返回true.public boolean isSymmetric(TreeNode root) { if(root == null){ return true; } return func(root,root); } public boolean func(TreeNode root1, TreeNode root2){ if(root1 == null && root2 == null){ return true; }else if(root1 == null || root2 == null){ return false; } if(root1.val != root2.val){ return false; } return func(root1.left,root2.right) && func(root1.right,root2.left); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
顺时针打印矩阵
题链
题解:按照从外到里每层每层的输出.定义四个指向left,right,top,bottom,每次打印完一层元素后,更新left,right,top,bottom的值直到出现left>right或者top>bottom.在每层打印的过程中,按照下述规则进行打印: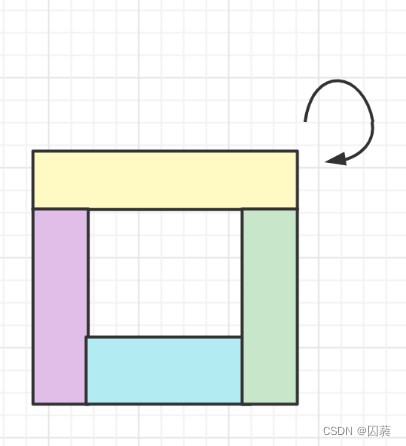
同时要考虑最里层如果只有一行或者一列的时候只需要更新其中的两组即可(黄色和绿色)public int[] spiralOrder(int[][] matrix) { if (matrix == null || matrix.length == 0 || matrix[0].length == 0) { return new int[0]; } int rows = matrix.length, columns = matrix[0].length; int[] order = new int[rows * columns]; int index = 0; int left = 0, right = columns - 1, top = 0, bottom = rows - 1; while (left <= right && top <= bottom) { for (int column = left; column <= right; column++) { order[index++] = matrix[top][column]; } for (int row = top + 1; row <= bottom; row++) { order[index++] = matrix[row][right]; } //当最里层只有一行或一列时不需要更新蓝色和紫色的区域. if (left < right && top < bottom) { for (int column = right - 1; column > left; column--) { order[index++] = matrix[bottom][column]; } for (int row = bottom; row > top; row--) { order[index++] = matrix[row][left]; } } left++; right--; top++; bottom--; } return order; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
包含min函数的栈
题链
题解:定义两个栈d1,d2,其中d1负责元素的进出,d2负责记录当前栈中的最小元素.d1就正常进出元素即可.对于d2而言,在push元素num1时和d2的栈顶元素进行比较,如果num1更小,则d2中也弹入num1.在pop栈d1的栈顶元素num时和d2的栈顶元素比较,如果相等,则弹出d2的栈顶元素.Deque<Integer> s; Deque<Integer> minS; public MinStack() { s = new LinkedList<>(); minS = new LinkedList<>(); } public void push(int x) { s.push(x); if(minS.size() == 0 || x <= minS.peek()){ minS.push(x); } } public void pop() { int x = s.pop(); if(x == minS.peek()){ minS.pop(); } } public int top() { return s.peek(); } public int min() { return minS.peek(); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
-
相关阅读:
了解一下pnpm
python线程
Flink分区之Flink分区策略整理
872. 叶子相似的树-遍历树存储数据对比
嵌入式必备技能---git与github
javacpp gradle集成
vue中在弹框中使用form表单,取消默认的回车提交效果-刷新页面
Java二叉树的镜像
Dubbo面试题汇总【40题】
1、java基本语法
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_52477733/article/details/126200641
