-
Reactor反应堆:EventLoop的执行流程
Reactor反应堆:EventLoop的执行流程
EventLoop相当于Reactor模型中的Reactor组件,是Event事件和Demultiplex多路分发器的桥梁。EventLoop的执行时序图如下:
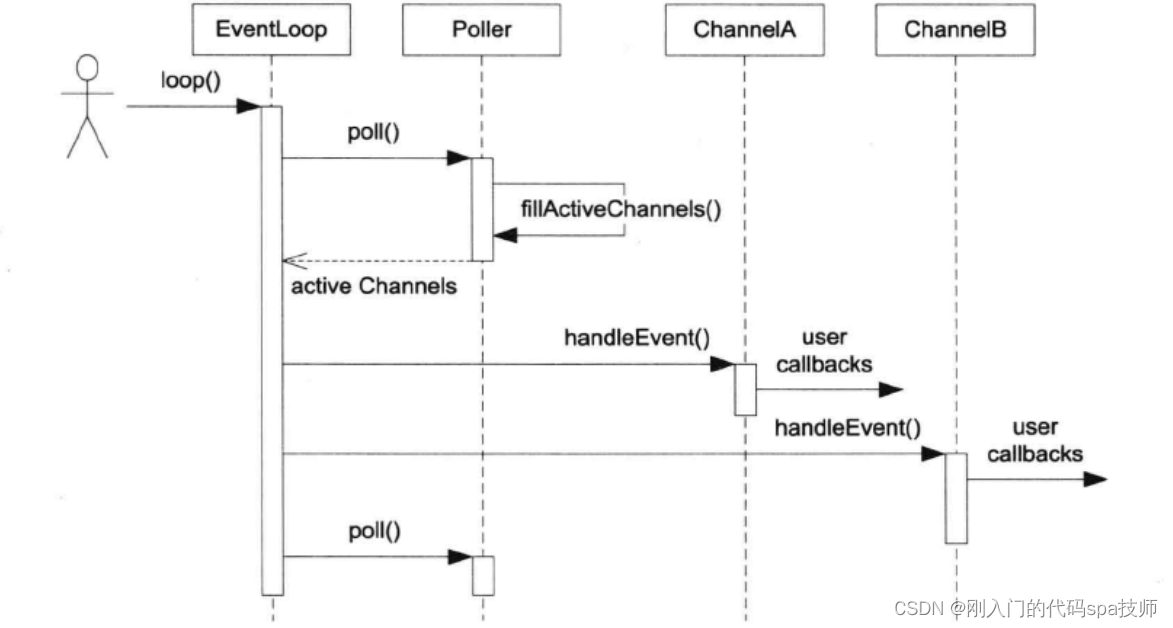
loop()的处理流程:- 调用poll()(对应的是epoll_wait),开启监听EventLoop上Poller注册的事件,
- poll()(对应的是epoll_wait)返回,执行fillActiveChannels()填充发生事件的Channel
- EventLoop获取active Channels,依次执行active Channels上发生的事件所注册的回调
- 下一轮循环
对mainLoop来说,Poller上只有一个fd就是listenfd,pool()即开始监听listenfd上到来的新连接,handleEvent()做的就是accept()得到connfd,并打包成Channel,然后通过eventfd唤醒subLoop把这个Channel添加到它的Poller中。如果只有一个loop,mainLoop就要把这个loop加入到自己的Poller上。
对subLoop来说,刚开始Poller上只监听了一个fd就是eventfd,随着mainLoop触发eventfd上的事件,subLoop上监听的fd除了eventfd外就是和accept(listenfd)得到的connfd了。接下来除了除了eventfd触发的新连接事件,还有就是connfd上触发的各种事件了。
重写EventLoop.h:
#pragma once #include "noncopyable.h" #include "Timestamp.h" #include "CurrentThread.h" #include#include #include #include #include class Channel; class Poller; //时间循环类 主要包含了两个大模块 Channel Poller(epoll的抽象) class EventLoop : noncopyable { public: using Functor = std::function<void()>; EventLoop(); ~EventLoop(); //开启事件循环 void loop(); //结束事件循环 void quit(); Timestamp pollReturnTime() const{ return pollReturnTime_; } //在当前Loop中执行 void runInLoop(Functor cb); //把cb放入队列中,唤醒loop所在的线程,执行cb void queueInLoop(Functor cb); //用来唤醒loop所在线程的,往eventfd写一个字节 void wakeup(); //EventLoop的方法 =》 Poller的方法 void updateChannel(Channel* channel); void removeChannel(Channel* channel); void hasChannel(Channel* channel); //判断EventLoop对象是否在自己的线程里面 bool isInLoopThread() const {return threadId_ == CurrentThread::tid(); } private: void handleRead(); // wake up, eventfd被触发 void doPendingFunctors(); //执行回调 using ChannelList = std::vector<Channel*>; std::atomic_bool looping_; std::atomic_bool quit_; const pid_t threadId_; //基类当前loop所在线程的id Timestamp pollReturnTime_; //poller返回发生事件的channels的时间点 std::unique_ptr<Poller> poller_; int wakeupFd_; //主要作用:当mainLoop获取新用户的channel,通过轮询算法选择一个subLoop,通过该成员唤醒subLoop处理channel std::unique_ptr<Channel> wakeupChannel_; ChannelList activeChannels_; std::atomic_bool callingPendingFunctors_; //标识当前线程释放有需要执行的回调操作 std::vector<Functor> pendingFunctors_; //存储loop需要执行的所有回调操作,线程不安全,因为poll()返回后会从这取回调,别的线程会往这放回调 std::mutex mutex_; //用来保护上面vector容器的线程安全操作 }; - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
mainLoop开启循环后,一次循环的执行流程如下:
- 调用poller_成员epoll_wait()监听新连接
- epoll_wait返回做回调,回调的任务就是把建立的连接打包成channel并关联到一个subLoop上,把处理的回调加到pendingFunctors_,并唤醒subLoop处理
- 下次循环
EventLoop中的接口大部分都是提供给subLoop使用的,subLoop一次循环的执行流程:
- 调用poller_成员epoll_wait()监听IO事件
- epoll_wait()返回,执行发生事件的回调
- 取出pendingFunctors_的回调并执行
重写EventLoop.cc:
#include "EventLoop.h" #include "Logger.h" #include "Poller.h" #include "Channel.h" #include#include #include #include #include //防止一个线程创建多个EventLoop __thread EventLoop* t_loopInThisThread = 0; //定义默认的Poller IO复用接口的超时时间 const int kPollTimeMs = 10000; //用来创建wakeupfd,用来唤醒subReactor处理新来的channel int createEventfd() { int evtfd = ::eventfd(0, EFD_NONBLOCK | EFD_CLOEXEC); if(evtfd < 0) { LOG_FATAL("eventfd error:%d \n",errno); } return evtfd; } EventLoop::EventLoop() :looping_(false) ,quit_(false) ,callingPendingFunctors_(false) ,threadId_(CurrentThread::tid()) ,poller_(Poller::newDefaultPoller(this)) ,wakeupFd_(createEventfd()) ,wakeupChannel_(new Channel(this, wakeupFd_)) { LOG_DEBUG("EventLoop created %p in thread %d \n", this, threadId_); if(t_loopInThisThread) { LOG_FATAL("Another EventLoop %p exists in this thread %d \n", t_loopInThisThread, threadId_); } else { t_loopInThisThread = this; } //设置wakeupfd的事件类型以及发生事件后的回调操作 wakeupChannel_->setReadCallback(std::bind(&EventLoop::handleRead, this)); //每个EventLoop都将监听wakeupChannel的EPOLLIN读事件 wakeupChannel_->enableReading(); } //开启事件循环 void EventLoop::loop() { looping_ = true; quit_ = false; //LOG_INFO("EventLoop %p start looping. \n", this); while(!quit_) { activeChannels_.clear(); //监听两类fd 一类是clientfd,另一种是wakeupfd pollReturnTime_ = poller_->poll(kPollTimeMs, &activeChannels_); for(Channel* channel : activeChannels_) { //Poller监听哪些channel发生事件了,然后上报给EventLoop,通知channel处理相应的事件 channel->handleEvent(pollReturnTime_); } //执行当前EventLoop事件循环需要处理的回调操作 /** * IO线程 mainloop accept fd 打包 =》 channel 分发给 subloop * mainLoop事先注册一个回调cb(需要subLoop来执行) wakeup subLoop后,执行下面的方法,执行之前mainLoop注册的cb操作 */ doPendingFunctors(); } LOG_INFO("EventLoop %p stop looping. \n", this); } //结束事件循环 1、loop在自己的线程调用quit 2、在非loop的线程中,调用loop的quit void EventLoop::quit() { quit_ = true; if(!isInLoopThread()) { wakeup(); } } //在当前Loop中执行 void EventLoop::runInLoop(Functor cb) { if(isInLoopThread()) //在当前loop线程中执行cb { cb(); } else //在非当前loop线程中执行cb,需要唤醒loop所在线程,执行cb { queueInLoop(cb); } } //把cb放入队列中,唤醒loop所在的线程,执行cb void EventLoop::queueInLoop(Functor cb) { { std::unique_lock<std::mutex> lock(mutex_); pendingFunctors_.emplace_back(cb); } //唤醒相应的,需要执行上面回调操作的loop线程 // ||callingPendingFunctors_表示当前loop正在执行回调,但是loop又有了新的回调,为了防止有回调未处理时阻塞等待 if(!isInLoopThread() || callingPendingFunctors_) { wakeup(); } } //用来唤醒loop所在线程的 向wakeupfd_写一个数据 void EventLoop::wakeup() { uint64_t one = 1; ssize_t n = write(wakeupFd_, &one, sizeof one); if(n != sizeof one) { LOG_ERROR("EventLoop::wakeup() write %lu bytes instead of 8 \n", n); } } //EventLoop的方法 =》 Poller的方法 void EventLoop::updateChannel(Channel* channel) { poller_->updateChannel(channel); } void EventLoop::removeChannel(Channel* channel) { poller_->removeChannel(channel); } void EventLoop::hasChannel(Channel* channel) { poller_->hasChannel(channel); } void EventLoop::doPendingFunctors() //执行回调 { std::vector<Functor> functors; callingPendingFunctors_ = true; { std::unique_lock<std::mutex> lock(mutex_); functors.swap(pendingFunctors_); } for(const Functor functor : functors) { functor(); //执行当前loop需要执行的回调操作 } callingPendingFunctors_ = false; } void EventLoop::handleRead() { uint64_t one = 1; ssize_t n = read(wakeupFd_, &one, sizeof one); if(n != sizeof one) { LOG_ERROR ("EventLoop::handleRead() reads %ld bytes instead of 8", n); } } EventLoop::~EventLoop() { wakeupChannel_->disableALL(); wakeupChannel_->remove(); ::close(wakeupFd_); t_loopInThisThread = nullptr; } - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
- 134
- 135
- 136
- 137
- 138
- 139
- 140
- 141
- 142
- 143
- 144
- 145
- 146
- 147
- 148
- 149
- 150
- 151
- 152
- 153
- 154
- 155
- 156
- 157
- 158
- 159
- 160
- 161
- 162
- 163
- 164
- 165
- 166
- 167
- 168
- 169
- 170
- 171
- 172
- 173
- 174
- 175
- 176
- 177
- 178
- 179
- 180
- 181
- 182
- 183
-
相关阅读:
一文读懂Elephant Swap,为何为ePLATO带来如此高的溢价?
sqlserver常用操作总结
用什么命令看Linux系统的体系架构
如何在Linux将Spring Boot项目的Jar包注册为开机自启动系统服务
竞赛 基于机器视觉的二维码识别检测 - opencv 二维码 识别检测 机器视觉
Advantage Actor-Critic优势演员-评论员(A2C)
zookeeper核心源码分析
Apollo安装全攻略
Android 自定义Edittext 和TextView 提示文字和填入内容不同的粗细组件
ArrayList 源码分析
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_43973403/article/details/126187520
