-
Day 87
_Spring技术–构造器注入
-
在实现类中定义参数类型,包括引用类型的参数和基本类型的参数
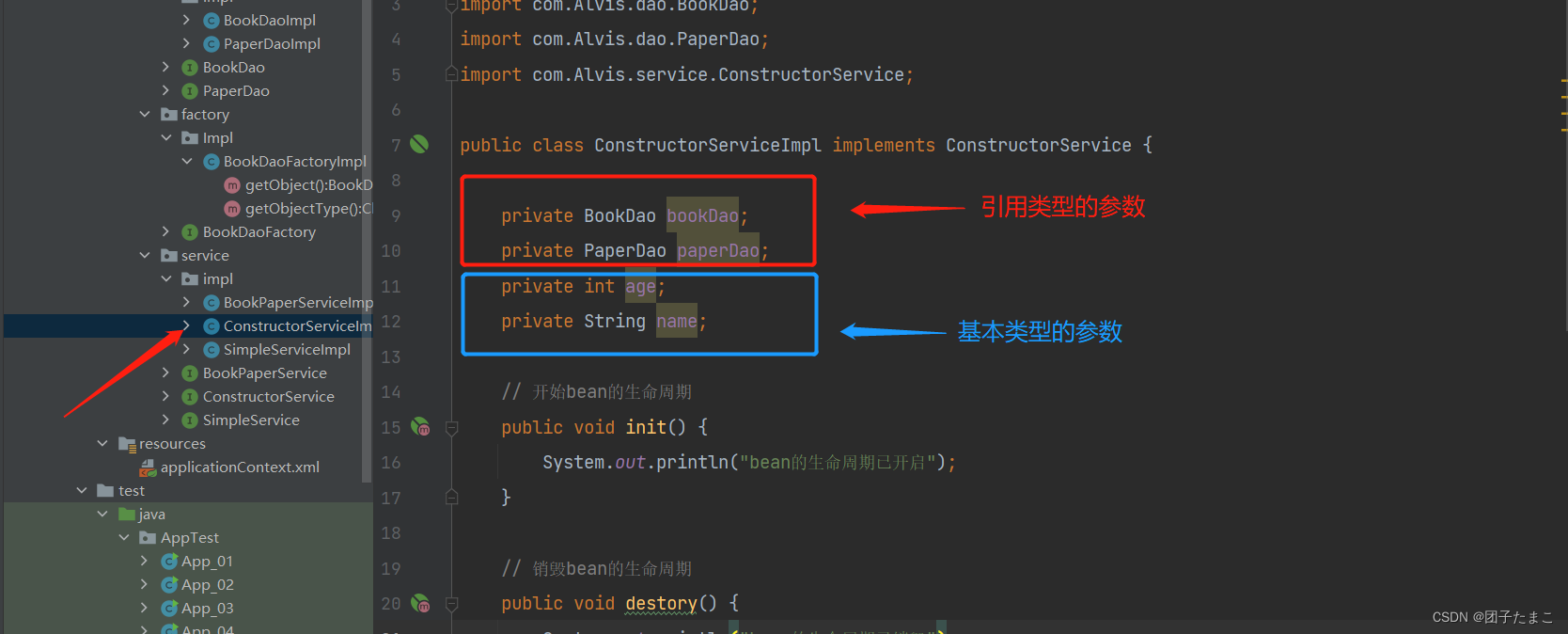
-
在applicationContext.xml文件中配置bean
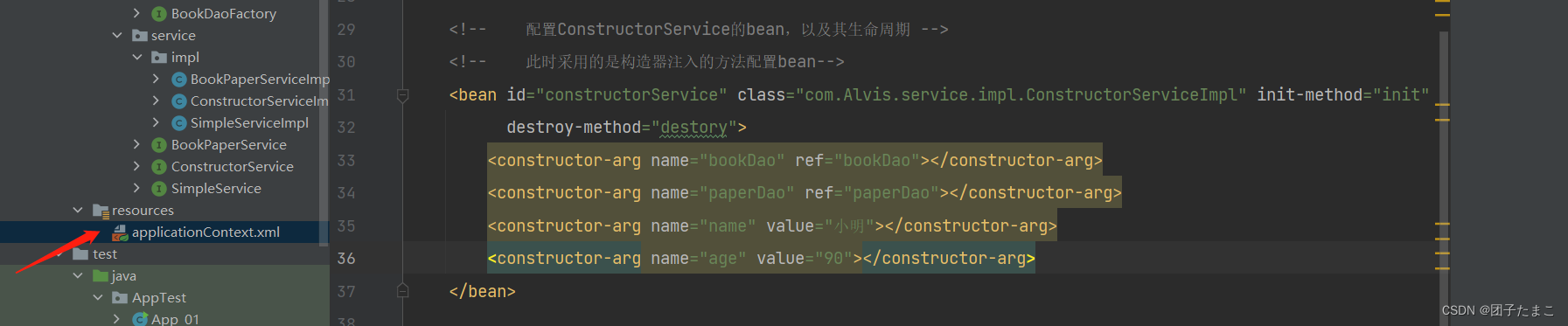
-
在test文件中编写java程序实现构造器注入的试验
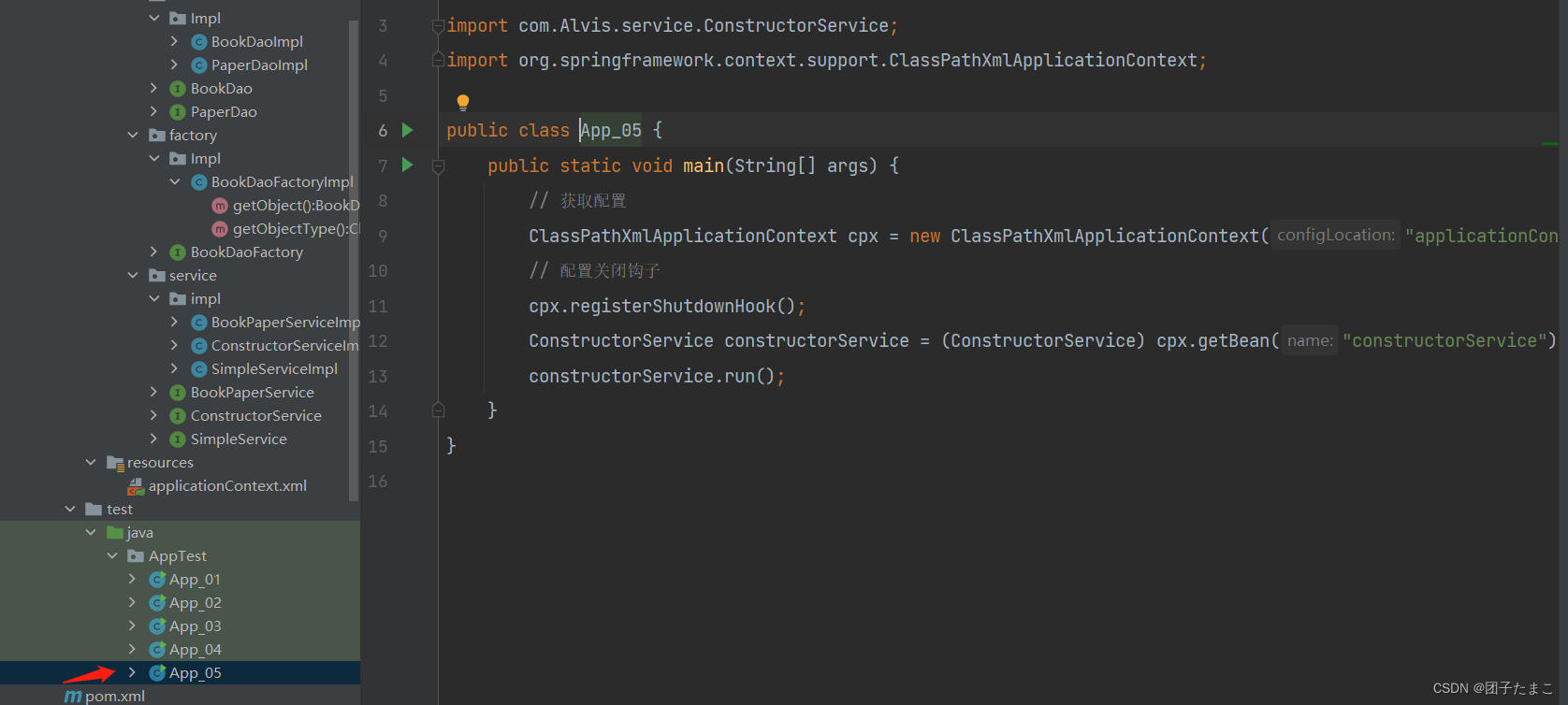
-
package AppTest; import com.Alvis.service.ConstructorService; import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; public class App_05 { public static void main(String[] args) { // 获取配置 ClassPathXmlApplicationContext cpx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml"); // 配置关闭钩子 cpx.registerShutdownHook(); ConstructorService constructorService = (ConstructorService) cpx.getBean("constructorService"); constructorService.run(); } } ============================================= 实现类已运行 init 已执行 bean 生命周期开启 bean 生命周期开始 bean的生命周期已开启 this is ConstructorService... this is BookDao ... this is PaperDao... name: 小明 age: 90 bean的生命周期已销毁 bean 生命周期已销毁 bean 的生命周期已销毁 destory 已执行 进程已结束,退出代码0- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
-
依赖注入方式选择:
- 强制依赖使用构造器进行,使用setter注入有概率不进行注入导致null对象出现
- 可选依赖使用setter注入进行,灵活性强
- Spring框架倡导使用构造器,第三方框架内部大多数采用构造器注入的形式进行数据初始化,这相对严谨
- 如果有必要可以两者同时使用,使用构造器注入完成强制依赖的注入,使用setter注入完成可选依赖的注入
- 实际开发过程中还要根据实际情况分析,如果受控对象没有提供setter方法就必须使用构造器注入
- 自己开发的模块推荐使用setter注入
_Spring技术–自动装配
-
IoC容器根据bean所依赖的资源在容器中自动查找并注入到bean中的过程称为自动装配
-
自动装配的方式:
- 按类型(常用)
- 按名称
- 按构造方法
-
在applicatinContext.xml文件中配置bean,将自动装配可以将之前的property步骤省略掉:
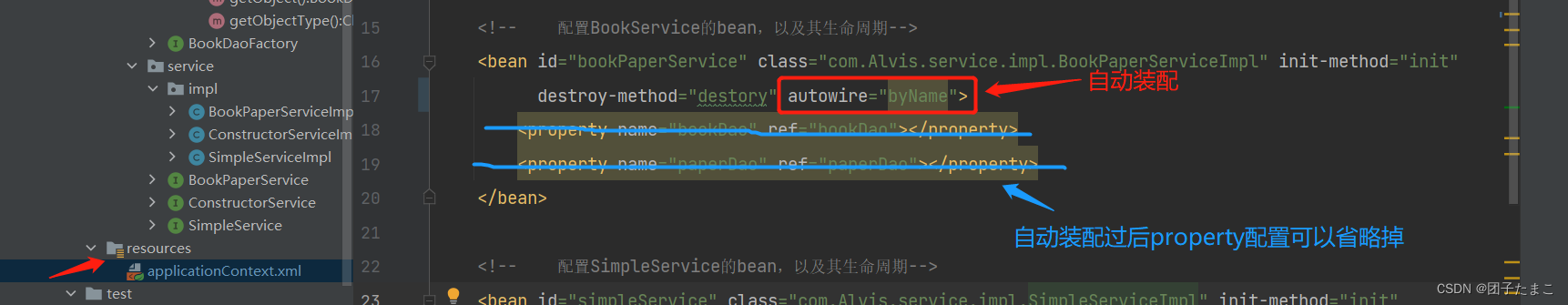
-
注意:
- 自动装配用于引用类型的依赖注入,不能对简单类型进行操作
- 使用按类型装配时(by Type)必须保障容器中相同类型的bean唯一,推荐使用
- 使用按名称装配时(by Name)必须保障容器中具有指定名称的bean,因变量名与配置耦合,不推荐使用
- 自动装配优先级低于setter注入与构造器注入,同时出现时自动装配配置失效
_Spring技术集合注入
-
不同集合的注入,在xml文件中bean的配置方式会有所不同,具体的方式如下所示:
-
Array集合注入:
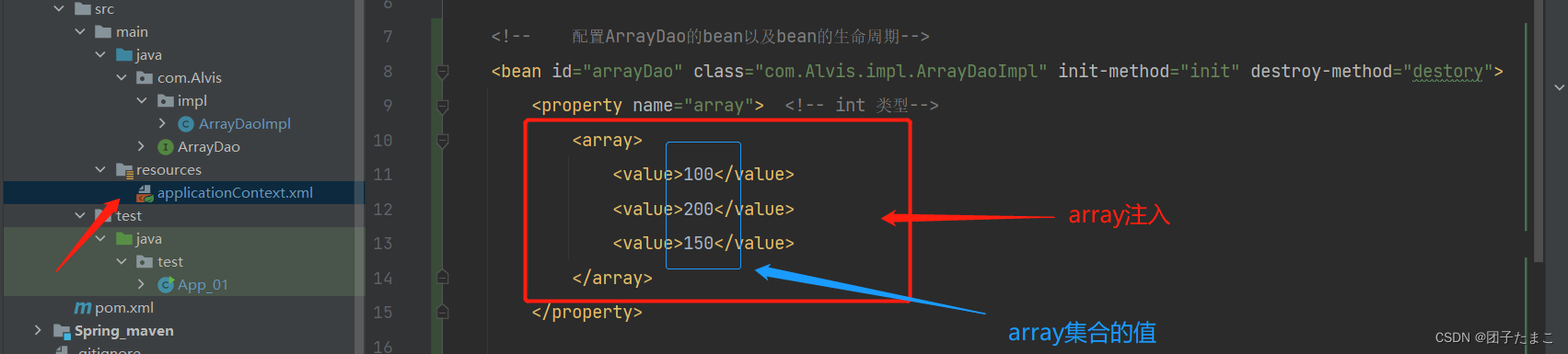
-
List集合注入:
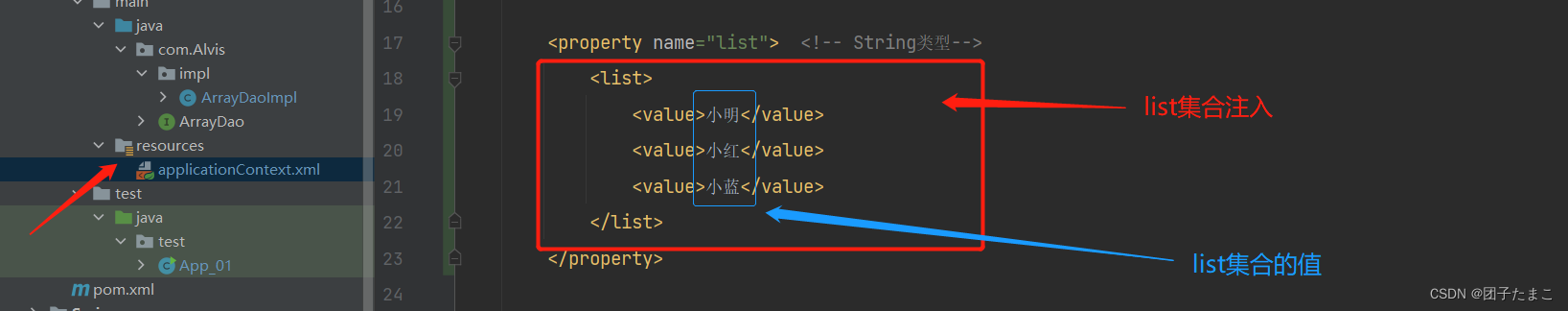
-
Set集合注入:
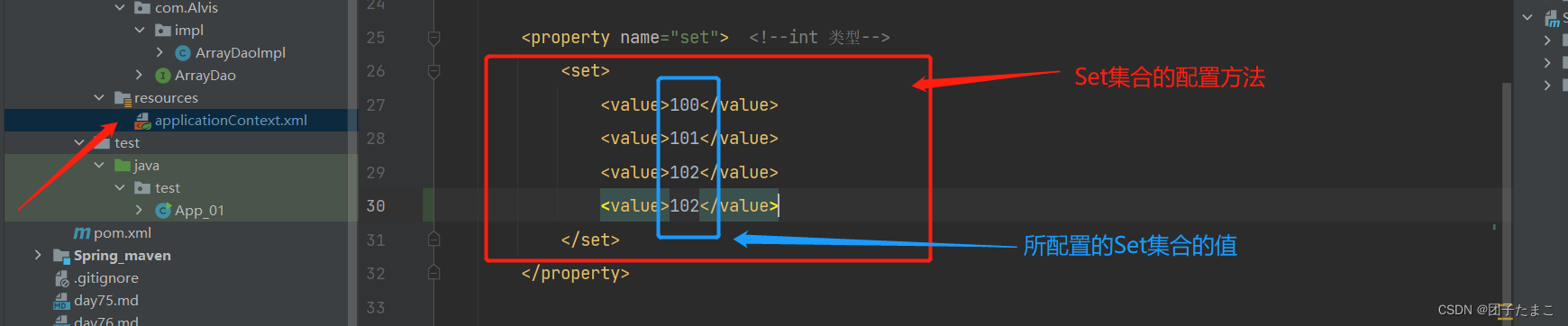
-
Map集合注入:
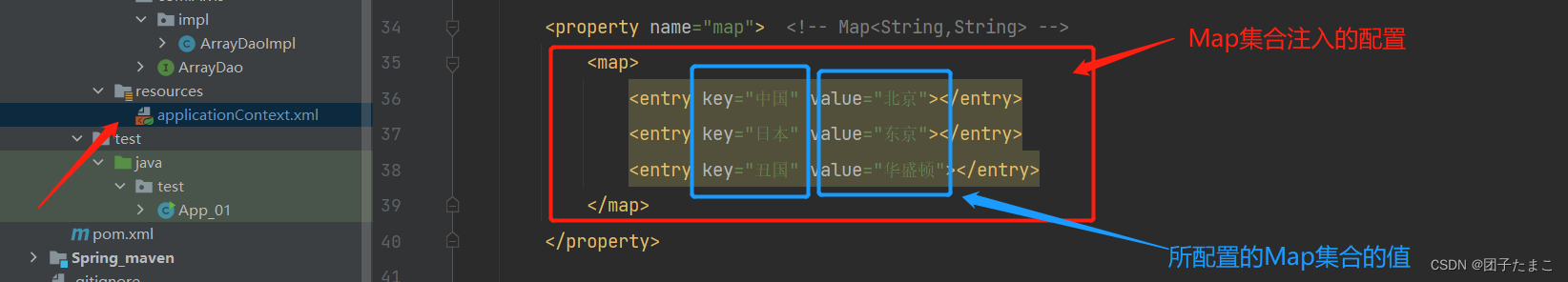
-
Properties集合注入:
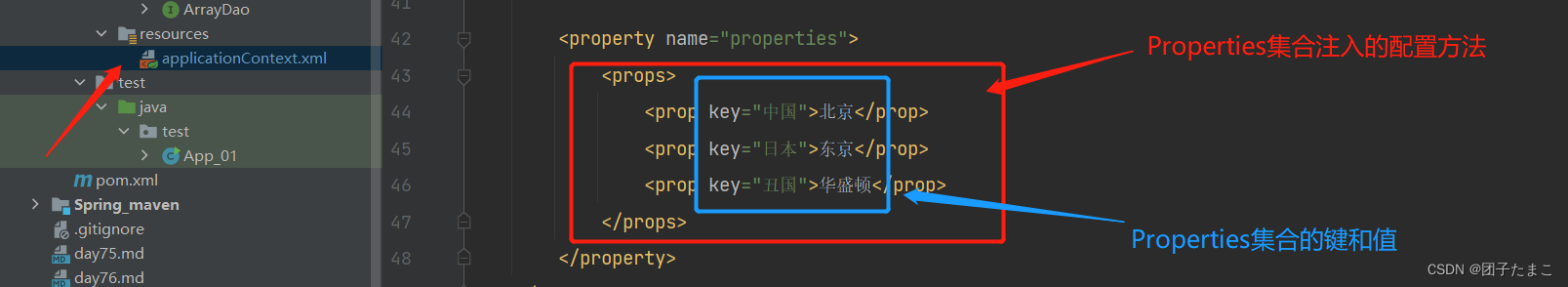
-
-
具体的实现类程序:
-
package com.Alvis.impl; import com.Alvis.ArrayDao; import java.lang.reflect.Array; import java.util.List; import java.util.Map; import java.util.Properties; import java.util.Set; public class ArrayDaoImpl implements ArrayDao { // 创建bean的生命周期 public void init() { System.out.println("bean 的生命周期已开启"); } // 销毁bean的生命周期 public void destory() { System.out.println("bean 的生命周期已销毁"); } // 定义所有类型的集合参数 private int[] array; private List<String> list; private Map<String,String> map; private Set<Integer> set; private Properties properties; // 生成其对应的set方法 public void setArray(int[] array) { this.array = array; } public void setList(List<String> list) { this.list = list; } public void setMap(Map<String, String> map) { this.map = map; } public void setSet(Set<Integer> set) { this.set = set; } public void setProperties(Properties properties) { this.properties = properties; } @Override public void run() { System.out.println("this is ArrayDao..."); // -------------------输出集合--------------------- System.out.print("Array: "); for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) { System.out.print(array[i]+" "); } System.out.println(); System.out.println("List: "+list); System.out.println("Set: " + set); System.out.println("Map: " + map); System.out.println("Properties: "+properties); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
-
-
在test文件中编写java程序实现对集合setter注入的调用:
-
package test; import com.Alvis.ArrayDao; import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; public class App_01 { public static void main(String[] args) { // 获取配置 ClassPathXmlApplicationContext cpx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml"); ArrayDao arrayDao = (ArrayDao) cpx.getBean("arrayDao"); arrayDao.run(); // 设置销毁bean的生命周期 cpx.registerShutdownHook(); } } ============================================ bean 的生命周期已开启 this is ArrayDao... Array: 100 200 150 List: [小明, 小红, 小蓝] Set: [100, 101, 102] Map: {中国=北京, 日本=东京, 丑国=华盛顿} Properties: {丑国=华盛顿, 中国=北京, 日本=东京} bean 的生命周期已销毁 进程已结束,退出代码0- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
-
-
-
相关阅读:
MindSpore论文解读 | EPRNet:应用于实时街景分割的高效金字塔表征网络
解码2022中国网安强星丨从“移动应用”到“万物互联”,梆梆安全做物联网时代的安全“守门人”
C++前缀和算法的应用:预算内的最多机器人数目
Docker快速安装
【实战-08】flink DataStream 如何实现去重
【Java】Java中的零拷贝
【李航统计学习笔记】第七章:支持向量机
LNMP网站架构部署
【JVM系列】JVM调优
LeetCode:66.加一
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/ALVIS_108/article/details/126192841
