-
[ESP32 Arduino]SD卡通过SPI的方式访问
说明: 这是学习笔记,仅做分享用途, 其中会引用其他博文的内容,时间关系不能一一将引用的文章都列举出来,如有冒犯,还请见谅
目录
参考资料
乐鑫官方文档非常的详细以及清晰, 在使用之前可以优先浏览一遍官方文档:
SD/SDIO/MMC 驱动程序 - ESP32 - — ESP-IDF 编程指南 v4.4 文档 (espressif.com)
以下博文可以参考:
1. Arduino+ESP32 之 SD卡读写 - 一匹夫 - 博客园 (cnblogs.com)
2. 玩转 ESP32 + Arduino (二十四) SD卡读写_finedayforu的博客-CSDN博客
学习过程记录
首要前提当然是把开发编译环境搭建好(这个需要自行研究,有时间我再整理一下):
vscode+platformio框架
platform: Arduino
在学习过程中需要明确自己想要做什么, 此次目的是能够读写SD卡的数据.
背景知识:
ESP32有两种使用SD卡的方法,一种是使用SPI接口访问SD卡,另一种是使用SDMMC接口访问SD卡 。
SD卡引脚定义图
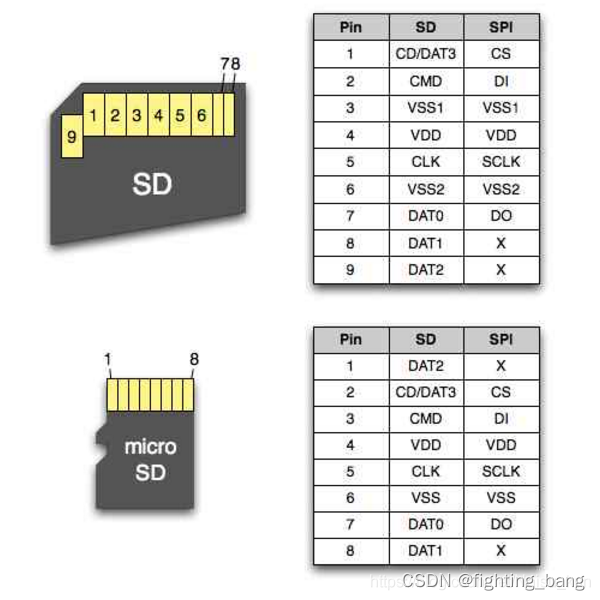
硬件原理图
Arduino core for the ESP32中SPI方式占用4个IO口,SDMMC方式占用6个IO口,手上的这块板子设计好了SD卡的电路,需要清楚的是他使用的接线方式是怎样的:

ESP32引脚图
显然这里使用的是SPI的方式访问SD卡的,在后面的API使用的时候就要注意不要用到SDMMC的API了.
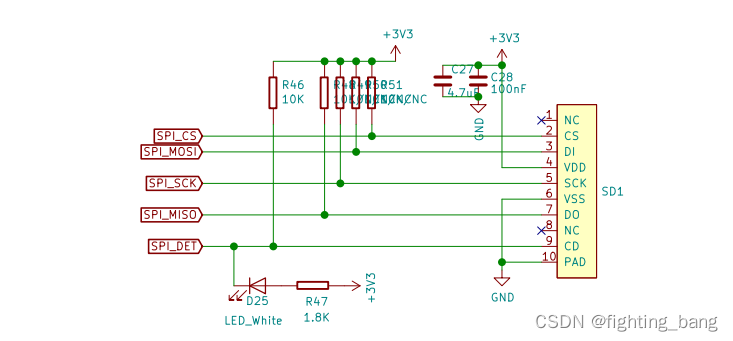
SD卡引脚图
实验代码
pio中提供了API以及sample code:

我们可以通过下面的位置查看SPI引脚是否和硬件是否一致,这有利于在出现问题的时候排查:
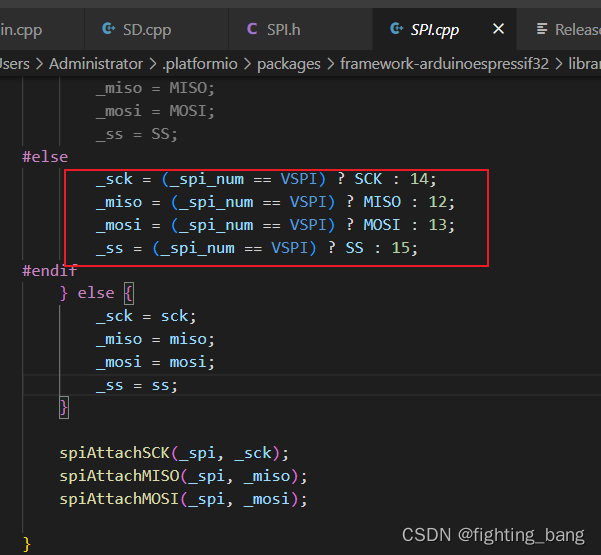
_spi_num这个变量的默认值为HSPI, _sck会被赋值为SCK, 和原理图中使用的引脚相同

SD_Test中有非常详细的API方法,运行一下看看现象:
- /*
- * Connect the SD card to the following pins:
- *
- * SD Card | ESP32
- * D2 -
- * D3 SS
- * CMD MOSI
- * VSS GND
- * VDD 3.3V
- * CLK SCK
- * VSS GND
- * D0 MISO
- * D1 -
- */
- #include "FS.h"
- #include "SD.h"
- #include "SPI.h"
- void listDir(fs::FS &fs, const char * dirname, uint8_t levels){
- Serial.printf("Listing directory: %s\n", dirname);
- File root = fs.open(dirname);
- if(!root){
- Serial.println("Failed to open directory");
- return;
- }
- if(!root.isDirectory()){
- Serial.println("Not a directory");
- return;
- }
- File file = root.openNextFile();
- while(file){
- if(file.isDirectory()){
- Serial.print(" DIR : ");
- Serial.println(file.name());
- if(levels){
- listDir(fs, file.path(), levels -1);
- }
- } else {
- Serial.print(" FILE: ");
- Serial.print(file.name());
- Serial.print(" SIZE: ");
- Serial.println(file.size());
- }
- file = root.openNextFile();
- }
- }
- void createDir(fs::FS &fs, const char * path){
- Serial.printf("Creating Dir: %s\n", path);
- if(fs.mkdir(path)){
- Serial.println("Dir created");
- } else {
- Serial.println("mkdir failed");
- }
- }
- void removeDir(fs::FS &fs, const char * path){
- Serial.printf("Removing Dir: %s\n", path);
- if(fs.rmdir(path)){
- Serial.println("Dir removed");
- } else {
- Serial.println("rmdir failed");
- }
- }
- void readFile(fs::FS &fs, const char * path){
- Serial.printf("Reading file: %s\n", path);
- File file = fs.open(path);
- if(!file){
- Serial.println("Failed to open file for reading");
- return;
- }
- Serial.print("Read from file: ");
- while(file.available()){
- Serial.write(file.read());
- }
- file.close();
- }
- void writeFile(fs::FS &fs, const char * path, const char * message){
- Serial.printf("Writing file: %s\n", path);
- File file = fs.open(path, FILE_WRITE);
- if(!file){
- Serial.println("Failed to open file for writing");
- return;
- }
- if(file.print(message)){
- Serial.println("File written");
- } else {
- Serial.println("Write failed");
- }
- file.close();
- }
- void appendFile(fs::FS &fs, const char * path, const char * message){
- Serial.printf("Appending to file: %s\n", path);
- File file = fs.open(path, FILE_APPEND);
- if(!file){
- Serial.println("Failed to open file for appending");
- return;
- }
- if(file.print(message)){
- Serial.println("Message appended");
- } else {
- Serial.println("Append failed");
- }
- file.close();
- }
- void renameFile(fs::FS &fs, const char * path1, const char * path2){
- Serial.printf("Renaming file %s to %s\n", path1, path2);
- if (fs.rename(path1, path2)) {
- Serial.println("File renamed");
- } else {
- Serial.println("Rename failed");
- }
- }
- void deleteFile(fs::FS &fs, const char * path){
- Serial.printf("Deleting file: %s\n", path);
- if(fs.remove(path)){
- Serial.println("File deleted");
- } else {
- Serial.println("Delete failed");
- }
- }
- void testFileIO(fs::FS &fs, const char * path){
- File file = fs.open(path);
- static uint8_t buf[512];
- size_t len = 0;
- uint32_t start = millis();
- uint32_t end = start;
- if(file){
- len = file.size();
- size_t flen = len;
- start = millis();
- while(len){
- size_t toRead = len;
- if(toRead > 512){
- toRead = 512;
- }
- file.read(buf, toRead);
- len -= toRead;
- }
- end = millis() - start;
- Serial.printf("%u bytes read for %u ms\n", flen, end);
- file.close();
- } else {
- Serial.println("Failed to open file for reading");
- }
- file = fs.open(path, FILE_WRITE);
- if(!file){
- Serial.println("Failed to open file for writing");
- return;
- }
- size_t i;
- start = millis();
- for(i=0; i<2048; i++){
- file.write(buf, 512);
- }
- end = millis() - start;
- Serial.printf("%u bytes written for %u ms\n", 2048 * 512, end);
- file.close();
- }
- void setup(){
- Serial.begin(115200);
- if(!SD.begin()){
- Serial.println("Card Mount Failed");
- return;
- }
- uint8_t cardType = SD.cardType();
- if(cardType == CARD_NONE){
- Serial.println("No SD card attached");
- return;
- }
- Serial.print("SD Card Type: ");
- if(cardType == CARD_MMC){
- Serial.println("MMC");
- } else if(cardType == CARD_SD){
- Serial.println("SDSC");
- } else if(cardType == CARD_SDHC){
- Serial.println("SDHC");
- } else {
- Serial.println("UNKNOWN");
- }
- uint64_t cardSize = SD.cardSize() / (1024 * 1024);
- Serial.printf("SD Card Size: %lluMB\n", cardSize);
- listDir(SD, "/", 0);
- createDir(SD, "/mydir");
- listDir(SD, "/", 0);
- removeDir(SD, "/mydir");
- listDir(SD, "/", 2);
- writeFile(SD, "/hello.txt", "Hello ");
- appendFile(SD, "/hello.txt", "World!\n");
- readFile(SD, "/hello.txt");
- deleteFile(SD, "/foo.txt");
- renameFile(SD, "/hello.txt", "/foo.txt");
- readFile(SD, "/foo.txt");
- testFileIO(SD, "/test.txt");
- Serial.printf("Total space: %lluMB\n", SD.totalBytes() / (1024 * 1024));
- Serial.printf("Used space: %lluMB\n", SD.usedBytes() / (1024 * 1024));
- }
- void loop(){
- }
列出了SD下所有文件目录,并且创建了对应的文件:

-
相关阅读:
Linux内核内存管理:详解虚拟地址空间-MMU
91.(leaflet之家)leaflet态势标绘-进攻方向绘制
Docker的使用
使用Spring Boot限制在一分钟内某个IP只能访问10次
Spring 框架学习(九)---- Spring 整合 Mybatis 框架
[安卓app毕业设计源码]精品基于Uniapp+SSM实现的家庭客栈/民宿管理系统实现的App[包运行成功]
pytest 的使用===谨记
使用Java统计gitlab代码行数
search——single list
lua基础之io
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_38609565/article/details/126190990
