-
NIO+代码实现---Buffer+Channel+Selector
NIO+代码实现—Buffer+Channel+Selector
Buffer
缓冲区实质是一块可读写数据的内存块,可以理解是一个容器对象(含数组)。
ByteBuffer最底层就是字节数组。。。。
而Buffer类作为缓冲区的最顶层抽象母类,解析一下buffer类的源码
public abstract class Buffer { // Invariants: mark <= position <= limit <= capacity private int mark = -1; private int position = 0; private int limit; private int capacity;- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 上面四个字段是所有的缓冲区都拥有的通用字段
mark,postion,limit,capacity
- capacity:容量
- limit:表示缓冲区的当前终点
- position:位置,下一个要读写位置的索引
- mark:标记,表明当前操作是在读还是写,使用buffer.filp()进行读写转化。
代码实现buffer
package com.ws.nio; import java.nio.IntBuffer; /** * @author 王顺 * @description * @date 2022/8/3 */ public class BasicBuffer { public static void main(String[] args) { //Buffer到底是什么 //创建一个buffer,大小为5,即可以存放5个int IntBuffer intBuffer = IntBuffer.allocate(5); //向buffer存放数据 for (int i = 0; i < intBuffer.capacity(); i++) { intBuffer.put(i * 2); } //从buffer读取数据 //将buffer转化,读写切换 intBuffer.flip(); while (intBuffer.hasRemaining()) { System.out.println(intBuffer.get()); } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
Channel
Channel在NIO中是一个接口,public interface Channel extendds CloseAble{}
- 将NIO中的Channel看成Bio中的流
- BIO中的流是单向的,例如FileInputStream对象只能进行读取数据的操作,而NIO中的通道是双向的,可以读操作,可以写操作
- 常用Channel类有,FileChannel,DatagramChannel,ServerSocketChannel和SocketChannel
- FileChannel用于文件的数据读写
- 常用方法
- read(ByteBuffer buffer):从通道读取数据到缓冲区中
- write(ByteBuffer buffer):把缓冲区的数据写到通道中
- TransferFrom(xxx):从目标通道中复制数据到当前通道
- TransferTo:把数据从当前通道复制给目标通道
- DatagreamChannel用于UDP的数据读写
- ServerScoketChannel和SocketChannel是最常用的
- ServerSocketChannel和SocketChannel用于TCP的数据读写
- ServerSocketChannel对应BIO的ServerSocket
- SocketChannel对应BIO的Socket
代码实现buffer+Channe通信—输出实战
package com.ws.nio; import java.io.FileOutputStream; import java.nio.ByteBuffer; import java.nio.channels.FileChannel; /** * @author 王顺 * @description * @date 2022/8/3 */ public class NIOFileChannel { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{ String str = "hello ws"; //创建一个输出流--BIO原始的流 FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream("d:\\test.txt"); //创建一个FileChannel---理解为NIO的通道是包裹着原始BIO的流的 //这里需要了解就是FileChannel真实类型是FileChannelImpl,因为FileChannel是抽象类 FileChannel fileChannel = fileOutputStream.getChannel(); //创建一个缓冲区 ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024); //将str放入缓冲区--缓冲区的写入 byteBuffer.put(str.getBytes()); //缓冲区转化--从写入到读--一开始是从客户端写数据到缓冲区,后面是从缓冲区读到管道里面 byteBuffer.flip(); //从缓冲区读到管道里面 fileChannel.write(byteBuffer); fileOutputStream.close(); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
代码实现buffer+Channe通信—输入实战
package com.ws.nio; import java.io.FileInputStream; import java.io.InputStream; import java.nio.ByteBuffer; import java.nio.channels.FileChannel; /** * @author 王顺 * @description * @date 2022/8/3 */ public class NIOFileChannel02 { /** *@Author: wangshun *@date: 2022/8/3 14:33 *@Description: 从本地文件夹获取数据到控制台 *@Version: 1.0 */ public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{ //获取BIO文件输出流 FileInputStream fileInputStream=new FileInputStream("d:\\test.txt"); //获取NIO通道--属于该输出流的通道 //实际类型是FileChannelImpl,因为fileChannel为抽象类 FileChannel fileChannel = fileInputStream.getChannel(); //新建缓冲区 ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024); //将通道数据读入到buffer中 int read = fileChannel.read(byteBuffer); //由于缓冲区是ByteBuffer,所以现在缓冲区里面的数据都是字节类型,需要转化成string System.out.println(new String(byteBuffer.array())); fileInputStream.close(); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
代码实现buffer+Channe通信—输入+输出实战
package com.ws.nio; import java.io.File; import java.io.FileInputStream; import java.io.FileOutputStream; import java.nio.ByteBuffer; import java.nio.channels.FileChannel; /** * @author 王顺 * @description * @date 2022/8/3 */ public class NIOFileChannel03 { /** *@Author: wangshun *@date: 2022/8/3 14:46 *@Description: 使用通道和方法read ,write,完成文件的拷贝--从1.txt拷贝到2.txt-- * !!!!!!要求只允许使用一个buffer!!!!!!! *@Version: 1.0 */ public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{ File file = new File("d:\\test.txt"); //新建缓冲区 ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate((int) file.length()); //新建输入流 FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream(file); FileChannel channel = fileInputStream.getChannel(); //读取到缓冲区数据了 channel.read(byteBuffer); File file2 = new File("d:\\test2.txt"); //新建输出流 FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream(file2); channel=fileOutputStream.getChannel(); //刚开始没写这个,直接channel.write,不会报错,也会生成文件,但是文件里面没有内容! byteBuffer.flip(); channel.write(byteBuffer); fileInputStream.close(); fileOutputStream.close(); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
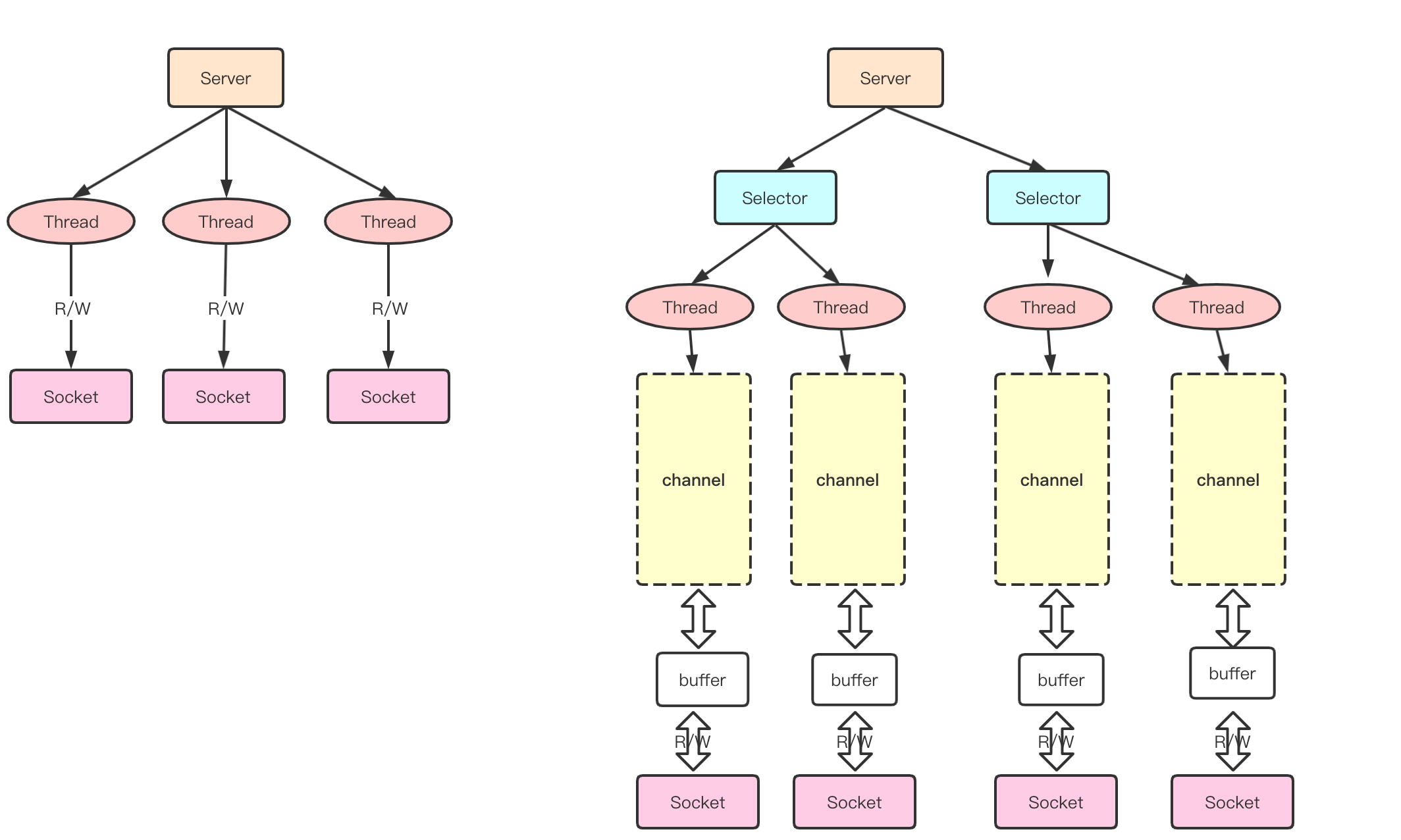
Selector
Selector能够监测多个注册的通道上是否有事件发生
只有在连接真正有读写事件发生时,才会进行读写,就大大减少了系统的开销
避免了多线程之间上下文切换的开销
常用方法
- open方法:获取到一个选择器对象
- select(long timeOut):监控所有注册的通道,当其中有IO操作可以进行的时候,将对应的SelectorKey加入到内部集合中并返回,参数用来设置超时时间。
!!!Selector,SelectorKey,ServerSocketChannel,SocketChannel关系!!!
牢记于心,整体流程
- 服务器端启动一个ServerSocketChannel
- 当有客户端连接的时候,会通过ServerSocketChannel生成一个SocketChannel
- 将得到的SocketChannel注册到Selector上(通过register(Selector sel,int ops),ops是对于该通道具体关注哪个事件)
- 注册后会返回一个SelectorKey,会和Selector关联(以集合方式关联)
- 关联后,会让selector进行监听,通过select方法,返回有事件发生的通道的SelectorKey
- 得到各个有事件发生的SelectorKey,维护在自己的集合中,再通过SelectorKey反向获取SocketChannel channel()
- 最后通过得到的Channel完成所有业务处理
NIO代码服务器端
package com.ws.nio; import java.net.InetSocketAddress; import java.nio.ByteBuffer; import java.nio.channels.*; import java.util.Iterator; import java.util.Set; /** * @author 王顺 * @description * @date 2022/8/4 */ public class NIOServer { /** *@Author: wangshun *@date: 2022/8/4 19:02 *@Description: 自定义NIO服务器端 *@Version: 1.0 */ public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{ //创建ServerSocketChannel ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel=ServerSocketChannel.open(); //创建一个Selector对象 Selector selector = Selector.open(); //绑定服务器端口 serverSocketChannel.socket().bind(new InetSocketAddress(7777)); //设置为非阻塞 serverSocketChannel.configureBlocking(false); //把ServerSocketChannel注册到selector里面,关系事件为连接事件OP_ACCEPT serverSocketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT); //循环等待客户端连接 while (true) { //对于该Selector,如果当前通道1000ms内没有事件(这里是客户端连接事件),啥不干直接返回 if (selector.select(1000) == 0) { System.out.println("服务器端等待了1s,无连接"); continue; } //如果返回的>0,就说明这1s内有客户端连接,这里就会获取到该通道对应的SelectorKey //通过SelectorKey反向获取到该通道! Set<SelectionKey> selectionKeys = selector.selectedKeys(); //遍历set,获取到所有有事件发生的通道 Iterator<SelectionKey> keyIterator = selectionKeys.iterator(); while (keyIterator.hasNext()) { //获取到SelectorKey SelectionKey key = keyIterator.next(); //根据key,对应的通道发生的事件做对应处理 if (key.isAcceptable()) {//如果是OP_ACCEPT,有新的客户端连接 System.out.println("当前有客户端连接,生成了一个SocketChannel"); //给该客户端生成一个SocketChannel SocketChannel socketChannel = serverSocketChannel.accept(); socketChannel.configureBlocking(false); //将当前SocketChannel注册到Selector中,关注的是这个通道的读信号,同时给这个Channel关联要给buffer socketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ, ByteBuffer.allocate(1024)); } if (key.isReadable()) {//如果是OP_READ,发生了读事件 //通过key,反向获取到channel //这里强转成socketChannel SocketChannel socketChannel = (SocketChannel) key.channel(); //获取到该Channel关联的buffer--key的attachment方法就是该通道对应的缓冲区 ByteBuffer buffer = (ByteBuffer) key.attachment(); //将buffer读到客户端里面去 socketChannel.read(buffer); System.out.println("form 客户端:" + new String(buffer.array())); } //手动从集合中删除当前SelectorKey,防止重复操作 keyIterator.remove(); } } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
NIO客户端
package com.ws.nio; import java.net.InetSocketAddress; import java.nio.ByteBuffer; import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel; /** * @author 王顺 * @description * @date 2022/8/4 */ public class NIOClient { /** * @Author: wangshun * @date: 2022/8/4 19:34 * @Description: NIO客户端 * @Version: 1.0 */ public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { //得到一个网络通道 SocketChannel socketChannel = SocketChannel.open(); //设置非阻塞 socketChannel.configureBlocking(false); //提供服务器端的ip+端口 InetSocketAddress inetSocketAddress = new InetSocketAddress("127.0.0.1", 7777); //连接服务器 if (!socketChannel.connect(inetSocketAddress)) { while (!socketChannel.finishConnect()) { System.out.println("因为连接需要时间,客户端不会阻塞,可以做其他工作"); } } //连接成功,就直接发送数据 String str = "hello,ws"; ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.wrap(str.getBytes()); //将buffer数据写入channel socketChannel.write(byteBuffer); System.in.read(); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
最后结果:先运行server,再运行client。
服务器端等待了1s,无连接
服务器端等待了1s,无连接
服务器端等待了1s,无连接
服务器端等待了1s,无连接
服务器端等待了1s,无连接
服务器端等待了1s,无连接当前有客户端连接,生成了一个SocketChannel
form 客户端:hello,ws
服务器端等待了1s,无连接
服务器端等待了1s,无连接
服务器端等待了1s,无连接
服务器端等待了1s,无连接
服务器端等待了1s,无连接
服务器端等待了1s,无连接
服务器端等待了1s,无连接 -
相关阅读:
上周热点回顾(8.8-8.14)
某60区块链安全之整数溢出漏洞实战学习记录
Node.js 支付宝支付
阿里云云原生一体化数仓 - 数据安全能力解读
个人常用Linux命令
算法设计与分析 SCAU11091 最优自然数分解问题(优先做)
仿GitLab MR 是的对比文件内容,可以动态显示,隐藏没有变化的文件内容
JAVA设计模式--桥接模式【结构型模式】
三十四、Java Iterator(迭代器)
php socket说明 stream流说明
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/cxywangshun/article/details/126174794
