-
groovy基础学习
范围运算符
- class HelloGroovy {
- static void main(args) {
- def range = 5..10; //定义一个简单的整数范围,存储一个局部变量,下限为0,上限为1
- println(range);
- println(range.get(2));
- }
- }
Groovy 中的方法是使用返回类型或使用 def 关键字定义的。方法可以接收任意数量的参数。定义参数时,不必显式定义类型。可以添加修饰符,如 public,private 和 protected。默认情况下,如果未提供可见性修饰符,则该方法为 public。
- class Example {
- static def DisplayName() {
- println("This is how methods work in groovy");
- println("This is an example of a simple method");
- }
- static void main(String[] args) {
- DisplayName();
- }
- }
默认参数
如果没有值传递给方法的参数,则使用缺省值。 如果使用非默认和默认参数,则必须注意,默认参数应在参数列表的末尾定义。
groovy文件I/O
重点:file类
读取文件
- import java.io.File
- class Example {
- static void main(String[] args) {
- new File("E:/Example.txt").eachLine {
- line -> println "line : $line";
- }
- }
- }
读取文件的内容到字符串
可以使用文件类的text属性
- class Example {
- static void main(String[] args) {
- File file = new File("E:/Example.txt")
- println file.text
- }
- }
写入文件
使用write类
- import java.io.File
- class Example {
- static void main(String[] args) {
- new File('E:/','Example.txt').withWriter('utf-8') {
- writer -> writer.writeLine 'Hello World'
- }
- }
- }
获取文件的大小
如果要获取文件的大小,可以使用文件类的length属性来获取
- class Example {
- static void main(String[] args) {
- File file = new File("E:/Example.txt")
- println "The file ${file.absolutePath} has ${file.length()} bytes"
- }
- }
测试文件是否是目录
如果要查看路径是文件还是目录,可以使用File类的isFile和isDirectory选项
- class Example {
- static void main(String[] args) {
- def file = new File('E:/')
- println "File? ${file.isFile()}"
- println "Directory? ${file.isDirectory()}"
- }
- }
创建目录
如果要创建一个新目录,可以使用File类的mkdir函数。
- class Example {
- static void main(String[] args) {
- def file = new File('E:/Directory')
- file.mkdir()
- }
- }
删除文件
如果要删除文件,可以使用File类的delete功能。
- class Example {
- static void main(String[] args) {
- def file = new File('E:/Example.txt')
- file.delete()
- }
- }
复制文件
Groovy还提供将内容从一个文件复制到另一个文件的功能
- class Example {
- static void main(String[] args) {
- def src = new File("E:/Example.txt")
- def dst = new File("E:/Example1.txt")
- dst << src.text
- }
- }
获取目录内容
Groovy还提供了列出驱动器中的驱动器和文件的功能。
- class Example {
- static void main(String[] args) {
- def rootFiles = new File("test").listRoots()
- rootFiles.each {
- file -> println file.absolutePath
- }
- }
- }
使用File类的eachFile函数列出特定目录中的文件。
- class Example {
- static void main(String[] args) {
- new File("E:/Temp").eachFile() {
- file->println file.getAbsolutePath()
- }
- }
- }
递归显示目录及其子目录中的所有文件,则可以使用File类的eachFileRecurse函数
- class Example {
- static void main(String[] args) {
- new File("E:/temp").eachFileRecurse() {
- file -> println file.getAbsolutePath()
- }
- }
- }
特征
特征是语言的结构构造,允许 -
- 行为的组成。
- 接口的运行时实现。
- 与静态类型检查/编译的兼容性
它们可以被看作是承载默认实现和状态的接口。使用trait关键字定义 trait
可以使用 implement 关键字以类似于接口的方式实现 trait。
- class Example {
- static void main(String[] args) {
- Student st = new Student();
- st.StudentID = 1;
- st.Marks1 = 10;
- println(st.DisplayMarks());
- }
- }
- trait Marks {
- void DisplayMarks() {
- println("Display Marks");
- }
- }
- class Student implements Marks {
- int StudentID
- int Marks1;
- }
实现接口
Traits 可以实现接口,在这种情况下,使用 interface 关键字声明接口。
定义(interface)一个接口,
trait定义的Marks特征实现(继承)了Total接口,
Student类再继承Marks特征,拓展这个特征
实现类完成功能实现
- class Example {
- static void main(String[] args) {
- Student st = new Student();
- st.StudentID = 1;
- st.Marks1 = 10;
- println(st.DisplayMarks());
- println(st.DisplayTotal());
- }
- }
- interface Total {
- void DisplayTotal()
- }
- trait Marks implements Total {
- void DisplayMarks() {
- println("Display Marks");
- }
- void DisplayTotal() {
- println("Display Total");
- }
- }
- class Student implements Marks {
- int StudentID
- int Marks1;
- }
属性
特征可以定义属性。下面给出了具有属性的trait的示例。
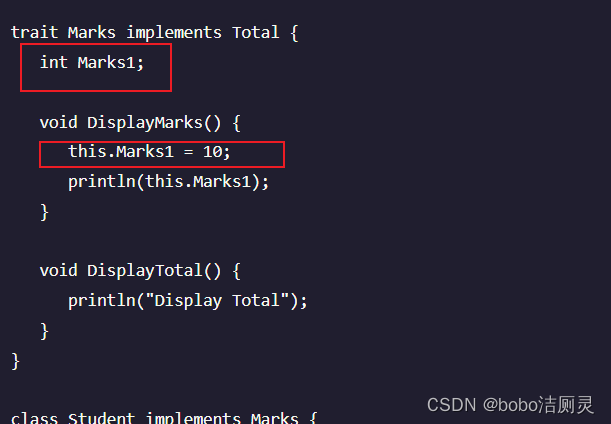
行为的构成
特征可以用于以受控的方式实现多重继承

扩展特征
特征可能扩展另一个特征,在这种情况下,必须使用extends关键字

Groovy闭包
闭包closure是一个短的匿名代码块。它通常跨越几行代码。一个方法甚至可以将代码块作为参数。它们是匿名的。
- class Example {
- static void main(String[] args) {
- def clos = {println "Hello World"};
- clos.call();
- }
- }
代码行 - {println“Hello World”}被称为闭包。此标识符引用的代码块可以使用call语句执行。
执行后,输出Hello World
闭包也可以包含形式参数,以使它们更有用,就像Groovy中的方法一样。
- class Example {
- static void main(String[] args) {
- def clos = {param->println "Hello ${param}"};
- clos.call("World");
- }
- }
使用$ {param},这导致closure接受一个参数。当通过clos.call语句调用闭包时,我们现在可以选择将一个参数传递给闭包。
运行后,输出Hello world
- class Example {
- static void main(String[] args) {
- def clos = {println "Hello ${it}"}; //隐式单个参数
- clos.call("World");
- }
- }
包可以在定义闭包时引用变量。下面定义了一个str1变量,并在clos中引用
- class Example {
- static void main(String[] args) {
- def str1 = "Hello";
- def clos = {param -> println "${str1} ${param}"}
- clos.call("World");
- // We are now changing the value of the String str1 which is referenced in the closure
- str1 = "Welcome";
- clos.call("World");
- }
- }
在方法中使用闭包
闭包也可以用作方法的参数。在Groovy中,很多用于数据类型(例如列表和集合)的内置方法都有闭包作为参数类型。
- class Example {
- //静态方法Display,以一个闭包为参数
- def static Display(clo) {
- // This time the $param parameter gets replaced by the string "Inner"
- clo.call("Inner");
- }
- static void main(String[] args) {
- def str1 = "Hello";
- def clos = { param -> println "${str1} ${param}" }
- clos.call("World");
- // We are now changing the value of the String str1 which is referenced in the closure
- str1 = "Welcome";
- clos.call("World");
- 将定义的闭包作为参数传递到Dispaly方法中
- // Passing our closure to a method
- Example.Display(clos);
- }
- }
-
相关阅读:
微信小程序原生加vant改变日历组件开始和结束的默认文案
tsconfig.json在配置文件中找不到任何输入,怎么办?
zabbix安装部署--创建监控项监控机器
【一:实战开发testng的介绍】
【技术分享】堆叠交换机替换指导
IOS安全测试学习-DVIA-v2
Kamiya丨Kamiya艾美捷大鼠微量白蛋白酶联免疫吸附试验说明书
.Net项目混淆/加密工具
软件架构设计(八) 基于架构的软件开发方法
在CARLA中手动开车,添加双目相机stereo camera,激光雷达Lidar
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/cvpatient/article/details/126171190
