-
【玩转CSS】详解定位
🔥一个人走得远了,就会忘记自己为了什么而出发,希望你可以不忘初心,不要随波逐流,一直走下去🎶
🦋 欢迎关注🖱点赞👍收藏🌟留言🐾
🦄 本文由 程序喵正在路上 原创,CSDN首发!
💖 系列专栏:HTML5+CSS3+移动端前端
🌠 首发时间:2022年8月5日
✅ 如果觉得博主的文章还不错的话,希望小伙伴们三连支持一下哦学习目标
✂ 能够说出为什么要用定位
✂ 能够说出定位的 4 种分类
✂ 能够说出 4 种定位各自的特点
✂ 能够说出为什么常用子绝父相布局
✂ 能够写出淘宝轮播图布局
✂ 能够说出显示隐藏的 2 种方式以及区别定位
1. 为什么需要定位
浮动可以让多个块级盒子一行没有缝隙排列显示,经常用于横向排列盒子
而定位则是可以让盒子自由地在某个盒子内移动位置或者固定屏幕中某个位置,并且可以压住其他盒子
2. 定位组成
定位:将盒子定在某一个位置,所以定位也是在摆放盒子,按照定位的方式移动盒子
定位 = 定位模式 + 边偏移
定位模式用于指定一个元素在文档中的定位方式,边偏移则决定了该元素的最终位置
定位模式
定位模式决定元素的定位方式,它通过 CSS 的 position 属性来设置,其值可以分为四个:
值 语义 static 静态定位 relative 相对定位 absolute 绝对定位 fixed 固定定位 边偏移
边偏移就是定位的盒子移动到最终位置,有 top、bottom、left 和 right 这 4 个属性
属性 实例 描述 top top: 80px顶端偏移量,定义元素相对于其父元素上边线的距离 bottom bottom: 80px底部偏移量,定义元素相对于其父元素下边线的距离 left left: 80px左侧偏移量,定义元素相对于其父元素左边线的距离 right right: 80px右侧偏移量,定义元素相对于其父元素右边线的距离 3. 静态定位 static
静态定位是元素的默认定位方式,也就是无定位的意思
语法:
选择器 { position: static; }
- 静态定位按照标准流特性来摆放位置,它没有边偏移
- 静态定位在布局时很少用到
4. 相对定位 relative
相对定位是元素在移动位置的时候,是相对于它原来的位置来说的
语法:
选择器 { position: relative; }
相对定位的特点:
- 它是相对于自己原来的位置来移动的
- 原来在标准流的位置继续占有,后面的盒子仍然以标准流的方式来对待它
我们通过一个简单的例子来看一下
DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <title>相对定位title> <style> .box1 { position: relative; top: 100px; left: 100px; width: 200px; height: 200px; background-color: skyblue; } .box2 { width: 200px; height: 200px; background-color: pink; } style> head> <body> <div class="box1"> div> <div class="box2"> div> body> html>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
运行结果
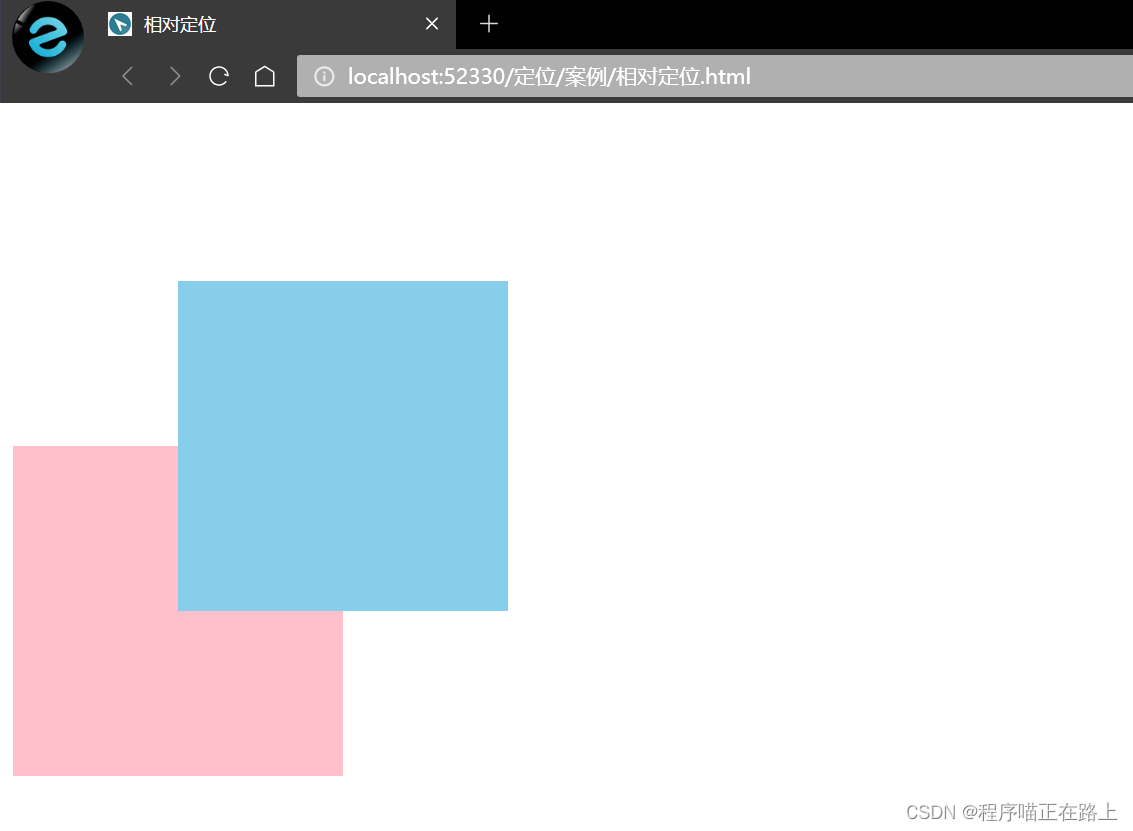
因此,相对定位是没有脱标的,其最典型的应用是来限制绝对定位5. 绝对定位 absolute
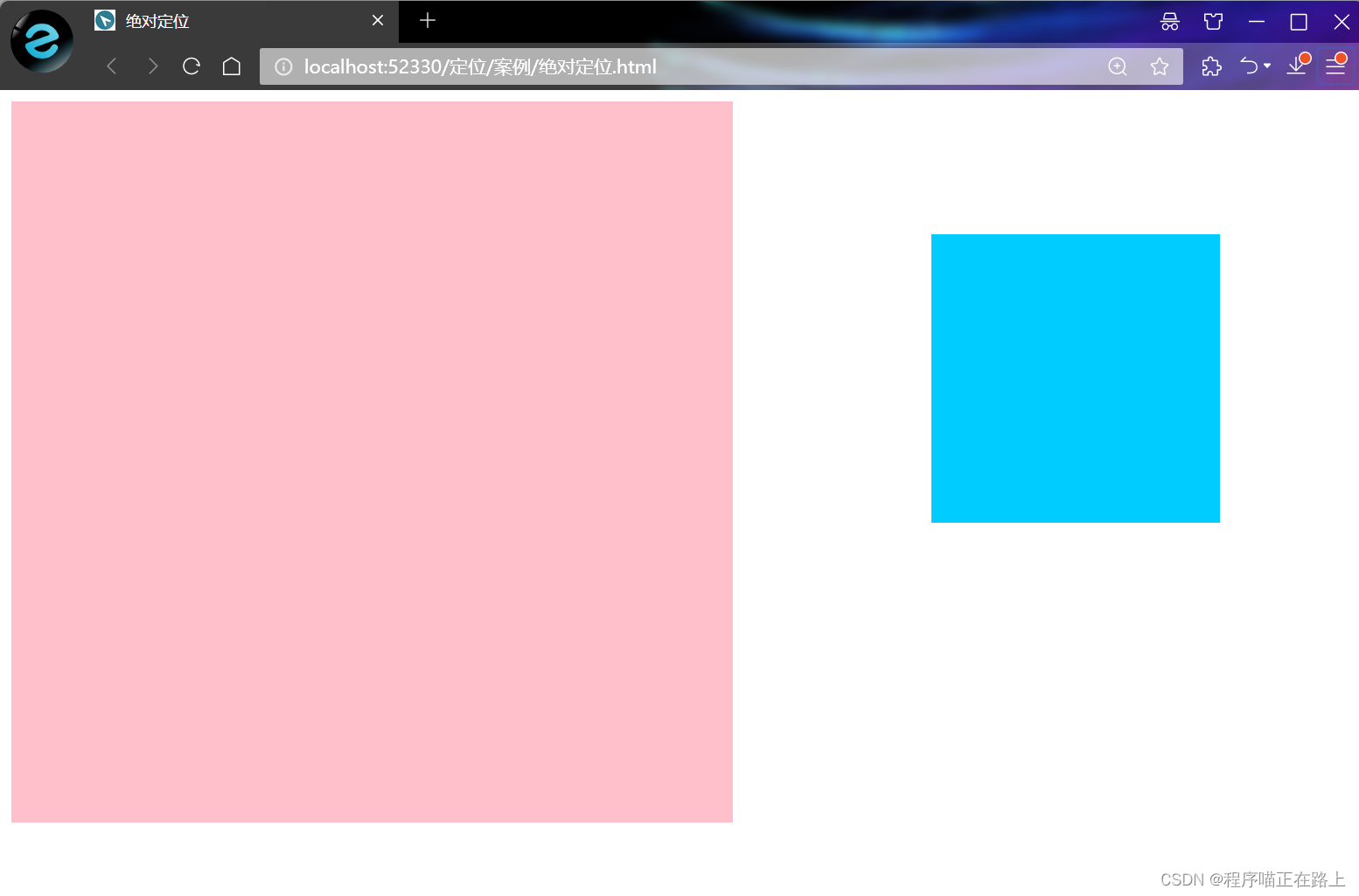
绝对定位是元素在移动位置的时候,是相对于它祖先元素来说的
语法:
选择器 { position: absolute; }
绝对定位的特点:
- 如果没有祖先元素或者祖先元素没有定位,则以浏览器为准定位(Document 文档)
代码演示
DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <title>绝对定位title> <style> .father { width: 500px; height: 500px; background-color: pink; } .son { position: absolute; top: 100px; right: 100px; width: 200px; height: 200px; background-color: #0CF; } style> head> <body> <div class="father"> <div class="son">div> div> body> html>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
运行结果
- 如果祖先元素有定位(相对、绝对、固定定位),则以最近一级有定位的祖先元素为参考点移动位置
代码演示
DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <title>绝对定位-父级有定位title> <style> .grandfather { position: relative; width: 800px; height: 800px; background-color: purple; padding: 50px; } .father { width: 500px; height: 500px; background-color: pink; } .son { position: absolute; top: 100px; right: 100px; width: 200px; height: 200px; background-color: #0CF; } style> head> <body> <div class="grandfather"> grandfather <div class="father"> father <div class="son">sondiv> div> div> body> html>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
运行结果

- 绝对定位不再占有原来的位置
6. 子绝父相的由来
子绝父相 —— 子级是绝对定位的话,父级要用相对定位
① 子级绝对定位,不会占有位置,可以放大盒子里面的任何一个地方,不会影响其他的盒子
② 父盒子需要加定位限制子盒子在父盒子内显示
③ 父盒子布局时,需要占有位置,因此父亲只能是相对定位这就是子绝父相的由来,所以相对定位经常用来作为绝对定位的父级
总结:因为父亲需要占有位置,因此是相对定位,子盒子不需要占有位置,则是绝对定位
当然,子绝父相不是永远不变的,如果父元素不需要占有位置,子相父绝也会遇到
子绝父相案例实战
实现下面的效果

在之前代码的基础上添加一些代码即可index.html

style.css
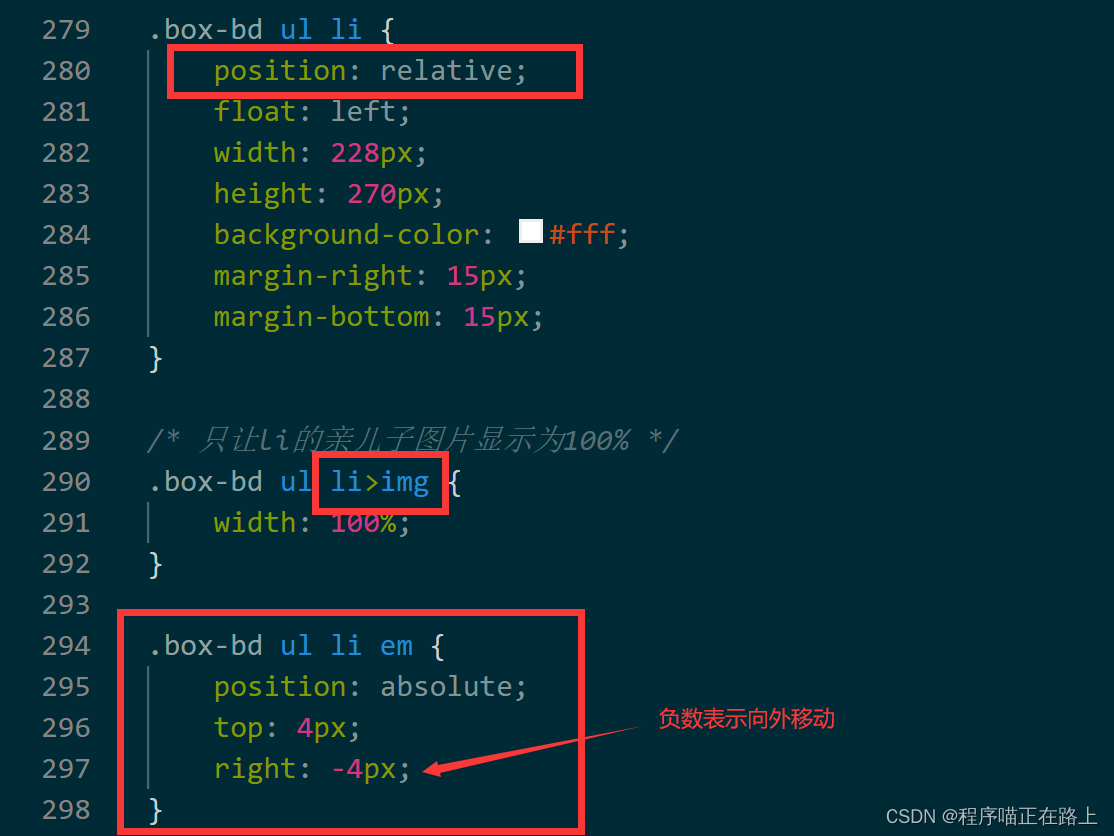
实现效果

7. 固定定位 fixed
固定定位是元素固定于浏览器可视区的位置,主要使用场景:在浏览器页面滚动时,让元素的位置保持不变
语法:
选择器 { position: fixed; }
固定定位的特点:
- 以浏览器的可视窗口为参照点移动元素
• 跟父元素没有任何关系
• 不随滚动条滚动 - 固定定位不存在占有原先的位置
固定定位也是脱标的,其实固定定位也可以看做是一种特殊的绝对定位
代码演示
DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <title>固定定位title> <style> body { height: 2000px; } .dj { position: fixed; top: 100px; left: 40px; } style> head> <body> <div class="dj"> <img src="../images/r_dj.png" alt=""> div> body> html>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
运行结果

可以看到,当我们的滚轮滚动时,固定定位的元素是不会动的固定定位小技巧:固定在版心右侧位置
步骤:
- 让固定定位的盒子
left: 50%,走到浏览器可视区(也可以看做版心)的一半位置 - 让固定定位的盒子
margin-left: 版心宽度的一半距离,多走版心宽度的一半位置
就可以让固定定位的盒子贴着版心右侧对齐了
代码演示
DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <title>固定定位小技巧title> <style> .w { width: 800px; height: 1400px; background-color: pink; margin: 0 auto; } .fixed { position: fixed; left: 50%; margin-left: 405px; width: 50px; height: 150px; background-color: #0CF; } style> head> <body> <div class="fixed">div> <div class="w">版心盒子 800像素div> body> html>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
运行结果

8. 粘性定位 sticky
粘性定位可以被认为是相对定位和固定定位的混合
语法:
选择器 { position: sticky; top: 10px; }
粘性定位的特点:
- 以浏览器的可视窗口为参照点移动元素(固定定位特点)
- 粘性定位占有原先的位置(相对定位特点)
- 必须添加 top、left、right、bottom 其中一个才有效
- 跟页面滚动搭配使用,兼容性较差
代码演示
DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <title>粘性定位title> <style> body { height: 3000px; } .nav { position: sticky; top: 0; width: 800px; height: 50px; background-color: #0CF; margin: 100px auto; } style> head> <body> <div class="nav">导航栏div> body> html>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
运行结果

9. 总结
定位模式 是否脱标 移动位置 是否常用 static 静态定位 否 不能使用边偏移 很少 relative 相对定位 否(占有位置) 相对于自身位置移动 常用 absolute 绝对定位 是(不占有位置) 带有定位的父级 常用 fixed 固定定位 是(不占有位置) 浏览器可视区 常用 sticky 粘性定位 否(占有位置) 浏览器可视区 当前阶段少 10. 定位叠放次序 z-index
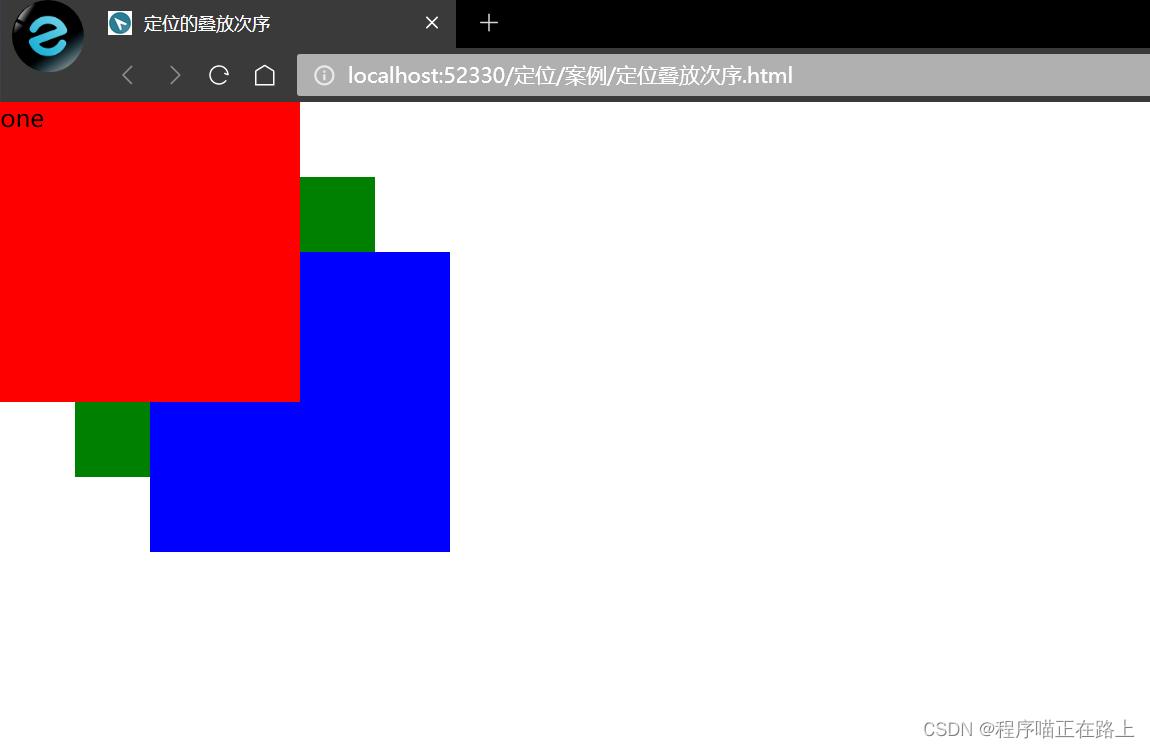
在使用定位布局时,可能会出现盒子重叠的情况。此时,可以用 z-index 来控制盒子的前后次序
语法:
选择器 { z-index: 1; }
- 数值可以是正整数、负整数或 0,默认是 auto,数值越大,盒子越靠上
- 如果属性值相同,则按照书写顺序,后来者居上
- 数字后面不能加单位
- 只有定位的盒子才有 z-index 属性
代码演示
DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <title>定位的叠放次序title> <style> .box { position: absolute; top: 0; left: 0; width: 200px; height: 200px; } .one { background-color: red; z-index: 1; } .two { background-color: green; left: 50px; top: 50px; } .three { background-color: blue; left: 100px; top: 100px; } style> head> <body> <div class="box one">onediv> <div class="box two">twodiv> <div class="box three">threediv> body> html>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
运行结果
11. 定位的拓展
怎么让绝对定位的盒子居中呢?
加了绝对定位的盒子不能通过 margin: 0 auto; 水平居中,但是可以通过一些技巧实现
代码演示
DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <title>绝对定位水平垂直居中title> <style> .box { position: absolute; left: 50%; margin-left: -100px; top: 50%; margin-top: -100px; width: 200px; height: 200px; background-color: #0CF; } style> head> <body> <div class="box">div> body> html>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
运行结果

定位特殊特性绝对定位和固定定位也和浮动类似
- 行内元素添加绝对或者固定定位,可以直接设置高度和宽度
- 块级元素添加绝对或者固定定位,如果不给宽度或者高度,默认大小是内容的大小
脱标的盒子不会触发外边距塌陷
浮动元素、绝对定位(固定定位)元素都不会触发外边距合并的问题
绝对定位(固定定位)会完全压住盒子
浮动元素不同,只会压住它下面标准流的盒子,但是不会压住下面标准流盒子里面的文字(图片)
但是绝对定位(固定定位)会压住下面标准流所有的内容
PS:给图片添加浮动,可以产生文字围绕着图片的效果
综合案例
案例:淘宝焦点图布局

- 大盒子类名为:tb-promo
- 里面先放一张图片
- 左右两个按钮用链接就好了,左箭头 prev,右箭头 next
- 底部小圆点 ul,类名为 promo-nav
代码实现
DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <title>淘宝网title> <style> * { margin: 0; padding: 0; } li { list-style: none; } .tb-promo { position: relative; width: 564px; height: 315px; margin: 100px auto; } .tb-promo img { width: 564px; height: 315px; } .prev, .next { position: absolute; top: 50%; margin-top: -15px; width: 20px; height: 30px; background: rgba(0, 0, 0, .3); text-align: center; line-height: 30px; color: #fff; text-decoration: none; } .prev { left: 0; border-top-right-radius: 15px; border-bottom-right-radius: 15px; } .next { right: 0; border-top-left-radius: 15px; border-bottom-left-radius: 15px; } .promo-nav { position: absolute; bottom: 15px; left: 50%; margin-left: -35px; width: 70px; height: 13px; background: rgba(255, 255, 255, .3); border-radius: 7px; } .promo-nav li { float: left; width: 8px; height: 8px; background-color: #fff; border-radius: 50%; margin: 3px; } .promo-nav .selected { background-color: #ff5000; } style> head> <body> <div class="tb-promo"> <img src="https://img.alicdn.com/imgextra/i2/6000000006499/O1CN01tvAkze1xsanRKfMEu_!!6000000006499-0-octopus.jpg" alt=""> <a href="#" class="prev"> < a> <a href="#" class="next"> > a> <ul class="promo-nav"> <li class="selected">li> <li>li> <li>li> <li>li> <li>li> ul> div> body> html>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
运行结果

元素的显示与隐藏
类似网站广告,当我们点击关闭就不见了,但是我们重新刷新界面,会重新出现
本质:让一个元素在页面中隐藏或显示出来
- display:显示隐藏
- visibility:显示隐藏
- overflow:溢出显示隐藏
1. display
display: none;—— 隐藏对象display: block;—— 除了转换为块级元素之外,同时还有显示元素的意思
DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <title>显示隐藏displaytitle> <style> .peppa { display: none; width: 200px; height: 200px; background-color: pink; } .george { width: 200px; height: 200px; background-color: skyblue; } style> head> <body> <div class="peppa">佩奇div> <div class="george">乔治div> body> html>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
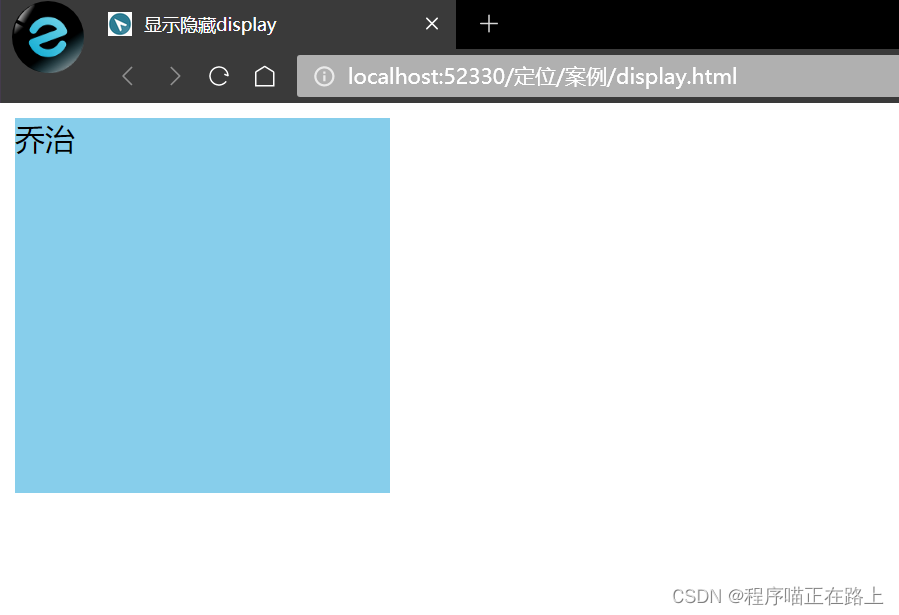
display 隐藏元素后,不再占有原来的位置后面应用及其广泛,搭配 JS 可以做很多网页特效
2. visibility
visibility 属性用于指定一个元素应可见还是隐藏
visibility: visible;—— 元素可见visibility: hidden;—— 元素隐藏
DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <title>显示隐藏visibilitytitle> <style> .peppa { visibility: hidden; width: 200px; height: 200px; background-color: pink; } .george { width: 200px; height: 200px; background-color: skyblue; } style> head> <body> <div class="peppa">佩奇div> <div class="george">乔治div> body> html>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
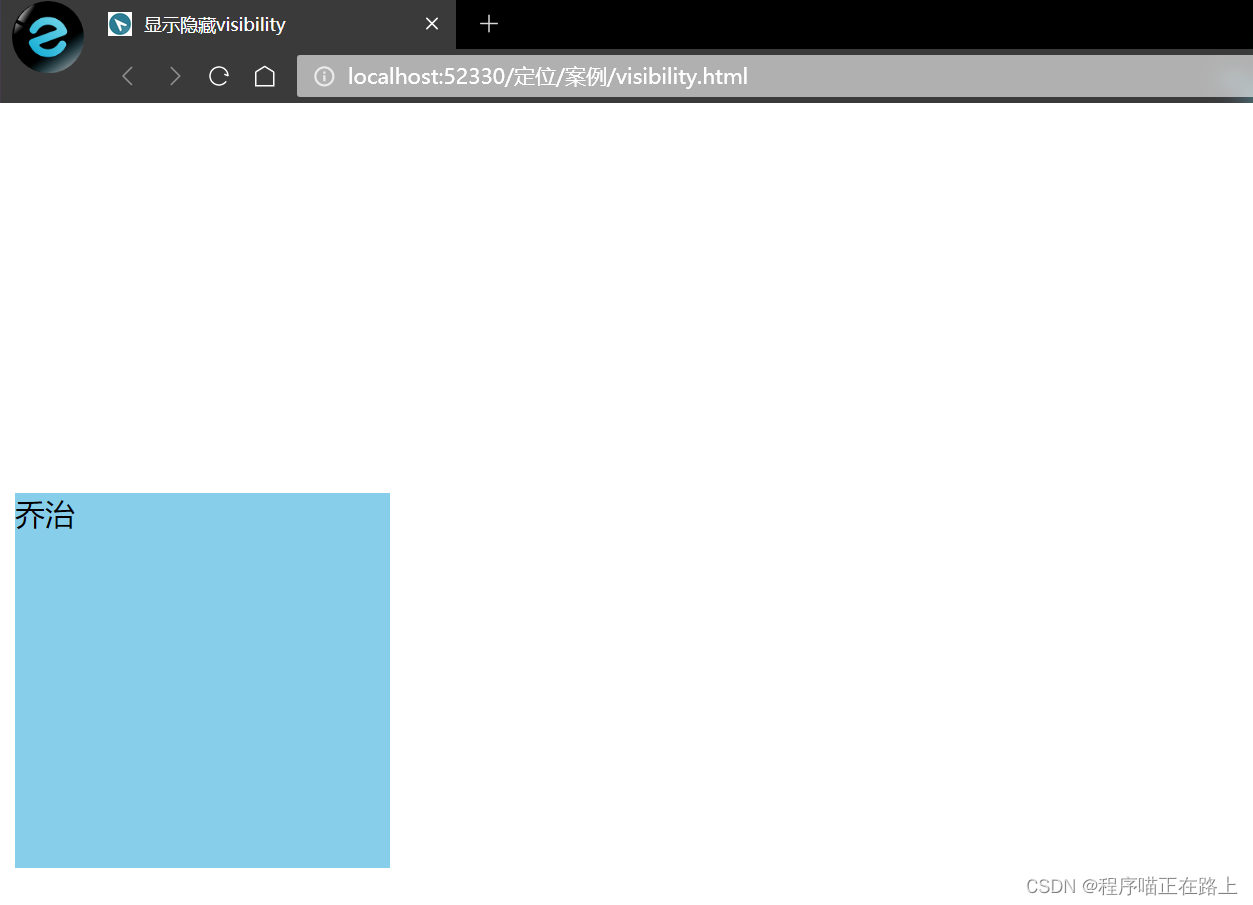
visibility 隐藏元素后,继续占有原来的位置如果隐藏元素想要原来位置,就用
visibility: hidden;
如果隐藏元素不想要原来位置,就用display: none;3. overflow
overflow 属性指定了如果内容溢出一个元素的边框(超过其指定高度及宽度)时,会发生什么
属性值 描述 visible 不剪切内容也不添加滚动条 hidden 不显示超过对象尺寸的内容,超出的部分隐藏掉 scroll 不管有没有超出内容,总是显示滚动条 auto 超出自动显示滚动条,不超出不显示滚动条 DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <title>溢出显示隐藏overflowtitle> <style> .peppa { /* overflow: hidden; */ /* overflow: scroll; */ overflow: auto; width: 200px; height: 200px; border: 3px solid cyan; margin: 100px auto; } style> head> <body> <div class="peppa"> 小猪佩奇是一只可爱的粉色小猪,她与弟弟乔治、爸爸、妈妈快乐地住在一起。小猪佩奇最喜欢做的事情是玩游戏,打扮的漂漂亮亮,度假,以及住在小泥坑里快乐的跳上跳下。除了这些,她还喜欢到处探险,虽然有些时候会遇到一些小状况,但总可以化险为夷,而且都会带给大家意外的惊喜 div> body> html>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28

一般情况下,我们都不想让溢出的内容显示出来,因为溢出的部分会影响布局但是如果有定位的盒子,请慎用
overflow: hidden;因为它会隐藏多余的部分4. 综合案例
需求:鼠标经过一个大盒子,会显示出半透明的黑色遮罩,移开则不显示
遮罩的盒子不占有位置,就需要用绝对定位和 display 配合使用
DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <title>Documenttitle> <style> .test { position: relative; width: 630px; height: 393px; background-color: pink; margin: 100px auto; } .test img { width: 100%; } .mask { position: absolute; display: none; top: 0; left: 0; width: 100%; height: 100%; background: rgba(0, 0, 0, .4) url(../images/arr.png) no-repeat center; } .test:hover .mask { display: block; } style> head> <body> <div class="test"> <div class="mask">div> <img src="../images/bgimg.png" alt=""> div> body> html>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
动图演示

🧸 这次的分享就到这里啦,继续加油哦^^
🐱 我是程序喵,陪你一点点进步
🍭 有出错的地方欢迎在评论区指出来,共同进步,谢谢啦 -
相关阅读:
WebGL实现简易的局部“马赛克”
BD就业复习第三天
【二叉树】链式结构的一些操作实现
CSS中常用的伪元素选择器
Centos7 编写开机监测gdm服务退出的脚本
[NAS] Synology (群晖) DSM同步数据到阿里云盘
链表OJ题(1)
NewStarCTF2023公开赛道-压缩包们
Rocket快速实战与高级原理详解
hive变更数据过程
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_62511863/article/details/126003392
