-
高维前缀和和子集dp(状压dp的一种)
首先,我们回顾一下一维前缀和和二维前缀和:
- //一维
- for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i)
- s[i] = s[i - 1] + a[i];
- //二维
- for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i)
- for (int j = 1; j <= m; ++j)
- s[i][j] = s[i - 1][j] + s[i][j - 1] - s[i - 1][j - 1] + a[i];
当然,也可以这么写:
- //一维
- for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i)
- s[i] += s[i - 1];
- //二维
- for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i)
- for (int j = 1; j <= m; ++j)
- f[i][j] += f[i - 1][j];
- for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i)
- for (int j = 1; j <= m; ++j)
- f[i][j] += f[i][j - 1];
(至于第二种写法,详细的解释可以看这篇博客-->)
我们今天要解决的是这样一个问题:

也就是求出对于每个i,在二进制下j∈i的所有子集的和.要解决这个问题,我们可以直接枚举子集计算,时间复杂度是
 .然而,我们可以参照二维前缀和的实现,利用高维前缀和优化成
.然而,我们可以参照二维前缀和的实现,利用高维前缀和优化成 .
.- for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j)
- for (int i = 0; i < (1 << n); ++i)
- if (i >> j & 1)
- a[i] += a[i ^ (1 << j)];
类似的,我们也可以求出超集和:
 ,也就是后缀和.
,也就是后缀和.- for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j)
- for (int i = 0; i < (1 << n); ++i)
- if (!(i >> j & 1))
- a[i] += a[i ^ (1 << j)];
或者我们也可以求出高维前缀和后缀差分:
- for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j)
- for (int i = 0; i < (1 << n); ++i)
- if (i >> j & 1)
- a[i] -= a[i ^ (1 << j)];
- for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j)
- for (int i = 0; i < (1 << n); ++i)
- if (!(i >> j & 1))
- a[i] -= a[i ^ (1 << j)];
动态规划中,有一种问题就是基于高维前缀和的,也就是子集dp.一般以位运算的形式呈现.
我们通过解决几道子集dp的例题来熟悉做法:
[ARC100C] Or Plus Max

思路:注意到i | j <= k,我们可以先求出满足i | j <= k时,最大的两个
 和
和 ,但是直接计算比较困难,我们可以先求出i | j == k时的最大值和次大值,然后在最后求的时候对于i | j <= k的答案取个前缀max即可得到答案.而求出i | j == k时a的最大值和次大值,我们可以用高维前缀和求解.具体做法如下:我们用f[K]存 在下标为K的子集的所有a[i]中 最大的a[i]和次大的a[i],然后用高维前缀和维护,最后取前缀max.
,但是直接计算比较困难,我们可以先求出i | j == k时的最大值和次大值,然后在最后求的时候对于i | j <= k的答案取个前缀max即可得到答案.而求出i | j == k时a的最大值和次大值,我们可以用高维前缀和求解.具体做法如下:我们用f[K]存 在下标为K的子集的所有a[i]中 最大的a[i]和次大的a[i],然后用高维前缀和维护,最后取前缀max.代码:
- #include
- #define int long long
- #define IOS ios::sync_with_stdio(false), cin.tie(0)
- #define ll long long
- // #define double long double
- #define ull unsigned long long
- #define PII pair
- #define PDI pair
- #define PDD pair
- #define debug(a) cout << #a << " = " << a << endl
- #define point(n) cout << fixed << setprecision(n)
- #define all(x) (x).begin(), (x).end()
- #define mem(x, y) memset((x), (y), sizeof(x))
- #define lbt(x) (x & (-x))
- #define SZ(x) ((x).size())
- #define inf 0x3f3f3f3f
- #define INF 0x3f3f3f3f3f3f3f3f
- namespace nqio{const unsigned R = 4e5, W = 4e5; char *a, *b, i[R], o[W], *c = o, *d = o + W, h[40], *p = h, y; bool s; struct q{void r(char &x){x = a == b && (b = (a = i) + fread(i, 1, R, stdin), a == b) ? -1 : *a++;} void f(){fwrite(o, 1, c - o, stdout); c = o;} ~q(){f();}void w(char x){*c = x;if (++c == d) f();} q &operator >>(char &x){do r(x);while (x <= 32); return *this;} q &operator >>(char *x){do r(*x); while (*x <= 32); while (*x > 32) r(*++x); *x = 0; return *this;} template<typename t> q&operator>>(t &x){for (r(y),s = 0; !isdigit(y); r(y)) s |= y == 45;if (s) for (x = 0; isdigit(y); r(y)) x = x * 10 - (y ^ 48); else for (x = 0; isdigit(y); r(y)) x = x * 10 + (y ^ 48); return *this;} q &operator <<(char x){w(x);return *this;}q &operator<< (char *x){while (*x) w(*x++); return *this;}q &operator <<(const char *x){while (*x) w(*x++); return *this;}template<typename t> q &operator<< (t x) {if (!x) w(48); else if (x < 0) for (w(45); x; x /= 10) *p++ = 48 | -(x % 10); else for (; x; x /= 10) *p++ = 48 | x % 10; while (p != h) w(*--p);return *this;}}qio; }using nqio::qio;
- using namespace std;
- const int N = (1 << 18) + 10;
- int n;
- struct rec {
- int mx, secmx;
- }a[N];
- //注意:不要把i和j(状态和位数搞反了)
- void solve() {
- qio >> n;
- for (int i = 0; i < 1 << n; ++i) qio >> a[i].mx;
- for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j)
- for (int i = 0; i < 1 << n; ++i)
- if (i >> j & 1) {
- int pre = i ^ (1 << j);
- rec ans;
- ans.mx = max(a[i].mx, a[pre].mx);
- if (a[i].mx > a[pre].mx) ans.secmx = max(a[i].secmx, a[pre].mx);
- else ans.secmx = max(a[i].mx, a[pre].secmx);
- a[i] = ans;
- }
- int ans = 0;
- for (int i = 1; i < 1 << n; ++i) {
- ans = max(ans, a[i].mx + a[i].secmx);
- qio << ans << '\n';
- }
- }
- signed main() {
- // IOS;
- int T = 1;
- // qio >> T;
- while (T--) solve();
- }
CF1208F Bits And Pieces

思路:我们考虑贪心地从高位到低位放1,具体来说,我们假设当前的答案是ans,在高位放了若干个1,现在考虑第bit位是否能放1,我们先让令x = ans | (1 << bit),然后枚举d_i的值,当然,我们是枚举x的子集,因为d_i和(d_j&d_k)的或值为x,那么,此时我们需要一个在全集x内d_i的补集的超集,假设在全集x内d_i的补集为t,要求t的超集,使用高维后缀和,由于要满足i < j < k,我们应该尽可能往前地选d_i,尽可能往后面选d_j和d_k,于是我们mn[x]维护值为x的超集所在下标的最小值,mx[x]维护值为x的超集的下标最大的最大值和次大值,对于后者,由于两个都是x的超集,那么两个与起来也一定是x的超集.回到判断这一位能否填1这个问题上,在我们枚举完d_i和d_j&d_k之后,我们只要判断d_i的下标最小值是否小于d_j的下标次小值即可.
代码:
- #include
- #define int long long
- #define IOS ios::sync_with_stdio(false), cin.tie(0)
- #define ll long long
- // #define double long double
- #define ull unsigned long long
- #define PII pair
- #define PDI pair
- #define PDD pair
- #define debug(a) cout << #a << " = " << a << endl
- #define point(n) cout << fixed << setprecision(n)
- #define all(x) (x).begin(), (x).end()
- #define mem(x, y) memset((x), (y), sizeof(x))
- #define lbt(x) (x & (-x))
- #define SZ(x) ((x).size())
- #define inf 0x3f3f3f3f
- #define INF 0x3f3f3f3f3f3f3f3f
- namespace nqio{const unsigned R = 4e5, W = 4e5; char *a, *b, i[R], o[W], *c = o, *d = o + W, h[40], *p = h, y; bool s; struct q{void r(char &x){x = a == b && (b = (a = i) + fread(i, 1, R, stdin), a == b) ? -1 : *a++;} void f(){fwrite(o, 1, c - o, stdout); c = o;} ~q(){f();}void w(char x){*c = x;if (++c == d) f();} q &operator >>(char &x){do r(x);while (x <= 32); return *this;} q &operator >>(char *x){do r(*x); while (*x <= 32); while (*x > 32) r(*++x); *x = 0; return *this;} template<typename t> q&operator>>(t &x){for (r(y),s = 0; !isdigit(y); r(y)) s |= y == 45;if (s) for (x = 0; isdigit(y); r(y)) x = x * 10 - (y ^ 48); else for (x = 0; isdigit(y); r(y)) x = x * 10 + (y ^ 48); return *this;} q &operator <<(char x){w(x);return *this;}q &operator<< (char *x){while (*x) w(*x++); return *this;}q &operator <<(const char *x){while (*x) w(*x++); return *this;}template<typename t> q &operator<< (t x) {if (!x) w(48); else if (x < 0) for (w(45); x; x /= 10) *p++ = 48 | -(x % 10); else for (; x; x /= 10) *p++ = 48 | x % 10; while (p != h) w(*--p);return *this;}}qio; }using nqio::qio;
- using namespace std;
- const int N = 1e6 + 10, M = (1 << 21) + 5;
- PII mx[M];
- int mn[M], a[N], n;
- PII max(PII x, PII y) {
- int temp[4] = {x.first, y.first, x.second, y.second};
- sort(temp, temp + 4), reverse(temp, temp + 4);
- return make_pair(temp[0], temp[1]);
- }
- bool check(int x) {
- for (int i = x; i; i = (i - 1) & x) if (mn[x ^ i] < mx[i].second) return true;
- return mn[x] < mx[0].second;
- }
- void solve() {
- qio >> n;
- for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) qio >> a[i];
- mem(mn, 0x3f);
- for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) mn[a[i]] = min(mn[a[i]], i);
- for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) mx[a[i]] = max(mx[a[i]], make_pair(i, 0));
- for (int j = 0; j < 21; ++j)
- for (int i = 0; i < (1 << 21); ++i)
- if (!(i >> j & 1ll)) {
- mn[i] = min(mn[i], mn[i ^ (1 << j)]);
- mx[i] = max(mx[i], mx[i ^ (1 << j)]);
- }
- int ans = 0;
- for (int i = 21; ~i; --i)
- if (check(ans | (1 << i))) ans |= (1 << i);
- qio << ans << "\n";
- }
- signed main() {
- // IOS;
- int T = 1;
- // qio >> T;
- while (T--) solve();
- }
CF449D Jzzhu and Numbers

思路:首先,看到最后的结果恰好一个1都没选,可以使用容斥原理.假设
 为选的数为x的超集(等会会解释为什么不是子集而是超集)的方案数,
为选的数为x的超集(等会会解释为什么不是子集而是超集)的方案数,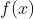 为选的数刚好为x的方案数.那么
为选的数刚好为x的方案数.那么 .
.但是我们也可以反过来,
 ,(注意,以上的x+1,x+2并不是真正的x+1,x+2,这些指的是x的超集)也就是说对g(x)差分,就可以得到f(x).然后g(x)可以用高维后缀和求,具体来说,假设x的一个子集是pre,那么g(x) += g(pre).
,(注意,以上的x+1,x+2并不是真正的x+1,x+2,这些指的是x的超集)也就是说对g(x)差分,就可以得到f(x).然后g(x)可以用高维后缀和求,具体来说,假设x的一个子集是pre,那么g(x) += g(pre).接下来我们看另外一道相似的题目:

这道题就是选出a1,a2,...an中的若干个数求或得到(1 << m) - 1,这道题我们与上面相反,假设

为选的数为x的子集,然后我们用高维前缀和维护.其他的跟上面的一模一样.
这题为什么又选子集了呢?
首先,要选出一堆数与起来至少为x,说明至少要选x的超集,但是选出一堆数或起来至少为x,我们却没办法找到规律,因为我们有可能选x的超集,也有可能选其子集,但是我们换个角度,选出一堆数或起来至多为x,那么我们就只能选x的子集了.然后构造差分时,也是使用前缀.
代码1:
- #include
- #define int long long
- #define IOS ios::sync_with_stdio(false), cin.tie(0)
- #define ll long long
- // #define double long double
- #define ull unsigned long long
- #define PII pair
- #define PDI pair
- #define PDD pair
- #define debug(a) cout << #a << " = " << a << endl
- #define point(n) cout << fixed << setprecision(n)
- #define all(x) (x).begin(), (x).end()
- #define mem(x, y) memset((x), (y), sizeof(x))
- #define lbt(x) (x & (-x))
- #define SZ(x) ((x).size())
- #define inf 0x3f3f3f3f
- #define INF 0x3f3f3f3f3f3f3f3f
- namespace nqio{const unsigned R = 4e5, W = 4e5; char *a, *b, i[R], o[W], *c = o, *d = o + W, h[40], *p = h, y; bool s; struct q{void r(char &x){x = a == b && (b = (a = i) + fread(i, 1, R, stdin), a == b) ? -1 : *a++;} void f(){fwrite(o, 1, c - o, stdout); c = o;} ~q(){f();}void w(char x){*c = x;if (++c == d) f();} q &operator >>(char &x){do r(x);while (x <= 32); return *this;} q &operator >>(char *x){do r(*x); while (*x <= 32); while (*x > 32) r(*++x); *x = 0; return *this;} template<typename t> q&operator>>(t &x){for (r(y),s = 0; !isdigit(y); r(y)) s |= y == 45;if (s) for (x = 0; isdigit(y); r(y)) x = x * 10 - (y ^ 48); else for (x = 0; isdigit(y); r(y)) x = x * 10 + (y ^ 48); return *this;} q &operator <<(char x){w(x);return *this;}q &operator<< (char *x){while (*x) w(*x++); return *this;}q &operator <<(const char *x){while (*x) w(*x++); return *this;}template<typename t> q &operator<< (t x) {if (!x) w(48); else if (x < 0) for (w(45); x; x /= 10) *p++ = 48 | -(x % 10); else for (; x; x /= 10) *p++ = 48 | x % 10; while (p != h) w(*--p);return *this;}}qio; }using nqio::qio;
- using namespace std;
- const int N = 1e6 + 10, M = (1 << 21) + 5, MOD = 1e9 + 7;
- int n, a[N], f[M], qp[M] = {1};
- void work(int x) {
- for (int j = 0; j < 21; ++j)
- for (int i = 0; i < (1 << 21); ++i)
- if (!(i >> j & 1))
- f[i] = ((f[i] + f[i ^ (1ll << j)] * x % MOD) % MOD + MOD) % MOD;
- }
- void solve() {
- qio >> n;
- for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) qio >> a[i], ++f[a[i]], qp[i] = (qp[i - 1] << 1ll) % MOD;
- work(1);
- for (int i = 0; i < (1 << 21); ++i) f[i] = qp[f[i]] - 1;
- work(-1);
- qio << f[0] << '\n';
- }
- signed main() {
- // IOS;
- int T = 1;
- // qio >> T;
- while (T--) solve();
- }
代码2:
- #include
- #define int long long
- #define IOS ios::sync_with_stdio(false), cin.tie(0)
- #define ll long long
- // #define double long double
- #define ull unsigned long long
- #define PII pair
- #define PDI pair
- #define PDD pair
- #define debug(a) cout << #a << " = " << a << endl
- #define point(n) cout << fixed << setprecision(n)
- #define all(x) (x).begin(), (x).end()
- #define mem(x, y) memset((x), (y), sizeof(x))
- #define lbt(x) (x & (-x))
- #define SZ(x) ((x).size())
- #define inf 0x3f3f3f3f
- #define INF 0x3f3f3f3f3f3f3f3f
- namespace nqio{const unsigned R = 4e5, W = 4e5; char *a, *b, i[R], o[W], *c = o, *d = o + W, h[40], *p = h, y; bool s; struct q{void r(char &x){x = a == b && (b = (a = i) + fread(i, 1, R, stdin), a == b) ? -1 : *a++;} void f(){fwrite(o, 1, c - o, stdout); c = o;} ~q(){f();}void w(char x){*c = x;if (++c == d) f();} q &operator >>(char &x){do r(x);while (x <= 32); return *this;} q &operator >>(char *x){do r(*x); while (*x <= 32); while (*x > 32) r(*++x); *x = 0; return *this;} template<typename t> q&operator>>(t &x){for (r(y),s = 0; !isdigit(y); r(y)) s |= y == 45;if (s) for (x = 0; isdigit(y); r(y)) x = x * 10 - (y ^ 48); else for (x = 0; isdigit(y); r(y)) x = x * 10 + (y ^ 48); return *this;} q &operator <<(char x){w(x);return *this;}q &operator<< (char *x){while (*x) w(*x++); return *this;}q &operator <<(const char *x){while (*x) w(*x++); return *this;}template<typename t> q &operator<< (t x) {if (!x) w(48); else if (x < 0) for (w(45); x; x /= 10) *p++ = 48 | -(x % 10); else for (; x; x /= 10) *p++ = 48 | x % 10; while (p != h) w(*--p);return *this;}}qio; }using nqio::qio;
- using namespace std;
- const int N = 1e6 + 10, M = (1 << 21) + 5, MOD = 1e9 + 7;
- int n, m, f[M], qp[M] = {1};
- void work(int x) {
- for (int j = 0; j < 21; ++j)
- for (int i = 0; i < (1 << 21); ++i)
- if (i >> j & 1)
- f[i] = ((f[i] + f[i ^ (1ll << j)] * x % MOD) % MOD + MOD) % MOD;
- }
- void solve() {
- qio >> n >> m;
- for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) qp[i] = (qp[i - 1] << 1ll) % MOD;
- for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
- int k, st = 0;
- qio >> k;
- for (int j = 1, x; j <= k; ++j) qio >> x, --x, st |= (1ll << x);
- ++f[st];
- }
- work(1);
- for (int i = 0; i < (1 << 21); ++i) f[i] = (qp[f[i]] - 1) % MOD;
- work(-1);
- qio << f[(1 << m) - 1] << '\n';
- }
- signed main() {
- // IOS;
- int T = 1;
- // qio >> T;
- while (T--) solve();
- }
-
相关阅读:
Java项目:ssm在线选课管理系统
数据库新技术【分布式数据库】
架构设计实践:熟悉架构设计方法论,并动手绘制架构设计图
Python:实现circle sort圆形排序算法(附完整源码)
在 Idea 中配置远程 tomcat 并部署
Java泛型中的T与?
求助帖:React Native failed installing Ruby Gems(rn 下载 Runby Gems 失败)
【经典面试题-LeetCode134:加油站问题(Java实现)】
从零开始搭建医药领域知识图谱实现智能问答与分析服务(含码源):含Neo4j基于垂直网站数据的医药知识图谱构建、医药知识图谱的自动问答等
Codeforces Global Round 21 C. Fishingprince Plays With Array
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/CK1513710764/article/details/126147952
