-
数据结构---顺序表,链表
目录
前言
这篇文章主要讲顺序表和链表,有几点需要大家注意一下:1.在学习的时候如果认为看着比较吃力的话,建议先去看看c语言--指针于结构体。2.当我们学习数据结构更多的是要练习,一遍一遍的把练习把基础打牢固。3.我们希望大家都能养成爱画图的习惯,很多时候图画出来了,思路就清晰了,代码就自然出来。4.遇到bug多调试,不熟不要怕慢慢就熟了。在这里与君共勉,互相加油,互相学习。
线性表
线性表的概念
线性表(linear list)是n个具有相同特性的数据元素的有限序列。 线性表是一种在实际中广泛使用的数据结构,常见的线性表:顺序表、链表、栈、队列、字符串...
线性表在逻辑上是线性结构,也就说是连续的一条直线。但是在物理结构上并不一定是连续的,线性表在物理上存储时,通常以数组和链式结构的形式存储。

顺序表
顺序表的概念
顺序表是用一段物理地址连续的存储单元依次存储数据元素的线性结构,一般情况下采用数组存储。在数组上完成数据的增删查改。
顺序表的结构
1. 静态顺序表:使用定长数组存储元素。

2.动态顺序表:使用动态开辟的数组存储。

静态顺序表只适用于确定知道需要存多少数据的场景。静态顺序表的定长数组导致N定大了,空间开多了浪费,开少了不够用。所以现实中基本都是使用动态顺序表,根据需要动态的分配空间大小,所以下面我们实现动态顺序表。
接口实现
SeqList.h---头文件,声明
- #pragma once
- #include
- #include
- #include
- typedef int SLDateType;
- typedef struct SeqList
- {
- SLDateType* a;
- size_t size;
- size_t capacity;
- }SeqList;
- //初始化
- void SeqListInit(SeqList* ps);
- //销毁
- void SeqListDestroy(SeqList* ps);
- //打印
- void SeqListPrint(SeqList* ps);
- //尾加
- void SeqListPushBack(SeqList* ps, SLDateType x);
- //头加
- void SeqListPushFront(SeqList* ps, SLDateType x);
- //头删
- void SeqListPopFront(SeqList* ps);
- //尾删
- void SeqListPopBack(SeqList* ps);
- //顺序表查找
- int SeqListFind(SeqList* ps, SLDateType x);
- //顺序表在pos位置插入x
- void SeqListInsert(SeqList* ps, size_t pos, SLDateType x);
- //顺序表删除pos位置的值
- void SeqListErase(SeqList* ps, size_t pos);
SeqList.c---函数实现
- #define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
- #include "SeqList.h"
- void SeqListInit(SeqList* ps)//初始化
- {
- assert(ps);
- ps->a = NULL;
- ps->size = ps->capacity = 0;
- }
- void SeqListDestroy(SeqList* ps)//销毁
- {
- assert(ps);
- free(ps->a);
- ps->a = NULL;
- ps->size = ps->capacity = 0;
- }
- void SeqListPrint(SeqList* ps)//打印
- {
- assert(ps);
- for (size_t i = 0; i < ps->size; i++)
- {
- printf("%d ", ps->a[i]);
- }
- printf("\n");
- }
- void SLCheckCapacity(SeqList* ps)//检查
- {
- if (ps->size==ps->capacity)
- {
- SLDateType newCapcity = ps->capacity==0 ? 4 : ps->capacity * 2;
- SLDateType* temp = (SLDateType*)realloc(ps->a, sizeof(ps->a)*newCapcity);
- if (temp == NULL)
- {
- perror("realloc fail");
- return;
- }
- ps->a = temp;
- ps->capacity = newCapcity;
- }
- }
- void SeqListPushBack(SeqList* ps, SLDateType x)//尾加
- {
- assert(ps);
- SLCheckCapacity(ps);
- ps->a[ps->size] = x;
- ps->size++;
- }
- void SeqListPushFront(SeqList* ps, SLDateType x)//头加
- {
- assert(ps);
- SLCheckCapacity(ps);
- int end = ps->size-1;
- while (end >= 0)
- {
- ps->a[end+1] = ps->a[end];
- end--;
- }
- ps->a[0] = x;
- ps->size++;
- }
- void SeqListPopFront(SeqList* ps)//头删
- {
- assert(ps);
- if (ps->size == 0)
- {
- return;
- }
- SLDateType str = 0;
- SLDateType end = ps->size - 1;
- while (str <= end)
- {
- ps->a[str] = ps->a[str + 1];
- str++;
- }
- ps->size--;
- }
- void SeqListPopBack(SeqList* ps)//尾删
- {
- assert(ps);
- if (ps->size == 0)
- {
- return;
- }
- ps->size--;
- }
- int SeqListFind(SeqList* ps, SLDateType x)//顺序表插入
- {
- assert(ps);
- int end = ps->size - 1;
- while (end>=0)
- {
- if (ps->a[end] == x)
- return end;
- end--;
- }
- return -1;
- }
- void SeqListInsert(SeqList* ps, size_t pos, SLDateType x)//顺序表在pos位置插入x
- {
- assert(ps);
- if (pos < 0 || pos >(ps->size - 1))
- {
- printf("输入错误\n");
- return;
- }
- for (size_t i = ps->size; i > pos; i--)
- {
- ps->a[i] = ps->a[i - 1];
- }
- ps->a[pos] = x;
- ps->size++;
- }
- void SeqListErase(SeqList* ps, size_t pos)//顺序表删除pos位置的值
- {
- assert(ps);
- if (pos < 0 || pos >(ps->size - 1))
- {
- printf("输入错误\n");
- return;
- }
- for (size_t i = pos; i < ps->size; i++)
- {
- ps->a[i] = ps->a[i+1];
- }
- ps->size--;
- }
test.c---测试
- #define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
- #include "SeqList.h"
- int main()
- {
- SeqList s;
- SeqListInit(&s);
- SeqListPushBack(&s, 1);
- SeqListPrint(&s);
- SeqListPushFront(&s, 2);
- SeqListPushFront(&s, 3);
- SeqListPrint(&s);
- SeqListPopFront(&s);
- SeqListPrint(&s);
- int ret = SeqListFind(&s, 2);
- if (ret == 1)
- printf("yes\n");
- else
- printf("no\n");
- SeqListInsert(&s, 1, 5);
- SeqListPrint(&s);
- SeqListErase(&s, 1);
- SeqListPrint(&s);
- }
这里建议实现一个函数了就先测试了来,后面过多了就容易看着眼花缭乱的。大神就另当别论!
相关面试题分析
例题1
原地移除数组中所有的元素val,要求时间复杂度为O(N),空间复杂度为O(1)。链接
实现过程:

实现代码:
- int removeElement(int* nums, int numsSize, int val){
- int src=0,dest=0;
- while(src{if(nums[src]==val){src++;}else{nums[dest++]=nums[src++];}}return dest;}
例题2
删除排序数组中的重复项:链接
实现过程:

实现代码:
- int removeDuplicates(int* nums, int numsSize){
- if (numsSize == 0) {
- return 0;
- }
- int src=1,dest=0;
- while(src{if(nums[src]==nums[dest]){src++;}else{dest++;nums[dest]=nums[src];src++;}}return dest+1;}
例题3
合并两个有序数组:链接
实现过程---2种情况::


实现代码:
- void merge(int* nums1, int nums1Size, int m, int* nums2, int nums2Size, int n){
- int src=m-1,dest=n-1;
- int end=m+n-1;
- while(src>=0&&dest>=0)
- {
- if(nums1[src]>nums2[dest])
- {
- nums1[end]=nums1[src];
- src--;
- end--;
- }
- else
- {
- nums1[end]=nums2[dest];
- end--;
- dest--;
- }
- }
- while(dest>=0)
- {
- nums1[end]=nums2[dest];
- end--;
- dest--;
- }
- }
- //方法二--插入快排
- int cmp(void* dest,void* src)
- {
- return *(int*)dest-*(int*)src;
- }
- void merge(int* nums1, int nums1Size, int m, int* nums2, int nums2Size, int n){
- for (int i=0;i!=n;i++){
- nums1[m+i] = nums2[i];
- }
- qsort(nums1,n+m,sizeof(int),cmp);
- }
顺序表的问题及思考
问题:
1. 中间/头部的插入删除,时间复杂度为O(N)
2. 增容需要申请新空间,拷贝数据,释放旧空间。会有不小的消耗。
3. 增容一般是呈2倍的增长,势必会有一定的空间浪费。例如当前容量为100,满了以后增容到200,我们再继续插入了5个数据,后面没有数据插入了,那么就浪费了95个数据空间。
如何解决这一问题呢?下面给出了链表的结构来看看。
链表
链表的概念及结构
概念:
链表是一种物理存储结构上非连续、非顺序的存储结构,数据元素的逻辑顺序是通过链表中的指针链接次序实现的 。


链表的分类
实际中链表的结构非常多样,以下情况组合起来就有8种链表结构:
单向或者双向

带头或者不带头

循环或者非循环

虽然有这么多的链表的结构,但是我们实际中最常用还是两种结构:

1. 无头单向非循环链表:结构简单,一般不会单独用来存数据。实际中更多是作为其他数据结构的子结构,如哈希桶、图的邻接表等等。另外这种结构在笔试面试中出现很多。
2. 带头双向循环链表:结构最复杂,一般用在单独存储数据。实际中使用的链表数据结构,都是带头双向循环链表。另外这个结构虽然结构复杂,但是使用代码实现以后会发现结构会带来很多优势,实现反而简单了,后面代码实现了就知道了。
单链表的实现
在学习单链表之前,我们需要弄明白我们是否需要改变我们传过去的参数?如果需要改变那我们传参的时候,实现功能的函数用什么接受参数?我们知道单链表是需要结构体来实现的,一个是存数据一个是存地址,那么结构体中的变量就应该是一个int类型的数据和一个指针。当我们明白结构体重的变量之后,我们会发现实现增删改查就是改变指针中的地址。数据有地址,指针也有地址。所需要改变指针地址时,我们就用二级指针来接受指针的地址。下面就是说明为什么需要用二级指针来接受。

接口实现
SList.h--函数声明
- #define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
- #include
- #include
- #include
- typedef int SLTDateType;
- //创建结构体
- typedef struct SListNode
- {
- SLTDateType data;
- struct SListNode* next;
- }SListNode;
- // 动态申请一个节点
- SListNode* BuySListNode(SLTDateType x);
- // 单链表打印
- void SListPrint(SListNode* phead);
- // 单链表尾插
- void SListPushBack(SListNode** pphead, SLTDateType x);
- // 单链表的头插
- void SListPushFront(SListNode** pphead, SLTDateType x);
- // 单链表的尾删
- void SListPopBack(SListNode** pphead);
- // 单链表头删
- void SListPopFront(SListNode** pphead);
- // 单链表查找
- SListNode* SListFind(SListNode* plist, SLTDateType x);
- // 单链表在pos位置之后插入x
- void SListInsertAfter(SListNode* pos, SLTDateType x);
- // 单链表删除pos位置之后的值
- void SListEraseAfter(SListNode* pos);
- // 单链表的销毁
- void SListDestroy(SListNode* phead);
SList.c--功能实现
- #include "SList.h"
- // 动态申请一个节点
- SListNode* BuySListNode(SLTDateType x)
- {
- SListNode* newnode = (SListNode*)malloc(sizeof(SListNode)* 1);
- if (newnode == NULL)
- {
- perror("malloc fail");
- exit(-1);
- }
- newnode->data = x;
- newnode->next = NULL;
- return newnode;
- }
- // 单链表打印
- void SListPrint(SListNode* phead)
- {
- assert(phead);
- SListNode*cur = phead;
- while (cur != NULL)
- {
- printf("%d->", cur->data);
- cur = cur->next;
- }
- printf("NULL\n");
- }
- // 单链表尾插
- void SListPushBack(SListNode** pphead, SLTDateType x)
- {
- assert(pphead);
- SListNode* newnode = BuySListNode(x);
- if (*pphead == NULL)//为空
- {
- *pphead = newnode;
- }
- else//不为空
- {
- SListNode* tail = *pphead;
- while (tail->next != NULL)
- {
- tail = tail->next;
- }
- tail->next = newnode;
- }
- }
- // 单链表的头插
- void SListPushFront(SListNode** pphead, SLTDateType x)
- {
- assert(pphead);
- SListNode* newnode = BuySListNode(x);
- newnode->next = *pphead;
- *pphead = newnode;
- }
- // 单链表的尾删
- void SListPopBack(SListNode** pphead)
- {
- assert(pphead);
- if (*pphead == NULL)
- {
- return;
- }
- SListNode* tail = *pphead;
- while (tail->next->next != NULL)
- {
- tail = tail->next;
- }
- free(tail->next);
- tail->next = NULL;
- }
- // 单链表头删
- void SListPopFront(SListNode** pphead)
- {
- assert(pphead);
- if (*pphead == NULL)
- {
- return;
- }
- SListNode* del = *pphead;
- *pphead = del->next;
- free(del);
- del = NULL;
- }
- // 单链表查找
- SListNode* SListFind(SListNode* plist, SLTDateType x)
- {
- assert(plist);
- while (plist->data!= x)
- {
- plist = plist->next;
- }
- if (plist == NULL)
- {
- return NULL;
- }
- else
- return plist;
- }
- // 单链表在pos位置之后插入x
- void SListInsertAfter( SListNode* pos, SLTDateType x)
- {
- assert(pos);
- SListNode*newnode= BuySListNode(x);
- newnode->next = pos->next;
- pos->next = newnode;
- }
- // 单链表删除pos位置之后的值
- void SListEraseAfter(SListNode* pos)
- {
- assert(pos);
- //SListNode*newnode = pos->next;
- //
- //if (newnode != NULL)
- //{
- // SListNode* nextnext = newnode->next;
- // free(newnode);
- // pos->next = nextnext;
- //}
- SListNode*newnode = pos;
- if (newnode->next != NULL)
- {
- SListNode*nextnext = newnode->next->next;
- free(newnode->next);
- pos->next = nextnext;
- }
- }
- // 单链表的销毁
- void SListDestroy(SListNode* phead)
- {
- assert(phead);
- free(phead->next);
- phead->data = 0;
- phead->next= NULL;
- }
Test.c--测试
- #include "SList.h"
- //尾插展示
- void TestSList1()
- {
- SListNode* plist=NULL;
- SListPushBack(&plist, 1);
- SListPushBack(&plist, 3);
- SListPushBack(&plist, 7);
- SListPrint(plist);
- }
- //头查展示
- void TestSList2()
- {
- SListNode* plist = NULL;
- SListPushFront(&plist, 1);
- SListPushFront(&plist, 7);
- SListPushFront(&plist, 11);
- SListPrint(plist);
- }
- // 单链表的尾删
- void TestSList3()
- {
- SListNode* plist = NULL;
- SListPushFront(&plist, 1);
- SListPushFront(&plist, 7);
- SListPushFront(&plist, 11);
- SListPopBack(&plist);
- SListPopBack(&plist);
- SListPrint(plist);
- }
- void TestSList4()
- {
- SListNode* plist = NULL;
- SListPushFront(&plist, 2);
- SListPushFront(&plist, 8);
- SListPushFront(&plist, 9);
- SListPopFront(&plist);
- SListPrint(plist);
- SListNode* pos = SListFind(plist, 8);
- if (pos)
- {
- //
- pos->data *= 10;
- printf("\n");
- }
- else
- {
- printf("\n");
- }
- SListPrint(plist);
- }
- void TestSList5()
- {
- SListNode* plist = NULL;
- SListPushFront(&plist, 2);
- SListPushFront(&plist, 2);
- SListPushFront(&plist, 3);
- SListPushFront(&plist, 4);
- SListNode* pos = SListFind(plist, 2);
- SListInsertAfter(pos, 4);
- SListPrint(plist);
- }
- void TestSList6()
- {
- SListNode* plist = NULL;
- SListPushFront(&plist, 4);
- SListPushFront(&plist, 5);
- SListPushFront(&plist, 7);
- SListPushFront(&plist, 8);
- SListPushFront(&plist, 8);
- SListPushFront(&plist, 8);
- SListNode* pos = SListFind(plist,7);
- SListEraseAfter(pos);
- SListPrint(plist);
- }
- void TestSList7()
- {
- SListNode* plist = NULL;
- SListPushFront(&plist, 4);
- SListPushFront(&plist, 5);
- SListPushFront(&plist, 7);
- SListDestroy(plist);
- SListPrint(plist);
- }
- int main()
- {
- TestSList1();
- TestSList2();
- TestSList3();
- TestSList4();
- TestSList5();
- TestSList6();
- TestSList7();
- }
链表面试题
例题1
删除链表中等于给定值 val 的所有结点 :链接
图文解析:
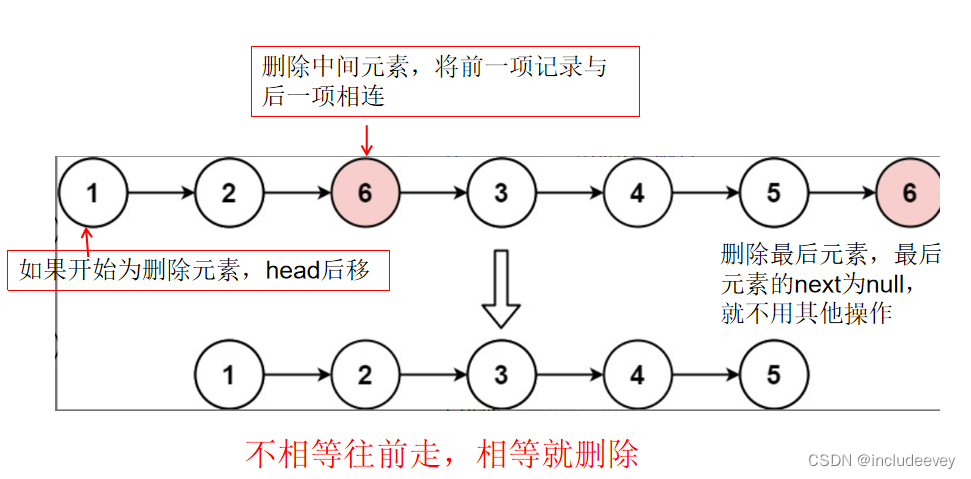
实现代码:
- struct ListNode* removeElements(struct ListNode* head, int val){
- struct ListNode* plist=NULL;
- struct ListNode* newnod=head;
- while(newnod)
- {
- if(newnod->val!=val)
- {
- plist=newnod;
- newnod=newnod->next;
- }
- else
- {
- if(plist==NULL)
- {
- head=newnod->next;
- free(newnod);
- newnod=head;
- }
- else
- {
- plist->next=newnod->next;
- free(newnod);
- newnod=plist->next;
- }
- }
- }
- return head;
- }
例题2
反转一个单链表:链接
方法1:我们用plist来改变地址指向,最开始将首元素next地址置为空,再将首元素地址赋予plist,将第二个元素的next地址改成第一个元素地址,接下来依次循环。主要是用plist与next保存地址。
图文解析:

实现代码:
- struct ListNode* reverseList(struct ListNode* head){
- struct ListNode* plist=NULL;
- struct ListNode* cur=head;
- while(cur)
- {
- struct ListNode* next=cur->next;
- cur->next=plist;
- plist=cur;
- cur=next;
- }
- return plist;
- }
方法2:我们用n1,n2,n3进行同时移动,将n1赋值为null,n2为首元素,n3为首元素next,我们改变了地址指向后,n1,n2,n3依次向右的移动,n1为n2,n2为n3,直到n2位空,用返回n1。
图文解析:

实现代码:
- struct ListNode* reverseList(struct ListNode* head){
- struct ListNode* n1=NULL;
- struct ListNode* n2=head;
- struct ListNode* n3=NULL;
- while(n2)
- {
- n3=n2->next;
- n2->next=n1;
- n1=n2;
- n2=n3;
- }
- return n1;
- }
例题3:
给定一个带有头结点 head 的非空单链表,返回链表的中间结点。如果有两个中间结点,则 返回第二个中间结点:链接
图文解析:

实现代码:
- struct ListNode* middleNode(struct ListNode* head){
- struct ListNode* slow=head;
- struct ListNode* fsat=head;
- while(fsat&&fsat->next)
- {
- fsat=fsat->next->next;
- slow=slow->next;
- }
- return slow;
- }
例题4
输入一个链表,输出该链表中倒数第k个结点:链接
图文解析:

实现代码:
- struct ListNode* FindKthToTail(struct ListNode* pListHead, int k ) {
- struct ListNode* fast=pListHead;
- struct ListNode* slow=pListHead;
- struct ListNode* cur=pListHead;
- int count=0;
- while(cur)
- {
- cur=cur->next;
- count++;
- }
- if(pListHead==NULL||k==0||k>count)
- {
- return NULL;
- }
- while(k--&&fast)
- {
- fast=fast->next;
- }
- while(fast)
- {
- fast=fast->next;
- slow=slow->next;
- }
- return slow;
- }
注意:有两个特殊情况,当k(倒数第几个)=0时,链表为空是,k>count(链表长度)时,返回null
例题5
图文解析:
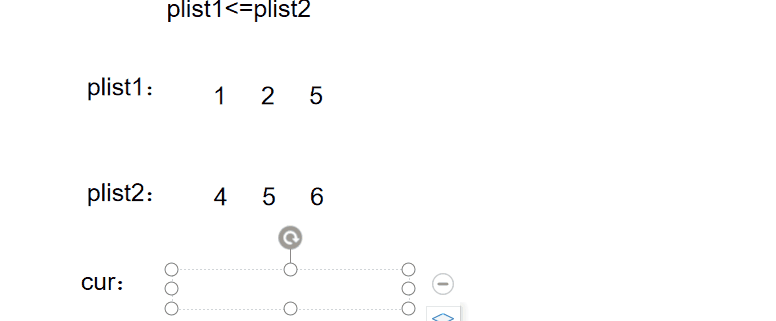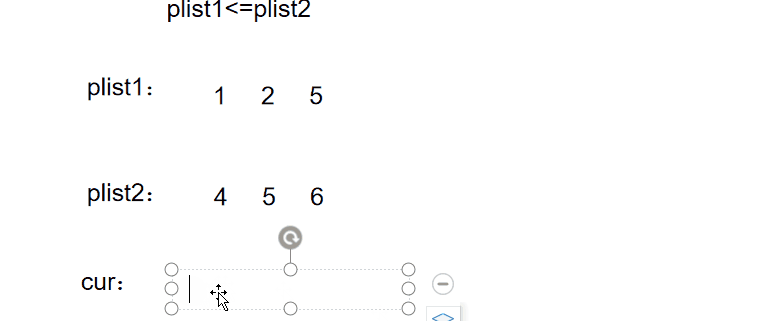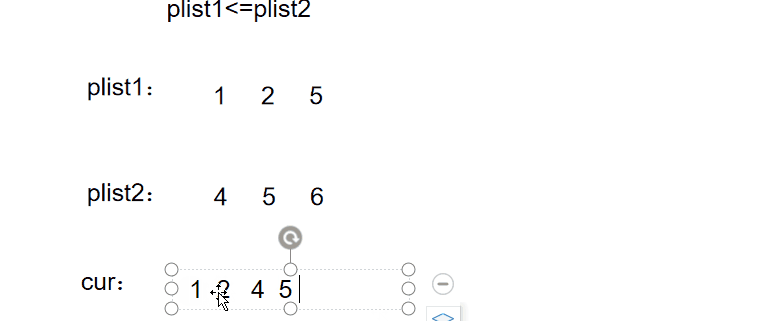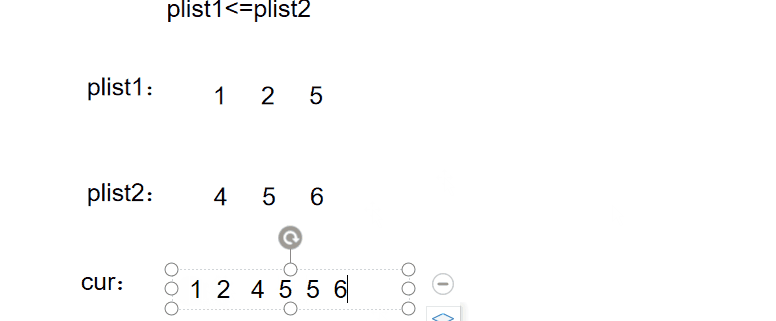
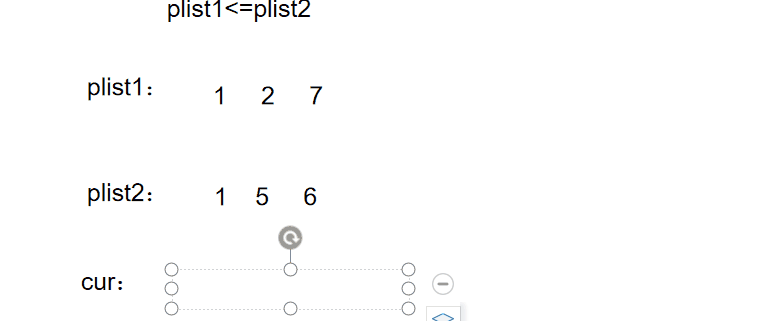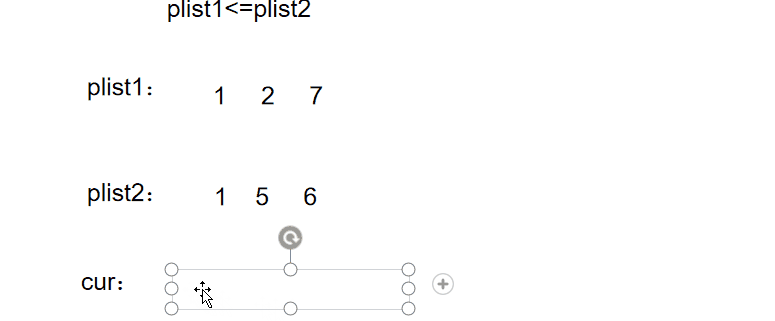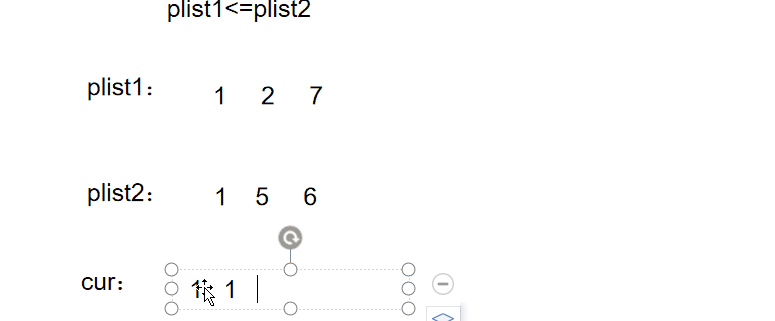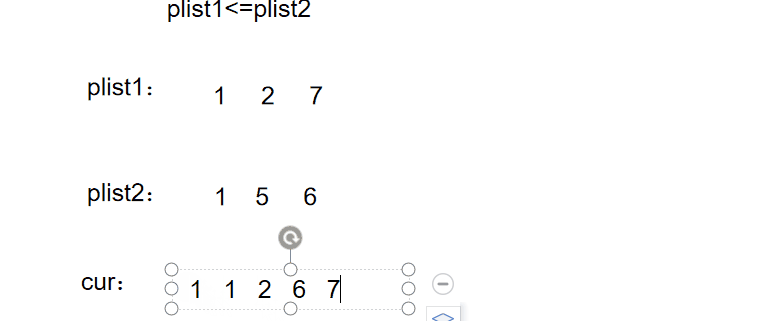
实现代码:
- struct ListNode* mergeTwoLists(struct ListNode* list1, struct ListNode* list2){
- struct ListNode* cur=(struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
- cur->next=NULL;
- struct ListNode* prve=cur;
- struct ListNode* plist1=list1;
- struct ListNode* plist2=list2;
- while(plist1&&plist2)
- {
- if((plist1->val) <=(plist2->val))
- {
- prve->next=plist1;
- prve=prve->next;
- plist1=plist1->next;
- }
- else
- {
- prve->next=plist2;
- prve=prve->next;
- plist2=plist2->next;
- }
- }
- if(plist1)
- {
- prve->next=plist1;
- }
- else
- {
- prve->next=plist2;
- }
- return cur->next;
- }
建议:这里建议建立一个头指针,用了头指针避免了很多判断,如果不用头指针,需要判断两个list链表是否为空,头元素到底是从list1开始还是从list2开始
例题6:
图文解析:

实现代码:
- class Partition {
- public:
- ListNode* partition(ListNode* pHead, int x) {
- struct ListNode* plist1, *plist2;
- struct ListNode* head1,* head2;
- head1 = plist1 = (struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
- head2= plist2 = (struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
- struct ListNode* cur = pHead;
- while(cur)
- {
- if(cur->val{head1->next=cur;head1=head1->next;cur=cur->next;}else{head2->next=cur;head2=head2->next;cur=cur->next;}}head2->next=NULL;head1->next=plist2->next;pHead=plist1->next;return pHead;}};
例题7:
链表的回文结构:链接
图文解析:

实现代码:
- //寻找中间点
- struct ListNode* middleNode(struct ListNode* head){
- struct ListNode* slow=head;
- struct ListNode* fsat=head;
- while(fsat&&fsat->next)
- {
- fsat=fsat->next->next;
- slow=slow->next;
- }
- return slow;
- }
- //逆置中间以后
- struct ListNode* reverseList(struct ListNode* head){
- struct ListNode* plist=NULL;
- struct ListNode* newnode=head;
- while(newnode)
- {
- struct ListNode* next=newnode->next;
- newnode->next=plist;
- plist=newnode;
- newnode=next;
- }
- return plist;
- }
- //判断是否是回文
- class PalindromeList {
- public:
- bool chkPalindrome(ListNode* A) {
- ListNode* cur=A;
- ListNode* mid= middleNode(cur);
- ListNode*rmid =reverseList (mid);
- while(rmid)
- {
- if(rmid->val!=A->val)
- return false;
- A=A->next;
- rmid=rmid->next;
- }
- return true;
- }
- };
例题8
输入两个链表,找出它们的第一个公共结点:链接
图文解析:

实现代码:
- struct ListNode *getIntersectionNode(struct ListNode *headA, struct ListNode *headB) {
- int len1=0,len2=0;
- struct ListNode* plist1=headA;
- struct ListNode* plist2=headB;
- while(plist1)
- {
- len1++;
- plist1=plist1->next;
- }
- while(plist2)
- {
- len2++;
- plist2=plist2->next;
- }
- if(plist1!=plist2)
- {
- return NULL;
- }
- int len=abs(len1-len2);
- plist1=headA;
- plist2=headB;
- if(len1>len2)
- {
- while(len--)
- {
- plist1=plist1->next;
- }
- }
- else
- {
- while(len--)
- {
- plist2=plist2->next;
- }
- }
- while(plist1!=plist2)
- {
- plist1=plist1->next;
- plist2=plist2->next;
- }
- return plist1;
- }
例题9:
给定一个链表,判断链表中是否有环:例题
【思路】 快慢指针,即慢指针一次走一步,快指针一次走两步,两个指针从链表其实位置开始运行, 如果链表 带环则一定会在环中相遇,否则快指针率先走到链表的末尾。比如:陪女朋友到操作跑步减 肥。 【扩展问题】
为什么快指针每次走两步,慢指针走一步可以?
假设链表带环,两个指针最后都会进入环,快指针先进环,慢指针后进环。当慢指针刚 进环时,可能就和快指针相遇了,最差情况下两个指针之间的距离刚好就是环的长度。 此时,两个指针每移动一次,之间的距离就缩小一步,不会出现每次刚好是套圈的情 况,因此:在满指针走到一圈之前,快指针肯定是可以追上慢指针的,即相遇。
快指针一次走3步,走4步, ...n步行吗?

实现代码:
- bool hasCycle(struct ListNode *head) {
- struct ListNode *headA=head;
- struct ListNode *headB=head;
- while(headA&&headA->next)
- {
- headA=headA->next->next;
- headB=headB->next;
- if(headA==headB)
- {
- return true;
- }
- }
- return false;
- }
例题10:
给定一个链表,返回链表开始入环的第一个结点。 如果链表无环,则返回 NULL:链接
方法1:
结论 :让一个指针从链表起始位置开始遍历链表,同时让一个指针从判环时相遇点的位置开始绕环 运行,两个指针都是每次均走一步,最终肯定会在入口点的位置相遇。
证明
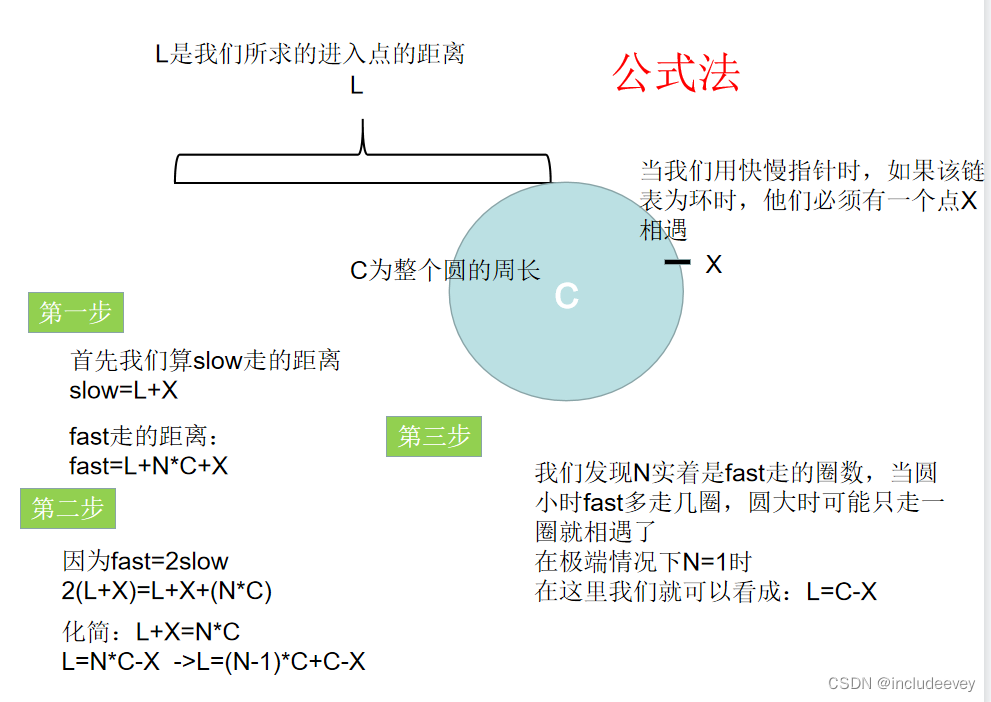
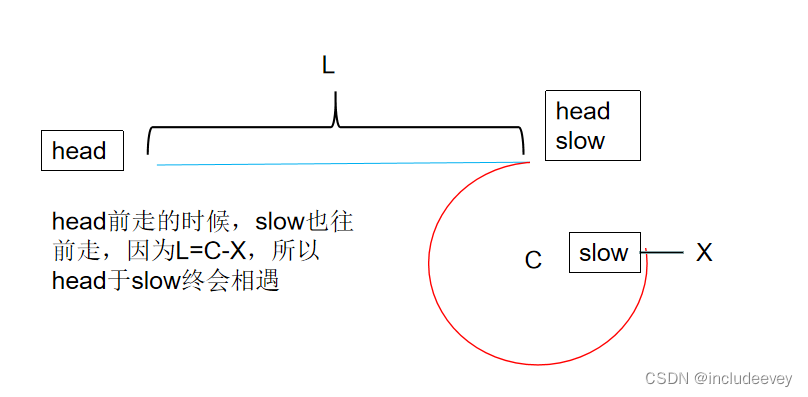
实现代码:
- struct ListNode *detectCycle(struct ListNode *head) {
- struct ListNode *fastA=head;
- struct ListNode *slow = head, *fast = head;
- while (fast != NULL&&fast->next != NULL) {
- slow = slow->next;
- fast = fast->next->next;
- if (fast == slow) {
- struct ListNode* ptr = head;
- while (ptr != slow) {
- ptr = ptr->next;
- slow = slow->next;
- }
- return ptr;
- }
- }
- return NULL;
- }
方法2:
图文解析:
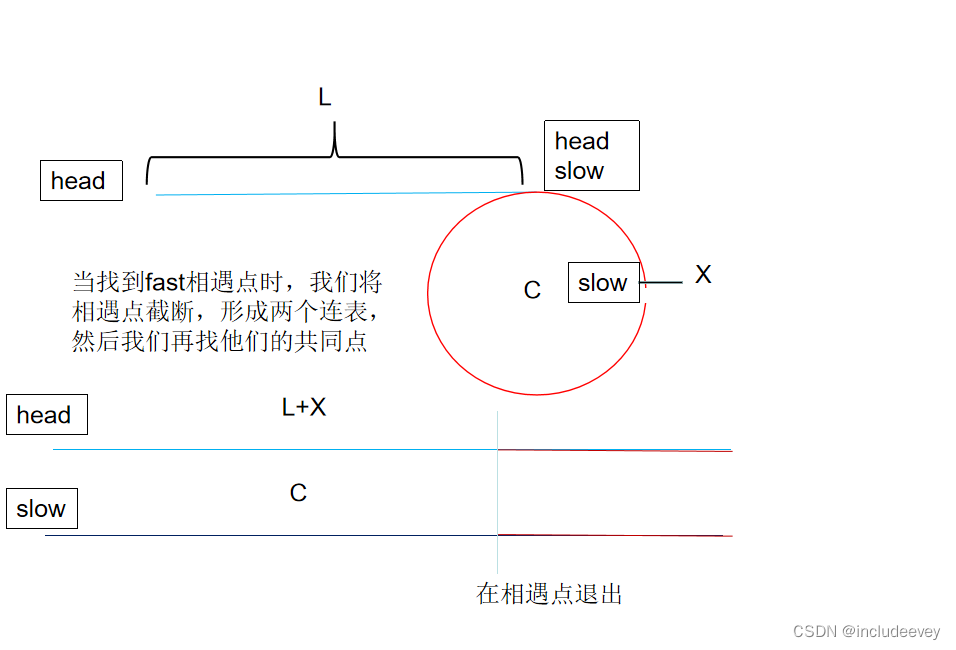
代码实现:--自己实现
例题11
给定一个链表,每个结点包含一个额外增加的随机指针,该指针可以指向链表中的任何结点 或空结点:链接
图文解析:

代码实现:
- struct Node* copyRandomList(struct Node* head) {
- struct Node* cur=head;
- struct Node* next=NULL;
- struct Node* copy=NULL;
- //插入copy节点
- while(cur)
- {
- next=cur->next;
- copy=(struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
- copy->val=cur->val;
- cur->next=copy;
- copy->next=next;
- cur=next;
- }
- //更新random
- cur=head;
- while(cur)
- {
- copy=cur->next;
- if(cur->random==NULL)
- {
- copy->random=NULL;
- }
- else
- {
- copy->random=cur->random->next;
- }
- cur=cur->next->next;
- }
- //分解与恢复
- struct Node* copyhead=NULL,*copytail=NULL;
- cur=head;
- while(cur)
- {
- copy=cur->next;
- next=copy->next;
- if(copytail==NULL)
- {
- copyhead=copytail=copy;
- }
- else
- {
- copytail->next=copy;
- copytail=copytail->next;
- }
- cur->next=next;
- cur=next;
- }
- return copyhead;
- }
双向链表
接口的实现
List.h
- #include
- #include
- #include
- typedef int LTDataType;
- typedef struct ListNode
- {
- LTDataType _data;
- struct ListNode* _next;
- struct ListNode* _prev;
- }ListNode;
- // 创建返回链表的头结点.
- ListNode* ListCreate();
- // 双向链表销毁
- void ListDestory(ListNode* pHead);
- // 双向链表打印
- void ListPrint(ListNode* pHead);
- // 双向链表尾插
- void ListPushBack(ListNode* pHead, LTDataType x);
- // 双向链表尾删
- void ListPopBack(ListNode* pHead);
- // 双向链表头插
- void ListPushFront(ListNode* pHead, LTDataType x);
- // 双向链表头删
- void ListPopFront(ListNode* pHead);
- // 双向链表查找
- ListNode* ListFind(ListNode* pHead, LTDataType x);
- // 双向链表在pos的前面进行插入
- void ListInsert(ListNode* pos, LTDataType x);
- // 双向链表删除pos位置的节点
- void ListErase(ListNode* pos);
List.c
- #include "List.h"
- // 创建返回链表的头结点.
- ListNode* ListCreate()
- {
- ListNode* gurad = (ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(ListNode));
- if (gurad == NULL)
- {
- perror("malloc fail");
- exit(-1);
- }
- gurad->_next=gurad ;
- gurad->_prev=gurad;
- return gurad;
- }
- // 双向链表销毁
- void ListDestory(ListNode* pHead)
- {
- assert(pHead);
- ListNode* cur = pHead->_next;
- while (cur!=pHead)
- {
- ListNode* next = cur->_next;
- free(cur);
- cur = next;
- }
- }
- // 双向链表打印
- void ListPrint(ListNode* pHead)
- {
- assert(pHead);
- ListNode* cur = pHead->_next;
- while (cur != pHead)
- {
- ListNode* next = cur->_next;
- printf("%d<==>", cur->_data);
- cur = cur->_next;
- }
- printf("\n");
- }
- //创造新节点
- ListNode* BuyListNode(LTDataType x)
- {
- ListNode* newnode = (ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(ListNode));
- if (newnode == NULL)
- {
- perror("malloc fail");
- exit(-1);
- }
- newnode->_data = x;
- newnode->_next = NULL;
- newnode->_prev = NULL;
- return newnode;
- }
- // 双向链表尾插
- void ListPushBack(ListNode* pHead, LTDataType x)
- {
- assert(pHead);
- ListNode* cur = BuyListNode(x);
- ListNode* prve = pHead->_prev;
- prve->_next = cur;
- cur->_prev = prve;
- cur->_next = pHead;
- pHead->_prev = cur;
- //ListInsert(pHead, x);
- }
- // 双向链表尾删
- void ListPopBack(ListNode* pHead)
- {
- assert(pHead);
- ListNode* prve1 = pHead->_prev;
- ListNode* prve2 = prve1->_prev;
- prve2->_next = pHead;
- pHead->_prev = prve2;
- free(prve1);
- prve1 = NULL;
- //ListErase(pHead->_prev);
- }
- // 双向链表头插
- void ListPushFront(ListNode* pHead, LTDataType x)
- {
- assert(pHead);
- ListNode* cur = BuyListNode(x);
- ListNode* next = pHead->_next;
- pHead->_next = cur;
- cur->_prev = pHead;
- next->_prev = cur;
- cur->_next = next;
- //ListInsert(pHead->_next, x);
- }
- // 双向链表头删
- void ListPopFront(ListNode* pHead)
- {
- assert(pHead);
- ListNode* next1 = pHead->_next;
- ListNode* next2 = next1->_next;
- pHead->_next = next2;
- next2->_prev = pHead;
- free(next1);
- next1 = NULL;
- //ListErase(pHead->_next);
- }
- // 双向链表查找
- ListNode* ListFind(ListNode* pHead, LTDataType x)
- {
- assert(pHead);
- ListNode* cur = pHead->_next;
- while (cur != pHead)
- {
- if (cur->_data == x)
- return cur;
- cur = cur->_next;
- }
- return NULL;
- }
- // 双向链表在pos的前面进行插入
- void ListInsert(ListNode* pos, LTDataType x)
- {
- assert(pos);
- ListNode* cur = BuyListNode(x);
- ListNode* prev = pos->_prev;
- prev->_next = cur;
- cur->_prev = prev;
- pos->_prev = cur;
- cur->_next = pos;
- }
- // 双向链表删除pos位置的节点
- void ListErase(ListNode* pos)
- {
- assert(pos);
- ListNode* prev = pos->_prev;
- ListNode* next = pos->_next;
- next->_prev = prev;
- prev->_next = next;
- free(pos);
- }
Test.c
- #include "List.h"
- //尾插-打印-尾删-打印
- void Test1()
- {
- ListNode* plist = ListCreate();
- ListPushBack(plist,4);
- ListPushBack(plist, 5);
- ListPushBack(plist, 8);
- ListPushBack(plist, 9);
- ListPrint(plist);
- ListPopBack(plist);
- ListPrint(plist);
- }
- //头查-打印-头删-打印-查找
- void Test2()
- {
- ListNode* plist = ListCreate();
- ListPushFront(plist, 1);
- ListPushFront(plist, 2);
- ListPushFront(plist, 3);
- ListPushFront(plist, 4);
- ListPrint(plist);
- ListPopFront(plist);
- ListPrint(plist);
- ListNode*ret = ListFind(plist, 2);
- if (ret != NULL)
- printf("yes\n");
- else
- printf("no\n");
- }
- //pos的前面插入-打印-pos的前面删除-打印
- void Test3()
- {
- ListNode* plist = ListCreate();
- ListPushFront(plist, 1);
- ListPushFront(plist, 2);
- ListPushFront(plist, 3);
- ListPushFront(plist, 4);
- ListInsert(plist->_next, 5);
- ListPrint(plist);
- ListErase(plist->_next);
- ListPrint(plist);
- }
- int main()
- {
- Test1();
- Test2();
- Test3();
- return 0;
- }
顺序表和链表的区别


顺序表与链表相比:顺序表CPU高速缓存命中率更高
CPU高速缓存:在寄存器与主存之间的缓存,寄存器访问速度是非常快的,但主存访问速度较慢,更不上寄存器的访问速度,所以不可能让寄存器一直等主存,为了提高效率我们就需要高速缓存(三级缓存)来将主存的数据先加载到缓存中。
CPU指向指如何访问内存:先看数据在不在三级缓存,在(命中),直接访问。不在(不命中),先加载到缓存,在访问。加载进缓存时不会一次加载一个数据,是将数据周边的数据一起加载(一段数据)--加载多少取决于硬件,为了更高效的加载
如何理解 顺序表CPU高速缓存命中率更高:因为顺序表的结构关系,它的数据具有连续性的,当我们CPU访问的时候,主存加载到缓存时是直接将一段数据直接加载,正因为它是连续寄存器寻找有用数据时就更加容易命中(更加容易找到数据),带来的好处就是效率的提高。与之相反链表的数据不具有连续性,当寄存器访问的时候该数据周围的地址不连续,访问一些没有用的数据,缓存的内存也是有限,所以也就浪费了缓存的内存。
如何知道自己的电脑的三级缓存:打开任务管理器,选择性能


-
相关阅读:
Python:实现quantum entanglement量子纠缠技术算法(附完整源码)
复盘一个诡异的Bug
Nacos 长轮询实现方式-配置中心源码
基于OSAL 实现UART、LED、ADC等基础示例 4
leetcode中级2,Sorting and Searching:347. 前 K 个高频元素
el-tree 获取当前勾选节点的选中状态以及选中值对象 触发check-change多次事件问题原因
浅谈用匈牙利算法寻找二分图的最大匹配
JVS规则引擎及智能BI又更新新功能啦!赶紧来试试
[pytest] requests模块
《学术小白学习之路13》基于DTM和主题共现网络——实现主题时序演化网络分析(数据代码在结尾)
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/includeevey/article/details/126038255
