-
【ACWing 算法基础】模拟散列表
一. 模板
(1) 拉链法 int h[N], e[N], ne[N], idx; // 向哈希表中插入一个数 void insert(int x) { int k = (x % N + N) % N; e[idx] = x; ne[idx] = h[k]; h[k] = idx ++ ; } // 在哈希表中查询某个数是否存在 bool find(int x) { int k = (x % N + N) % N; // // c++中如果是负数 那他取模也是负的 所以 加N 再 %N 就一定是一个正数 for (int i = h[k]; i != -1; i = ne[i]) if (e[i] == x) return true; return false; } (2) 开放寻址法 int h[N]; // 如果x在哈希表中,返回x的下标;如果x不在哈希表中,返回x应该插入的位置 int find(int x) { int t = (x % N + N) % N; while (h[t] != null && h[t] != x) { t ++ ; if (t == N) t = 0; } return t; // 如果这个位置是空的, 则返回的是他应该存储的位置 }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 寻找大于 i 的最小的质数(确定N)
for (int i = 1e5; i; ++i) { bool flag = true; // 判断是否为质数; for (int j = 2; j * j <= i; ++j) { // 从2检测到i的一半,小于i/2不存在时,大于i/2肯定也不存在 if (i % j == 0) { flag = false; // 不为质数 break; } } if (flag) { // 找到质数 cout << i << endl; break; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
二. 总结
- 拉链法

- 开放寻址法
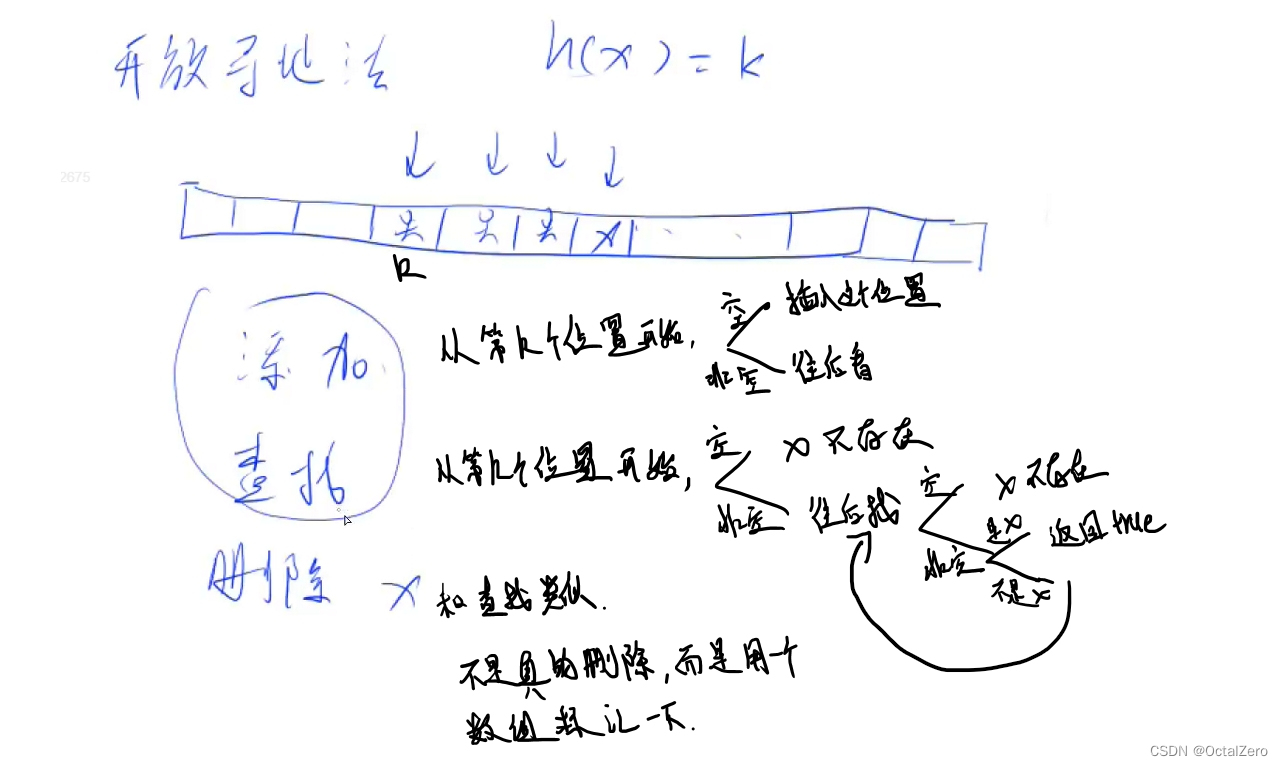
- 散列表原理

三. 例题

AC代码:
- 拉链法
#include#include using namespace std; const int N = 100003; // 取大于1e5的第一个质数,取质数冲突的概率最小 int h[N], e[N], ne[N], idx; // 插入一个数 x void insert(int x) { int k = (x % N + N) % N; // 映射到hash表 e[idx] = x; ne[idx] = h[k]; h[k] = idx++; } // 查询数 x 是否在集合中出现过 bool find(int x) { int k = (x % N + N) % N; // 映射到hash表 for (int i = h[k]; i != -1; i = ne[i]) { // 遍历链表 if (e[i] == x) return true; } return false; } int main() { ios::sync_with_stdio(false); cin.tie(0); cout.tie(0); int n; cin >> n; memset(h, -1, sizeof h); // memset 按字节复制 -1 为 0XFF,复制后为0xFFFFFFFF也为-1 char op; int x; while (n--) { cin >> op >> x; if (op == 'I') insert(x); else { if(find(x)) puts("Yes"); else puts("No"); } } } - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 开放寻址法
#include#include using namespace std; //开放寻址法一般开 数据范围的 2~3倍, 这样大概率就没有冲突了 const int N = 2e5 + 3; //大于数据范围的第一个质数 const int null = 0x3f3f3f3f; //规定空指针为 null 0x3f3f3f3f int h[N]; // 如果x在哈希表中,返回x的下标;如果x不在哈希表中,返回x应该插入的位置 int find(int x) { int t = (x % N + N) % N; while (h[t] != null && h[t] != x) { t++; if (t == N) { t = 0; } } return t; // 如果这个位置是空的, 则返回的是他应该存储的位置 } int main() { int n; cin >> n; memset(h, 0x3f, sizeof h); //规定空指针为 0x3f3f3f3f while (n--) { string op; int x; cin >> op >> x; if (op == "I") { h[find(x)] = x; } else { if (h[find(x)] == null) { puts("No"); } else { puts("Yes"); } } } return 0; } - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
-
相关阅读:
【目标检测】46、YOLOv4 | AlexeyAB大神接棒 引入其他模块来实现更快更好的 YOLO 网络
让我们谈谈密码哈希
【软件设计师21天-考点整理】4)计算机系统构成及硬件基础知识
Internet Download Manager永久版功能强大的网络下载器
Streamlit 构建大语言模型 (LLM) web 界面
unity打包webgl 部署到本地Web服务器
什么是Streamlit
密码学系列0-总述
vim 不常见但好用的命令
云原生Devops 的实现方法
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/m0_51139226/article/details/126138863
