-
python绘制云雨图(raincloud plot) 【官方教程翻译】
官方github: https://github.com/RainCloudPlots/RainCloudPlots
Raincloud 的 Python 实现是一个名为 PtitPrince 的包,它写在 seaborn 之上,这是一个 Python 绘图库,用于从 pandas 数据帧中获取漂亮的绘图。
import pandas as pd import seaborn as sns import os import matplotlib.pyplot as plt #sns.set(style="darkgrid") #sns.set(style="whitegrid") #sns.set_style("white") sns.set(style="whitegrid",font_scale=2) import matplotlib.collections as clt import ptitprince as pt- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
#图片保存及输出设置 savefigs = True figs_dir = '../figs/tutorial_python' if savefigs: # Make the figures folder if it doesn't yet exist #如果没有找到文件夹,先创建此文件夹 if not os.path.isdir('../figs/tutorial_python'): os.makedirs('../figs/tutorial_python') def export_fig(axis,text, fname): if savefigs: axis.text() axis.savefig(fname, bbox_inches='tight')- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
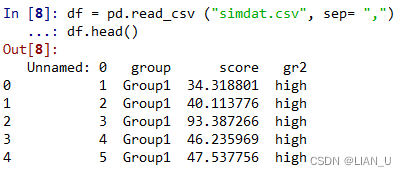
df = pd.read_csv ("simdat.csv", sep= ",") df.head()- 1
- 2
该图可以让读者初步了解数据集:哪个组的平均值更大,这种差异是否可能显着。 此图中仅显示每组分数的平均值和标准差。
f, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(7, 7)) sns.barplot(x = "group", y = "score", data = df, capsize= .1) plt.title("Figure P1\n Bar Plot") if savefigs: plt.savefig('.\\figs\\tutorial_python\\figureP01.png', bbox_inches='tight')- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5

为了了解我们的数据集的分布,我们可以绘制一个“云”,即直方图的平滑版本:# plotting the clouds f, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(7, 5)) dy="group" dx="score" ort="h" pal = sns.color_palette(n_colors=1) ax=pt.half_violinplot(x=dx, y=dy, data=df, palette=pal, bw=.2, cut=0., scale="area", width=.6, inner=None, orient=ort) plt.title("Figure P2\n Basic Rainclouds") if savefigs: plt.savefig('.\\figs\\tutorial_python\\figureP02.png', bbox_inches='tight')- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
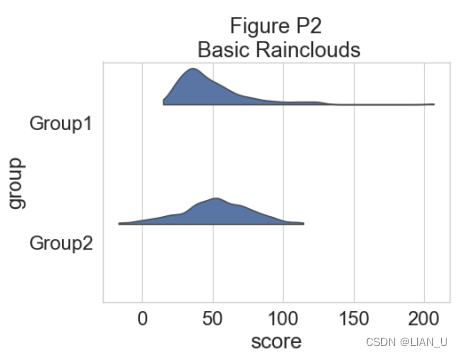
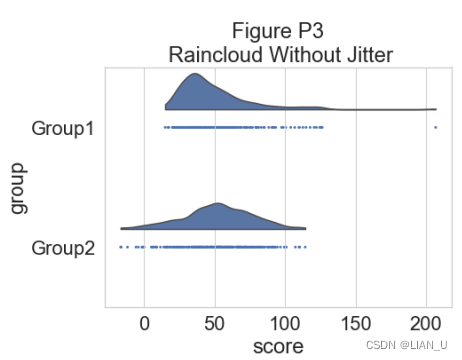
为了更精确地了解分布并说明数据中的潜在异常值或其他模式,我们现在添加“雨”,即数据点的简单单维表示:
# adding the rain f, ax=plt.subplots(figsize=(7, 5)) ax=pt.half_violinplot(x=dx, y=dy, data=df, palette=pal, bw=.2, cut=0., scale="area", width=.6, inner=None, orient=ort) ax=sns.stripplot(x=dx, y=dy, data=df, palette=pal, edgecolor="white", size=3, jitter=0, zorder=0, orient=ort) plt.title("Figure P3\n Raincloud Without Jitter") if savefigs: plt.savefig('.\\figs\\tutorial_python\\figureP03.png', bbox_inches='tight')- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
# adding jitter to the rain f, ax =plt.subplots(figsize=(7, 5)) ax=pt.half_violinplot(x=dx, y=dy, data=df, palette=pal, bw=.2, cut=0., scale="area", width=.6, inner=None, orient=ort) ax=sns.stripplot(x=dx, y=dy, data=df, palette=pal, edgecolor="white", size=3, jitter=1, zorder=0, orient=ort) plt.title("Figure P4\n Raincloud with Jittered Data") if savefigs: plt.savefig('.\\figs\\tutorial_python\\figureP04.png', bbox_inches='tight')- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7

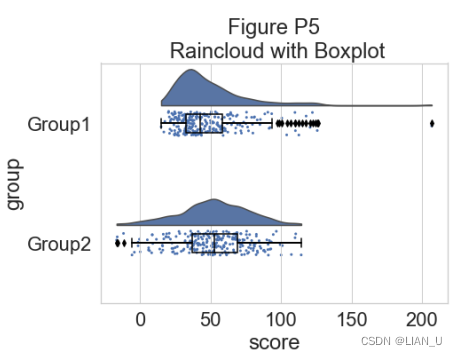
这样可以很好地了解数据点的分布情况,但中位数和四分位数并不明显,很难一目了然地确定统计差异。 因此,我们添加了一个“空”箱线图来显示中位数、四分位数和异常值:#adding the boxplot with quartiles f, ax=plt.subplots(figsize=(7, 5)) ax=pt.half_violinplot(x=dx, y=dy, data=df, palette=pal, bw=.2, cut=0., scale="area", width=.6, inner=None, orient=ort) ax=sns.stripplot(x=dx, y=dy, data=df, palette=pal, edgecolor="white", size=3, jitter=1, zorder=0, orient=ort) ax=sns.boxplot(x=dx, y=dy, data=df, color="black", width=.15, zorder=10, showcaps=True, boxprops={'facecolor':'none',"zorder":10}, showfliers=True, whiskerprops{'linewidth':2,"zorder":10}, saturation=1, orient=ort) plt.title("Figure P5\n Raincloud with Boxplot") if savefigs: plt.savefig('../figs/tutorial_python/figureP05.png', bbox_inches='tight')- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
现在我们可以设置一个调色板来表征两组:#adding color pal="Set2" f, ax=plt.subplots(figsize=(7, 5)) ax=pt.half_violinplot(x=dx, y=dy, data=df, palette=pal, bw=.2, cut=0., scale="area", width=.6, inner=None, orient=ort) ax=sns.stripplot(x=dx, y=dy, data=df, palette=pal, edgecolor="white", size=3, jitter=1, zorder=0, orient=ort) ax=sns.boxplot(x=dx, y=dy, data=df, color="black", width=.15, zorder=10, showcaps=True, boxprops={'facecolor':'none',"zorder":10}, showfliers=True, whiskerprops={'linewidth':2,"zorder":10}, saturation=1, orient=ort) plt.title("Figure P6\n Tweaking the Colour of Your Raincloud")- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12

我们可以使用函数 pt.Raincloud 来添加一些自动化:#same thing with a single command: now x **must** be the categorical value dx="group"; dy="score"; ort="h"; pal="Set2"; sigma=.2 f, ax=plt.subplots(figsize=(7, 5)) pt.RainCloud(x=dx, y=dy, data=df, palette=pal, bw=sigma, width_viol = .6, ax = ax, orient = ort) plt.title("Figure P7\n Using the pt.Raincloud function") if savefigs: plt.savefig('../figs/tutorial_python/figureP07.png', bbox_inches='tight')- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8

‘move’ 参数可用于移动箱线图下方的雨量,在某些情况下提供更好的原始数据可见性:#moving the rain below the boxplot dx="group"; dy="score"; ort="h"; pal="Set2"; sigma=.2 f,ax=plt.subplots(figsize=(7, 5)) ax=pt.RainCloud(x=dx, y=dy, data=df, palette=pal, bw=sigma, width_viol=.6, ax=ax, orient=ort, move=.2) plt.title("Figure P8\n Rainclouds with Shifted Rain")- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6

此外,raincloud 函数同样适用于列表或 np.array,如果您更喜欢使用它们而不是数据框输入:# Usage with a list/np.array input dx=list(df["group"]); dy=list(df["score"]) f, ax=plt.subplots(figsize=(7, 5)) ax=pt.RainCloud(x=dx, y=dy, palette=pal, bw=sigma, width_viol=.6, ax=ax, orient=ort) plt.title("Figure P9\n Rainclouds with List/Array Inputs")- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6

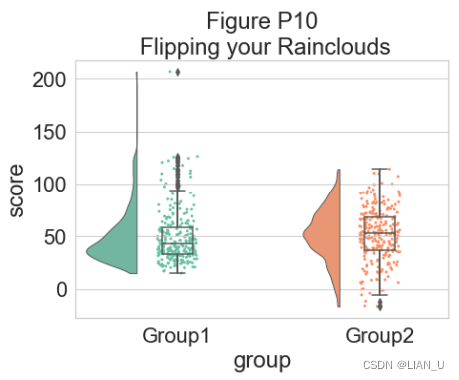
对于某些数据,您可能希望将雨云的方向翻转为“petit prince”图。 您可以使用 pt.RainCloud 函数中的 ‘orient’ 标志来执行此操作:# Changing orientation dx="group"; dy="score"; ort="v"; pal="Set2"; sigma=.2 f, ax=plt.subplots(figsize=(7, 5)) ax=pt.RainCloud(x=dx, y=dy, data=df, palette=pal, bw=sigma, width_viol=.5, ax=ax, orient=ort) plt.title("Figure P10\n Flipping your Rainclouds")- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
您还可以更改用于生成数据概率分布函数的平滑核。 为此,您调整 sigma 参数:#changing cloud smoothness dx="group"; dy="score"; ort="h"; pal="Set2"; sigma=.05 f, ax=plt.subplots(figsize=(7, 5)) ax=pt.RainCloud(x=dx, y=dy, data=df, palette=pal, bw=sigma, width_viol=.6, ax=ax, orient=ort) plt.title("Figure P11\n Customizing Raincloud Smoothness")- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6

最后,使用 pointplot 标志,您可以添加一条连接组平均值的线。 这对于更复杂的数据集很有用,例如重复测量或因子数据。 下面我们通过改变各个图的色调、不透明度或闪避元素来说明使用雨云绘制此类数据的几种不同方法:#adding a red line connecting the groups' mean value (useful for longitudinal data) dx="group"; dy="score"; ort="h"; pal="Set2"; sigma=.2 f, ax=plt.subplots(figsize=(7, 5)) ax=pt.RainCloud(x=dx, y=dy, data=df, palette=pal, bw=sigma, width_viol=.6, ax=ax, orient=ort, pointplot=True) plt.title("Figure P12\n Adding Lineplots to Emphasize Factorial Effects")- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6

另一个灵活的选择是使用 Facet Grids 来分隔不同的组或因子水平,如下所示:# Rainclouds with FacetGrid g=sns.FacetGrid(df, col="gr2", height=6) g=g.map_dataframe(pt.RainCloud, x="group", y="score", data=df, orient="h") g.fig.subplots_adjust(top=0.75) g.fig.suptitle("Figure P13\n Using FacetGrid for More Complex Designs", fontsize=26)- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5

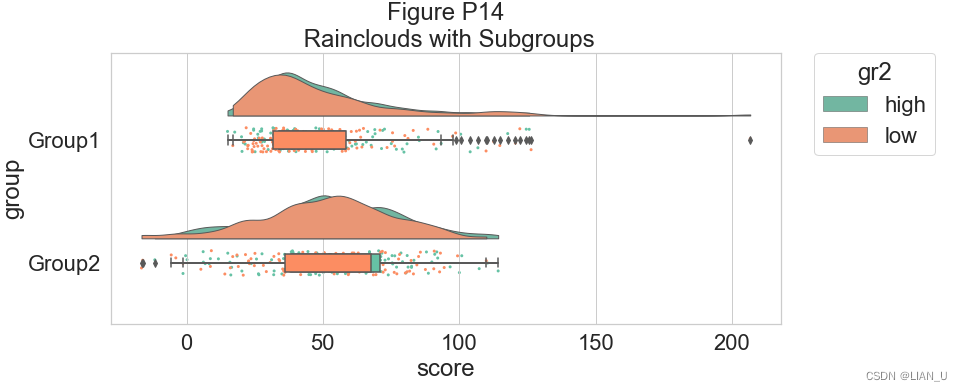
作为一种替代方法,可以使用色调输入将不同的子组直接绘制在彼此之上,从而促进它们的比较:# Hue Input for Subgroups dx="group"; dy="score"; dhue="gr2"; ort="h"; pal="Set2"; sigma=.2 f, ax=plt.subplots(figsize=(12, 5)) ax=pt.RainCloud(x=dx, y=dy, hue=dhue, data=df, palette=pal, bw=sigma, width_viol=.7, ax=ax, orient=ort) plt.title("Figure P14\n Rainclouds with Subgroups")- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
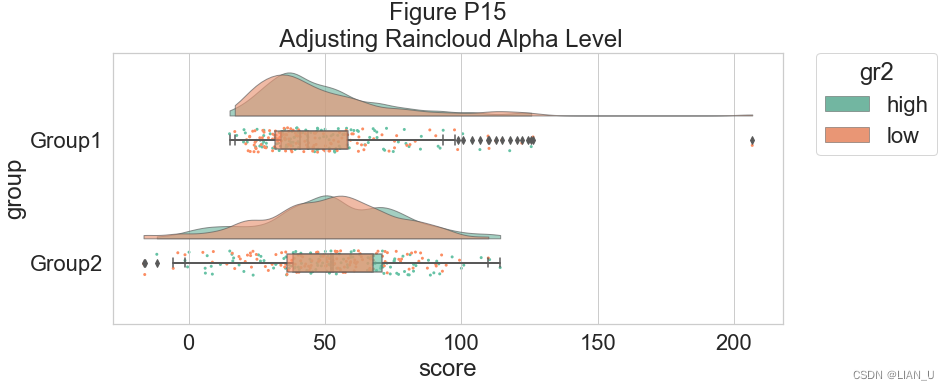
为了提高该图的可读性,我们使用相关标志(0-1 alpha 强度)调整 alpha 级别:# Setting alpha level f, ax=plt.subplots(figsize=(12, 5)) ax=pt.RainCloud(x=dx, y=dy, hue=dhue, data=df, palette=pal, bw=sigma, width_viol=.7, ax=ax, orient=ort , alpha=.65) plt.title("Figure P15\n Adjusting Raincloud Alpha Level")- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
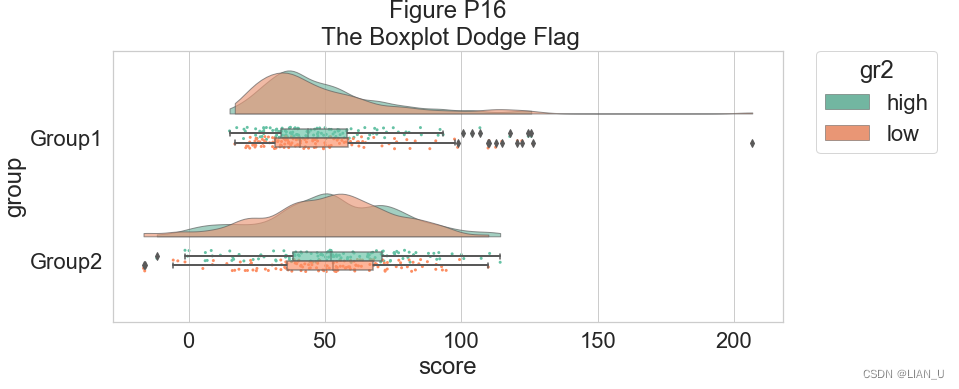
我们可以将 dodge 标志设置为 true,而不是让两个箱线图相互混淆,从而增加交互性:#The Doge Flag f, ax=plt.subplots(figsize=(12, 5)) ax=pt.RainCloud(x=dx, y=dy, hue=dhue, data=df, palette=pal, bw=sigma, width_viol=.7, ax=ax, orient=ort , alpha=.65, dodge=True) plt.title("Figure P16\n The Boxplot Dodge Flag")- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
最后,我们可能希望在我们的图表中添加一个传统的线图,以帮助检测因子主效应和交互作用。 例如,我们在每个箱线图中绘制了平均值:#same, with dodging and line f, ax=plt.subplots(figsize=(12, 5)) ax=pt.RainCloud(x=dx, y=dy, hue=dhue, data=df, palette=pal, bw=sigma, width_viol=.7, ax=ax, orient=ort , alpha=.65, dodge=True, pointplot=True) plt.title("Figure P17\n Dodged Boxplots with Lineplots")- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6

这是相同的图,但现在使用“移动”参数再次将单个观测值移动到箱线图下方:#moving the rain under the boxplot f, ax=plt.subplots(figsize=(12, 5)) ax=pt.RainCloud(x=dx, y=dy, hue=dhue, data=df, palette=pal, bw=sigma, width_viol=.7, ax=ax, orient=ort , alpha=.65, dodge=True, pointplot=True, move=.2) plt.title("Figure P18\n Shifting the Rain with the Move Parameter")- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6

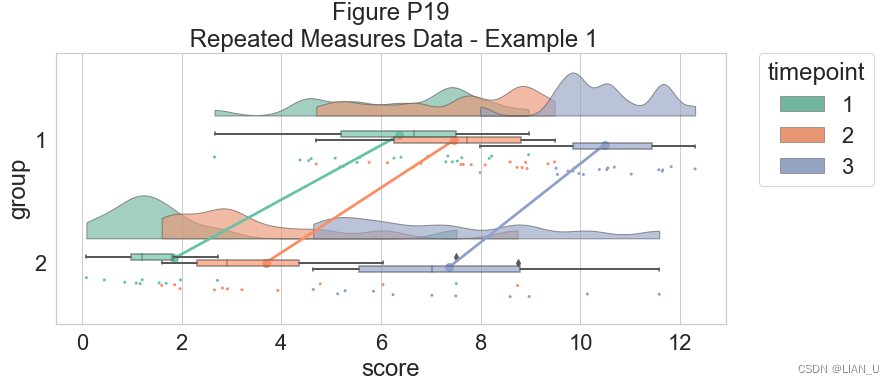
作为我们的最后一个示例,我们将考虑具有两组和三个时间点的复杂重复测量设计。 目标是说明我们复杂的相互作用和主要影响,同时保持雨云图的透明性:# Load in the repeated data df_rep=pd.read_csv("repeated_measures_data.csv", sep=",") df_rep.columns=["score", "timepoint", "group"] df_rep.head()- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4

# Plot the repeated measures data dx="group"; dy="score"; dhue="timepoint"; ort="h"; pal="Set2"; sigma=.2 f, ax=plt.subplots(figsize=(12, 5)) ax=pt.RainCloud(x=dx, y=dy, hue=dhue, data=df_rep, palette=pal, bw=sigma, width_viol=.7, ax=ax, orient=ort , alpha=.65, dodge=True, pointplot=True, move=.2) plt.title("Figure P19\n Repeated Measures Data - Example 1")- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
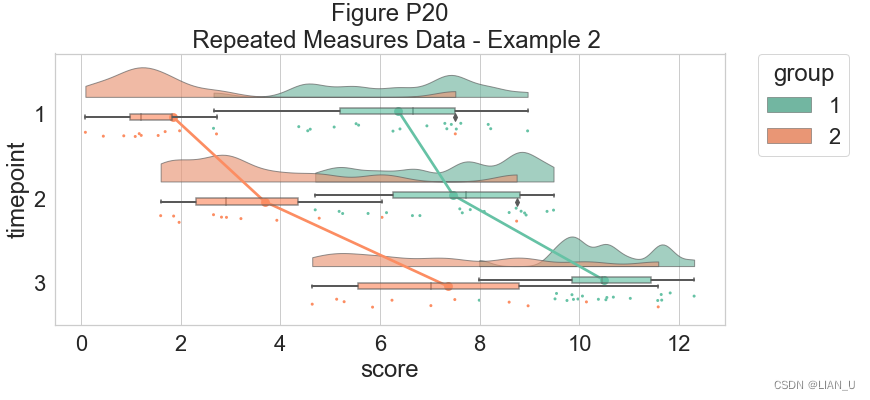
# Now with the group as hue dx="timepoint"; dy="score"; dhue="group" f, ax=plt.subplots(figsize=(12, 5)) ax=pt.RainCloud(x=dx, y=dy, hue=dhue, data=df_rep, palette=pal, bw=sigma, width_viol=.7, ax=ax, orient=ort , alpha=.65, dodge=True, pointplot=True, move=.2) plt.title("Figure P20\n Repeated Measures Data - Example 2")- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
-
相关阅读:
推荐系统中的特征工程
站长热议:百家号是如何挂外部超链接的?
企业信息化与电子商务>供应链信息流
微服务系列之分布式日志 ELK
小李移动开发成长记 —— 大话小程序
【pygame游戏】用Python实现一个蔡徐坤大战篮球的小游戏,可还行?【附源码】
VTK——模拟深度相机拍摄深度图
GuavaCache、EVCache、Tair、Aerospike 缓存框架比较
搭建直播带货源码,商品带货销售不止直播一种方式
XML解析
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_43779943/article/details/126133122