-
人工智能框架实战精讲:Keras项目-英文语料的文本分类实战与调参优化
Keras项目-英文语料的文本分类实战
一、机器学习模型
1.1 数据简介
读取数据,本次使用的数据集是英文数据集。
都是已经标注好的情感2分类数据集,1为积极,0为消极。

三个数据集都存在data文件夹下,需要遍历文件夹取得相应数据集
1.2 数据读取与预处理
将文本读取进来
import pandas as pd """ 数据读取,其中0表示消极,1表示积极 """ filepath_dict = {'yelp': 'data/yelp_labelled.txt', 'amazon': 'data/amazon_cells_labelled.txt', 'imdb': 'data/imdb_labelled.txt'} df_list = [] for source, filepath in filepath_dict.items(): df = pd.read_csv(filepath, names=['sentence', 'label'], sep='\t') df['source'] = source df_list.append(df) df = pd.concat(df_list) print(df.head())- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
sentence label source 0 Wow... Loved this place. 1 yelp 1 Crust is not good. 0 yelp 2 Not tasty and the texture was just nasty. 0 yelp 3 Stopped by during the late May bank holiday of... 1 yelp 4 The selection on the menu was great and so wer... 1 yelp- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
读取数据之后,需要将数据转化为对应的向量,计算机是不识别文字,只认识数字,所以需要将文字转化为对应的数字,计算机才能进行计算。
最为传统的将文字转为数字的模型就是池袋模型,本文先使用池袋模型对文字进行编码
假设有这么2段话:sentences = ['John likes ice cream, ‘John hates chocolate.’]
vectorizer.vocabulary_就是将文字转为数字位置编码
vectorizer.transform(sentences).toarray() 转为对应池袋模型的ndarray矩阵
可以看出出现的词为1,不出现为0,出现一次加1""" 文本数据特征 """ sentences = ['John likes ice cream cream', 'John hates chocolate chocolate.'] from sklearn.feature_extraction.text import CountVectorizer vectorizer = CountVectorizer(min_df=0, lowercase=False) vectorizer.fit(sentences) print (vectorizer.vocabulary_) print (vectorizer.transform(sentences).toarray())- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
{'John': 0, 'likes': 5, 'ice': 4, 'cream': 2, 'hates': 3, 'chocolate': 1} [[1 0 2 0 1 1] [1 2 0 1 0 0]]- 1
- 2
- 3
可以通过池袋模型对文本特征进行最简单的特征提取,将每一个文本都转为了对应的向量
1.3 数据切分与逻辑回归模型构建
先将数据集按照测试集与验证集,按照一定比例切分,设定好随机种子的值,以便于查看调参的结果。
先使用一个数据集进行实验
""" 数据集切分 """ from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split df_yelp = df[df['source'] == 'yelp'] sentences = df_yelp['sentence'].values y = df_yelp['label'].values sentences_train, sentences_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(sentences, y, test_size=0.25, random_state=1000)- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
划分好数据集后,需要将文本特征转化为向量特征,就按照上文介绍的池袋模型,将文本向量化
""" 特征制作 """ from sklearn.feature_extraction.text import CountVectorizer vectorizer = CountVectorizer() vectorizer.fit(sentences_train) X_train = vectorizer.transform(sentences_train) X_test = vectorizer.transform(sentences_test)- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
制作好数据输出后,就可以输出给模型进行学习,模型训练效果的好坏很大一部分取决于数据特征的处理。本次实验以机器学习的逻辑回归模型作为基础模型,来对比深度学习模型效果
""" 基础模型 """ from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression classifier = LogisticRegression() classifier.fit(X_train, y_train) score = classifier.score(X_test, y_test) print("Accuracy:", score)- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
Accuracy: 0.796
综合对比三分数据集的实验结果
""" 综合对比3份数据 """ for source in df['source'].unique(): df_source = df[df['source'] == source] sentences = df_source['sentence'].values y = df_source['label'].values sentences_train, sentences_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split( sentences, y, test_size=0.25, random_state=1000) vectorizer = CountVectorizer() vectorizer.fit(sentences_train) X_train = vectorizer.transform(sentences_train) X_test = vectorizer.transform(sentences_test) classifier = LogisticRegression() classifier.fit(X_train, y_train) score = classifier.score(X_test, y_test) print('Accuracy for {} data: {:.4f}'.format(source, score))- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
Accuracy for yelp data: 0.7960
Accuracy for amazon data: 0.7960
Accuracy for imdb data: 0.7487逻辑回归模型的训练结果的准确率大概都在80%左右。
二、全连接神经网络模型
2.1 模型训练
上文通过池袋模型特征学习得到的文本特征,有一个缺点,那就是特别的稀疏,大部分的数据都是0。
在sklearn中对于这么稀疏的数据,在表述的时候为节省内存,就会用位置信息记录有数值的信息。比如(254,1)就代表在254列这个位置的值为1。
而深度学习模型,keras并不支持之种的表达格式,因为深度学习网络每一层输出的数据应该维度都是相同的,需要正常的向量格式。
所以需要将X_train,X_test做一个转换
定义神经网络输出的维度input_dim是多少,就是等于每一条X的维度
网络定义比较简单,第一层就得到10特征,第二层就得到1个结果。
""" 神经网络模型 """ from keras.models import Sequential from keras import layers # 稀疏矩阵转换 X_train = X_train.toarray() #标准数据 X_test = X_test.toarray() #定义神经网络输出的维度是多少,就是每一条X的维度 input_dim = X_train.shape[1] # Number of features #--------------------------------------定义网络----------------------- model = Sequential() #结构 model.add(layers.Dense(10, input_dim=input_dim, activation='relu')) #表示处于0,1的概念 model.add(layers.Dense(1, activation='sigmoid')) #模型优化 model.compile(loss='binary_crossentropy', optimizer='adam', metrics=['accuracy']) model.summary() #训练 history = model.fit(X_train, y_train, epochs=100, verbose=False, #不打印训练结果 validation_data=(X_test, y_test), batch_size=10) #性能好可以设置大一点,效果可能会更好 #------------------------模型评估--------------------------- #保存loss和accurary loss, accuracy = model.evaluate(X_train, y_train, verbose=False) print("Training Accuracy: {:.4f}".format(accuracy)) loss, accuracy = model.evaluate(X_test, y_test, verbose=False) print("Testing Accuracy: {:.4f}".format(accuracy))- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
可以看出网络有点过拟合了
Model: "sequential_1" _________________________________________________________________ Layer (type) Output Shape Param # ================================================================= dense_1 (Dense) (None, 10) 25060 _________________________________________________________________ dense_2 (Dense) (None, 1) 11 ================================================================= Total params: 25,071 Trainable params: 25,071 Non-trainable params: 0 _________________________________________________________________ Training Accuracy: 1.0000 Testing Accuracy: 0.7914- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
2.2 模型结果展示
定义一个画图函数,用来查看模型训练过程
""" 结果展示 """ import matplotlib.pyplot as plt plt.style.use('ggplot') def plot_history(history,name): acc = history.history['accuracy'] val_acc = history.history['val_accuracy'] loss = history.history['loss'] val_loss = history.history['val_loss'] x = range(1, len(acc) + 1) plt.figure(figsize=(12, 5)) plt.subplot(1, 2, 1) plt.plot(x, acc, 'b', label='Training acc') plt.plot(x, val_acc, 'r', label='Validation acc') plt.title('Training and validation accuracy') plt.legend() plt.subplot(1, 2, 2) plt.plot(x, loss, 'b', label='Training loss') plt.plot(x, val_loss, 'r', label='Validation loss') plt.title('Training and validation loss') plt.legend() #plt.show() plt.savefig(str(name)+'.png') plot_history(history,name='base_nn')- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
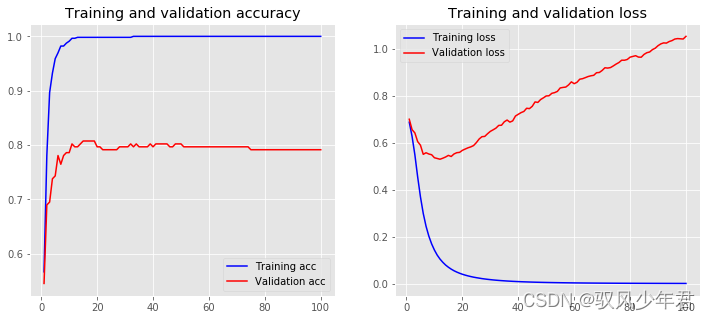
模型只是初步的模型,并未调优。
三、WordEmebeding-全连接神经网络
3.1数据序列化
刚才的深度学习网络,还存在一些问题,首先,池袋模型的特征表达效果有限。
其次,刚才是以一句话作为整体,细粒度上还不够,并未深入探讨词的贡献程度,词之间的相互关系。
所以,引入需要对刚才的全连接网络进行升级一下,考虑一下词之间的关系。
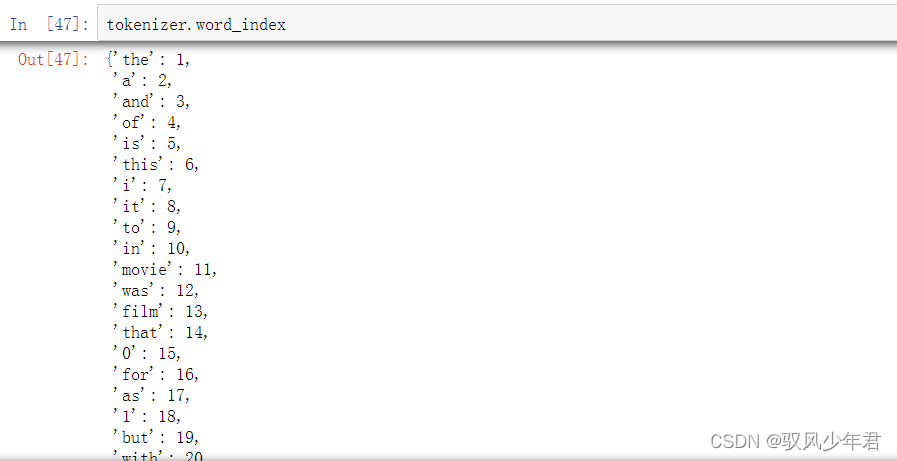
用Keras中的Tokenizer将词转换为相应的索引
vocab_size 代表语料库的大小,一般都需要进行加1操作,可能是由于从0开始计数的原因。vocab_size 通过训练过后的tokenizer.word_index的长度获取,就是语料库中有多少个不重复的单词。
""" Word Embeddings """ from keras.preprocessing.text import Tokenizer tokenizer = Tokenizer(num_words=5000) tokenizer.fit_on_texts(sentences_train) #将词转为索引 X_train = tokenizer.texts_to_sequences(sentences_train) X_test = tokenizer.texts_to_sequences(sentences_test) vocab_size = len(tokenizer.word_index) + 1 # Adding 1 because of reserved 0 index print(sentences_train[2]) print(X_train[2])- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
I am a fan of his ... This movie sucked really bad. [7, 150, 2, 932, 4, 49, 6, 11, 563, 45, 30]- 1
- 2
将文本转为相应的词的索引之后,还存在一个问题,那就是每个文本的长度都不一样,而深度学习网络需要每个文本的长度都是一致的,所以还需要对文本进行长度一致的标准化。
最简单的就是统计语料中文本的普遍长度是多少,本文设置为30,太长的就切割,太短的就填充0
""" 补齐 """ from keras.preprocessing.sequence import pad_sequences maxlen = 30 X_train = pad_sequences(X_train, padding='post', maxlen=maxlen) X_test = pad_sequences(X_test, padding='post', maxlen=maxlen) print(X_train[0, :])- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
[170 116 390 35 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0]3.2 Embedding Layer Model
input_dim,一般就是语料库中不重复单词的大小
output_dim,就是文本映射成多少维度的向量,自己定义将每个词映射成多少维
keras.layers.Embedding(input_dim, output_dim, embeddings_initializer=‘uniform’, embeddings_regularizer=None, activity_regularizer=None, embeddings_constraint=None, mask_zero=False, input_length=None)- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
input_dim: int > 0。词汇表大小, 即,最大整数 index + 1。
output_dim: int >= 0。词向量的维度。在keras中,数据是以张量的形式表示的,张量的形状称之为shape,表示从最外层向量逐步到达最底层向量的降维解包过程。比如,一个一阶的张量[1,2,3]的shape是(3,);
一个二阶的张量[[1,2,3],[4,5,6]]的shape是(2,3);一个三阶的张量[[[1],[2],[3]],[[4],[5],[6]]]的shape是(2,3,1)。input_shape就是指输入张量的shape。例如,input_dim=784,说明输入是一个784维的向量,这相当于一个一阶的张量,它的shape就是(784,)。因此,input_shape=(784,)。
input_dim = input_shape(input_dim,)
input_dim, input_length = input_shape(input_length, input_dim)
通俗来说,input_length就是输入数据的长度,Input_dim就是数据的维度。比如一条数据内容是: “人人车” , one hot编码后是 [[1 0] [1 0] [0 1]]表示 ,则 batch_size = 3, input_dim = 2.
""" Embedding Layer """ from keras.models import Sequential from keras import layers embedding_dim = 50 model = Sequential() model.add(layers.Embedding(input_dim=vocab_size, #输入为语料库的大小再+1 output_dim=embedding_dim, #将其 input_length=maxlen)) model.add(layers.Flatten()) model.add(layers.Dense(10, activation='relu')) model.add(layers.Dense(1, activation='sigmoid')) model.compile(optimizer='adam', loss='binary_crossentropy', metrics=['accuracy']) model.summary()- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
其中embedding_1 (Embedding) (None, 30, 50) :
None就是预料文本的有多少个,一般不做定义。30代表每条文本有多少个词,我们上面定义了30个词,50代表每个词训练层50维。
embedding_1 (Embedding) (None, 30, 50) 是一个3维的,全连接是一个2维的特征提取,所以需要将3维的转化为2维度的数据。可以将每个词向量进行拼接拉长,转化为2维度的向量。如下所示
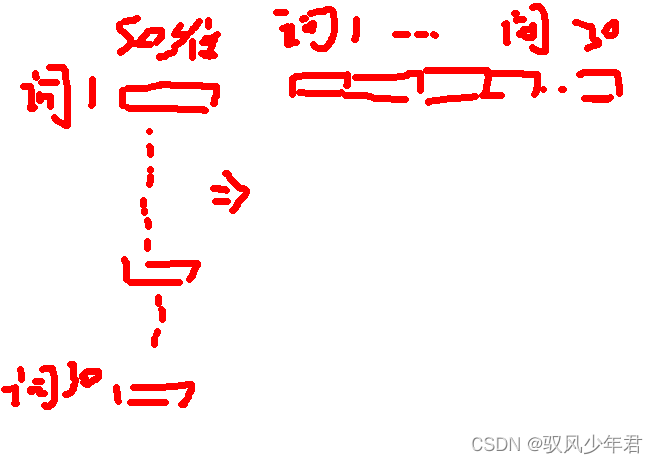
拉长后,就变成30*50=1500了
Model: "sequential_2" _________________________________________________________________ Layer (type) Output Shape Param # ================================================================= embedding_1 (Embedding) (None, 30, 50) 128750 _________________________________________________________________ flatten_1 (Flatten) (None, 1500) 0 _________________________________________________________________ dense_3 (Dense) (None, 10) 15010 _________________________________________________________________ dense_4 (Dense) (None, 1) 11 ================================================================= Total params: 143,771 Trainable params: 143,771 Non-trainable params: 0- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
模型训练
""" 重新训练 """ history = model.fit(X_train, y_train, epochs=20, verbose=False, validation_data=(X_test, y_test), batch_size=10) loss, accuracy = model.evaluate(X_train, y_train, verbose=False) print("Training Accuracy: {:.4f}".format(accuracy)) loss, accuracy = model.evaluate(X_test, y_test, verbose=False) print("Testing Accuracy: {:.4f}".format(accuracy)) plot_history(history,name='base_Embedding Layer')- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
Training Accuracy: 1.0000
Testing Accuracy: 0.6203
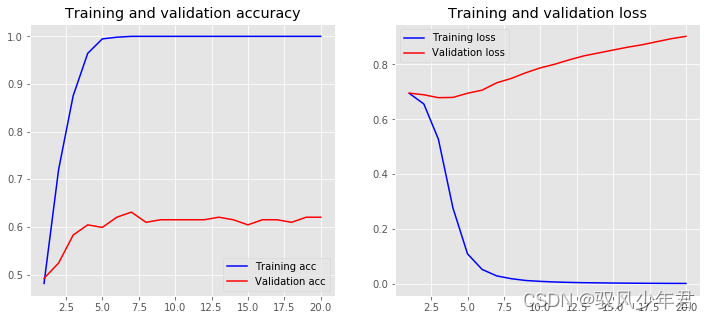
发现模型性能结果还不如机器学习,还未进行调优
3.3 特征提取
上文的方法将词进行叠在一起,导致词的特征太多,学习起来效果还不如原来的模型。所以还需要一个特征提取的方法。
用了一个全局特征提取GlobalMaxPool1D(),这是一个1维的maxpooling,将每一列找最大的,就pooling成1个值。所以(30,50)就变成了(,50)了
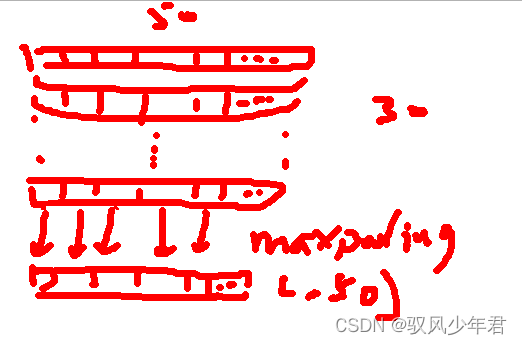
再接入全连接层""" pooling特征压缩 """ from keras.models import Sequential from keras import layers embedding_dim = 50 model = Sequential() model.add(layers.Embedding(input_dim=vocab_size, output_dim=embedding_dim, input_length=maxlen)) model.add(layers.GlobalMaxPool1D()) model.add(layers.Dense(10, activation='relu')) model.add(layers.Dense(1, activation='sigmoid')) model.compile(optimizer='adam', loss='binary_crossentropy', metrics=['accuracy']) model.summary() history = model.fit(X_train, y_train, epochs=50, verbose=False, validation_data=(X_test, y_test), batch_size=10) loss, accuracy = model.evaluate(X_train, y_train, verbose=False) print("Training Accuracy: {:.4f}".format(accuracy)) loss, accuracy = model.evaluate(X_test, y_test, verbose=False) print("Testing Accuracy: {:.4f}".format(accuracy)) plot_history(history,name='pooling')- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
Model: "sequential_3" _________________________________________________________________ Layer (type) Output Shape Param # ================================================================= embedding_2 (Embedding) (None, 30, 50) 128750 _________________________________________________________________ global_max_pooling1d_1 (Glob (None, 50) 0 _________________________________________________________________ dense_5 (Dense) (None, 10) 510 _________________________________________________________________ dense_6 (Dense) (None, 1) 11 ================================================================= Total params: 129,271 Trainable params: 129,271 Non-trainable params: 0 _________________________________________________________________ D:\Anaconda3\envs\tf3\lib\site-packages\tensorflow_core\python\framework\indexed_slices.py:424: UserWarning: Converting sparse IndexedSlices to a dense Tensor of unknown shape. This may consume a large amount of memory. "Converting sparse IndexedSlices to a dense Tensor of unknown shape. " Training Accuracy: 1.0000 Testing Accuracy: 0.7647- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
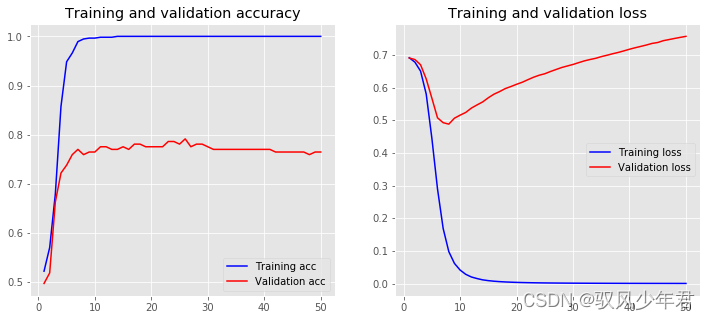
四、Word2Vec-全连接神经网络
4.1获取每个词的词向量
对于上文的word2beding是被认为定义成50维的,每条文本都被训练层30*50的文本向量表达,但是这个50是我们自己人为随机定义的,然后交给网络去训练,在训练过程中实现对每个词向量表达的调整。
但是这个有个问题,我们不知道网络训练的词向量的效果到底如何,不知道是否50维度就可以很好的表达出每个词在上下文中的含义。
所以我们可以预先用别人训练好的词向量模型,获取到每个词的向量的最佳表达,来提升模型的性能。
读取本地的glove词向量模型,来读取每个词的词向量,需要传入词向量位置,词编码字典tokenizer.word_index,词向量维度embedding_dim,本地的词向量是多少维度的embedding_dim就定义为多少维。
需要那些词,就取出那些词,预先构造一个都是0的embedding_matrix,将每个词的向量都按tokenizer.word_index顺序的填充进去。
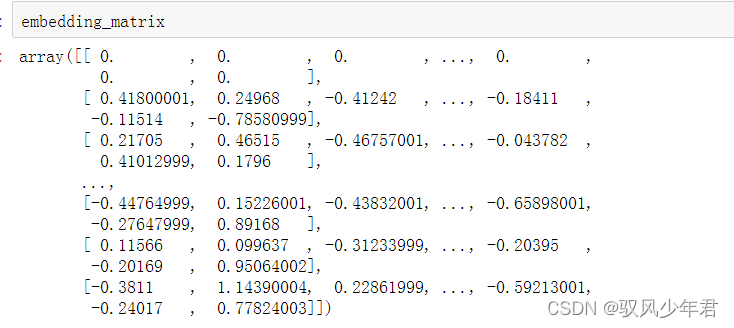
""" 词向量模型 """ import numpy as np #过滤无关词语 def create_embedding_matrix(filepath, word_index, embedding_dim): vocab_size = len(word_index) + 1 # keras文档中指定需要+1 embedding_matrix = np.zeros((vocab_size, embedding_dim)) with open(filepath,encoding='utf-8') as f: for line in f: word, *vector = line.split() if word in word_index: idx = word_index[word] embedding_matrix[idx] = np.array( vector, dtype=np.float32)[:embedding_dim] return embedding_matrix embedding_dim = 50 embedding_matrix = create_embedding_matrix('data/glove.6B.50d.txt',tokenizer.word_index, embedding_dim)- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
4.2 模型训练
和上面的模型训练差不多,修改了两个参数weights=[embedding_matrix],trainable=False。embedding_matrix是传入相应的词向量模型,trainable=False表示是否对传入的词向量再次进行训练。
""" 重新训练 """ model = Sequential() model.add(layers.Embedding(vocab_size, embedding_dim, weights=[embedding_matrix], input_length=maxlen, trainable=False)) model.add(layers.GlobalMaxPool1D()) model.add(layers.Dense(10, activation='relu')) model.add(layers.Dense(1, activation='sigmoid')) model.compile(optimizer='adam', loss='binary_crossentropy', metrics=['accuracy']) model.summary() history = model.fit(X_train, y_train, epochs=50, verbose=False, validation_data=(X_test, y_test), batch_size=10) loss, accuracy = model.evaluate(X_train, y_train, verbose=False) print("Training Accuracy: {:.4f}".format(accuracy)) loss, accuracy = model.evaluate(X_test, y_test, verbose=False) print("Testing Accuracy: {:.4f}".format(accuracy)) plot_history(history,name='wordvec')- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
Model: "sequential_4" _________________________________________________________________ Layer (type) Output Shape Param # ================================================================= embedding_3 (Embedding) (None, 30, 50) 128750 _________________________________________________________________ global_max_pooling1d_2 (Glob (None, 50) 0 _________________________________________________________________ dense_7 (Dense) (None, 10) 510 _________________________________________________________________ dense_8 (Dense) (None, 1) 11 ================================================================= Total params: 129,271 Trainable params: 521 Non-trainable params: 128,750 _________________________________________________________________ Training Accuracy: 0.7914 Testing Accuracy: 0.7380- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
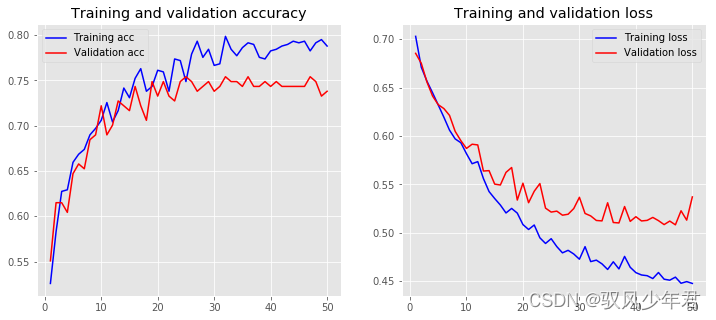
训练次数还不够,模型还没到一个拟合的状态
4.3 继续训练词向量
别人训练的词向量模型,可以是基于通用的任务,对于当前任务的适用性可能还不高,可以自己在别人训练的基础上,继续进行训练,更加适合自己领域下的词向量模型。
将trainable=True就行
""" 训练Embedding Layer """ model = Sequential() model.add(layers.Embedding(vocab_size, embedding_dim, weights=[embedding_matrix], input_length=maxlen, trainable=True)) model.add(layers.GlobalMaxPool1D()) model.add(layers.Dense(10, activation='relu')) model.add(layers.Dense(1, activation='sigmoid')) model.compile(optimizer='adam', loss='binary_crossentropy', metrics=['accuracy']) model.summary() history = model.fit(X_train, y_train, epochs=50, verbose=False, validation_data=(X_test, y_test), batch_size=10) loss, accuracy = model.evaluate(X_train, y_train, verbose=False) print("Training Accuracy: {:.4f}".format(accuracy)) loss, accuracy = model.evaluate(X_test, y_test, verbose=False) print("Testing Accuracy: {:.4f}".format(accuracy)) plot_history(history,name='wordvec_train=True')- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
Model: "sequential_4" _________________________________________________________________ Layer (type) Output Shape Param # ================================================================= embedding_3 (Embedding) (None, 30, 50) 128750 _________________________________________________________________ global_max_pooling1d_2 (Glob (None, 50) 0 _________________________________________________________________ dense_7 (Dense) (None, 10) 510 _________________________________________________________________ dense_8 (Dense) (None, 1) 11 ================================================================= Total params: 129,271 Trainable params: 521 Non-trainable params: 128,750 _________________________________________________________________ Training Accuracy: 0.7914 Testing Accuracy: 0.7380- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18

继续学习,有过拟合风险,还未加入drop层;结构可能越来越好,也可能越来约差。
五、LSTM文本分类模型
LSTM是按个对每个词向量进行计算,需要传入序列的数字,所以不需要Pooling。
用LSTM代替GlobalMaxPool1D来提取特征。
下面的LSTM中是第二层,所以不需要定义Input-dim,直接定义先得到多少个输出特征。
其中return_sequences=False,表示只要最后一个结果y30,return_sequences=True,表示也需要中间结果,那就是y1-y30。
如果后面再连接一个LSTM,就需要设置为True
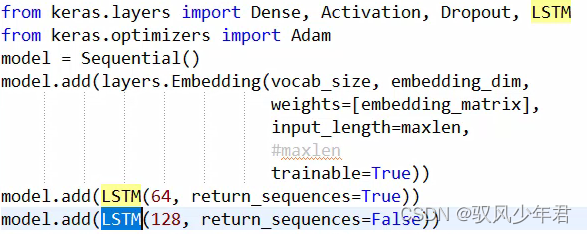
""" LSTM模型 """ from keras.layers import Dense, Activation, Dropout, LSTM from keras.optimizers import Adam model = Sequential() model.add(layers.Embedding(vocab_size, embedding_dim, weights=[embedding_matrix], input_length=maxlen, #maxlen trainable=True)) model.add(LSTM(64, return_sequences=False)) model.add(layers.Dense(10, activation='relu')) model.add(layers.Dense(1, activation='sigmoid')) opt = Adam(lr=0.001) model.compile(optimizer=opt, loss='binary_crossentropy', metrics=['accuracy']) model.summary() history = model.fit(X_train, y_train, epochs=50, validation_data=(X_test, y_test), batch_size=64) loss, accuracy = model.evaluate(X_train, y_train, verbose=False) print("Training Accuracy: {:.4f}".format(accuracy)) loss, accuracy = model.evaluate(X_test, y_test, verbose=False) print("Testing Accuracy: {:.4f}".format(accuracy)) plot_history(history,name='LSTM')- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
GlobalMaxPool1D来提取特征
Model: "sequential_6" _________________________________________________________________ Layer (type) Output Shape Param # ================================================================= embedding_5 (Embedding) (None, 30, 50) 128750 _________________________________________________________________ lstm_1 (LSTM) (None, 64) 29440 _________________________________________________________________ dense_11 (Dense) (None, 10) 650 _________________________________________________________________ dense_12 (Dense) (None, 1) 11 ================================================================= Total params: 158,851 Trainable params: 158,851 Non-trainable params: 0 _________________________________________________________________- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
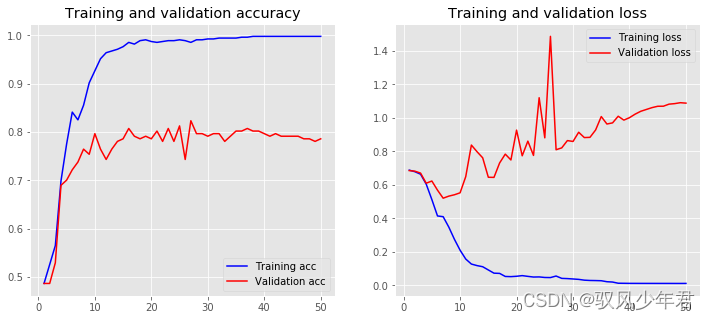
Epoch 50/50
561/561 [==============================] - 0s 248us/step - loss: 0.0120 - accuracy: 0.9982 - val_loss: 1.0881 - val_accuracy: 0.7861
Training Accuracy: 0.9982
Testing Accuracy: 0.7861
六、CNN文本分类模型
用卷积神经网络来提取文本数据
其中设置layers.Conv1D(128, 5, activation=‘relu’),一维的卷积核。
128表示用不同的128卷积特征图去卷积文本向量,所以每个卷积核对得到1个特征图
1维5表示卷积核的长度,原本长度为30的词的向量,卷积后变成30-5+1=26个。
""" CNN模型 """ embedding_dim = 50 model = Sequential() model.add(layers.Embedding(vocab_size, embedding_dim, input_length=maxlen)) model.add(layers.Conv1D(128, 5, activation='relu')) model.add(layers.GlobalMaxPooling1D()) model.add(layers.Dense(10, activation='relu')) model.add(layers.Dense(1, activation='sigmoid')) model.compile(optimizer='adam', loss='binary_crossentropy', metrics=['accuracy']) model.summary() history = model.fit(X_train, y_train, epochs=10, verbose=True, validation_data=(X_test, y_test), batch_size=10) loss, accuracy = model.evaluate(X_train, y_train, verbose=False) print("Training Accuracy: {:.4f}".format(accuracy)) loss, accuracy = model.evaluate(X_test, y_test, verbose=False) print("Testing Accuracy: {:.4f}".format(accuracy)) plot_history(history,name='CNN')- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
Model: "sequential_7" _________________________________________________________________ Layer (type) Output Shape Param # ================================================================= embedding_6 (Embedding) (None, 30, 50) 128750 _________________________________________________________________ conv1d_1 (Conv1D) (None, 26, 128) 32128 _________________________________________________________________ global_max_pooling1d_4 (Glob (None, 128) 0 _________________________________________________________________ dense_13 (Dense) (None, 10) 1290 _________________________________________________________________ dense_14 (Dense) (None, 1) 11 ================================================================= Total params: 162,179 Trainable params: 162,179 Non-trainable params: 0- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
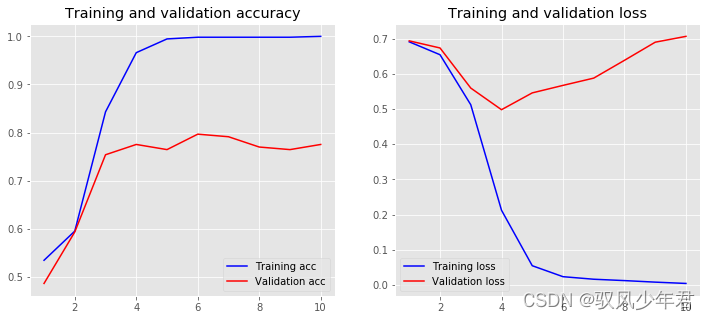
Epoch 10/10
561/561 [==============================] - 0s 433us/step - loss: 0.0039 - accuracy: 1.0000 - val_loss: 0.7069 - val_accuracy: 0.7754
Training Accuracy: 1.0000
Testing Accuracy: 0.7754
七、模型调优
7.1定义参数范围
模型中有很多参数,对于参数的不同,都可能提升模型的性能。
先定于一个模型架构,定义好相应的参数,构建成函数的形式 create_mode。
在对相应的参数来设置一个可变范围
例如设定filter的个数,卷积kernel的 长度,文本训练的embeding的大小等。
param_grid = dict(num_filters=[32, 64, 128],
kernel_size=[3, 5, 7],
embedding_dim=[50],
maxlen=[30])""" 调参 """ def create_model(num_filters, kernel_size, vocab_size, embedding_dim, maxlen): model = Sequential() model.add(layers.Embedding(vocab_size, embedding_dim, input_length=maxlen)) model.add(layers.Conv1D(num_filters, kernel_size, activation='relu')) model.add(layers.GlobalMaxPooling1D()) model.add(layers.Dense(10, activation='relu')) model.add(layers.Dense(1, activation='sigmoid')) model.compile(optimizer='adam', loss='binary_crossentropy', metrics=['accuracy']) return model param_grid = dict(num_filters=[32, 64, 128], kernel_size=[3, 5, 7], embedding_dim=[50], maxlen=[30])- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
7.2 模型调优
用sklearn来的RandomizedSearchCV,和keras的KerasClassifier随机搜索来调参数
在KerasClassifier传入定义的函数模型,以及其他参数,verbose=False表示不显示迭代。KerasClassifier(build_fn=create_model,
epochs=epochs, batch_size=64,
verbose=False)RandomizedSearchCV中传入得到的KerasClassifier模型,以及参数统计,n_iter=5表示随机选择5次,定义好交叉验证等参数。
RandomizedSearchCV(estimator=model, param_distributions=param_grid,
cv=3, verbose=1, n_iter=5)最后进行训练,获取最优的参数,并保存下来。
from keras.wrappers.scikit_learn import KerasClassifier from sklearn.model_selection import RandomizedSearchCV # 超参数 epochs = 20 embedding_dim = 50 maxlen = 30 output_file = 'data/output.txt' # 参数选择 for source, frame in df.groupby('source'): print('Running grid search for data set :', source) #----------------------------数据预处理----------------------------- sentences = df['sentence'].values y = df['label'].values sentences_train, sentences_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split( sentences, y, test_size=0.25, random_state=1000) tokenizer = Tokenizer(num_words=5000) tokenizer.fit_on_texts(sentences_train) X_train = tokenizer.texts_to_sequences(sentences_train) X_test = tokenizer.texts_to_sequences(sentences_test) vocab_size = len(tokenizer.word_index) + 1 X_train = pad_sequences(X_train, padding='post', maxlen=maxlen) X_test = pad_sequences(X_test, padding='post', maxlen=maxlen) # ----------------------------参数空间-------------------- param_grid = dict(num_filters=[32, 64, 128], kernel_size=[3, 5, 7], vocab_size=[vocab_size], embedding_dim=[embedding_dim], maxlen=[maxlen]) model = KerasClassifier(build_fn=create_model, epochs=epochs, batch_size=64, verbose=False) grid = RandomizedSearchCV(estimator=model, param_distributions=param_grid, cv=3, verbose=1, n_iter=5) grid_result = grid.fit(X_train, y_train) # 测试结果 test_accuracy = grid.score(X_test, y_test) with open(output_file, 'a') as f: s = ('Running {} data set\nBest Accuracy : ' '{:.4f}\n{}\nTest Accuracy : {:.4f}\n\n') output_string = s.format( source, grid_result.best_score_, grid_result.best_params_, test_accuracy) print(output_string) f.write(output_string)- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
Running grid search for data set : amazon Fitting 3 folds for each of 5 candidates, totalling 15 fits Running amazon data set Best Accuracy : 0.8083 {'vocab_size': 4603, 'num_filters': 128, 'maxlen': 30, 'kernel_size': 3, 'embedding_dim': 50} Test Accuracy : 0.8253 Running grid search for data set : imdb Fitting 3 folds for each of 5 candidates, totalling 15 fits Running imdb data set Best Accuracy : 0.8122 {'vocab_size': 4603, 'num_filters': 32, 'maxlen': 30, 'kernel_size': 3, 'embedding_dim': 50} Test Accuracy : 0.8355 Running grid search for data set : yelp Fitting 3 folds for each of 5 candidates, totalling 15 fits Running yelp data set Best Accuracy : 0.8030 {'vocab_size': 4603, 'num_filters': 64, 'maxlen': 30, 'kernel_size': 3, 'embedding_dim': 50} Test Accuracy : 0.8108- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
-
相关阅读:
Python Number degrees()实例讲解
2022年上半年系统集成项目管理工程师下午真题及答案解析
丁鹿学堂:promise深入解读(一)
Aspose.Words 操作 Word 画 EChart 图
微服务架构最佳实践:故障恢复和容错策略
模态逻辑介绍
修复YOLOFacePose中存在关键点异常的问题
EFK+tomcat
TCP/IP网络协议通信函数接口
智慧公厕厂家,揭秘公厕升级的实际应用功能
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_44951759/article/details/126122916
