-
Spring Security OAuth2 入门
- 1. 概述
- 2. 引入 Spring Security OAuth2 依赖
- 3. 配置资源服务器
- 4. 配置授权服务器
- 4.1 授权码模式
- Spring Security Setting
- 4.2 密码模式
- 4.3 简化模式
- 4.4 客户端模式
- 4.5 如何选择?
- 4.6 为什么有 Client 编号和密码
- 5. 刷新令牌
- 5.1 获取刷新令牌
- 5.2 “刷新”访问令牌
- 5.3 为什么需要有刷新令牌
- 6. 删除令牌
- 6.1 删除访问令牌
- 6.2 删除刷新令牌
- 6.3 RFC7009 - OAuth2 Token Revocation
- 7. 令牌元数据
- 666. 彩蛋
1. 概述
本文,我们来入门 Spring Security OAuth2.0 的使用。通过本文,希望你对 OAuth2.0 有一次身临其境的感受。
另外,这是一篇入门的文章,所以实际场景下,需要做一些微调。当然,需要微调的地方,笔者会在示例中说明,以免误导。
如果你是 OAuth2.0 的萌新,建议先通读阮一峰大神的 《理解OAuth 2.0》。因为,本文不会去阐述 OAuth2.0 概念部分的内容。或者,也可以看看 《OAuth 2.0最简向导》 ,比较生动形象。
阅读完本文后,你想要更加深入的理解 OAuth2.0 ,可以阅读如下两本书籍:
- 《OAuth2 in Action》 重原理
- 《OAuth2 2.0 Cookbook》 重实践,基于 Spring Security OAuth2 。
阅读完本文后,你想要了解源码,可以阅读老徐的两篇文章:
- 《Re:从零开始的Spring Security OAuth2(二)》
- 《Re:从零开始的Spring Security OAuth2(三)》
OK,一波安利之后,我们来一起进入正文。对于 Spring Security OAuth2 的配置,大体来说,就是两步:
- 配置授权服务器( AuthorizationServer )
- 配置资源服务器( ResourceServer )
2. 引入 Spring Security OAuth2 依赖
在 pom.xml 文件中,引入如下:
org.springframework.boot spring-boot-starter-parent 1.5.16.RELEASE org.springframework.boot spring-boot-starter-web org.springframework.boot spring-boot-starter-security org.springframework.security.oauth spring-security-oauth2因为,我们使用的是 SpringBoot 的版本为 1.5.16.RELEASE ,所以使用的 Spring Security 的版本为 4.2.8.RELEASE ,Spring Security OAuth2 的版本为 2.2.0.15.RELEASE 。
3. 配置资源服务器
一般情况下,资源服务器指的是,我们提供 API 的应用或服务。例如,订单服务、商品服务。考虑到让整个示例更加简单,本文先将它和授权服务器放在一个 Maven 项目中。
① 创建一个 Controller 类
/**
* 示例模块 Controller
*/
@RestController
@RequestMapping(“/api/example”)
public class ExampleController {
@RequestMapping(“/hello”)
public String hello() {
return “world”;
}
}- 非常简单,这是一个示例模块的 Controller ,提供 /api/example/hello 接口。
② 配置资源服务器
// 资源服务配置
@Configuration
@EnableResourceServer
public class OAuth2ResourceServer extends ResourceServerConfigurerAdapter {
@Override
public void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.authorizeRequests()
// 对 “/api/**” 开启认证
.anyRequest()
.authenticated()
.and()
.requestMatchers()
.antMatchers(“/api/**”);
}
}- @Configuration 注解,保证 OAuth2ResourceServer 能够被 SpringBoot 扫描到配置。
- @EnableResourceServer 注解,开启资源服务器。
- 继承( extends ) ResourceServerConfigurerAdapter 类,并覆写 #configure(HttpSecurity http) 方法,配置对 HTTP 请求中,匹配 /api/**" 路径,开启认证的验证。
4. 配置授权服务器
在 OAuth2.0 中,定义了四种授权模式:
- 授权码模式( authorization code )
- 密码模式( resource owner password credentials )
- 简化模式( implicit )
- 客户端模式( client credentials )
所以,笔者在 SpringBoot-Labs/lab-02 目录下,每一种方式,都提供了一个 Maven 项目示例。
4.1 授权码模式
Maven 项目结构如下:

Maven 项目结构
对应 GitHub 地址:
https://github.com/YunaiV/SpringBoot-Labs/tree/master/lab-02/authorization-code-server① 配置授权服务器
// 授权服务器配置
@Configuration
@EnableAuthorizationServer
public class OAuth2AuthorizationServer extends AuthorizationServerConfigurerAdapter {
@Override
public void configure(ClientDetailsServiceConfigurer clients) throws Exception {
clients.inMemory() // <1>
// <2> begin …
.withClient(“clientapp”).secret(“112233”) // Client 账号、密码。
.redirectUris(“http://localhost:9001/callback”) // 配置回调地址,选填。
.authorizedGrantTypes(“authorization_code”) // 授权码模式
.scopes(“read_userinfo”, “read_contacts”) // 可授权的 Scope
// <2> end …
// .and().withClient() // 可以继续配置新的 Client // <3>
;
}
}- @Configuration 注解,保证 OAuth2AuthorizationServer 能够被 SpringBoot 扫描到配置。
- @EnableAuthorizationServer 注解,开启授权服务器。
- <1> 处,基于内存,为了方便测试。实际情况下,最好放入数据库中,方便管理。
- <2> 处,创建一个 Client 配置。
- <3> 处,可以使用 #and() 方法,继续添加另外的 Client 配置。
② 配置登陆账号
创建 application.properties 文件,并配置如下:
# Spring Security Setting
security.user.name=yunai
security.user.password=1024- 这里配置了一个账号为 “yunai” ,密码为 “1024” 的登陆账户。
- 实际生产环境下,登陆账号的数据,肯定是放在数据库中。
③ 启动项目
@SpringBootApplication
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args);
}
}启动项目
④ 获取授权码
4.1 浏览器打开
http://localhost:8080/oauth/authorizeclient_id=clientapp&redirect_uri=http://localhost:9001/callback&response_type=code&scope=read_userinfo- client_id 参数,必传,为我们在 OAuth2AuthorizationServer 中配置的 Client 的编号。
- redirect_url 参数,可选,回调地址。当然,如果 client_id 对应的 Client 未配置 redirectUris 属性,会报错。
- response_type 参数,必传,返回结果为授权码。
- scope 参数,可选,申请授权的 Scope 。如果多个,使用逗号分隔。
- state 参数,可选,表示客户端的当前状态,可以指定任意值,认证服务器会原封不动地返回这个值。
- 未在上述 URL 中体现出来。
4.2 浏览器打开后,效果如下:
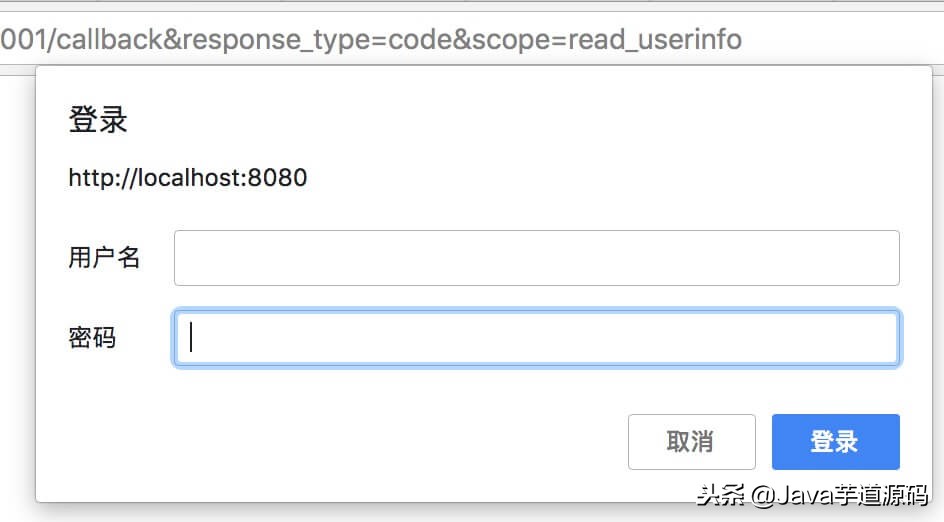
浏览器
- 输入在 「② 配置登陆账号」 中配置的登陆账号 “yunai” / “1024” 。
- 实际生产情况下,我们以 QQ 三方登陆作为例子,如下图:
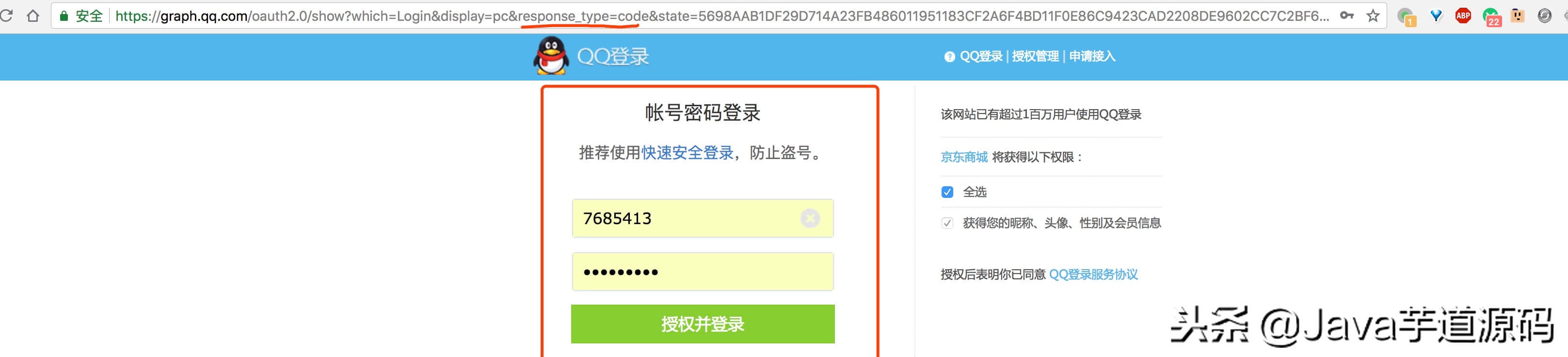
- QQ 示例
4.3 登陆成功,选择允许所有申请的 Scope ,点击【Authorize】按钮,确认授权。如下图:
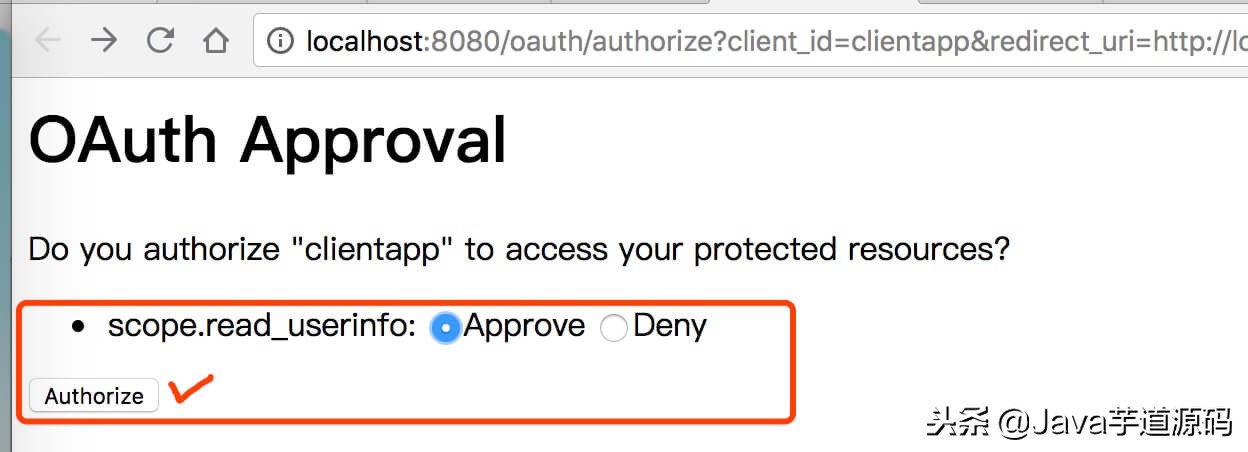
Authorize
4.4 授权完成,回调 redirect_uri 地址。如下图所示:
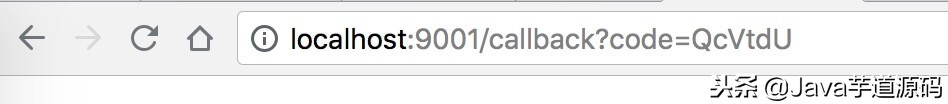
回调地址
- code 参数,就是返回的授权码。
⑤ 获取访问令牌
curl -X POST --user clientapp:112233 http://localhost:8080/oauth/token -H “content-type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded” -d “code=UydkmV&grant_type=authorization_code&redirect_uri=http%3A%2F%2Flocalhost%3A9001%2Fcallback&scope=read_userinfo”
- –user clientapp:112233 处,填写我们在 OAuth2AuthorizationServer 中配置的 Client 的编号和密码。
- code=UydkmV 处,填写在 「④ 获取授权码」 中获取的授权码( code ) 。
返回结果示例如下:
{
“access_token”: “e60e41f2-2ad0-4c79-97d5-49af38e5c2e8”,
“token_type”: “bearer”,
“expires_in”: 43199,
“scope”: “read_userinfo”
}- access_token 属性,访问令牌。非空。
- token_type 属性,令牌类型,可以是 “bearer” 或 “mac” 类型。非空。
- expires_in 属性,过期时间,单位为秒。一般情况下,非空。
- scope 属性,权限范围。如果与 Client 申请的范围一致,此项可省略。
- refresh_token 属性,刷新令牌,用来获取下一次的访问令牌。
- 在授权码模式下,允许为空。
可能有部分胖友是 Windows 电脑,可以参考 《windows(64位)下使用 curl 命令》 来安装一个 curl 命令。
当然,如果胖友使用 Postman ,可以参看如下两图:
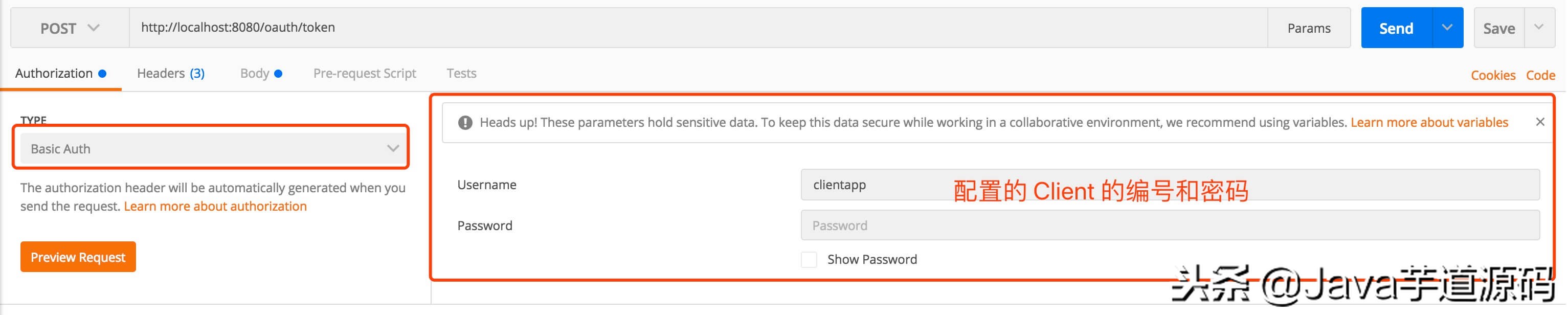
- 图 1
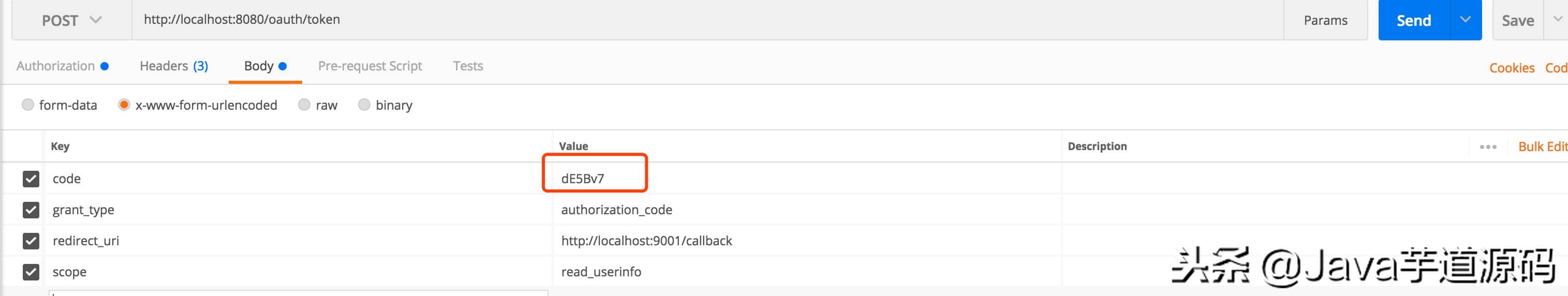
- 图 2
⑥ 调用资源服务器的 API
curl -X GET http://localhost:8080/api/example/hello -H “authorization: Bearer e60e41f2-2ad0-4c79-97d5-49af38e5c2e8”
- authorization: Bearer e60e41f2-2ad0-4c79-97d5-49af38e5c2e8 处,填写指定的访问令牌类型和访问令牌。例如此处分别为,“Bearer”、“e60e41f2-2ad0-4c79-97d5-49af38e5c2e8” 。
如果胖友使用 Postman ,可以参看如下图:
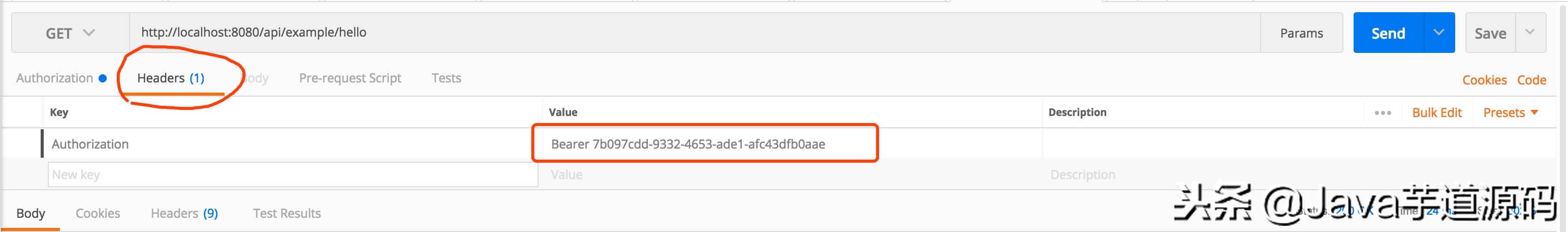
- 图
4.2 密码模式
Maven 项目结构如下:
Maven 项目结构
对应 GitHub 地址:
https://github.com/YunaiV/SpringBoot-Labs/tree/f8d701cbd9b2a4f2cee3a7f2186148bcdf859895/lab-02/resource-owner-password-credentials-server① 配置授权服务器
// 授权服务器配置
@Configuration
@EnableAuthorizationServer
public class OAuth2AuthorizationServer extends AuthorizationServerConfigurerAdapter {
// 用户认证
@Autowired
private AuthenticationManager authenticationManager;
@Override
public void configure(AuthorizationServerEndpointsConfigurer endpoints) throws Exception {
endpoints.authenticationManager(authenticationManager);
}
@Override
public void configure(ClientDetailsServiceConfigurer clients) throws Exception {
clients.inMemory()
.withClient(“clientapp”).secret(“112233”) // Client 账号、密码。
.authorizedGrantTypes(“password”) // 密码模式
.scopes(“read_userinfo”, “read_contacts”) // 可授权的 Scope
// .and().withClient() // 可以继续配置新的 Client
;
}
}- 配置 Client 的方式,和【授权码模式】基本一致。差别在于:
- 无需配置 `redirectUris` 属性,因为不需要回调地址。
- 配置授权模式为【密码模式】。
- 另外,需要引入AuthenticationManager来支持【密码模式】,否则会报 “Resolved [error=“unsupported_grant_type”, error_description=“Unsupported grant type: password”]” 异常。
② 配置登陆账号
和【授权码模式】一致。
③ 启动项目
和【授权码模式】一致。
④ 获取访问令牌
curl -X POST --user clientapp:112233 http://localhost:8080/oauth/token -H “accept: application/json” -H “content-type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded” -d “grant_type=password&username=yunai&password=1024&scope=read_userinfo”
- 和【授权码模式】差异比较大。
- 直接请求 oauth/token 接口,获得访问令牌。
- 请求参数带上了 username 和 password ,就用户的登陆账号和密码。
- 请求参数 grant_type 为 password ,表示【密码模式】。
返回结果示例如下:
{
“access_token”: “68de6eb9-5672-4e47-a3e6-110404285ba9”,
“token_type”: “bearer”,
“expires_in”: 43199,
“scope”: “read_userinfo”
}- 和【授权码模式】一致。
⑤ 调用资源服务器的 API
和【授权码模式】一致。
4.3 简化模式
Maven 项目结构如下:

Maven 项目结构
对应 GitHub 地址:
https://github.com/YunaiV/SpringBoot-Labs/tree/f8d701cbd9b2a4f2cee3a7f2186148bcdf859895/lab-02/implicit-server① 配置授权服务器
// 授权服务器配置
@Configuration
@EnableAuthorizationServer
public class OAuth2AuthorizationServer extends AuthorizationServerConfigurerAdapter {
@Override
public void configure(ClientDetailsServiceConfigurer clients) throws Exception {
clients.inMemory()
.withClient(“clientapp”).secret(“112233”) // Client 账号、密码。
.redirectUris(“http://localhost:9001/callback”) // 配置回调地址,选填。
.authorizedGrantTypes(“implicit”) // 授权码模式
.scopes(“read_userinfo”, “read_contacts”) // 可授权的 Scope
// .and().withClient() // 可以继续配置新的 Client
;
}
}- 和【授权码模式】基本一致。差别仅仅在于:配置授权模式为【简化模式】。
FROM 《理解 OAuth 2.0》
简化模式(implicit grant type)不通过第三方应用程序的服务器,直接在浏览器中向认证服务器申请令牌,跳过了"授权码"这个步骤,因此得名。所有步骤在浏览器中完成,令牌对访问者是可见的,且客户端不需要认证。
② 配置登陆账号
和【授权码模式】一致。
③ 启动项目
和【授权码模式】一致。
④ 获取授权码
4.1 浏览器打开
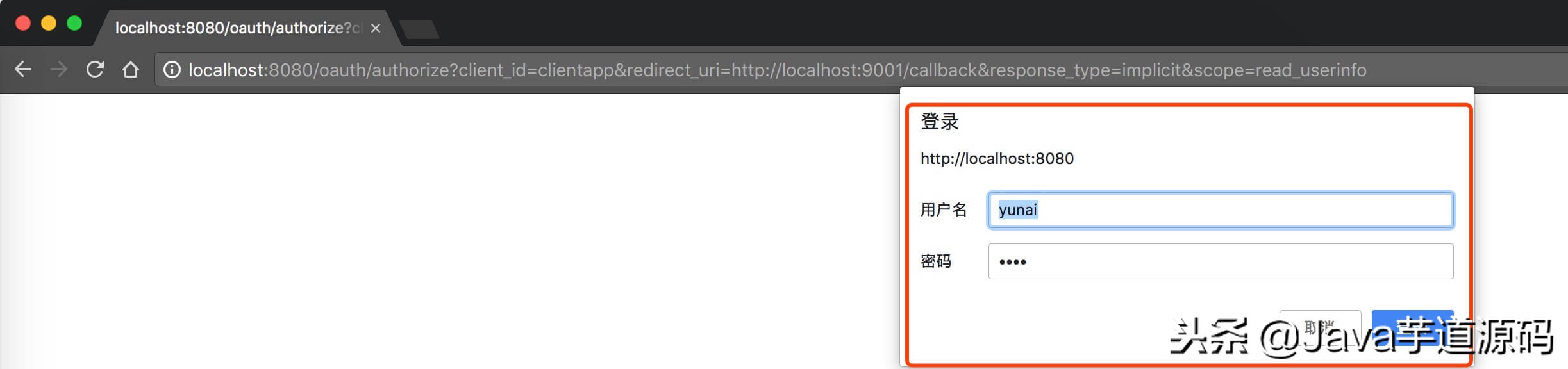
http://localhost:8080/oauth/authorizeclient_id=clientapp&redirect_uri=http://localhost:9001/callback&response_type=implicit&scope=read_userinfo- 和【授权码模式】基本一致。差别仅仅在于:请求参数 response_type 为 “implicit” 简化模式。
4.2 浏览器打开后,效果如下:
浏览器
- 和【授权码模式】基本一致,输入在 「② 配置登陆账号」 中配置的登陆账号 “yunai” / “1024” 。
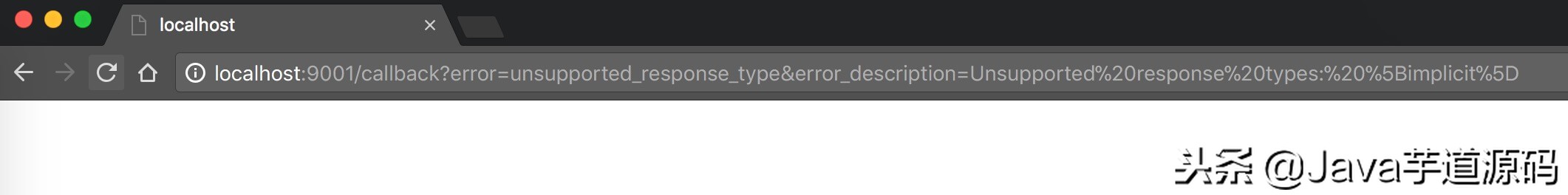
4.3 登陆成功,直接授权完成,回调 redirect_uri 地址。如下图所示:
浏览器
- 和【授权码模式】基本不一致的有两点:
- 登陆成功后,无需选择允许所有申请的 Scope ,直接授权完成。
- 返回的不是授权码,而是访问令牌。
总的来说,【简化模式】是【授权码模式】的简化模式。
⑤ 调用资源服务器的 API
和【授权码模式】一致。
4.4 客户端模式
Maven 项目结构如下:
Maven 项目结构
对应 GitHub 地址:
https://github.com/YunaiV/SpringBoot-Labs/tree/f8d701cbd9b2a4f2cee3a7f2186148bcdf859895/lab-02/client-credentials-server① 配置授权服务器
和【密码模式】一致。
② 配置登陆账号
它无需配置登陆账号。因为它没有用户的概念,直接与授权服务器交互,通过 Client 的编号( client_id )和密码( client_secret )来保证安全性。
③ 启动项目
和【密码模式】一致。
④ 获取访问令牌
curl -X POST “http://localhost:8080/oauth/token” --user clientapp:112233 -d “grant_type=client_credentials&scope=read_contacts”
- 和【密码模式】基本一致,差别如下:
- 请求参数无需带上了 `username` 和 `password` 。
- 请求参数 `grant_type` 为 `client_credentials` ,表示【密码模式】。
返回结果示例如下:
{
“access_token”:“cb2bdfd8-18fa-4b8f-b525-10587bd672e8”,
“token_type”:“bearer”,
“expires_in”:43199,
“scope”:“read_contacts”
}- 和【密码模式】一致。
⑤ 调用资源服务器的 API
和【密码模式】一致。
总的来说,【客户端模式】是【密码模式】的简化模式。
4.5 如何选择?
可能很多胖友,有跟笔者一样的困惑。下面笔者引用杨波老师的一张图,相信能解决我们的困扰。如下图所示:
FROM 《深度剖析 OAuth2 和微服务安全架构》

授权类型选择
当然,对于黄框部分,对于笔者还是比较困惑的。笔者认为,第三方的单页应用 SPA ,也是适合采用 Authorization Code Grant 授权模式的。例如,《微信网页授权》 :
具体而言,网页授权流程分为四步:
1、引导用户进入授权页面同意授权,获取code
2、通过code换取网页授权access_token(与基础支持中的access_token不同)
3、如果需要,开发者可以刷新网页授权access_token,避免过期
4、通过网页授权access_token和openid获取用户基本信息(支持UnionID机制)
所以,笔者猜测,之所以图中画的是 Implicit Grant 的原因是,受 Google 的 《OAuth 2.0 for Client-side Web Applications》 一文中,推荐使用了 Implicit Grant 。
当然,具体使用 Implicit Grant 还是 Authorization Code Grant 授权模式,没有定论。笔者,偏向于使用Authorization Code Grant,对于第三方客户端的场景。
4.6 为什么有 Client 编号和密码
我们看到上述四种授权模式,无论是哪一种,最终调用授权服务器时,都会传递 Client 编号和密码,这是为什么呢?通过 Client 编号和密码,授权服务器可以知道调用的来源以及正确性。这样,即使“坏人”拿到 Access Token ,但是没有 Client 编号和密码,也不能和授权服务器发生有效的交互。
5. 刷新令牌
在 「4. 配置授权服务器」 中,我们一直没有看到我们期盼的刷新令牌( refresh token )的身影。这是为什么呢?因为我们在配置 Spring Security OAuth2 并未配置,获取访问令牌的同时,获取刷新令牌。
那么,怎么配置开启获取刷新令牌的功能呢?我们来看看 「5.1 获取刷新令牌」 。
5.1 获取刷新令牌
因为【密码模式】相对简单,我们直接在原有程序上做改造。对应 GitHub 地址:
https://github.com/YunaiV/SpringBoot-Labs/tree/master/lab-02/authorization-code-server-with-refresh-token 。在步骤上,如果和原有【密码模式】保持一致的地方,下文会进行省略,并标注“和原有一致”。
① 配置授权服务器
// 授权服务器配置
@Configuration
@EnableAuthorizationServer
public class OAuth2AuthorizationServer extends AuthorizationServerConfigurerAdapter {
// 用户认证
@Autowired
private AuthenticationManager authenticationManager;
@Override
public void configure(AuthorizationServerEndpointsConfigurer endpoints) throws Exception {
endpoints.authenticationManager(authenticationManager);
}
@Override
public void configure(ClientDetailsServiceConfigurer clients) throws Exception {
clients.inMemory()
.withClient(“clientapp”).secret(“112233”) // Client 账号、密码。
.authorizedGrantTypes(“password”, “refresh_token”) // 密码模式 // <1>
.scopes(“read_userinfo”, “read_contacts”) // 可授权的 Scope
// .and().withClient() // 可以继续配置新的 Client
;
}
}- 在 <1> 处,我们很神奇的多配置了一个 “refresh_token” ,用于开启获取刷新令牌的功能。但是但是但是,OAuth2 的授权模式说好的是四种的么,怎么又出现了 “refresh_token” 这种授权模式?淡定,在 Spring Security OAtuh2 中,“refresh_token” 作为一种特殊的授权模式配置,用于开启获取刷新令牌的功能。所以,其它授权模式如果开启获取刷新令牌的功能,需要在 #authorizedGrantTypes(…) 设置时,多传入 “refresh_token” 方法参数。
② 配置登陆账号
和原有一致。
③ 启动项目
和原有一致。
④ 获取访问令牌
curl -X POST --user clientapp:112233 http://localhost:8080/oauth/token -H “accept: application/json” -H “content-type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded” -d “grant_type=password&username=yunai&password=1024&scope=read_userinfo”
- 和原有一致。
返回结果示例如下:
{
“access_token”:“092a2286-04e7-4e7d-8c20-19fbe25865ff”,
“token_type”:“bearer”,
“refresh_token”:“afeeb083-997f-4ea8-9334-aab6c1696cca”,
“expires_in”:43199,
“scope”:“read_userinfo”
}- 在原有的基础上,多返回了 “refresh_token” 刷新令牌。美滋滋。
⑤ 调用资源服务器的 API
和原有一致。
5.2 “刷新”访问令牌
因为访问访问令牌会自动过期,通过使用刷新令牌,可以获得新的访问令牌。注意,访问令牌获取到的是新的,不是老的哈。这也是为什么,在标题上,笔者对刷新加了双引号。
curl -i -X POST -u ‘clientapp:112233’ http://localhost:8080/oauth/token -H “accept: application/json” -d ‘grant_type=refresh_token&refresh_token=afeeb083-997f-4ea8-9334-aab6c1696cca’
- 调用接口还是 “oauth/token” ,差别在于传入的请求参数 grant_type 为 “refresh_token”,使用刷新令牌。
- 请求参数 refresh_token 为上面获取到的刷新令牌 “afeeb083-997f-4ea8-9334-aab6c1696cca” 。
返回结果示例如下:
{
“access_token”:“507eb761-4b25-4159-b927-ef3eff5e7eff”,
“token_type”:“bearer”,
“refresh_token”:“afeeb083-997f-4ea8-9334-aab6c1696cca”,
“expires_in”:43199,
“scope”:“read_userinfo”
}- 获得的访问令牌为 “507eb761-4b25-4159-b927-ef3eff5e7eff” ,是新的。并且,过期时间也变成新的。
笔者在看 OAuth2.0 的刷新令牌时,一直有个疑惑:刷新令牌是否有过期时间?答案是,有。但是,笔者不太确定,在 Spring Security OAuth2 中,如果不设置刷新令牌的过期时间,刷新时间是否无限长?当然,这个貌似也并不重要。因为,在实际使用中,我们肯定是需要显示( 主动 )设置刷新令牌的过期时间,使用 ClientBuilder#
refreshTokenValiditySeconds(intrefreshTokenValiditySeconds) 方法,示例如下:@Override
public void configure(ClientDetailsServiceConfigurer clients) throws Exception {
clients.inMemory()
.withClient(“clientapp”).secret(“112233”) // Client 账号、密码。
.authorizedGrantTypes(“password”, “refresh_token”) // 密码模式
.scopes(“read_userinfo”, “read_contacts”) // 可授权的 Scope
.refreshTokenValiditySeconds(1200) // 1200 秒过期
// .and().withClient() // 可以继续配置新的 Client
;
}刷新令牌过期时,返回结果示例如下:
{
“error”:“invalid_token”,
“error_description”:“Invalid refresh token (expired): 7139d075-c4ea-48f0-9dbb-6f65fa6dbeb0”
}- 如果胖友要测试这个效果,可以把刷新令牌过期时间设置为 1 秒。
5.3 为什么需要有刷新令牌
出于安全性的考虑,访问令牌的过期时间比较短,刷新令牌的过期时间比较长。这样,如果访问令牌即使被盗用走,那么在一定的时间后,访问令牌也能在较短的时间吼过期。当然,安全也是相对的,如果使用刷新令牌后,获取到新的访问令牌,访问令牌后续又可能被盗用。
另外,刷新令牌是可选项,不一定会返回。
笔者整理了下,大家常用开放平台的令牌过期时间,让大家更好的理解:
- 小米开放平台
- 《Access Token 生命周期》
- Access Token :90 天有效期
- Refresh Token :10 年有效期
- 微信开放平台
- 《网站应用微信登录开发指南》
- Access Token :2 小时有效期
- Refresh Token :未知有效期
- 腾讯开放平台
- 《获取 Access_Token》
- Access Token :90 天有效期
- Refresh Token :未知有效期
6. 删除令牌
实际在 OAuth2 时,有删除访问令牌和刷新令牌的需求。例如:用户登出系统。虽然说,可以通过客户端本地删除令牌的方式实现。但是,考虑到真正的彻底的实现删除令牌,必然服务端自身需要删除令牌。
在 Spring Security OAuth2 中,并没有提供内置的接口,所以需要自己去实现。笔者参看 《Spring Security OAuth2 – Simple Token Revocation》 文档,实现删除令牌的 API 接口。
因为【密码模式】相对简单,我们直接在原有程序上做改造。对应 GitHub 地址: 。注意,如下仅仅是 Demo ,实际生产环境下需要做改造。
6.1 删除访问令牌
① 新增删除访问令牌的 API 接口
@Autowired
private ConsumerTokenServices tokenServices;
@RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.POST, value = “api/access_token/revoke”)
public String revokeToken(@RequestParam(“token”) String token) {
tokenServices.revokeToken(token);
return token;
}- 使用 ConsumerTokenServices#revokeToken(String tokenValue) 方法,删除访问令牌。
注意,实际生产环境下,授权服务器和资源服务器是不在一起的,所以此处仅仅是示例。主要是为了介绍 ConsumerTokenServices#revokeToken(String tokenValue) 方法的使用。
② 访问删除访问令牌的 API 接口。
curl -X POST http://localhost:8080/api/access_token/revoke -H “authorization: Bearer 23874e0b-a1d8-4337-9551-7b9be1ebaebe” -d “token=23874e0b-a1d8-4337-9551-7b9be1ebaebe”
移除成功后,在使用当前访问令牌,就会报如下错误:
{
“error”:“invalid_token”,
“error_description”:“Invalid access token: 23874e0b-a1d8-4337-9551-7b9be1ebaebe”
}
另外,也可以参考
https://github.com/geektime-geekbang/oauth2lab/blob/master/lab05/oauth-server/src/main/java/io/spring2go/config/RevokeTokenEndpoint.java 的实现。6.2 删除刷新令牌
① 新增删除访问令牌的 API 接口
@Autowired(required = false) // <1>
private TokenStore tokenStore;
@RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.POST, value = “api/refresh_token/revoke”)
public String revokeRefreshToken(@RequestParam(“token”) String token) {
tokenStore.removeRefreshToken(new DefaultOAuth2RefreshToken(token));
return token;
}- <1> 处,使用了 required = false 的原因是,本示例并未显示声明 TokenStore Bean 对象交给 Spring 管理,所以无法注入。 所以 「6.2 删除刷新令牌」 是一个无法跑通的示例。
- 重点在于,调用 TokenStore#removeRefreshToken(OAuth2RefreshToken token) 方法,删除刷新令牌。
② 访问删除刷新令牌的 API 接口。
curl -X POST http://localhost:8080/api/refresh_token/revoke -H “authorization: Bearer 52e85411-ac1d-4844-bf03-cf5633e4eecd” -d “token=ead4734a-ca5c-45bf-ac25-9a92291a9fe1”
移除成功后,在使用当前刷新令牌,就会报如下错误:
{
“error”:“invalid_token”,
“error_description”:“Invalid refresh token: ead4734a-ca5c-45bf-ac25-9a92291a9fe1”
}
另外,也可以参考
https://github.com/geektime-geekbang/oauth2lab/blob/master/lab05/oauth-server/src/main/java/io/spring2go/config/TokenController.java 的实现。6.3 RFC7009 - OAuth2 Token Revocation
在 OAuth2 中,删除令牌,标准的说法为 OAuth2 Token 撤销,对应 RFC7009 。感兴趣的胖友,可以看看。
FROM 《OAuth2 Token 撤销(RFC7009 - OAuth2 Token Revocation)》
简单来说,这个协议规定了一个Authorization server提供一个怎样的API来供Client撤销access_token或者refresh_token。
比如Client发起一个如下的请求:
POST /revoke HTTP/1.1
Host: server.example.com
Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded
Authorization: Basic czZCaGRSa3F0MzpnWDFmQmF0M2JW
token=45ghiukldjahdnhzdauz&token_type_hint=refresh_token
其中各项含义如下:
- /revoke:是Authorization Server需要提供的API地址,Client使用Post方式请求这个地址。
- Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded:固定此格式。
- Authorization: Basic czZCaGRSa3F0MzpnWDFmQmF0M2JW:访问受保护资源的授权凭证。
- token:必选,可以是access_token或者refresh_token的内容。
- token_type_hint:可选,表示token的类型,值为”access_token“或者"refresh_token"。
如果撤销成功,则返回一个HTTP status code为200的响应就可以了。
7. 令牌元数据
FROM 《OAuth2 Token 元数据(RFC7662 - OAuth2 Token Introspection)》
简单的总结来说,这个规范是为OAuth2扩展了一个API接口(Introspection Endpoint),让第三方Client可以查询上面提到的那些信息(比如,access_token是否还有效,谁颁发的,颁发给谁的,scope又哪些等等的元数据信息)。
比如Client发起一个如下的请求:
POST /introspect HTTP/1.1
Host: server.example.com
Accept: application/json
Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded
Authorization: Bearer 23410913-abewfq.123483
token=2YotnFZFEjr1zCsicMWpAA&token_type_hint=access_token
看起来和上面的撤销Token的请求差不多,其中各项含义如下:
- /introspect:是Authorization Server需要提供的API地址,Client使用Post方式请求这个地址。
- Accept:application/json:表示Authorization Server需要返回一个JSON格式的数据。
- Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded:固定此格式。
- Authorization: Basic czZCaGRSa3F0MzpnWDFmQmF0M2JW:访问受保护资源的授权凭证。
- token:必选,可以是access_token或者refresh_token的内容。
- token_type_hint:可选,表示token的类型,值为”access_token“或者"refresh_token"。
如果请求成功,则会返回如下的信息:
1 {
2 “active”: true,
3 “client_id”: “l238j323ds-23ij4”,
4 “token_type”:“access_token”,
5 “username”: “jdoe”,
6 “scope”: “read write dolphin”,
7 “sub”: “Z5O3upPC88QrAjx00dis”,
8 “aud”: “https://protected.example.net/resource”,
9 “iss”: “https://server.example.com/”,
10 “exp”: 1419356238,
11 “iat”: 1419350238,
12 “nbf”: 1419350238,
13 “jti”: “abcdefg”
14 “extension_field”: “twenty-seven”
15 }JSON各项属性含义如下(其中有些信息是在JSON Web Token中定义的,参考链接有详细的介绍):
- active:必须的。表示token是否还是有效的。
- client_id:可选的。表示token所属的Client。比如上面的在线打印并且包邮的网站。
- token_type:可选的。表示token的类型。对应传递的token_type_hint。
- user_name:可选的。表示token的授权者的名字。比如上面的小明。
- scope:可选的。和上篇5.1.1 Authorization Request中的可选参数scope对应,表示授权给Client访问的范围,比如是相册,而不是小明的日志以及其他受保护资源。
- sub:可选的。token所属的资源拥有者的唯一标识,JWT定义的。也就是小明的唯一标识符。
- aud:可选的。token颁发给谁的,JWT定义的。
- iss:可选的。token的颁发者,JWT定义的。
- exp:可选的。token的过期时间,JWT定义的。
- iat:可选的。iss颁发token的时间,JWT定义的。
- nbf:可选的。token不会在这个时间之前被使用,JWT定义的。
- jti:可选的。token的唯一标识,JWT定义的。
- extension_field:可以自己扩展相关其他属性。
其中大量的信息都是可选的信息,而且可以自己扩展需要的属性信息,从这些属性中就可以解决我们上面提到的access_token对于Client不透明的问题。
我们注意到其中有很多属于JWT定义的属性,那么这个JWT是什么东西?它解决了什么问题?感兴趣的胖友,可以看看 《JSON Web Token (JWT)》 。
对于令牌元数据 API 接口的实现,笔者这里就暂时不提供。如果有需要的胖友,可以看看 TokenStore 的两个 API :
- #readAccessToken(String tokenValue) 方法,读取指定的访问令牌的信息。
- #readRefreshToken(String tokenValue) 方法,读取指定的刷新令牌的信息。
666. 彩蛋
一万个注意,本文仅仅是 Spring Security OAuth2 的入门文章。实际生产使用时,还需要做很多事情。例如:
- 使用关系数据库,持久化存储 Client 和令牌信息。例如,使用 JdbcTokenStore 。
- 授权服务器和资源服务器分离。例如,使用 RemoteTokenServices 。
- 使用缓存服务器,提升 Client 和令牌信息的访问速度。例如,使用 RedisTokenStore 。
推荐阅读文章:
- CatalpaFlat 《Spring Security OAuth2 深入解析》
- 小东子 《Spring Security OAuth2 开发指南》
- 聊聊架构 《轻松筹 1.6 亿注册用户的 Passport 账户体系架构设计》
先自我介绍一下,小编13年上师交大毕业,曾经在小公司待过,去过华为OPPO等大厂,18年进入阿里,直到现在。深知大多数初中级java工程师,想要升技能,往往是需要自己摸索成长或是报班学习,但对于培训机构动则近万元的学费,着实压力不小。自己不成体系的自学效率很低又漫长,而且容易碰到天花板技术停止不前。因此我收集了一份《java开发全套学习资料》送给大家,初衷也很简单,就是希望帮助到想自学又不知道该从何学起的朋友,同时减轻大家的负担。添加下方名片,即可获取全套学习资料哦
-
相关阅读:
【redis】redis滑动时间窗口算法实现限流
如何查看dll文件内导出函数名称
《TCP/IP网络编程》阅读笔记--基于Windows实现Hello Word服务器端和客户端
2-11.基金管理人的合规管理
unittest自动测试多个用例时,logging模块重复打印解决
Kubeadm方式快速搭建K8S集群1.20版本
[深入研究4G/5G/6G专题-46]: L3信令控制-2-软件功能与流程的切分-DU网元的信令
【cartographer_ros】六: 发布和订阅路标landmark信息
web开发技术
Java程序启动后首次访问很慢--JVM预热
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/embelfe_segge/article/details/126114160