-
unity使用Dijkstra算法实现自动寻路
前言
最近开始做新的功能模块——章节关卡。在做的过程中看到一个要求:根据当前关卡位置,点击任意已开放的关卡,主角自动寻路至该处。
数据准备
关卡配置表如下:
map = { [1] = { coordinate = { 1, 1, }, link = { 2, 3, }, }, [2] = { coordinate = { 2, 1, }, link = { 1, 3, }, }, [3] = { coordinate = { 3, 2, }, link = { 4, 3, }, }, [4] = { coordinate = { 8, 2, }, link = { 2, 3, }, }, [5] = { coordinate = { 3, 3, }, link = { 2, 3, }, }, [6] = { coordinate = { 5, 3, }, link = { 2, 3, }, }, [7] = { coordinate = { 9, 3, }, link = { 2, 3, }, }, [8] = { coordinate = { 2, 4, }, link = { 2, 3, }, }, }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
map的key值代表第X关。
coordinate代表对应关卡的坐标位置,例如:{2,1}代表坐标位置为x=2,y=1。
link代表与之相连的关卡,{2,3}代表与关卡2和关卡3相连。(即表示有通路)尝试1
看到自动寻路,第一反应就是AStar算法。毕竟自动寻路嘛,那肯定得是A了。上次使用A还是在上次…enen,还是几年前上学时候,当时也只是学习了该算法的思路伪代码。要说用到实践里,那就是一个鸡蛋了。加上这么长时间过去了,只问其名,却已忘记其身,不得不借助www:度娘,我来了~。
首先找一篇通俗易懂的文章,看看算法的思路吧,代码的事后面再说~
先说下这个算法:A*算法主要用于求最短路径。算法的主要思想是:
参考自:https://blog.csdn.net/Zhouzi_heng/article/details/115035298
(1) 把起点加入 open list 。(2) 重复如下过程:
a. 遍历 open list ,查找 F 值最小的节点,把它作为当前要处理的节点。 b. 把这个节点移到 close list 。 c. 对当前方格的 8 个相邻方格的每一个方格? ◆ 如果它是不可抵达的或者它在 close list 中,忽略它。否则,做如下操作。 ◆ 如果它不在 open list 中,把它加入 open list ,并且把当前方格设置为它的父亲,记录该方格的 F , G 和 H 值。 ◆ 如果它已经在 open list 中,检查这条路径 ( 即经由当前方格到达它那里 ) 是否更好,用 G 值作参考。更小的 G 值表示这是更好的路径。如果是这样,把它的父亲设置为当前方格,并重新计算它 的 G 和 F 值。如果你的 open list 是按 F 值排序的话,改变后你可能需要重新排序。 d.停止,当你 ◆把终点加入到了 open list 中,此时路径已经找到了,或者 ◆查找终点失败,并且 open list 是空的,此时没有路径。- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
(3)保存路径。从终点开始,每个方格沿着父节点移动直至起点,这就是你的路径。
详情可见:推荐一篇大佬的A*算法文章:https://blog.csdn.net/xinzhilinger/article/details/119643810
搞懂了算法的思想后,我们其实是不需要自己写代码的,因为网上已经有很多成功的案例了,我们只需要站在巨人的肩膀上操作,去使用它。找到一个A算法的脚本如下:
https://mp.csdn.net/mp_download/manage/download/UpDetailed
那么怎么去使用它呢?
由于A算法是在网格上寻路的,因此我们需要先创建地图网格,使用Star.New(),观察发现Astar.cs脚本发现,需要的参数是String该网格是由网格的长宽,以及每个位置的信息(是否能通过,1代表可通过0代表不可通过)构成的,类似于这样:

第一行的两个值分表达标地图网格的长宽,除去第一行后可以发现,剩下的是一个10*10的网格,每个格子上有一个数字(值为0或者1),代表是否可以通过。
那么,第一步,我们需要先将上面给我们的配置信息转换为对应的网格字段,方法如下:--判断某个位置是路还是障碍物 local function CheckRoadOrBarrier(x,y) for k,v in pairs(map) do local coordinate = v.coordinate if coordinate[1] == x and coordinate[2] == y then return 1--是路 end end return 0--障碍物 end local fu nction CreateMapData() --长宽 local width = 10 local heigth = 10 local map = string.format("%s,%s",width,heigth) for i=1,heigth do map = map.."\n" for j=1,width do if j == 1 then map = string.format("%s%s",map,CheckRoadOrBarrier(i,j)) else map = string.format("%s,%s",map,CheckRoadOrBarrier(i,j)) end end end printlog(map,"生成的地图信息????") return map end- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
网格数据转换好后,我们需要开始初始化Astar算法:
local function InitAStar() current = AStarPoint.New(0,0)--默认初始位置在(0,0)坐标点 local map = CreateMapData() astar = AStar.New(map) astar:SetMapWidthAndHeigth(10, 10) end- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
接下来,是时候展现我们真正的技术了:我们开始真正使用Astar算法了。
local function GetShortPath(_x,_y,_finishfunc) local _next = AStarPoint.New(_x,_y) local path = astar:FindPath(current, _next) if path == nil or path.Count == 0 then _finishfunc(false) return else _finishfunc(true) end end local targetPos = Vector2.New(4,6)--目标位置,假设是(4,6)点,实际应用中以鼠标点击位置为准 GetShortPath(targetPos.x,targetPos.y,function (_bool) if _bool then --找到最短路径,可以前往目的地 else --没有通路,不能前往目的地 end end)- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
运行程序后我发现,额,貌似有点尴尬,这个算法和我的需求不符合,我的需求只知道哪些点之间有路,
用Astar来寻路的话,反而将问题复杂化了,最主要是不可行,典型的没读懂题意。网格可视化实现
一再陷入沉思中,既然算法还没想好,那就先按照配置,把关卡生成出来再试着找解决办法吧:
首先需要按照制定坐标生成关卡图标:
local function ShowLevelIcon() --关卡图标的父节点和关卡预制根据实际需要赋值 -- local parent = base.arena -- local prefab = base.levelPrefab local num = table.tablelen(map)--关卡数量 for i=1,num do local data = map[i] local obj = utils.addchild(parent , prefab)--实例化物体并制定父节点 local x = data.coordinate[1] local y = data.coordinate[2] obj.transform.localPosition = Vector3.New(x , y , 0) SetActive(obj , true) end end- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
接着需要根据关卡图标的位置和相连关系,生成通路。但是在此之前,我们需要将配置信息转化为通路信息:例如:{{x1,y1},{x2,y2}}这种格式,代表(x1,y1)与(x2,y2)之间有通路。
local function GetRoadPos() local allRoadPos = {} for i,v in ipairs(map) do local pos1 = v.coordinate for i,v in ipairs(v.link) do local pos2 = map[v].coordinate local pos = {pos1,pos2} table.insert(base.allRoadPos,pos) end end printlog(allRoadPos,"allRoadPos ===lxlxlxl") return allRoadPos end- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
运行发现,同一通路可能会存在多条相同的路径,这肯定是不符合我们需求的,因此我们需要将相同的路径唯一化处理:即需要再插入新路径前判断该路径是否已存在即可。
local function CheckExitRoad(pos,allRoadPos) for i,v in ipairs(allRoadPos) do if (pos[1] == v[1] and pos[2] == v[2]) or (pos[2] == v[1] and pos[1] == v[2]) then return true end end return false end local function GetRoadPos() local allRoadPos = {} for i,v in ipairs(map) do local pos1 = v.coordinate for i,v in ipairs(v.link) do local pos2 = map[v].coordinate local pos = {pos1,pos2} local bol = base.CheckExitRoad(pos,allRoadPos) if not bol then table.insert(base.allRoadPos,pos) end end end printlog(allRoadPos,"allRoadPos ===lxlxlxl") return allRoadPos end- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
有了路径数据,要生成路径就很简单了,直接根据坐标信息在指定位置实例化预制。需要注意的是:只关心生成位置是远远不够的,我们还需要根据两点的坐标计算出两点的距离,从而控制路径的长短。
求两点间距离,lua已经为我们封装好了:local distance = Vector2.Distance(endPos , startPos)- 1
有了位置长短,还需要控制路径的旋转角度,只有合适的旋转角度才能在视觉上构成真正的通路。
旋转角度的求解如下:local rorationZ = math.atan2((x2-x1),(y2-y1))*180/math.pi-90--求旋转角度 local rotation = obj.transform.localRotation obj.transform.localRotation = Quaternion.Euler(rotation.x,rotation.y,-rorationZ)- 1
- 2
- 3
既然思路我们知道了,只需要闭上眼睛,把代码写出来了:
local function ShowRoad() --关卡路径的父节点和关卡路径预制,根据实际需要赋值 -- local parent = base.arena -- local prefab = base.roadPrefab local allRoadPos = GetRoadPos(map) local num = table.tablelen(allRoadPos) for i=1,num do local pos = allRoadPos[i] local pos1 = pos[1] local pos2 = pos[2] local x1 = pos1[1] local x2 = pos2[1] local y1 = pos1[2] local y2 = pos2[2] obj.transform.localPosition = Vector2.New(x1, y1); local obj = utils.addchild(base.arena , base.roadPrefab) local rect = obj:GetComponent("RectTransform") local startPos = Vector3.New(x1, y1,0); local endPos = Vector3.New(x2, y2,0); rect.pivot = Vector2.New(0, 0.5); local distance = Vector2.Distance(endPos , startPos) rect.sizeDelta = Vector2.New(distance, rect.sizeDelta.y); local rorationZ = math.atan2((x2-x1),(y2-y1))*180/math.pi-90--求旋转角度 local rotation = obj.transform.localRotation obj.transform.localRotation = Quaternion.Euler(rotation.x,rotation.y,-rorationZ) SetActive(obj , true) end end- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
运行效果如下:
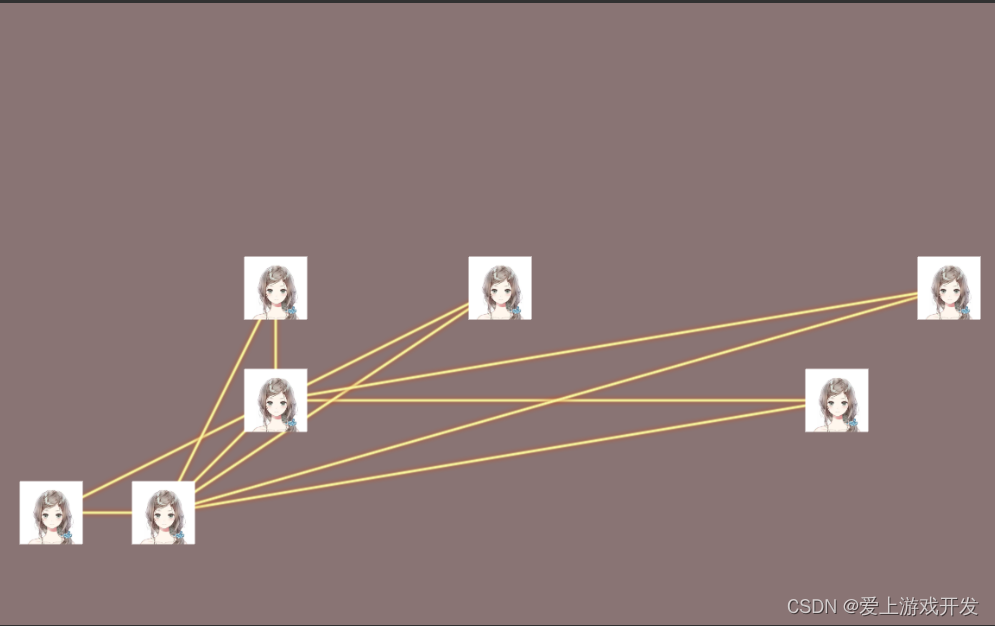
尝试2
仔细看看这个网格图,貌似在哪见过哪儿见过,努力一回忆,这不就是大学求最短路径的那种图嘛。
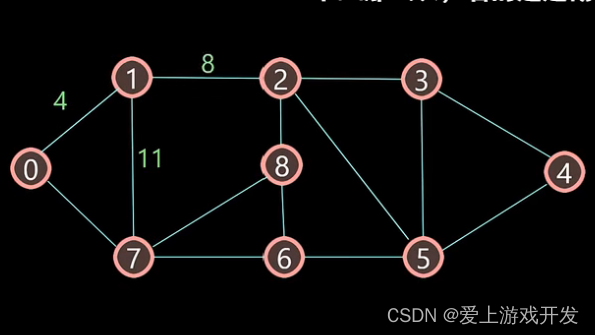

毕竟我也是上过学的,貌似是使用Dijkstra算法算法求最短路径。确认过眼神,你是对的算法。--创建Dijkstra算法权中路径表 local function CreateEdges() local edges = {} for i,v in ipairs(map) do local pos1 = v.coordinate[1]*10+v.coordinate[2] edges[pos1] = {} for a,b in ipairs(v.link) do local coordinate1 = v.coordinate local coordinate2 = base.node_coordinate_proto[b].coordinate local x = coordinate2[1] - coordinate1[1] local y = coordinate2[2] - coordinate1[2] local pos2 = coordinate2[1]*10+coordinate2[2] edges[pos1][pos2] = math.sqrt(x * x + y * y) end end printlog(edges,"edges =??????????") return edges end- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
运行发现,对于下图33——>32的路径,不存在32——>33的路径,这样写出来的程序肯定是有bug的。因为这个路径表的路径是带有方向的,即a与b之间有一条通路,a可以通往b,但b不可以通往a,这肯定是我们不愿意看到的,因此,我们还需要加入逆向路径:即当有a——>b路径时,我们需要判断是否存在b——>a的路径,不存在时需要手动添加。
local function CreateEdges() local edges = {} for i,v in ipairs(map) do local pos1 = v.coordinate[1]*10+v.coordinate[2] edges[pos1] = {} for a,b in ipairs(v.link) do local coordinate1 = v.coordinate local coordinate2 = base.node_coordinate_proto[b].coordinate local x = coordinate2[1] - coordinate1[1] local y = coordinate2[2] - coordinate1[2] local pos2 = coordinate2[1]*10+coordinate2[2] edges[pos1][pos2] = math.sqrt(x * x + y * y) end end printlog(edges,"edges =??????????") --添加逆向路径 for k,v in pairs(edges) do for a,b in pairs(v) do local pos = a edges[pos] = edges[pos] or {} local isExit = false for n,m in pairs(edges[pos]) do if n == k then --已经有逆向路径 isExit = true break end end if not isExit then edges[pos][k] = b end end end printlog(edges,"edges =添加逆向路径后的输出??????????") return edges end- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
使用Dijkstra算法:
local coordinate = map[1].coordinate currPos = coordinate[1]*10+coordinate[2] local function GetShortPath(_x,_y,_finishfunc) local edges = CreateEdges() local targetPos = _x*10+_y local path = dijkstra.StartDijkstra(currPos,targetPos,edges) printlog(path,"最短路径???") if path == nil then _finishfunc(false) return else _finishfunc(true) currPos = targetPos end end local targetPos = Vector2.New(4,6)--目标位置,假设是(4,6)点,实际应用中以鼠标点击位置为准 GetShortPath(targetPos.x,targetPos.y,function (_bool) if _bool then --找到最短路径,可以前往目的地 else --没有通路,不能前往目的地 end end)- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
算法测试通过之后,为了让肉眼清楚的看到路径,我们需要放上一个小人,在路上走动。
首先实例化小人:--prefab是将要实例化的对象parent是挂载的父节点 local player = GameObject.Instantiate(prefab, parent.transform)- 1
- 2
根据需要到达的坐标,移动小人
function chapterLevel.MoveToPos(path,idx,len) local pos = path[idx] local y = pos%10 local x = (pos-y)/10 local target = Vector3.New(x*100,y*100,0) local mypos = player.transform.localPosition if target.x == mypos.x and target.y == mypos.y then return end ChangeDir(target) local distance = Vector3.Distance(target , player.transform.localPosition) local time = distance/400 playerAnim:SetBool("run", true) player.transform:DOLocalMove(target, time):SetEase(Ease.Linear):OnComplete( function () if idx<=1 then playerAnim:SetBool("idle", false) else base.MoveToPos(path,idx-1,len)--递归执行两点之间的移动 end end ) end GetShortPath(coordinate[1],coordinate[2],function (_bool,path) if _bool then local len = table.tablelen(path) base.MoveToPos(path,len-1,len) end end)- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
为了让小人看上去逼真一点,我们需要给他加上动画,根据需要,加上跑步和待机动画
local playerAnim = utils.getcom(player, "Animator")--获取动画组件- 1
当需要移动的时候执行:
playerAnim:SetBool("run", true)- 1
移动结束执行:
base.playerAnim:SetBool("idle", true)- 1
因为人物移动时,按照常理来说都是面朝移动方向的,所以我们还需要加上人物转向的代码:
local function GetAngle(from , to, anglen) local angle = Vector2.Angle(from,to) local sign = nil if Vector3.Dot(Vector3.New(0,0,1),Vector3.Cross(Vector3.New(from.x,from.y,0),Vector3.New(to.x,to.y,0))) > 0 then sign = 1 else sign = -1 end return angle * sign end local mydirNor = Vector2.New(1,0)--开始默认朝向 local funciton ChangeDir(target) local oppsitionVec = target - player.transform.localPosition local dirNor = Vector2.Normalize(Vector2.New(oppsitionVec.x,oppsitionVec.y)) local anglen = Vector3.New(0,1,0) local angle = GetAngle(mydirNor , dirNor, anglen) mydirNor = dirNor player.transform.rotation = Quaternion.AngleAxis(angle, anglen)*player.transform.rotation end- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
这时候运行发现,几近完美。效果如下:

使用Dijkstra算法人物移动完整代码入下:
--创建Dijkstra算法需要的路径表 local function CreateEdges() local edges = {} for i,v in ipairs(map) do local pos1 = v.coordinate[1]*10+v.coordinate[2] edges[pos1] = {} for a,b in ipairs(v.link) do local coordinate1 = v.coordinate local coordinate2 = base.node_coordinate_proto[b].coordinate local x = coordinate2[1] - coordinate1[1] local y = coordinate2[2] - coordinate1[2] local pos2 = coordinate2[1]*10+coordinate2[2] edges[pos1][pos2] = math.sqrt(x * x + y * y) end end printlog(edges,"edges =??????????") --添加逆向路径 for k,v in pairs(edges) do for a,b in pairs(v) do local pos = a edges[pos] = edges[pos] or {} local isExit = false for n,m in pairs(edges[pos]) do if n == k then --已经有逆向路径 isExit = true break end end if not isExit then edges[pos][k] = b end end end printlog(edges,"edges =添加逆向路径后的输出??????????") return edges end --利用Dijkstra算法获取最短路径 function chapterLevel.GetShortPath(_x,_y,_finishfunc) local edges = CreateEdges() local targetPos = _x*10+_y local path = dijkstra.StartDijkstra(currPos,targetPos,edges)--使用Dijkstra算法获取最短路径 printlog(path,"最短路径???") if table.tablelen(path) <=1 then--只有一个点代表是起点,没有通路 _finishfunc(false) return else _finishfunc(true,path) currPos = targetPos end end --获取当前朝向与目标朝向之间的角度 local function GetAngle(from , to, anglen) local angle = Vector2.Angle(from,to) local sign = nil if Vector3.Dot(Vector3.New(0,0,1),Vector3.Cross(Vector3.New(from.x,from.y,0),Vector3.New(to.x,to.y,0))) > 0 then sign = 1 else sign = -1 end local signed_angle = angle * sign return signed_angle end --改变人物朝向 local function ChangeDir(target) local oppsitionVec = target - player.transform.localPosition local dirNor = Vector2.Normalize(Vector2.New(oppsitionVec.x,oppsitionVec.y)) local anglen = Vector3.New(0,1,0) local angle = GetAngle(base.mydirNor , dirNor, anglen) base.mydirNor = dirNor base.herogo.transform.rotation = Quaternion.AngleAxis(angle, anglen)*base.herogo.transform.rotation end --根据最短路径执行移动操作 function chapterLevel.MoveToPos(path,idx,len) local pos = path[idx] local y = pos%10 local x = (pos-y)/10 local target = Vector3.New(x*100,y*100,0) local mypos = player.transform.localPosition if target.x == mypos.x and target.y == mypos.y then return end ChangeDir(target) local distance = Vector3.Distance(target , player.transform.localPosition) local time = distance/400 playerAnim:SetBool("run", true) player.transform:DOLocalMove(target, time):SetEase(Ease.Linear):OnComplete( function () if idx<=1 then playerAnim:SetBool("idle", false) else base.MoveToPos(path,idx-1,len)--递归执行两点之间的移动 end end ) end -- 点击某个关卡图标 local function ClickLevelItem(_go,idx) printlog(idx,"点击了的关卡下标") local coordinate = map[idx].coordinate GetShortPath(coordinate[1],coordinate[2],function (_bool,path) if _bool then local len = table.tablelen(path) base.MoveToPos(path,len-1,len) end end) end- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
-
相关阅读:
【SpringBoot】详细介绍SpringBoot中Entity类中的getters和setters
如何使用SQL系列 之 如何在SQL中使用视图
设计模式:工厂方法模式(C#、JAVA、JavaScript、C++、Python、Go、PHP):
IDEA通过Docker插件部署SpringBoot项目
SpringBoot如何集成Log模块呢?
艾美捷ProSci丨ProSci AADACL1 肽说明书
萤火虫模糊回归算法(Matlab代码实现)
金蝶云星空简单账表动态列名汇总
如何在微信小程序中集成认证服务—手机号码篇
消息队列的原理与基本使用
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/shirln/article/details/125498483
