-
PyQt5快速开发与实战 7.4 事件处理机制入门 and 7.5 窗口数据传递
PyQt5快速开发与实战
7. 第7章 PyQt5 信号与槽
7.4 事件处理机制入门
当采用信号和槽机制处理不了时,才考虑时候事件处理机制。
7.4.1 事件和信号与槽的区别
信号与槽可以说是对事件处理机制的高级封装,如果说事件是用来创建窗口控件的,那么信号与槽就是用来对这个窗口控件进行使用的。比如一个按钮,当使用这个按钮时,只关心clicked信号,至于这个按钮如何接收并处理鼠标点击事件,然后再发射这个信号,则不用关心。但是如果要重载一个按钮,这时就要关心这个问题了。比如可以改变它的行为:在鼠标按键按下时触发clicked信号,而不是在释放时。
7.4.2 常见事件类型
PyQt是对Qt的封装,Qt程序是事件驱动的,它的每个动作都由幕后某个事件所触发。
Qt事件的类型有很多,常见的Qt事件:
- 键盘事件:按键按下和松开。
- 鼠标事件:鼠标指针移动、鼠标按键按下和松开。
- 拖放事件:用鼠标进行拖放。
- 滚轮事件:鼠标滚轮滚动。
- 绘屏事件:重绘屏幕的某些部分。
- 定时事件:定时器到时。
- 焦点事件:键盘焦点移动。
- 进入和离开事件:鼠标指针移入Widget内,或者移出。
- 移动事件:Widget的位置改变
- 大小改变事件:Widget的大小改变
- 显示和隐藏事件:Widget显示和隐藏
- 窗口事件:窗口是否为当前窗口。
还有一些常见的Qt事件,比如 Socket事件、剪贴板事件、字体改变事件、布局改变事件等。
7.4.3 使用事件处理的方法
PyQt提供了如下5种事件处理和过滤方法(由弱到强),其中只有前两种方法使用最频繁。
-
重新实现事件函数
比如 mousePressEvent()、keyPressEvent()、paintEvent()。这是最常规的事件处理方法。
-
重新实现QObject.event()
一般用在 PyQt没有提供该事件的处理函数的情况下,即增加新事件时。
-
安装事件过滤器
如果对QObject 调用installEventFilter,则相当于为这个 QObject 安装了一个事件过滤器,对于QObject的全部事件来说,它们都会先传递到事件过滤函数eventFilter中,在这个函数中我们可以抛弃或者修改这些事件,比如可以对自己感兴趣的事件使用自定义的事件处理机制,对其他事件使用默认的事件处理机制。由于这种万法会对调用installEventFilter 的所有QObject的事件进行过滤,因此如果要更过滤的事件比较多,则会降低程序的性能。
-
在QApplication中安装事件过滤器
这种方法比上一种方法更强大:QApplication的事件过滤器将捕获所有 QObject的所有事件,而且第一个获得该事件。也就是说,在将事件发送给其他任何一个事件过滤器之前(就是在第三种方法之前),都会先发送给QApplication的事件过滤器。
-
重新实现QApplication的notify()方法
PyQt使用notify()来分发事件。要想在任何事件处理器之前捕获事件,唯一的方法就是重新实现QApplication的notify()。在实践中,在调试时才会使用这种方法。
7.4.4 经典案例分析
前两种事件处理案例
import sys from PyQt5.QtCore import (QEvent, QTimer, Qt) from PyQt5.QtWidgets import (QApplication, QMenu, QWidget) from PyQt5.QtGui import QPainter class Widget(QWidget): def __init__(self, parent=None): super(Widget, self).__init__(parent) self.justDoubleClicked = False self.key = "" self.text = "" self.message = "" self.resize(400, 300) self.move(100, 100) self.setWindowTitle("Events") QTimer.singleShot(0, self.giveHelp) # 避免窗口大小重绘事件的影响,可以把参数0改变成3000(3秒),然后在运行,就可以明白这行代码的意思。 def giveHelp(self): self.text = "请点击这里触发追踪鼠标功能" self.update() # 重绘事件,也就是触发paintEvent函数。 '''重新实现关闭事件''' def closeEvent(self, event): print("Closed") '''重新实现上下文菜单事件''' def contextMenuEvent(self, event): menu = QMenu(self) oneAction = menu.addAction("&One") twoAction = menu.addAction("&Two") oneAction.triggered.connect(self.one) twoAction.triggered.connect(self.two) if not self.message: menu.addSeparator() threeAction = menu.addAction("Thre&e") threeAction.triggered.connect(self.three) menu.exec_(event.globalPos()) '''上下文菜单槽函数''' def one(self): self.message = "Menu option One" self.update() def two(self): self.message = "Menu option Two" self.update() def three(self): self.message = "Menu option Three" self.update() '''重新实现绘制事件''' def paintEvent(self, event): text = self.text i = text.find("\n\n") if i >= 0: text = text[0:i] if self.key: # 若触发了键盘按钮,则在文本信息中记录这个按钮信息。 text += "\n\n你按下了: {0}".format(self.key) painter = QPainter(self) painter.setRenderHint(QPainter.TextAntialiasing) painter.drawText(self.rect(), Qt.AlignCenter, text) # 绘制信息文本的内容 if self.message: # 若消息文本存在则在底部居中绘制消息,5秒钟后清空消息文本并重绘。 painter.drawText(self.rect(), Qt.AlignBottom | Qt.AlignHCenter, self.message) QTimer.singleShot(5000, self.clearMessage) QTimer.singleShot(5000, self.update) '''清空消息文本的槽函数''' def clearMessage(self): self.message = "" '''重新实现调整窗口大小事件''' def resizeEvent(self, event): self.text = "调整窗口大小为: QSize({0}, {1})".format( event.size().width(), event.size().height()) self.update() '''重新实现鼠标释放事件''' def mouseReleaseEvent(self, event): # 若鼠标释放为双击释放,则不跟踪鼠标移动 # 若鼠标释放为单击释放,则需要改变跟踪功能的状态,如果开启跟踪功能的话就跟踪,不开启跟踪功能就不跟踪 if self.justDoubleClicked: self.justDoubleClicked = False else: self.setMouseTracking(not self.hasMouseTracking()) # 单击鼠标 if self.hasMouseTracking(): self.text = "开启鼠标跟踪功能.\n" + \ "请移动一下鼠标!\n" + \ "单击鼠标可以关闭这个功能" else: self.text = "关闭鼠标跟踪功能.\n" + \ "单击鼠标可以开启这个功能" self.update() '''重新实现鼠标移动事件''' def mouseMoveEvent(self, event): if not self.justDoubleClicked: globalPos = self.mapToGlobal(event.pos()) # 窗口坐标转换为屏幕坐标 self.text = """鼠标位置: 窗口坐标为:QPoint({0}, {1}) 屏幕坐标为:QPoint({2}, {3}) """.format(event.pos().x(), event.pos().y(), globalPos.x(), globalPos.y()) self.update() '''重新实现鼠标双击事件''' def mouseDoubleClickEvent(self, event): self.justDoubleClicked = True self.text = "你双击了鼠标" self.update() '''重新实现键盘按下事件''' def keyPressEvent(self, event): self.key = "" if event.key() == Qt.Key_Home: self.key = "Home" elif event.key() == Qt.Key_End: self.key = "End" elif event.key() == Qt.Key_PageUp: if event.modifiers() & Qt.ControlModifier: self.key = "Ctrl+PageUp" else: self.key = "PageUp" elif event.key() == Qt.Key_PageDown: if event.modifiers() & Qt.ControlModifier: self.key = "Ctrl+PageDown" else: self.key = "PageDown" elif Qt.Key_A <= event.key() <= Qt.Key_Z: if event.modifiers() & Qt.ShiftModifier: self.key = "Shift+" self.key += event.text() if self.key: self.key = self.key self.update() else: QWidget.keyPressEvent(self, event) '''重新实现其他事件,适用于PyQt没有提供该事件的处理函数的情况,Tab键由于涉及焦点切换,不会传递给keyPressEvent,因此,需要在这里重新定义。''' def event(self, event): if (event.type() == QEvent.KeyPress and event.key() == Qt.Key_Tab): self.key = "在event()中捕获Tab键" self.update() return True return QWidget.event(self, event) if __name__ == "__main__": from pyqt5_plugins.examples.exampleqmlitem import QtCore QtCore.QCoreApplication.setAttribute(QtCore.Qt.AA_EnableHighDpiScaling) app = QApplication(sys.argv) form = Widget() form.show() app.exec_()- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
- 134
- 135
- 136
- 137
- 138
- 139
- 140
- 141
- 142
- 143
- 144
- 145
- 146
- 147
- 148
- 149
- 150
- 151
- 152
- 153
- 154
- 155

第三种事件处理方法
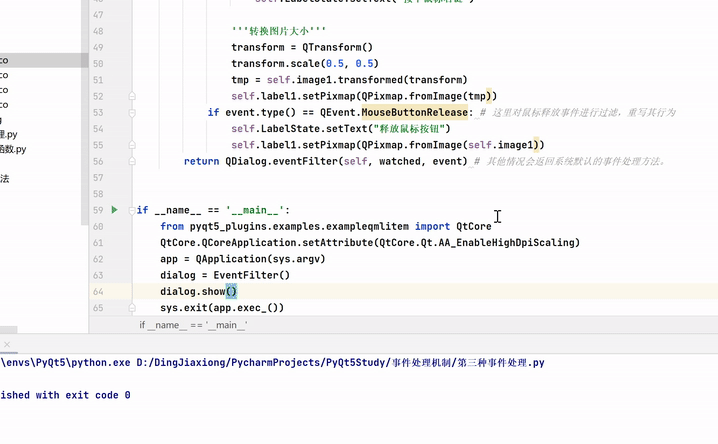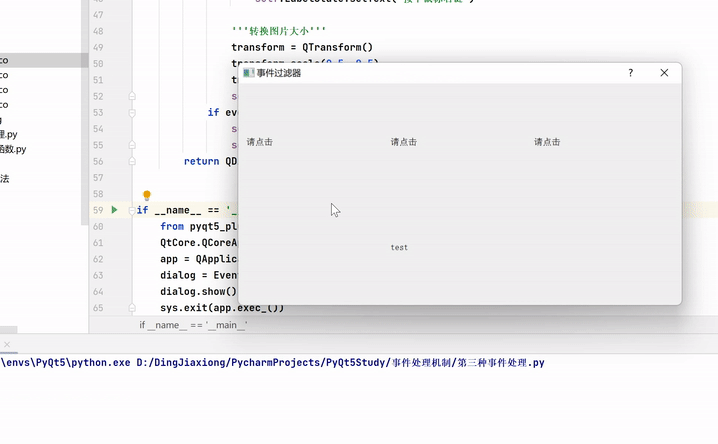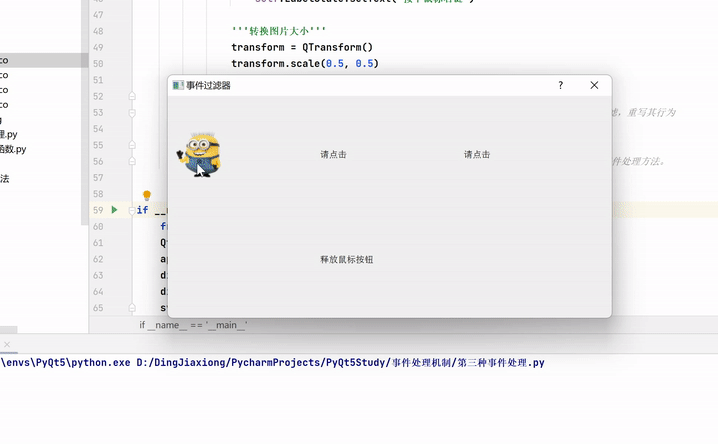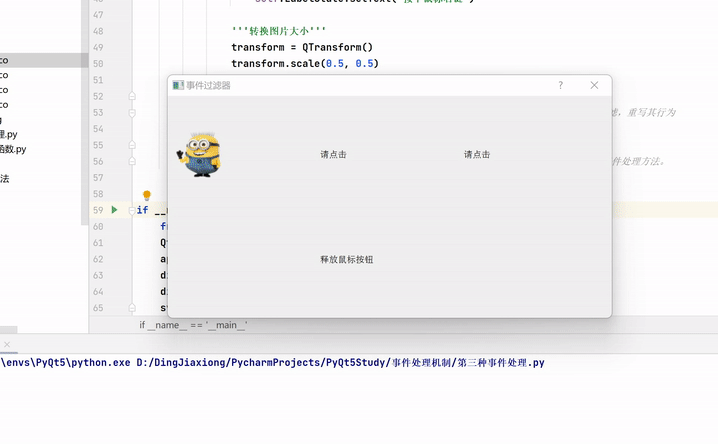
from PyQt5.QtGui import * from PyQt5.QtCore import * from PyQt5.QtWidgets import * import sys class EventFilter(QDialog): def __init__(self, parent=None): super(EventFilter, self).__init__(parent) self.setWindowTitle("事件过滤器") self.label1 = QLabel("请点击") self.label2 = QLabel("请点击") self.label3 = QLabel("请点击") self.LabelState = QLabel("test") self.image1 = QImage("images/cartoon1.ico") self.image2 = QImage("images/cartoon2.ico") self.image3 = QImage("images/cartoon3.ico") self.width = 600 self.height = 300 self.resize(self.width, self.height) self.label1.installEventFilter(self) self.label2.installEventFilter(self) self.label3.installEventFilter(self) mainLayout = QGridLayout(self) mainLayout.addWidget(self.label1, 500, 0) mainLayout.addWidget(self.label2, 500, 1) mainLayout.addWidget(self.label3, 500, 2) mainLayout.addWidget(self.LabelState, 600, 1) self.setLayout(mainLayout) def eventFilter(self, watched, event): if watched == self.label1: # 只对label1的点击事件进行过滤,重写其行为,其他的事件会被忽略 if event.type() == QEvent.MouseButtonPress: # 这里对鼠标按下事件进行过滤,重写其行为 mouseEvent = QMouseEvent(event) if mouseEvent.buttons() == Qt.LeftButton: self.LabelState.setText("按下鼠标左键") elif mouseEvent.buttons() == Qt.MidButton: self.LabelState.setText("按下鼠标中间键") elif mouseEvent.buttons() == Qt.RightButton: self.LabelState.setText("按下鼠标右键") '''转换图片大小''' transform = QTransform() transform.scale(0.5, 0.5) tmp = self.image1.transformed(transform) self.label1.setPixmap(QPixmap.fromImage(tmp)) if event.type() == QEvent.MouseButtonRelease: # 这里对鼠标释放事件进行过滤,重写其行为 self.LabelState.setText("释放鼠标按钮") self.label1.setPixmap(QPixmap.fromImage(self.image1)) return QDialog.eventFilter(self, watched, event) # 其他情况会返回系统默认的事件处理方法。 if __name__ == '__main__': from pyqt5_plugins.examples.exampleqmlitem import QtCore QtCore.QCoreApplication.setAttribute(QtCore.Qt.AA_EnableHighDpiScaling) app = QApplication(sys.argv) dialog = EventFilter() dialog.show() sys.exit(app.exec_())- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
7.5 窗口数据传递
在开发程序时,如果这个程序只有一个窗口,则应该关心这个窗口里面的各个控件之间是如何传递数据的;如果这个程序有多个窗口,那么还应该关心不同的窗口之间是如何传递数据的。
7.5.1 单个窗口数据传递
对于具有单一窗口的程序来说,一个控件的变化会影响另一个控件的变化,这种变化利用信号与槽机制非常容易解决。
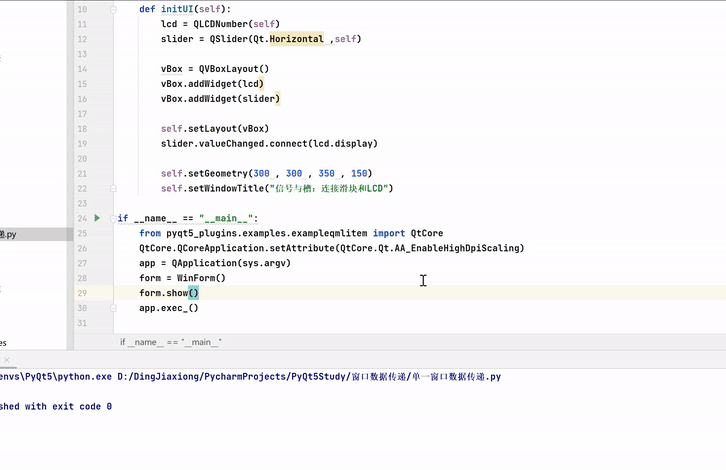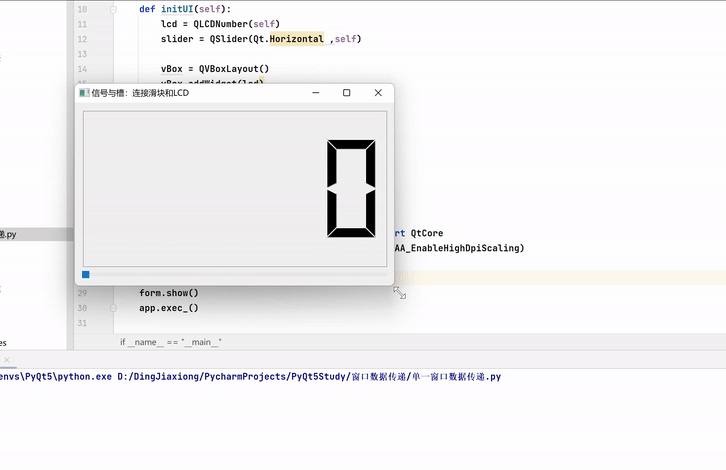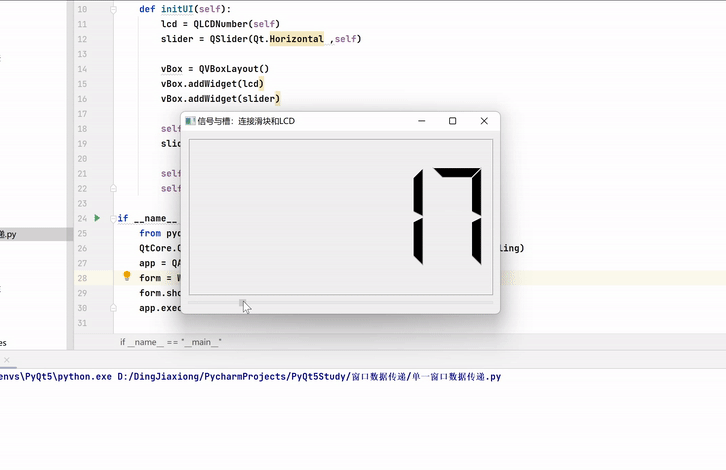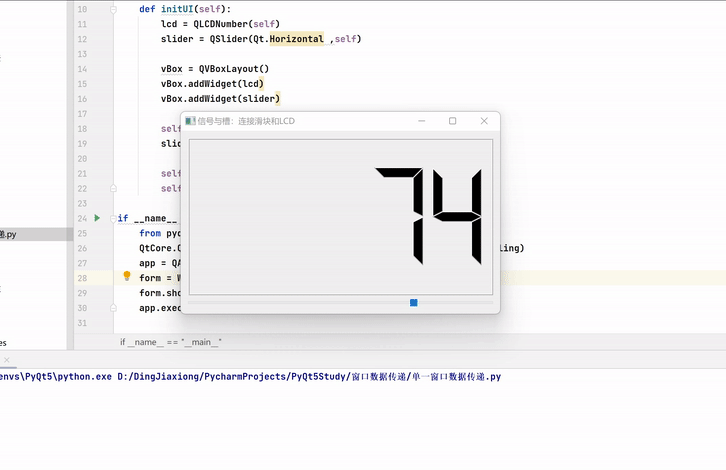
案例——使用滑块控制LCD变化
import sys from PyQt5.QtWidgets import * from PyQt5.QtCore import * class WinForm(QWidget): def __init__(self): super().__init__() self.initUI() def initUI(self): lcd = QLCDNumber(self) slider = QSlider(Qt.Horizontal ,self) vBox = QVBoxLayout() vBox.addWidget(lcd) vBox.addWidget(slider) self.setLayout(vBox) slider.valueChanged.connect(lcd.display) self.setGeometry(300 , 300 , 350 , 150) self.setWindowTitle("信号与槽:连接滑块和LCD") if __name__ == "__main__": from pyqt5_plugins.examples.exampleqmlitem import QtCore QtCore.QCoreApplication.setAttribute(QtCore.Qt.AA_EnableHighDpiScaling) app = QApplication(sys.argv) form = WinForm() form.show() app.exec_()- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
7.5.2 多窗口数据传递:调用属性
在PyQt编程过程中,经常会遇到输入或选择多个参数的问题。把多个参数写到一个窗口中,主窗口会显得很臃肿,所以一般是添加一个按钮,调用对话框,在对话框中进行参数的选择,关闭对话框时将参数值返回给主窗口。
PyQt提供了一些标准的对话框类,用于输入数据、修改数据、更改应用的设置等,常见的有QFileDialog、QInputDialog、QColorDialog、QFontDialog等。在不同
的窗口之间传参有两种常用的方式:一种是在自定义对话框之间通过属性传参;另一种是在窗口之间使用信号与槽机制传参。示例:
自定义对话框
from PyQt5.QtCore import * from PyQt5.QtGui import * from PyQt5.QtWidgets import * class DateDialog(QDialog): def __init__(self, parent=None): super(DateDialog, self).__init__(parent) self.setWindowTitle('DateDialog') # 在布局中添加部件 layout = QVBoxLayout(self) self.datetime = QDateTimeEdit(self) self.datetime.setCalendarPopup(True) self.datetime.setDateTime(QDateTime.currentDateTime()) layout.addWidget(self.datetime) # 使用两个button(ok和cancel)分别连接accept()和reject()槽函数 buttons = QDialogButtonBox( QDialogButtonBox.Ok | QDialogButtonBox.Cancel, Qt.Horizontal, self) buttons.accepted.connect(self.accept) buttons.rejected.connect(self.reject) layout.addWidget(buttons) # 从对话框中获取当前日期和时间 def dateTime(self): return self.datetime.dateTime() # 静态方法创建对话框并返回 (date, time, accepted) @staticmethod def getDateTime(parent=None): dialog = DateDialog(parent) result = dialog.exec_() date = dialog.dateTime() return (date.date(), date.time(), result == QDialog.Accepted)- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
调用对话框的主窗口文件
import sys from PyQt5.QtCore import * from PyQt5.QtGui import * from PyQt5.QtWidgets import * from DateDialog import DateDialog class WinForm(QWidget): def __init__(self, parent=None): super(WinForm, self).__init__(parent) self.resize(400, 90) self.setWindowTitle('对话框关闭时返回值给主窗口例子') self.lineEdit = QLineEdit(self) self.button1 = QPushButton('弹出对话框1') self.button1.clicked.connect(self.onButton1Click) self.button2 = QPushButton('弹出对话框2') self.button2.clicked.connect(self.onButton2Click) gridLayout = QGridLayout() gridLayout.addWidget(self.lineEdit) gridLayout.addWidget(self.button1) gridLayout.addWidget(self.button2) self.setLayout(gridLayout) def onButton1Click(self): dialog = DateDialog(self) result = dialog.exec_() date = dialog.dateTime() self.lineEdit.setText(date.date().toString()) print('\n日期对话框的返回值') print('date=%s' % str(date.date())) print('time=%s' % str(date.time())) print('result=%s' % result) dialog.destroy() def onButton2Click(self): date, time, result = DateDialog.getDateTime() self.lineEdit.setText(date.toString()) print('\n日期对话框的返回值') print('date=%s' % str(date)) print('time=%s' % str(time)) print('result=%s' % result) if result == QDialog.Accepted: print('点击确认按钮') else: print('点击取消按钮') if __name__ == "__main__": from pyqt5_plugins.examples.exampleqmlitem import QtCore QtCore.QCoreApplication.setAttribute(QtCore.Qt.AA_EnableHighDpiScaling) app = QApplication(sys.argv) form = WinForm() form.show() sys.exit(app.exec_())- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57

第一种方法:直接在主窗口程序中实例化该对话框,然后调用该对话框的函数来获取返回值,根据对话框的返回值单击确认按钮还是取消按钮来进行下一步操作。
第二种方法:在主窗口程序中调用子窗口的静态函数,实际上这种方法与第一种方法是一样的,只不过它是利用静态函数的特点,在于窗口的静态函数中创建头例化对象。
7.5.3 多窗口数据传递:信号与槽
对于多窗口的数据传递,一般是通过子窗口发射信号的,主窗口通过槽函数捕获这个信号,然后获取信号里面的数据。子窗口发射的信号有两种,其中一种是发射PyQt内置的一些信号;另一种是发射自定义的信号。
发射自定义信号的好处是,它的参数类型可以自定义。比如发射一个自定义信号,它的参数类型可以为int、str、dict、list 等;如果发射内置信号,则只能是特定的几个参数。
示例:
对话框2:
from PyQt5.QtCore import * from PyQt5.QtGui import * from PyQt5.QtWidgets import * class DateDialog(QDialog): Signal_OneParameter = pyqtSignal(str) def __init__(self, parent=None): super(DateDialog, self).__init__(parent) self.setWindowTitle('子窗口:用来发射信号') # 在布局中添加部件 layout = QVBoxLayout(self) self.label = QLabel(self) self.label.setText('前者发射内置信号\n后者发射自定义信号') self.datetime_inner = QDateTimeEdit(self) self.datetime_inner.setCalendarPopup(True) self.datetime_inner.setDateTime(QDateTime.currentDateTime()) self.datetime_emit = QDateTimeEdit(self) self.datetime_emit.setCalendarPopup(True) self.datetime_emit.setDateTime(QDateTime.currentDateTime()) layout.addWidget(self.label) layout.addWidget(self.datetime_inner) layout.addWidget(self.datetime_emit) # 使用两个button(ok和cancel)分别连接accept()和reject()槽函数 buttons = QDialogButtonBox( QDialogButtonBox.Ok | QDialogButtonBox.Cancel, Qt.Horizontal, self) buttons.accepted.connect(self.accept) buttons.rejected.connect(self.reject) layout.addWidget(buttons) self.datetime_emit.dateTimeChanged.connect(self.emit_signal) def emit_signal(self): date_str = self.datetime_emit.dateTime().toString() self.Signal_OneParameter.emit(date_str)- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
主窗口
import sys from PyQt5.QtCore import * from PyQt5.QtGui import * from PyQt5.QtWidgets import * from DateDialog2 import DateDialog class WinForm(QWidget): def __init__(self, parent=None): super(WinForm, self).__init__(parent) self.resize(400, 90) self.setWindowTitle('信号与槽传递参数的示例') self.open_btn = QPushButton('获取时间') self.lineEdit_inner = QLineEdit(self) self.lineEdit_emit = QLineEdit(self) self.open_btn.clicked.connect(self.openDialog) self.lineEdit_inner.setText('接收子窗口内置信号的时间') self.lineEdit_emit.setText('接收子窗口自定义信号的时间') grid = QGridLayout() grid.addWidget(self.lineEdit_inner) grid.addWidget(self.lineEdit_emit) grid.addWidget(self.open_btn) self.setLayout(grid) def openDialog(self): dialog = DateDialog(self) '''连接子窗口的内置信号与主窗口的槽函数''' dialog.datetime_inner.dateTimeChanged.connect(self.deal_inner_slot) '''连接子窗口的自定义信号与主窗口的槽函数''' dialog.Signal_OneParameter.connect(self.deal_emit_slot) dialog.show() def deal_inner_slot(self, date): self.lineEdit_inner.setText(date.toString()) def deal_emit_slot(self, dateStr): self.lineEdit_emit.setText(dateStr) if __name__ == "__main__": from pyqt5_plugins.examples.exampleqmlitem import QtCore QtCore.QCoreApplication.setAttribute(QtCore.Qt.AA_EnableHighDpiScaling) app = QApplication(sys.argv) form = WinForm() form.show() sys.exit(app.exec_())- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52

-
相关阅读:
深入了解Java8新特性-日期时间API之ZonedDateTime类
强大易用的开源 建站工具Halo
ARM Cortex-M3从汇编到C,从Boot到应用的教程
APP应用开发sdk版本过低可能性原因问题排查及解决方案
某城商银行生产容器云平台详细设计方案分享及经验总结
计算机网络 网络原理之Http
idea 将项目上传到gitee远程仓库具体操作
二、【redux】redux 完整版求和Demo
pytorch(b站小土堆学习笔记P1-P15)
Git同时配置和提交代码到Github和Gitee
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_44226181/article/details/126067196
