-
ReentrantLock 类 源代码详细解释
什么是可重入锁,怎么理解可重入?
所谓的可重入就是一个线程获取到了锁之后,同一个线程还是想要再次的获取到这个锁,那么这个锁可以再次的被获取到,那么这个锁就是可重入锁。否则这个,锁就是不可重入锁。
ReentrantLock 实现原理
public class ReentrantLock implements Lock, java.io.Serializable { ...... ...... }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
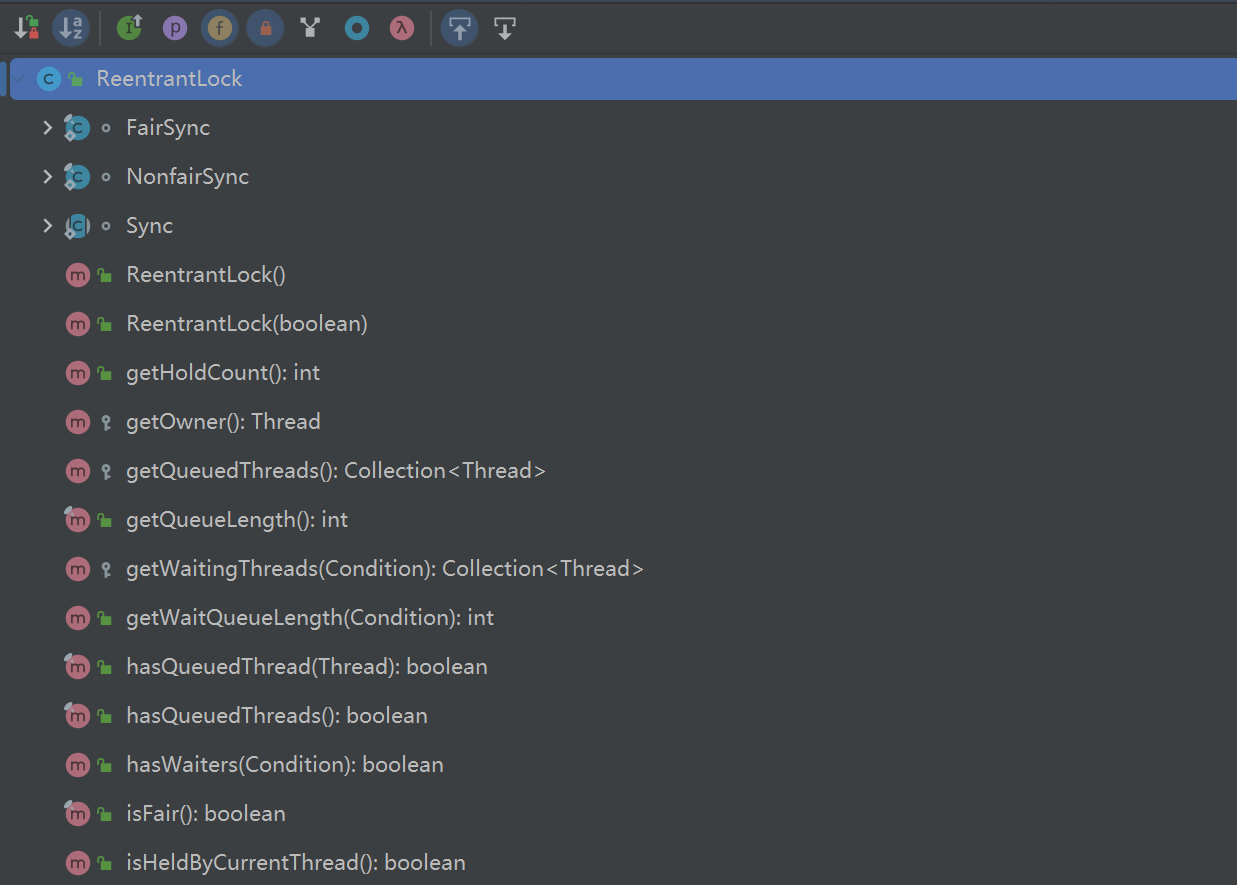
在 idea 打开这个类的时候,在 ReentrantLock 中存在三个内部类以及自己的一系列方法。一个公平锁的内部类,一个非公平锁的内部类,一个 Sync 类继承了抽象队列同步器,继承了相关的方法,可以使用多个等待条件实现同步在类的顶部可以看到实现了 Lock 接口,也就是有了基本的显式声明锁,获取锁的能力。同时实现了序列化接。Serialization(序列化)是一种将对象以一连串的字节描述的过程;反序列化deserialization是一种将这些字节重建成一个对象的过程。 对象数据需要在网络中传输的时候,或者将 Java 独享保存早磁盘的时候,需要使用序列化以及反序列化。
构造方法的实现
// 创造出来一个不公平的锁 /** * Creates an instance of {@code ReentrantLock}. * This is equivalent to using {@code ReentrantLock(false)}. */ public ReentrantLock() { sync = new NonfairSync(); } // 创建出来一个公平锁 /** * Creates an instance of {@code ReentrantLock} with the * given fairness policy. * * @param fair {@code true} if this lock should use a fair ordering policy */ public ReentrantLock(boolean fair) { sync = fair ? new FairSync() : new NonfairSync(); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
其他方法的实现
查看源代码的时候注意到:在这个类中的相关方法只是一个语法糖,真正调用的是内部类 Sync 引用调用的方法。所以说 ReentrantLock 就是一个基于 AQS 创建出来的可重入锁。一方面,ReentrantLock 具有自己特定的加锁,解锁的方法,另外一方便,由于这个类继承了 AQS ,所以具有 AQS 的特性。

ReentrantLock 核心 - Sync - 核心方法
/** * Base of synchronization control for this lock. Subclassed * into fair and nonfair versions below. Uses AQS state to * represent the number of holds on the lock. */ abstract static class Sync extends AbstractQueuedSynchronizer { private static final long serialVersionUID = -5179523762034025860L; /** * Performs {@link Lock#lock}. The main reason for subclassing * is to allow fast path for nonfair version. */ // 定义抽象方法,获取锁 abstract void lock(); /** * Performs non-fair tryLock. tryAcquire is implemented in * subclasses, but both need nonfair try for trylock method. */ /** 尝试获取到锁,拿到锁的话返回 true, 否则返回 false; 如果是当前线程已经获取到了锁,是可以重入的,这个是重入的核心 */ final boolean nonfairTryAcquire(int acquires) { // 获取当前的线程,就是什么线程调用了这个方法 final Thread current = Thread.currentThread(); // state 是 AQS 提供的变量,通过这个变量可以控制锁被线程获取的次数 int c = getState(); if (c == 0) { // 以为 c== 0 ,这个时候锁还是没有被线程获取到的 if (compareAndSetState(0, acquires)) { // 由于锁还没有被使用,这个直接把锁给当前的线程 setExclusiveOwnerThread(current); // 当前的线程获取到了锁,那么返回 true 即可 return true; } } else if (current == getExclusiveOwnerThread()) { // current == getExclusiveOwnerThread() // 当前线程和前面已经获取到锁的线程是一个线程,那么下面实现锁的重入 // 当前线程持有锁的时候, state + 1 int nextc = c + acquires; // 记录所重入的次数 // 拥有锁的线程数量大于 MAX_INTEGER 会变为负数,所以是 overflow if (nextc < 0) // overflow throw new Error("Maximum lock count exceeded"); // AQS 的 state 随着重入次数的增加而增加 setState(nextc); return true; } // 如果一个线程既不是第一次获取到锁,也不能实现重入,那么就返回 false return false; } protected final boolean tryRelease(int releases) { // 计算一个线程释放了锁之后的 state 的值 int c = getState() - releases; // 持有锁的线程不是当前的线程,那么无法释放资源的,谁拿了谁才能释放锁 if (Thread.currentThread() != getExclusiveOwnerThread()) // 抛出来异常,没有拿锁,竟然想要释放锁,不被允许 throw new IllegalMonitorStateException(); boolean free = false; // state == 0 的时候,需要将 free 改为 true 表示已经释放了 // 同时把持有者的信息抹掉,其他的线程才能继续的获取到锁 if (c == 0) { free = true; // 标志位修改 setExclusiveOwnerThread(null); // 持有锁的信息抹掉 } // 因为持有锁的线程把锁放了,这里的 state 也就是变为了 0 setState(c); // 释放成功,没有线程拿着这个锁了,free 就是 true, 其他的线程可以使用这个锁了 return free; } protected final boolean isHeldExclusively() { // While we must in general read state before owner, // we don't need to do so to check if current thread is owner return getExclusiveOwnerThread() == Thread.currentThread(); } final ConditionObject newCondition() { return new ConditionObject(); } // Methods relayed from outer class final Thread getOwner() { return getState() == 0 ? null : getExclusiveOwnerThread(); } final int getHoldCount() { return isHeldExclusively() ? getState() : 0; } final boolean isLocked() { return getState() != 0; } /** * Reconstitutes the instance from a stream (that is, deserializes it). */ private void readObject(java.io.ObjectInputStream s) throws java.io.IOException, ClassNotFoundException { s.defaultReadObject(); setState(0); // reset to unlocked state } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
ReentrantLock 核心 - NonfairSync
/** * Sync object for non-fair locks */ /** 这个是 ReentrantLock 中的非公平锁的实现源码,默认使用的是非公平锁 */ static final class NonfairSync extends Sync { private static final long serialVersionUID = 7316153563782823691L; /** * Performs lock. Try immediate barge, backing up to normal * acquire on failure. */ final void lock() { // 做一个 CAS 操作, CAS 成功,说明以前没有线程获取到锁 // 将当前线程独占锁,圈地 if (compareAndSetState(0, 1)) setExclusiveOwnerThread(Thread.currentThread()); else // 无法获取到锁,说明锁已经被占用了 // 调用下面的 acquare() 方法 // 注意:在 acquare() 中后面还有一系列的方法,这里没有展示出来 // 执行的逻辑就是: // 1.持有锁的线程是自己,那么重入即可 // 2.持有锁的线程不是自己,那么去 AQS 中排队 // 3.在 AQS 中排队使用的是双向链表。addWaiter() 方法中创造结点,把需要排队的线程信息放进去 // 按照尾插法将需要排队的线程放进去 Node 结点中保存 acquire(1); } /** 在非公平锁中获取锁还有下面的一种方式,使用 tryAcquire() 走的是 nonfairTryAcquire() 这个方法 */ protected final boolean tryAcquire(int acquires) { // 在 nonfairTryAcquire(1) 方法中传递 1 进去 // 进去到上面解析的代码中,存在两种情况: // 1.持有锁的线程是自己,那么重入即可 // 2.持有锁的线程不是自己,那么去 AQS 中排队 return nonfairTryAcquire(acquires); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
ReentrantLock 核心 - FairSync
按照排队的方式获取锁,FIFO 的原则,十分的公平
/** * Sync object for fair locks */ static final class FairSync extends Sync { private static final long serialVersionUID = -3000897897090466540L; final void lock() { acquire(1); } /** * Fair version of tryAcquire. Don't grant access unless * recursive call or no waiters or is first. */ protected final boolean tryAcquire(int acquires) { final Thread current = Thread.currentThread(); int c = getState(); if (c == 0) { /** * 公平锁与非公平锁很大的一个区别是: * 在尝试获取锁的时候,如果AQS的同步队列中有其他线程在等待获取锁 * 则尝试获取锁失败,需要进入AQS的同步队列排队 * hasQueuedPredecessors方法判断AQS的同步队列是否有线程在等待 */ if (!hasQueuedPredecessors() && compareAndSetState(0, acquires)) { setExclusiveOwnerThread(current); return true; } } else if (current == getExclusiveOwnerThread()) { int nextc = c + acquires; if (nextc < 0) throw new Error("Maximum lock count exceeded"); setState(nextc); return true; } return false; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
ReentrantLock() 类中非内部类剩下来的方法 0 部分省略
整体的代码执行了流程就是:
使用 Sync 类型的对象,调用相关的 lock() 的等方法。Sync 对象是基于公平锁实现还是基于非公平锁实现取决于构造方法。
这样通过构造方法实现了对于公平锁以及非公平锁的锁对象的控制。/** * Creates an instance of {@code ReentrantLock}. * This is equivalent to using {@code ReentrantLock(false)}. */ public ReentrantLock() { sync = new NonfairSync(); } /** * Creates an instance of {@code ReentrantLock} with the * given fairness policy. * * @param fair {@code true} if this lock should use a fair ordering policy */ public ReentrantLock(boolean fair) { sync = fair ? new FairSync() : new NonfairSync(); } /** * Acquires the lock. * *Acquires the lock if it is not held by another thread and returns * immediately, setting the lock hold count to one. * *
If the current thread already holds the lock then the hold * count is incremented by one and the method returns immediately. * *
If the lock is held by another thread then the * current thread becomes disabled for thread scheduling * purposes and lies dormant until the lock has been acquired, * at which time the lock hold count is set to one. */
public void lock() { sync.lock(); } public boolean tryLock() { return sync.nonfairTryAcquire(1); } public boolean tryLock(long timeout, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException { return sync.tryAcquireNanos(1, unit.toNanos(timeout)); } /** * Attempts to release this lock. * *If the current thread is the holder of this lock then the hold * count is decremented. If the hold count is now zero then the lock * is released. If the current thread is not the holder of this * lock then {@link IllegalMonitorStateException} is thrown. * * @throws IllegalMonitorStateException if the current thread does not * hold this lock */
public void unlock() { sync.release(1); } public Condition newCondition() { return sync.newCondition(); } public int getHoldCount() { return sync.getHoldCount(); } public boolean isHeldByCurrentThread() { return sync.isHeldExclusively(); } /** * Queries if this lock is held by any thread. This method is * designed for use in monitoring of the system state, * not for synchronization control. * * @return {@code true} if any thread holds this lock and * {@code false} otherwise */ public boolean isLocked() { return sync.isLocked(); } /** * Returns {@code true} if this lock has fairness set true. * * @return {@code true} if this lock has fairness set true */ public final boolean isFair() { return sync instanceof FairSync; } protected Thread getOwner() { return sync.getOwner(); } public final boolean hasQueuedThreads() { return sync.hasQueuedThreads(); } public final boolean hasQueuedThread(Thread thread) { return sync.isQueued(thread); } public final int getQueueLength() { return sync.getQueueLength(); } ...... ...... protected Collection<Thread> getQueuedThreads() { return sync.getQueuedThreads(); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
小结
本文详细的介绍了 ReentrantLock 的源代码,本文从四个方面介绍:三个 ReentrantLock 的内部类以及 ReentrantLock 类本身的方法。ReentrantLock 的实现原理其实是基于 AQS 的,同时 ReentrantLock 实例化构造对象的时候,可以选择是公平锁还是不公平锁。
-
相关阅读:
常见服务器运维管理面板整理汇总
Linux Shell脚本的10个有用的“面试问题和解答”
外包干了3个月,技术倒退2年。。。
JVM垃圾回收算法
2022中国国际防伪溯源技术展览会 | 防伪溯源 | 智慧包装 | 安全印刷
C++之构造函数、缺省构造函数
LeetCode每日一题:1488. 避免洪水泛滥(2023.10.13 C++)
Excel数据处理:动态数据分析报表、单元格数字格式、使用排序工具
集合collection listmapset
一文了解Spring框架
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_40417070/article/details/126060810