-
Python办公自动化【Word】
在Python中,可以使用
python-docx库来自动化操作 Word文档,首先需要通过 pip3 安装该库:pip3 install python-docx- 1
为了避免歧义,接下来文章中Word 表示Word软件本身,Word文档表示Word 软件中的文档。
1.1 读写 Word 文档
与 Excel 工作簿类似,Word 文档也有两种不同的文件格式,分别是2003版或更早之前的版本使用的
*.doc文件格式,以及 2007 版及之后的版本使用的*.docx文件格式。*.docx文件格式基于XML (可扩展标记语言),在相同数量下,占用空间更小,兼容性更高。python-docx只支持操作*.docx文件格式的Word文档,虽然Word 有*.doc与*.docx两种文件格式,但目前使用的 Word 文档绝大多数是*.docx文件格式的。如果遇到
*.doc文件格式的Word文档,可以将其中的内容复制,粘贴到*.docx文件格式的新文件中,再进行处理。首先介绍如何通过 python-docx 创建一个新的空白的 Word文档:
from docx import Document # 创建文档对象 document = Document() # 保存文档对象 扩展名只可以使用*.docx document.save("new.docx")- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
用 Document 方法创建文档对象,该文档对象对应着一个Word 文档;最后调用 save 方法传入具体的路径,将文档对象保存到本地。需要注意的是,在保存 Word 文档时,其扩展名必须使用
*.docx.1.2 *.doc 文件格式转换为 *.docx 文件格式
如果希望将大量的
*.doc文件格式的Word 文档转换为*.docx文件格式,可以使用 pypiwin32 第三方库,该库可以调用 Windows 操作系统中的方法实现 对 Word 文档的操作,但该库只可在 Windows 操作系统中安装与使用。首先通过 pip3 安装 pypiwin32:
pip3 install pypiwin32- 1
安装完成后,通过 win32com 使用 pypiwin32 第三方库,实现将 Word文档的文件格式由
*.doc转换为*.docx。from win32com import client # *.doc 文件格式的Word文档的路径 doc_path = 'exist.doc' docx_path = 'new_exist.docx' # 获取Word 应用程序对象 Word = client.Dispatch('Word.Application') # 打开对应的 Word文档 doc = Word.Documents.Open(doc_path) # 另存为 *.docx 文件格式,参数 12 表示 *.docx 文件格式 doc.SaveAs(docx_path, 12) # 关闭原来的 Word文档 doc.Close() # 退出Word 软件 Word.Quit()- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
上述代码只演示了如何将一个Word 文档的
*.doc文件格式转为*.docx文件格式,如果需要将大量的*.doc文件格式的Word 文档进行格式转换,使用 Python中的循环(while语句或者 for语句)即可。1.3 读取Word 文档中的段落
Word 文档中存在段落、图片、表格等多种不同类型的数据,本节介绍如何读取 Word 文档中的段落数据。
from docx import Document # 获取文档 doc = Document("exist.docx") # 遍历Word文档中的段落 for p in doc.paragraphs: # 输出word文档中的段落内容 print(p.text)- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
简单而言,我们只需要明确如下概念即可:
- 利用 Document 方法获取 Word 文档对象。
- Paragraph 对象表示 Word 文档中的段落对象。
- Paragraph 对象中的 text 对象表示段落中具体的文本内容。
1.4 读取 Word 文档中的表格
读取 Word 中的表格数据,可以通过 python-docx 提供的 tables 属性读取,代码如下:
rom docx import Document # 获取文档 doc = Document("table.docx") # 获取 Word 文档中的所有表格 tables = doc.tables # 选择第一个表格 table = tables[0] values = [] # 遍历表格的每一行 for row in table.rows: # 遍历每一行中的单元格 for cell in row.cells: # 将单元格中的数据添加到list中 values.append(cell.text) value = ' '.join(values) print(value) values = []- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
有时需要对比两个非常相似的表格以找到不同之处,此时怎么做呢?要解决这个问题,可以先将两个 Word 文档中的表格内容读入二维列表中,然后对列表中的内容进行比对,最终找到两个表格不同之处所对应的行号和列号。
使用
deepdiff第三方库,该库可以高效地比较不同对象的内容,并返回差异的内容,以及差异的位置。首先通过 pip安装deepdiff第三方库:pip install deepdiff- 1
安装完成之后,编写比较两个表格分的代码:
from docx import Document from deepdiff import DeepDiff def get_doc_values(path): # 获取表格中的内容 返回二维数组 doc = Document(path) tables = doc.tables table = tables[0] all_values = [] for row in table.rows: values = [] for cell in row.cells: # 将表格中单元格的值添加到values列表中 values.append(cell.text) all_values.append(values) return all_values table1 = get_doc_values("table.docx") table2 = get_doc_values("table_modify.docx") # 比较列表差异 ddiff = DeepDiff(table1, table2) print(ddiff) # 输出 ''' {'values_changed': {'root[2][1]': {'new_value': '1973', 'old_value': '1972'}, 'root[3][0]': {'new_value': 'JVAA', 'old_value': 'JAVA'}, 'root[3][1]': {'new_value': '1996', 'old_value': '1995'}}} '''- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
1.5 将文字写入Word文档
写入文字类型数据开始,
python-docx提供了add_paragrraph方法将文字类型数据以段落形式添加到 Word 文档中,代码如下:from docx import Document # 写入文档 doc = Document() # 添加标题 doc.add_heading("一级标题", level=1) # 添加段落 p2 = doc.add_paragraph("第二个段落") # 将新段落添加到已经有的段落之前 p1 = p2.insert_paragraph_before("第一个段落") p3 = doc.add_paragraph("新段落") # 追加内容 p3.add_run("加粗").bold = True p3.add_run("以及") p3.add_run("斜体").italic = True doc.save("new_doc.docx")- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
1.6 将图片写入 Word文档
python-dock提供了add_picture方法将图片添加到Word文档中:from docx import Document from docx.shared import Inches doc = Document() # 添加图片 doc.add_picture("1.jpg", width=Inches(1.25)) doc.save("new_pic.docx")- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
通过 width 或 height 参数设置插入Word文档中的图片大小,并通过 Inches 类来指定具体的大小,该类的度量单位是英寸。
1.7 将表格写入Word中
首先,
python-docx提供了add_table方法来创建空表格,此外,通过 style 属性还可以设置表格样式:from docx import Document doc = Document() # 创建table table = doc.add_table(rows=3, cols=4) # 设置table样式 table.style = "Table Grid" # 第一种方法 先获取行 再获取该行中对应的单元格 row = table.rows[0] row.cells[0].text = "第一行第一列" # 第二种方法 直接指行号和列号 cell = table.cell(0, 1) cell.text = "第一行第一列" doc.save('new3.docx')- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
如果将图片添加到表格中,将如何实现?
追加添加,代码如下:# 获取表格中的单元格对象 cell = table.cell(1, 0) # 获取单元格中的段落对象 p = cell.paragraphs[0] # 获取追加对象 run = p.add_run() run.add_picture("1.jpg", width=Inches(1.25)) doc.save("new3.docx")- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
1.8 插入有序列表与无序列表
有序列表与无序列表都可以通过
add_paragraph方法插入Word文档中,它们需要通过 style 参数设置其样式:from docx import Document doc = Document() # 有序列表 style = "List Number" doc.add_paragraph("有序列表1", style=style) doc.add_paragraph("有序列表2", style=style) doc.add_paragraph("有序列表3", style=style) # 无序列表 style = "List Bullet" doc.add_paragraph("无序列表1", style=style) doc.add_paragraph("无序列表2", style=style) doc.add_paragraph("无序列表3", style=style) doc.save("doc_list.docx")- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
修改Word 文档样式
2.1 文本格式
想要通过
python-docx控制Word文档样式,首先需要理解文本格式与样式的概念,这里先讨论文本格式:
python-docx将文本格式分为块对象与内联对象两种。1 块对象
块对象一般包括标题、段落、图片、表格、有序列表与无序列表。块对象的属性指定了块对象所在的位置,如缩进、段落之间的段间距等,常用的属性有 alignment(对齐方式)、index(缩进)、pace(行间距)等:
from docx import Document from docx.enum.text import WD_ALIGN_PARAGRAPH # 修改word文档样式 doc = Document() p1 = doc.add_paragraph("水平居中对齐") # 设置段落水平居中对齐 p1.paragraph_format.alignment = WD_ALIGN_PARAGRAPH.CENTER p2 = doc.add_paragraph("左对齐") # 设置段落左对齐 p2.paragraph_format.alignment = WD_ALIGN_PARAGRAPH.LEFT p3 = doc.add_paragraph("右对齐") # 设置段落右对齐 p3.paragraph_format.alignment = WD_ALIGN_PARAGRAPH.RIGHT doc.save('new.docx')- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
2 内联对象
块对象的所有内容都包括在内联对象中,一个块对象由一个或多个内联对象组成。内联对象一般包括文字、句子、段落等,通常通过内联对象的相关属相来指定字体的样式,如粗体、斜体、大小等:
from docx import Document from docx.shared import Pt p4 = doc.add_paragraph() run = p4.add_run("内联对象") font = run.font # 设置字体大小 font.size = Pt(35) # 设置字体为斜体 font.italic = True doc.save('new.docx')- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
2.2 Word 文档样式
Word 文档中常见的样式有段落样式、字符样式、表格样式等,
python-docx库样式定义在 styles 属性中,但它并不包含 Word 中所有的样式。
下面简单使用python-docx的styles属性定义样式:from docx import * from docx.shared import Pt # 获取python-docx支持的所有样式 styles = doc.styles # 选取style并设置style中的段落格式 style = styles["Heading 1"] p_format = style.paragraph_format # 设置左缩进 p_format.left_indent = Pt(25) # 使用样式 p = doc.add_paragraph("使用style设置段落样式", style=style) doc.save("doc_style.docx")- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
将
python-docx库中支持的所有表格样式输出:from docx import Document from docx.enum.style import * # 输出所有表格的样式 doc = Document() styles = doc.styles for style in styles: # 过滤表格样式 if style.type == WD_STYLE_TYPE.TABLE: # 输出当前样式的样式名 doc.add_paragraph(f"表格样式名称: {style.name}") # 创建表格并指定为当前样式 table = doc.add_table(3, 3, style=style) # 将内容添加到第一行 cells = table.rows[0].cells cells[0].text = "第一列内容" cells[1].text = "第二列内容" cells[2].text = "第三列内容" doc.add_paragraph("\n") doc.save("doc_all_style_list.docx")- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
使用 Word 模板
Word 模板指包括固定格式设置和版式设置的 Word文件,通过模板文件,可以快速生成美观的Word 文档,而不再需要重新设置各种样式的参数。
3.1 创建 Word 模板文件
对于不同的使用情景,Word 默认提供的各种模板文件并不能满足所有要求,此时可以自行创建一个符合自身需求的模板文件
下面创建一个入职证明Word模板,它用于证明新员工成功入职,其创建过程主要分为如下几步:
(1)创建一个普通的空白 Word 文档,在 Word 文档中输入相应的内容:

(2)选中 Word文档中的部分内容,如图,选中“同志”一词前的下划线“_”,然后在“插入” 选项卡中创建一个域,WPS与Word都具有该功能。

(3)在“域”对话框的 “域名”列表框中选择“MergeField”,然后在“域名”文本框中输入对应的名称,最后单击“确定”
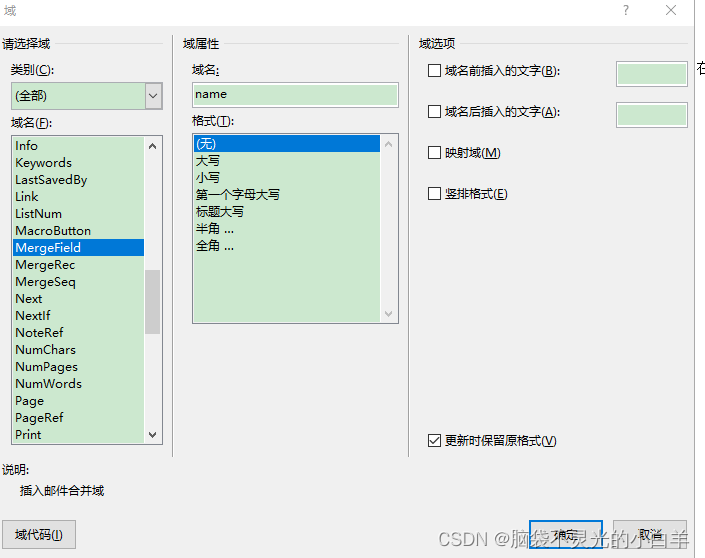
(4)至此,带有“《》”符号的域在Word模板中创建成功

3.2 使用Word 模板文件
使用域创建自定义 Word 模板的目的就是让程序来填充内容,通过
docx-mailmerge第三方库将数据填充到 Word 模板文件中,不过在使用前,需要先安装docx-mailmerge库:pip3 install docx-mailmerge- 1
docx-mailmerge 库在安装完成后即可使用:
from mailmerge import MailMerge template = "doc_templates.docx" doc = MailMerge(template) # 将内容添加到Word模板文件中 参数名与Word模板中的域名相同 doc.merge( name="二两", id="111222333", year="2021", month="8", day="30" ) doc.write("doc_templates_new.docx")- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
3.3 快速生成千份劳动合同
有一个Excel 表格,其中记录了1000 位求职者的姓名,现在需要为每位求职者生成相应的合同,并将合同中乙方的名字填写为求职者的姓名,该工作如何完成呢?
回顾前面的知识,不难想到,第一步当然是将合同文件转为Word模板文件,将要填写的信息的位置转为域。注意域只能使用英文名。用户可以根据自身的需求为不同的域设置不同的样式:
import pandas as pd from mailmerge import MailMerge # 读取求职者基本信息Excel表 job_seekers = pd.read_excel('求职者.xlsx') template = '合同.docx' doc = MailMerge(template) # 将数据填写到Word中 def merge(name): doc.merge(owner = '二两', # 甲方 party_b = name, # 乙方,求职者姓名 # 合同年月日 year = '2022', month = '7', day = '29') doc.write(f'合同/{name}_合同.dock') # 循环遍历求职者姓名 for i, name in job_seekers['name'].items(): merge(name) print('done!')- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
自动生成数据分析报告
4.1 处理Excel 数据
学生成绩数据如图所示,数据分析报告需要给出分数排在第一位的学生姓名及分数,此外还需要通过表格与柱状图展示出学生分数的排列情况。

首先生成学生成绩从大到小排序的柱状图:import pandas as pd import matplotlib.pyplot as plt # 自动生成数据分析报告 students = pd.read_excel("student_score.xlsx") # 就地排序 students.sort_values(by='Score', inplace=True, ascending=False) # 绘制柱状图 plt.bar(students["Name"], students["Score"], color="orange") plt.title("Student Score", fontsize=16) plt.xlabel("Name") plt.ylabel("Score") # 重铺x轴标签 plt.xticks(students.Name, rotation='90') # 紧凑型布局 plt.tight_layout() # 保存图片 plt.savefig("student_score.png")- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21

柱状图绘制完成后,接着获取分数排在第一位的学生信息。因为在绘制柱状图时已经通过 sort_values 方法对数据进行了排序,所以直接获取排在第一位的学生数据即可。
需要注意的是,用sort_values方法进行排序后的数据的下标并没有改变,此时直接通过下标获取的仍是原本排在第一位的数据,但是这并不是我们需要的。此时要么通过绝对位置获取数据,要么重新排序数据的下标,再通过下标获取数据:# 数据虽然被排序 但数据下标并没有改变 直接通过下标获取的依旧是原本的数据 print("原始下标: ", students["Name"][0]) # 方法一 通过iloc方法获取绝对的位置 print("绝对位置: ", students.iloc[0, :]["Name"]) # 方法二 对下标重新排序再取其中第一位 students.reset_index(drop=True, inplace=True) print("重新排序后的下标 ", students["Name"][0])- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
4.2 生成美观的数据分析报告
使用
python-docx库来生成数据分析报告:# 生成word文档 doc = Document() doc.add_heading("数据分析报告", level=0) # 绝对定位 获取分数排在第一位的学生信息 first_student = students.iloc[0, :]["Name"] first_score = students.iloc[0, :]["Score"] p = doc.add_paragraph("分数排在第一位的学生是: ") # 设置为粗体 p.add_run(str(first_student)).bold = True p.add_run(', 分数为 ') p.add_run(str(first_score)).bold = True p1 = doc.add_paragraph(f"总共有 {len(students['Name'])} 名学生参加了考试 学生考试总体情况为 ") # 添加表格 table = doc.add_table(rows=len(students["Name"]) + 1, cols=2) # 设置表格样式 table.style = "LightShading-Accent1" table.cell(0, 0).text = "学生姓名" table.cell(0, 1).text = "学生分数" # 添加数据到表中 for i, (index, row) in enumerate(students.iterrows()): table.cell(i + 1, 0).text = str(row["Name"]) table.cell(i + 1, 1).text = str(row["Score"]) # 添加图片 doc.add_picture("student_score.png") doc.save("student_score_analyze.docx") print("Done!")- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32

-
相关阅读:
多重背包-单调队列优化
这8个忠告会让你在2024过得更好
专访轮子哥:我在微软「造轮子」,一不小心成了知乎大V
3.6、媒体接入控制
软件流程和管理(一):预期的学习目标
Redis替代Session实现用户短信登录(超级消息解释)
go语言的第三方工具包:govaluate、flag、go-homedir、cast
QT - 模型与视图
golang中如何判断字符串是否包含另一字符串
【VsCode】vscode创建文件夹有小图标显示和配置
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_42588990/article/details/125816402


