-
protobuf 中复合数据类型的读写
背景
protobuf 在生成的 C++ 代码中为 .proto 文件中的每个 message 生成了对应的 C++ 类,并提供了数据成员的读写方法。
message 类型读写
①.message 示例
message Point { double lng = 1; double lat = 2; } message DemoMsg { int32 id = 1; Point pos = 2; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
②.成员赋值
通过 mutable_xxx 方法返回的指针给成员赋值:
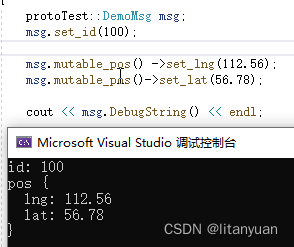
protoTest::DemoMsg msg; msg.set_id(100); msg.mutable_pos()->set_lng(112.56); msg.mutable_pos()->set_lat(56.78); cout << msg.DebugString() << endl;- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
通过 copyFrom 方法使用结构体赋值:
protoTest::DemoMsg msg; msg.set_id(100); protoTest::Point m_p; m_p.set_lng(112.56); m_p.set_lat(56.78); msg.mutable_pos()->CopyFrom(m_p); cout << msg.DebugString() << endl;- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
通过 set_allocated_xxx 成员函数传入指针进行赋值:
protoTest::DemoMsg msg; msg.set_id(100); protoTest::Point * m_p = new protoTest::Point; m_p->set_lng(112.56); m_p->set_lat(56.78); msg.set_allocated_pos(m_p); cout << msg.DebugString() << endl;- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
③.成员读取
通过成员函数 has_xxx 可以判断 message 类型的成员是否被赋值。
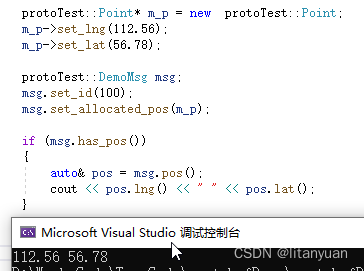
protoTest::Point* m_p = new protoTest::Point; m_p->set_lng(112.56); m_p->set_lat(56.78); protoTest::DemoMsg msg; msg.set_id(100); msg.set_allocated_pos(m_p); if (msg.has_pos()) { auto& pos = msg.pos(); cout << pos.lng() << " " << pos.lat(); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
map 类型读写
①.message 示例
message DemoMsg { map<int32,string> a = 1; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
②.成员赋值
map 类型成员赋值需通过 mutable_xxx 方法进行:
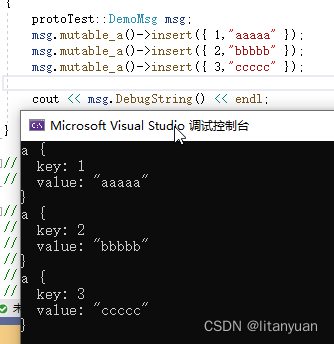
protoTest::DemoMsg msg; msg.mutable_a()->insert({ 1,"aaaaa" }); msg.mutable_a()->insert({ 2,"bbbbb" }); msg.mutable_a()->insert({ 3,"ccccc" }); cout << msg.DebugString() << endl;- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
③.成员读取
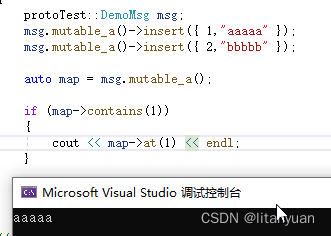
protoTest::DemoMsg msg; msg.mutable_a()->insert({ 1,"aaaaa" }); msg.mutable_a()->insert({ 2,"bbbbb" }); auto map = msg.mutable_a(); if (map->contains(1)) { cout << map->at(1) << endl; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
any 类型读写
①.概述
any 可以保存任意的已知类型的序列化数据,常用于对结构体数据的再包装,即可以把不同类型的 message 包装在同一个 message 中进行传输。
②.message 示例
syntax = "proto3"; import "google/protobuf/any.proto"; package protoTest; message Point { double lng = 1; double lat = 2; } message Node { int32 id = 1; string name = 2; } message DemoMsg { int32 id = 1; google.protobuf.Any data = 2; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
③.成员赋值
使用 any 类型的成员函数 PackFrom 来进行赋值。
protoTest::Point m_p; m_p.set_lng(112.56); m_p.set_lat(56.78); protoTest::DemoMsg msg; msg.set_id(1); msg.mutable_data()->PackFrom(m_p); cout << msg.DebugString() << endl;- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
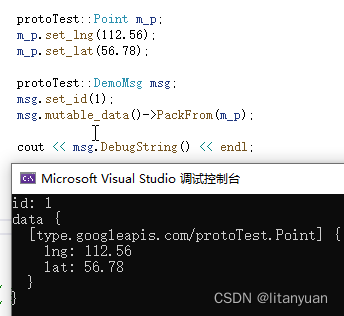
④.message 类型判断
通过成员函数 Is 可以判断是否为指定类型的数据。
protoTest::Point m_p; m_p.set_lng(112.56); m_p.set_lat(56.78); protoTest::Node m_node; m_node.set_id(1); m_node.set_name("Zhangsan"); protoTest::DemoMsg msg1; msg1.set_id(1); msg1.mutable_data()->PackFrom(m_p); protoTest::DemoMsg msg2; msg2.set_id(2); msg2.mutable_data()->PackFrom(m_node); auto checkAny = [&](const protoTest::DemoMsg& msg) { if (msg.data().Is<protoTest::Point>()) cout << " msgID:" << msg.id() << " 中 data 类型为 Point " << endl; else if( msg.data().Is<protoTest::Node>() ) cout << " msgID:" << msg.id() << " 中 data 类型为 Node " << endl; }; checkAny(msg1); checkAny(msg2);- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
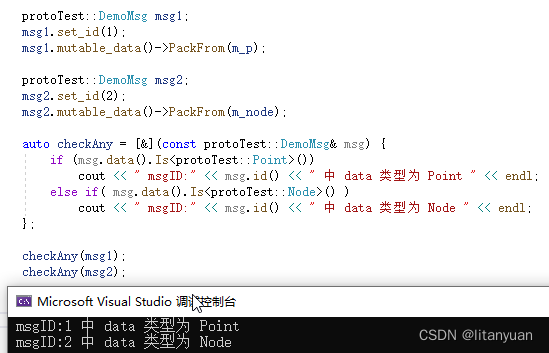
⑤.成员读取
通过成员函数 UnpackTo 可以把 any 数据还原成对应的结构体数据。
protoTest::Point m_p; m_p.set_lng(112.56); m_p.set_lat(56.78); protoTest::DemoMsg msg; msg.set_id(1); msg.mutable_data()->PackFrom(m_p); if (msg.data().Is<protoTest::Point>()) { protoTest::Point pos; if (msg.data().UnpackTo(&pos)) { cout << pos.DebugString() << endl; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
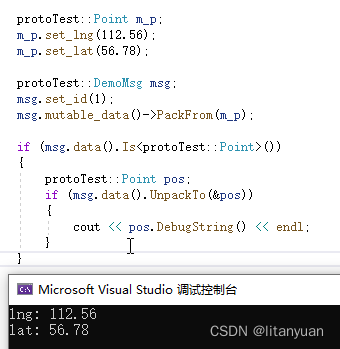
oneof 类型读写
①.概述
oneof 类型同 C++ 中的 union 类型,同一时刻只有一种类型有效。
②.message 示例
message DemoMsg { oneof test{ int32 id = 1; string name =2; }; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
③.成员赋值
直接使用 set_xxx 给相应的成员赋值即可,但只有最后一次赋值的数据有效。
protoTest::DemoMsg msg; msg.set_id(100); msg.set_name("123"); cout << msg.DebugString() << endl;- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
④.数据类型判断
通过 has_xxx 方法判断对应类型成员是否赋值:
protoTest::DemoMsg msg; msg.set_id(100); msg.set_name("123"); if (msg.has_name()) { cout << "msg 中为 string 类型" << endl; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
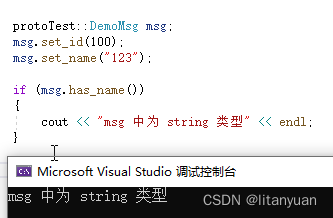
通过 xxx_case 方法当前判断保存的成员类型:
protoTest::DemoMsg msg; msg.set_id(100); msg.set_name("123"); switch (msg.test_case()) { case protoTest::DemoMsg::kId: cout << "msg 中为 int32 类型" << endl; break; case protoTest::DemoMsg::kName: cout << "msg 中为 string 类型" << endl; break; default: break; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
⑤.成员读取
先判断当前保存的字段类型,再读取数据。
protoTest::DemoMsg msg; msg.set_id(100); msg.set_name("123"); switch (msg.test_case()) { case protoTest::DemoMsg::kId: cout << msg.id() << endl; break; case protoTest::DemoMsg::kName: cout << msg.name() << endl; break; default: break; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13

-
相关阅读:
backup (攻防世界)
串口通信问题排查总结
如何画出优秀的架构图?
调度算法1
中国出口商对人民币波动持乐观态度!贬值“不会继续”!
Python接口自动化封装导出excel方法和读写excel数据
浅谈UI自动化测试
[云原生]微服务架构是什么
基于微信小程序的医院预约挂号系统,附源码、数据库
LeetCode 1704. 判断字符串的两半是否相似:小难懂的代码
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/lizhichao410/article/details/126053353
