-
Harbor高可用集群设计及部署(基于离线安装方式)
一、环境说明
1.1 架构图

【架构解析】:将Harbor的redis缓存组件、PostgreSQL数据库组件迁移到系统外部做高可用,使用外部共享存储实现多个Harbor实例的数据共享,Harbor实例可横向扩展。
1.2 主机清单
IP地址 主机名 描述 192.168.2.107 harbor1 Harbor实例1,8021端口 192.168.2.108 harbor2 Harbor实例2,8021端口 192.168.2.110 harbor-data 部署Harbor实例的共享存储、外部数据库、外部缓存服务 192.168.2.111 / 负载均衡VIP,8121端口 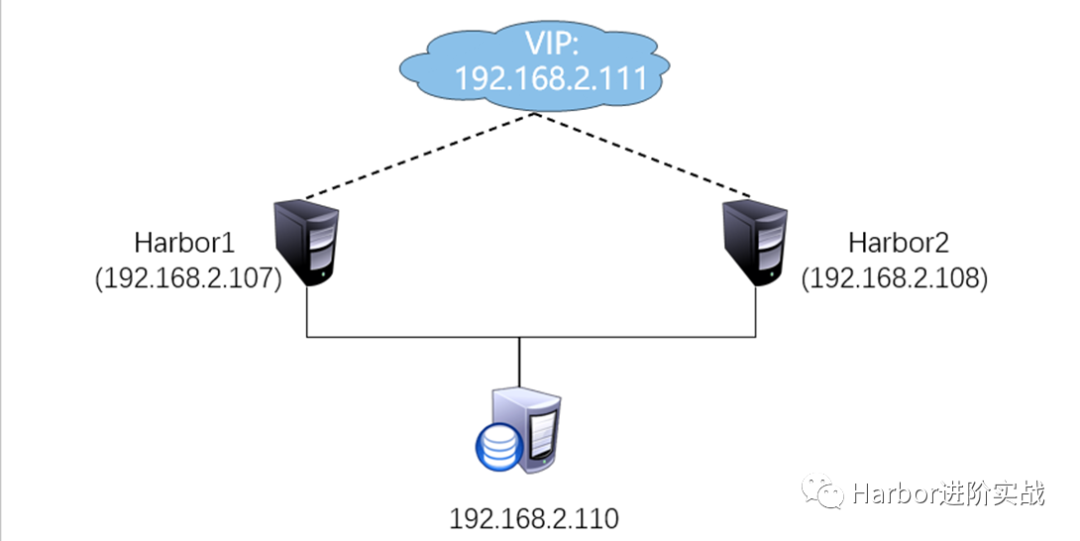
二、主机初始化
Harbor实例进行初始化
-
安装docker
-
安装docker-compose
-
配置内核参数
2.1 安装docker
- $ wget -O /etc/yum.repos.d/docker-ce.repo https://mirrors.aliyun.com/docker-ce/linux/centos/docker-ce.repo
- $ yum install -y docker-ce
- $ systemctl enable --now docker
- $ systemctl status docker
- $ cat <
/etc/docker/daemon.json - {
- "registry-mirrors": ["https://xcg41ct3.mirror.aliyuncs.com"],
- "exec-opts": ["native.cgroupdriver=systemd"],
- "registry-mirrors": ["https://3hjcmqfe.mirror.aliyuncs.com"],
- "log-driver": "json-file",
- "log-opts": {
- "max-size": "500m",
- "max-file": "2"
- }
- }
- EOF
- $ systemctl daemon-reload
- $ systemctl restart docker
exec-opts": ["native.cgroupdriver=systemd"], #驱动器 registry-mirrors: 镜像加速地址,可多个 max-file: log最多保留数量 live-restore: 重启docker不重启容器,多用于k8s上
2.2 安装docker-compose
安装docker-compose 1.18.0以上的版本,本处安装v2.2.3版本。
- $ wget https://github.com/docker/compose/releases/download/v2.2.3/docker-compose-linux-x86_64
- $ mv docker-compose-linux-x86_64 /usr/local/bin/docker-compose
- $ chmod +x /usr/local/bin/docker-compose
- $ docker-compose version
- Docker Compose version v2.2.3
2.3 配置内核参数
- $ modprobe br_netfilter
- $ cat >> /etc/sysctl.conf << EOF
- net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-ip6tables = 1
- net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-iptables = 1
- net.ipv4.ip_forward = 1 #路由转发
- EOF
- $ sysctl -p
三、使用NFS提供外部共享存储
在
192.168.2.110部署NFS服务提供共享存储给Harbor1实例、Harbor2实例使用。192.168.2.110作为NFS服务端,harbor实例为客户端。3.1 部署NFS服务端
1)安装并启动nfs
- $ yum install -y nfs-utils
- $ systemctl start nfs && systemctl enable nfs && systemctl status nfs
- $ chkconfig nfs on #设置为开机自启
2)创建共享目录
客户端的数据将远程存入到共享目录下。
$ mkdir -p /data/harbor_data3)修改配置
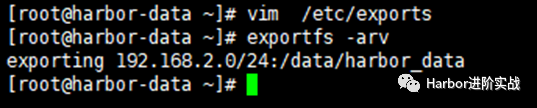
- $ cat /etc/exports
- /data/harbor_data 192.168.2.0/24(rw,no_root_squash) #允许哪个网段的客户端使用指定共享目录
- $ exportfs -arv #使配置文件生效
- exporting 192.168.2.0/24:/data/harbor_data
4)重启nfs服务
$ systemctl restart nfs5)检查共享目录信息
- $ showmount -e localhost
- export list for localhost:
- /data/harbor_data
3.2 部署客户端
在harbor1和harbor2上操作
- $ yum -y install nfs-utils
- $ systemctl start nfs-utils && systemctl enable nfs-utils && systemctl status nfs-utils
3.3 客户端挂载NFS共享存储
在harbor1和harbor2节点操作,创建实例的存储目录,然后挂载到NFS。
- $ mkdir -p /data/harbor_data
- $ cat <<EOF >> /etc/fstab
- 192.168.2.110:/data/harbor_data /data/harbor_data nfs defaults 0 0
- EOF
- $ mount -a
挂载格式:NFSIP:共享目录 本地目录 nfs defaults 0 0
-
测试是否可以正常使用:
- [root@harbor2 ~]# touch /data/harbor_data/test.txt
- [root@harbor1 ~]# ls /data/harbor_data/
- test.txt
四、部署Redis缓存服务(源码)
本处为演示环境,实际
生产环境请对Redis服务做高可用及数据备份。在
192.168.2.110部署Redis缓存服务,为harbor1和harbor2实例提供外部redis缓存服务。4.1 下载安装包
- $ wget https://download.redis.io/releases/redis-6.2.7.tar.gz
4.2 安装依赖包
$ yum install -y gcc gcc-c++4.3 源码编译
- $ mkdir -p /app/
- $ tar zxvf redis-6.2.7.tar.gz -C /app
- $ cd /app/redis-6.2.7/
- $ make #编译
- $ make install #安装
4.4 修改配置文件
redis默认只支持本地使用,本处需要修改几个参数:
-
外部可连接;
-
redis启动方式;
-
redis远程连接密码;
- $ vim /app/redis-6.2.7/redis.conf
- #bind 127.0.0.1 -::1 #75行,注释掉bind的行,允许任何主机连接;
- daemonize yes #259行,将no修改为yes,使redis可以使用守护进程方式启动;
- requirepass lidabai666 #903行,设置redis连接的auth密码(lidabai666)
4.5 启动Redis服务
前面配置了使用守护进程方式启动,所以直接使用systemctl则可以启动redis服务。
- $ pwd
- /app/redis-6.2.7
- $ redis-server redis.conf
4.6 服务验证
1)查看Redis服务版本
- $ redis-cli -v
- redis-cli 6.2.7
2)查看端口
redis默认监听6379端口
- $ ps aux | grep 6379
- root 6200 0.1 0.2 162416 10020 ? Ssl 17:59 0:00 redis-server *:6379
- root 6231 0.0 0.0 112720 984 pts/0 R+ 18:01 0:00 grep --color=auto 6379
3)客户端连接Redis
harbor1和harbor2作为redis客户端- $ which redis-cli #查看redis-cli工具位置
- /usr/local/bin/redis-cli
- [root@harbor-data redis-6.2.7]# scp /usr/local/bin/redis-cli 192.168.2.107:/usr/local/bin/
- [root@harbor-data redis-6.2.7]# scp /usr/local/bin/redis-cli 192.168.2.108:/usr/local/bin/
客户端使用redis-cli工具连接Redis服务器
[root@harbor1 ~]# redis-cli -h 192.168.2.110 -p 6379 -a lidabai666-a 参数指定redis连接密码
五、部署PostgreSQL外部存储服务(源码)
在
192.168.2.110主机以源码的方式安装PostgreSQL数据库服务,为harbor1和harbor2实例提供共享存储。5.1 新建postgres用户
默认超级用户(root)不能启动postgresql,需要手动建用户postgres。
- $ useradd postgres
- $ id postgres
- uid=1000(postgres) gid=1000(postgres) 组=1000(postgres)
5.2 安装依赖包
$ yum -y install readline-devel zlib-devel gcc zlib5.3 下载解压源码包
- $ wget https://ftp.postgresql.org/pub/source/v13.5/postgresql-13.5.tar.gz --no-check-certificate
- $ tar zxvf postgresql-13.5.tar.gz -C /app/
5.4 编译安装
- $ cd /app/postgresql-13.5/
- $ ./configure --prefix=/usr/local/postgresql
- $ make && make install
5.5 创建数据目录
- $ mkdir -p /data/postgresql/data
- $ chown -R postgres:postgres /usr/local/postgresql/
- $ chown -R postgres:postgres /data/postgresql/data/
5.6 设置postgres环境变量
- [root@harbor-data postgresql-13.5]# su - postgres
- [postgres@harbor-data ~]$ vim + .bash_profile
- PGHOME=/usr/local/postgresql #psql安装目录
- export PGHOME
- PGDATA=/data/postgresql/data #数据库目录
- export PGDATA
- PATH=$PATH:$HOME/bin:$HOME/.local/bin:$PGHOME/bin
- export PATH
- [postgres@harbor-data ~]$ source ./.bash_profile
- [postgres@harbor-data ~]$ which psql
- /usr/local/postgresql/bin/psql
查看版本 [postgres@harbor-data ~]$ psql -V psql (PostgreSQL) 13.5
5.7 初始化数据库
由于 Red Hat 系列发行版的政策,PostgreSQL 安装不会启用自动启动或自动初始化数据库。要完成数据库安装,您需要根据您的发行版执行以下步骤:
- [postgres@ceph3 ~]$ initdb
- ......
- You can change this by editing pg_hba.conf or using the option -A, or
- --auth-local and --auth-host, the next time you run initdb.
- Success. You can now start the database server using: #表示初始化成功
- pg_ctl -D /data/postgresql/data -l logfile start

5.8 启动PostgreSQL
根据刚才初始化成功后的提示执行启动命令!
- [postgres@harbor-data ~]$ pg_ctl -D /data/postgresql/data -l logfile start
- waiting for server to start.... done
- server started

5.9 设置(修改)Postgresql密码
默认psql本地登录是不需要密码的,即使我们设置了密码,也不需要密码就能登录。应为配置文件pg_hba.conf中的local设置为trust , 为了安全我们修改为 password,就是使用密码才能登陆,(当我们忘记密码的时间,也可以使用这用方式,先设置为trust之后,修改密码,然后在设置为password。)
- [postgres@harbor-data ~]$ psql
- psql (13.5)
- Type "help" for help.
- postgres=# \password
- Enter new password: #输入设置的密码 Lidabai666
- Enter it again: #确认密码(再次输入)
- postgres=# \q #退出

5.10 设置可远程登录PostgreSQL
- [postgres@harbor-data ~]$ vim /data/postgresql/data/postgresql.conf
- listen_addresses = '*' #60行,监听所有地址
- [postgres@harbor-data ~]$ vim + /data/postgresql/data/pg_hba.conf
- local all all password
- host all all 0.0.0.0/0 password
- host all all ::1/128 password

5.10 重启PostgreSQL
- $ pg_ctl -D /data/postgresql/data -l /data/postgresql/data/postgres.log restartwaiting for server to shut down.... done
- server stopped
- waiting for server to start.... done
- server started

5.11 创建数据库
Harbor 2.3.5需要创建的数据库:
-
notaryserver
-
notarysigner
-
registry
目前Harbor仅支持PostgraSQL数据库,需要手动在外部的PostgreSQL上创建registry、notary_signer、notary_servers三个数据库,Harbor启动时会自动在对应数据库下生成表。
因为本处主要是演示环境,PostgreSQL数据库的用户就以超级管理员
postgres为例,如果是生产环境,建议新建用户,并授予harbor、notary_signer、notary_servers三个数据库相对应的权限。- [postgres@harbor-data ~]$ psql
- Password for user postgres: #输入密码
- postgres=# create database registry;
- CREATE DATABASE
- postgres=# create database notary_signer;
- CREATE DATABASE
- postgres=# create database notary_servers;
- CREATE DATABASE
- postgres=# \l

5.12 创建用户
- postgres=# create user server with password 'lidabai666';
- CREATE ROLE
- postgres=# create user signer with password 'lidabai666';
- CREATE ROLE
- postgres=# \du

六、负载均衡设置(Nginx + Keepalived)
使用keepalived和Nginx实现harbor的高可用。在
harbor1和harbor2节点上安装keepalived服务来提供VIP实现负载均衡。Nginx服务则实现将来到VIP的请求转发到后端服务器组harbor6.1 安装nginx和keepalived
在harbor1和harbor2操作
- $ wget -O /etc/yum.repos.d/epel.repo http://mirrors.aliyun.com/repo/epel-7.repo
- $ yum install -y nginx keepalived
- $ yum -y install nginx-all-modules.noarch #安装nginx的stream模块
nginx从1.9.0开始新增了steam模块,用来实现四层协议的转发、代理、负载均衡等。二进制安装的nginx则在./configure时添加--with-stream参数来安装stream模块。
6.2 修改nginx配置文件
在harbor1和harbor2的Nginx服务配置文件一样。- $ vim /etc/nginx/nginx.conf
- user nginx;
- worker_processes auto; #自动设置nginx的工作进程数量
- error_log /var/log/nginx/error.log;
- pid /run/nginx.pid;
- include /usr/share/nginx/modules/*.conf;
- events {
- worker_connections 1024; #工作进程的连接数
- }
- # 四层负载均衡,为两台harbor提供负载均衡
- stream {
- log_format main '$remote_addr $upstream_addr - [$time_local] $status $upstream_bytes_sent';
- access_log /var/log/nginx/harbor-access.log main;
- upstream harbor{
- server 192.168.2.107:8021; # harbor1
- server 192.168.2.108:8021; # harbor2
- }
- server {
- listen 8121; #由于nginx与harbor节点复用,这个监听端口不能是8021,否则会冲突
- proxy_pass harbor;
- }
- }
- http {
- log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" '
- '$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" '
- '"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"';
- access_log /var/log/nginx/access.log main;
- sendfile on;
- tcp_nopush on;
- tcp_nodelay on;
- keepalive_timeout 65;
- types_hash_max_size 2048;
- include /etc/nginx/mime.types;
- default_type application/octet-stream;
- server {
- listen 80 default_server;
- server_name _;
- location / {
- }
- }
- }
检测nginx配置文件语法
- $ nginx -t
- nginx: the configuration file /etc/nginx/nginx.conf syntax is ok
- nginx: configuration file /etc/nginx/nginx.conf test is successful
6.3 修改keepalived配置
本处以harbor1为keepalived服务的主节点,harbor2为keepalived的备节点。主备节点的keepalived配置文件不一样。1)主节点(harbor1)
- [root@harbor1 ~]# cat /etc/keepalived/keepalived.conf
- ! Configuration File for keepalived
- global_defs {
- notification_email {
- 859281177@qq.com
- }
- router_id master1
- }
- vrrp_instance lidabai {
- state MASTER
- interface ens33
- mcast_src_ip:192.168.2.107
- virtual_router_id 107
- priority 100
- advert_int 1
- nopreempt
- authentication {
- auth_type PASS
- auth_pass 1111
- }
- virtual_ipaddress {
- 192.168.2.111/24 #虚拟VIP地址
- }
- track_script {
- chk_nginx
- }
- }
- ##### 健康检查
- vrrp_script chk_nginx {
- script "/etc/keepalived/check_nginx.sh"
- interval 2
- weight -20
- }
2)备节点(harbor2)
- [root@harbor2 ~]# cat /etc/keepalived/keepalived.conf
- ! Configuration File for keepalived
- global_defs {
- notification_email {
- 859281177@qq.com
- }
- router_id master2
- }
- vrrp_instance lidabai {
- state BACKUP
- interface ens33
- mcast_src_ip:192.168.2.108
- virtual_router_id 107
- priority 80 #权重
- advert_int 1
- nopreempt
- authentication {
- auth_type PASS
- auth_pass 1111
- }
- virtual_ipaddress {
- 192.168.2.111/24
- }
- track_script {
- chk_nginx
- }
- }
- vrrp_script chk_nginx {
- script "/etc/keepalived/check_nginx.sh"
- interval 2
- weight -20
- }
6.4 编写健康检查脚本
在主备节点(harbor1和harbor2)同样操作。- $ vim /etc/keepalived/check_nginx.sh
- #!/bin/bash
- #1、判断Nginx是否存活
- counter=`ps -C nginx --no-header | wc -l`
- if [ $counter -eq 0 ]; then
- #2、如果不存活则尝试启动Nginx
- service nginx start
- sleep 2
- #3、等待2秒后再次获取一次Nginx状态
- counter=`ps -C nginx --no-header | wc -l`
- #4、再次进行判断,如Nginx还不存活则停止Keepalived,让地址进行漂移
- if [ $counter -eq 0 ]; then
- service keepalived stop
- fi
- fi
- $ chmod +x /etc/keepalived/check_nginx.sh
6.5 启动服务
先启动master1和master2节点上的nginx服务,再启动keepalived服务
1)启动nginx服务
- [root@harbor1 ~]# systemctl enable --now nginx #启动nginx服务并设置开机自启
- [root@harbor2 ~]# systemctl enable --now nginx
- [root@harbor1 ~]# systemctl status nginx.service
- [root@harbor2 ~]# systemctl status nginx.service
2)启动keepalived服务
- [root@harbor1 ~]# systemctl enable --now keepalived
- [root@harbor2 ~]# systemctl enable --now keepalived
- [root@harbor1 ~]# systemctl status keepalived.service
- [root@harbor2 ~]# systemctl status keepalived.service
6.6 查看VIP
在harbor1节点查看VIP是否成功绑定。- [root@harbor1 ~]# ip addr
- ......
- 2: ens33: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc pfifo_fast state UP group default qlen 1000
- link/ether 00:0c:29:f1:a3:65 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
- inet 192.168.2.107/24 brd 192.168.2.255 scope global noprefixroute ens33
- valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
- inet 192.168.2.111/24 scope global secondary ens33 #VIP地址
- valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
- inet6 fe80::80b0:1d7f:b5d4:19e8/64 scope link tentative dadfailed
- ......
通过ifconfig是无法查看到VIP的,通过
hostname -I命令也可以查看到VIP。七、部署Harbor实例1
在harbor1 192.168.2.107主机上部署harbor服务
7.1 下载解压离线安装包
- $ mkdir /app #创建安装目录
- $ wget https://github.com/goharbor/harbor/releases/download/v2.3.5/harbor-offline-installer-v2.3.5.tgz
- $ tar zxvf harbor-offline-installer-v2.3.5.tgz -C /app/
7.2 修改配置文件
将配置文件模板复制为配置文件,然后修改对应参数。
- [root@harbor1 ~]# cd /app/harbor/
- [root@harbor1 harbor]# cp harbor.yml.tmpl harbor.yml
- [root@harbor1 harbor]# vim harbor.yml
- hostname: 192.168.2.107
- http:
- port: 8021
- #取消https安全加密访问方式:
- #https:
- # port: 443
- # certificate: /your/certificate/path
- # private_key: /your/private/key/path
- ## 启用外部代理,启用后hostname将不再使用
- external_url: http:192.168.2.111:8121
- ## 配置共享存储,即挂载的NFS目录
- data_volume: /data/harbor_data
- _version: 2.3.0
- ## 配置外部数据库
- external_database:
- harbor:
- host: 192.168.2.110 # 数据库主机地址
- port: 5432 # 数据库端口
- db_name: registry # 数据库名称
- username: postgres # 连接该数据库的用户名
- password: Lidabai666 # 连接数据库的密码
- ssl_mode: disable
- max_idle_conns: 2
- max_open_conns: 0
- notary_signer:
- host: 192.168.2.110
- port: 5432
- db_name: notary_signer
- username: postgres
- password: Lidabai666
- ssl_mode: disable
- notary_server:
- host: 192.168.2.110
- port: 5432
- db_name: notary_server
- username: postgres
- password: Lidabai666
- ssl_mode: disable
- ##配置外部Redis实例:
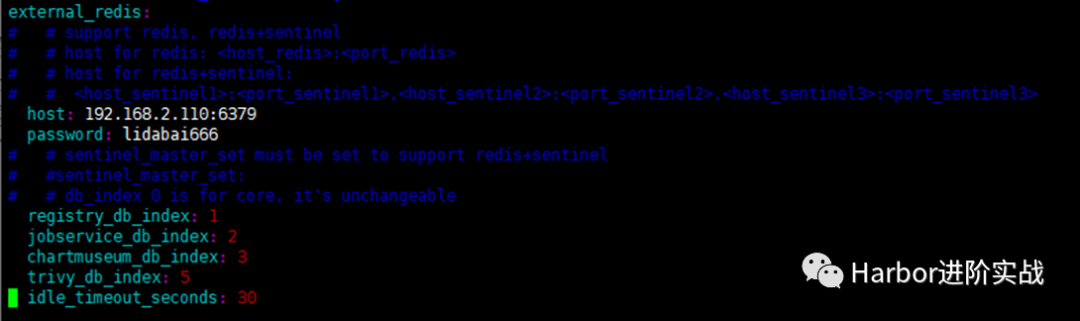
- external_redis:
- host: 192.168.2.110:6379 #redis服务IP地址和端口号。如果redis是哨兵模式,这里应该是host_sentinel1:port_sentinel1,host_sentinel2:port_sentinel2
- password: lidabai666 #连接外部redis服务的密码
- # sentinel_master_set: #仅在使用 Sentinel模式(哨兵模式)时使用
- registry_db_index: 1
- jobservice_db_index: 2 #job服务的数据库索引
- chartmuseum_db_index: 3 #chartmuseum插件的Redis索引
- trivy_db_index: 5 #Trivy扫描器的数据索引
- idle_timeout_seconds: 30 #超时时间
- #启用metrics数据采集插件:
- metric:
- enabled: true
- port: 9090
- path: /metrics

7.3 将配置文件注入到组件中
将harbor.yml配置文件的内容注入到各组件的配置文件中。
[root@harbor1 harbor]# ./prepare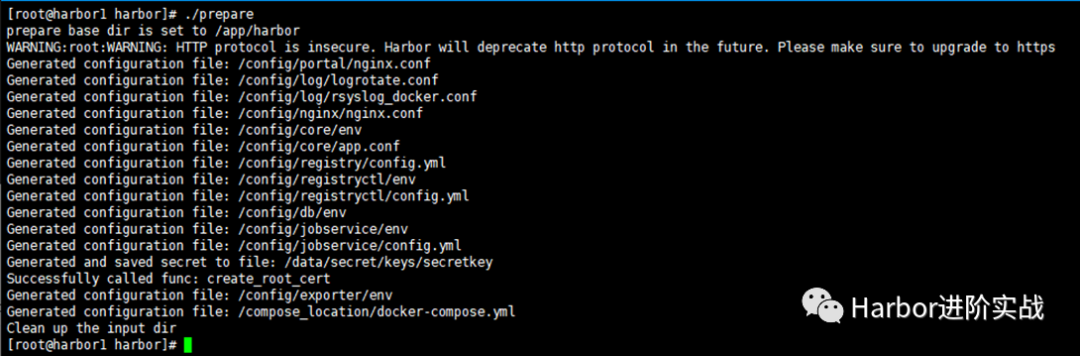
7.4 安装Harbor
安装期间会自动导入镜像,执行完成会自动启动Harbor服务。
[root@harbor1 harbor]# ./install.sh --with-trivy --with-chartmuseum

-Harbor has been installed and started successfully.- 表示安装成功!
7.5 查看服务状态
[root@harbor1 harbor]# docker-compose ps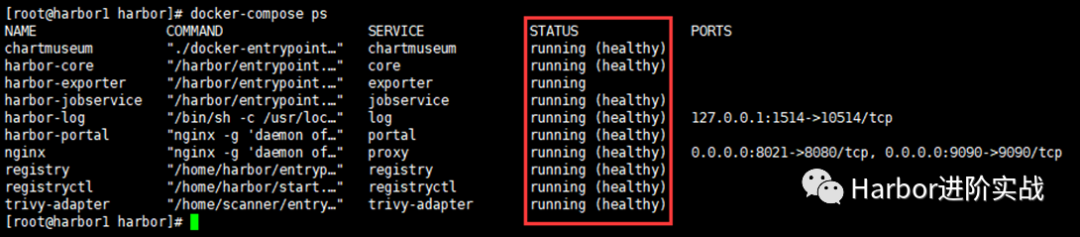
7.6 浏览器登录Harbor UI
使用实例主机IP+端口在浏览器访问harbor UI Http://192.168.2.107:8021

用户名:admin
密码:Harbor12345八、部署Harbor实例2
操作步骤跟部署Harbor实例1一致,仅将harbor.yml文件中hostname的值修改为当前主机的IP地址即可。
- $ mkdir /app
- $ wget https://github.com/goharbor/harbor/releases/download/v2.3.5/harbor-offline-installer-v2.3.5.tgz
- $ tar zxvf harbor-offline-installer-v2.3.5.tgz -C /app/
- $ scp 192.168.2.107:/app/harbor/harbor.yml /app/harbor/
- $ vim /app/harbor/harbor.yml’
- hostname: 192.168.2.108
九、服务验证
9.1 浏览器访问VIP和端口
http://192.168.2.111:8121
在Harbor UI界面测试镜像推送、拉取、创建用户、创建项目等是否正常
9.2 命令行登录Harbor
$ docker login http://192.168.2.111:8121 -u admin -p Harbor12345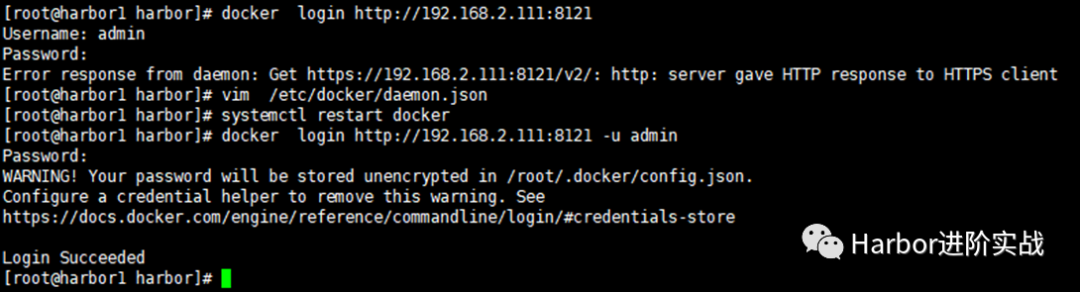
出现报错:
Error response from daemon: Get https://192.168.2.111:8121/v2/: http: server gave HTTP response to HTTPS client 在docker配置文件中添加参数:- [root@harbor1 harbor]# vim /etc/docker/daemon.json
- {
- "registry-mirrors": ["https://xcg41ct3.mirror.aliyuncs.com"],
- "exec-opts": ["native.cgroupdriver=systemd"],
- "registry-mirrors": ["https://3hjcmqfe.mirror.aliyuncs.com"],
- "insecure-registries": ["192.168.2.111:8121"],
- "log-driver": "json-file",
- "log-opts": {
- "max-size": "500m",
- "max-file": "2"
- }
- }
- [root@harbor1 harbor]# systemctl restart docker #然后重启docker
9.3 向Harbor推送镜像
- [root@harbor1 harbor]# docker pull alpine:3.16
- [root@harbor1 harbor]# docker tag alpine:3.16 192.168.2.111:8121/library/alpine:3.16
- [root@harbor1 harbor]# docker push 192.168.2.111:8121/library/alpine:3.16
然后可以在Harbor UI界面查看到镜像已经推送成功!

-
-
相关阅读:
IDEA配置自己的Maven以及创建Maven
Webpack打包
搭建网关服务器实现DHCP自动分配、HTTP服务和免密登录
集美大学 - 2840 - 实验2-1
dubbo telnet使用
并发任务队列(字节青训测试题)
mysql 用户控制命令
ChatGPT-4o模型功能介绍
PCBA方案|红外额温枪方案
耐蚀点蚀镀铜工艺
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/zfw_666666/article/details/126028310
