-
逻辑回归原理
1.sigmoid函数
公式:

自变量取值为任意实数,值域[0,1]
解释:将任意的输入映射到了[0,1]区间 ,我们在线性回归中可以得到一个预测值,再将该值映射到Sigmoid 函数中这样就完成了由值到概率的转换,也就是分类任务
预测函数:
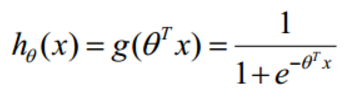
其中,

分类任务:
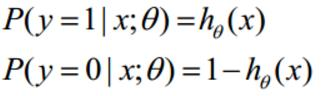
整合:

解释:对于二分类任务(0,1),整合后y取0只保留
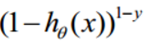 ,y取1只保留
,y取1只保留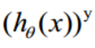
似然函数:

对数似然:
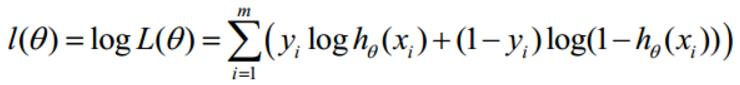
此时应用梯度上升求最大值,引入
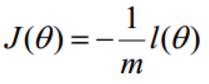
转换为梯度下降任务
求导过程:
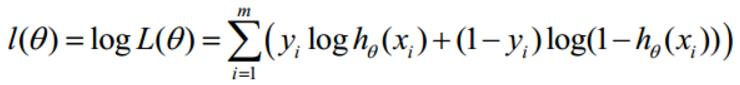

参数更新:
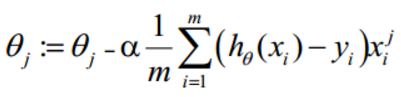
多分类的softmax:
2.代码实现
import numpy as np
from utils.features import prepare_for_training
from scipy.optimize import minimize
from utils.hypothesis import sigmoid
class LogisticRegression:
def __init__(self, data, labels, polynomial_degree=0, sinusoid_degree=0, normalize_data=False):(data_processed, features_mean,
features_deviation) = prepare_for_training(data, polynomial_degree, sinusoid_degree,
normalize_data)
self.data = data_processed
self.labels = labels
self.unique_labels = np.unique(labels)
self.features_mean = features_mean
self.features_deviation = features_deviation
self.polynomial_degree = polynomial_degree
self.sinusoid_degree = sinusoid_degree
self.normalize_data = normalize_data
# 数据预处理
num_unique_labels = len(np.unique(labels))
num_features = self.data.shape[1]
self.theta = np.zeros((num_unique_labels, num_features))def train(self, n_iterations=500):
cost_histories = []
num_features = self.data.shape[1]
for label_index, unique_label in enumerate(self.unique_labels):
current_initial_theta = np.copy(self.theta[label_index].reshape(num_features, 1))
current_lables = (self.labels == unique_label).astype(float)
(theta, cost_history) = LogisticRegression.gradient_descent(self.data, current_initial_theta,
current_lables, n_iterations)
self.theta[label_index]=theta.T
cost_histories.append(cost_history)
return self.theta,cost_histories@staticmethod
def gradient_descent(data, current_initial_theta, current_lables, n_iterations):
cost_history = []
num_fratures = data.shape[1]
result = minimize(
# 优化的目标
lambda x: LogisticRegression.cost_function(data, current_lables, x.reshape(num_fratures,1)),
# 初始化的权重参数
current_initial_theta,
# 选择优化策略
method='CG',
# 梯度下降迭代计算公式
jac=lambda x: LogisticRegression.gradient_step(data, current_lables, x.reshape(num_fratures,1)),
callback=lambda x: cost_history.append(
LogisticRegression.cost_function(data, current_lables, x.reshape(num_fratures,1))),
options={
"maxiter": n_iterations
}
)if not result.success:
raise ArithmeticError('Can not minimize cost function' + result.message)
theta = result.x.reshape(num_fratures,1)
return theta,cost_history@staticmethod
def cost_function(data, label, theta):
num_examples = data.shape[0]
prediction = LogisticRegression.hypothesis(data, theta)
y_true_cost = np.dot(label[label == 1].T, np.log(prediction[label == 1]))
y_false_cost = np.dot(1 - label[label == 0].T, np.log(1 - prediction[label == 0]))
cost = (-1 / num_examples) * (y_false_cost + y_true_cost)
return cost@staticmethod
def hypothesis(data, theta):
predictions = sigmoid(np.dot(data, theta))
return predictions@staticmethod
def gradient_step(data, label, theta):
num_examples = data.shape[0]
prediction = LogisticRegression.hypothesis(data, theta)
label_diff = prediction - label
gradients = (1 / num_examples) * np.dot(data.T, label_diff)
return gradients.T.flatten()def predict(self,data):
num_examples = data.shape[0]
data_processed = prepare_for_training(data, self.polynomial_degree, self.sinusoid_degree,
self.normalize_data)[0]
prediction = LogisticRegression.hypothesis(data_processed, self.theta.T)
arg = np.argmax(prediction,axis=1)
class_prediction = np.empty(arg.shape,dtype=object)
for index,unique_label in enumerate(self.unique_labels):
class_prediction[arg == index] = unique_label
return class_prediction.reshape((num_examples,1))3.测试代码
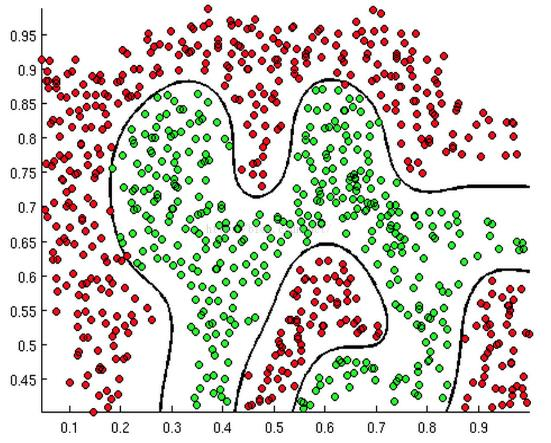
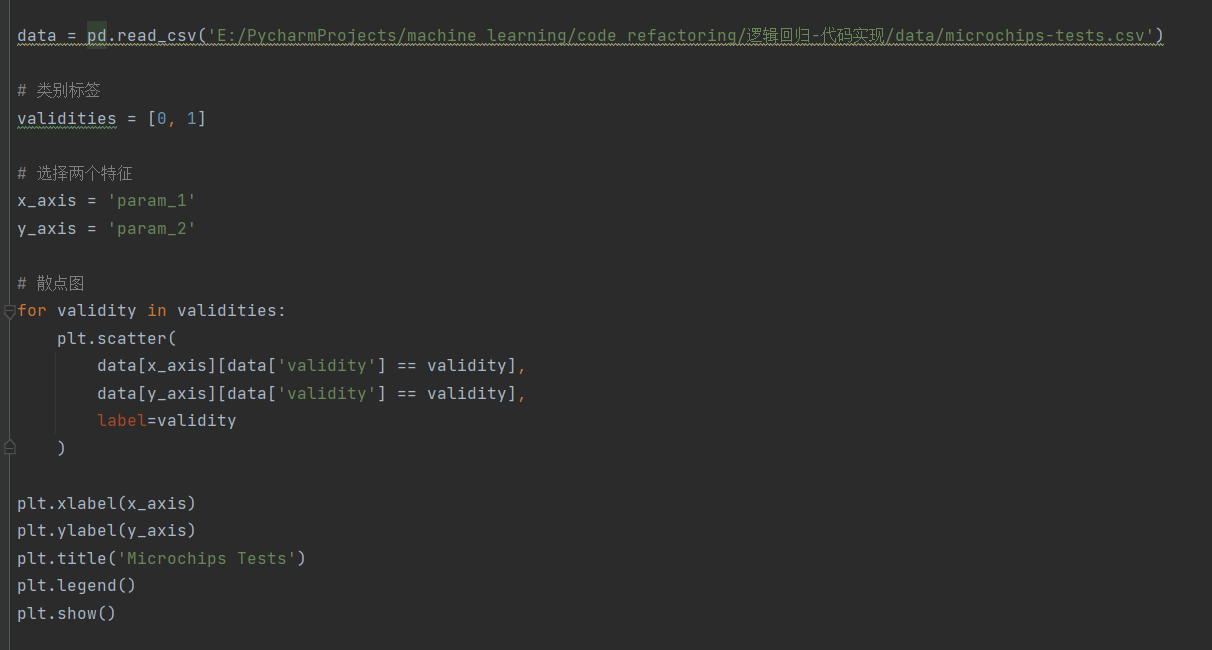
1.数据展示
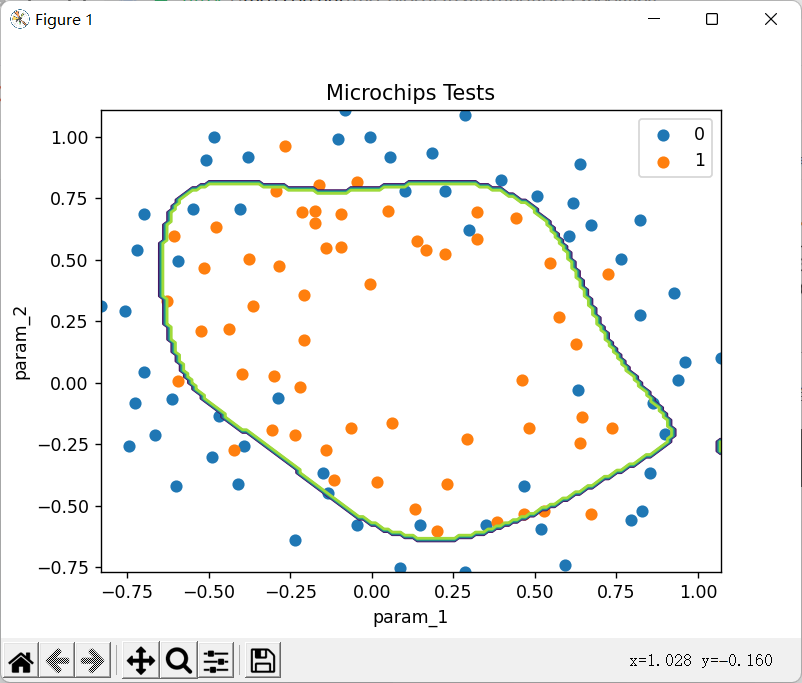
如图所示,我们使用了一个环形的数据分布进行测试,要想进行比较准确的分类,决策边界需要一个圆形
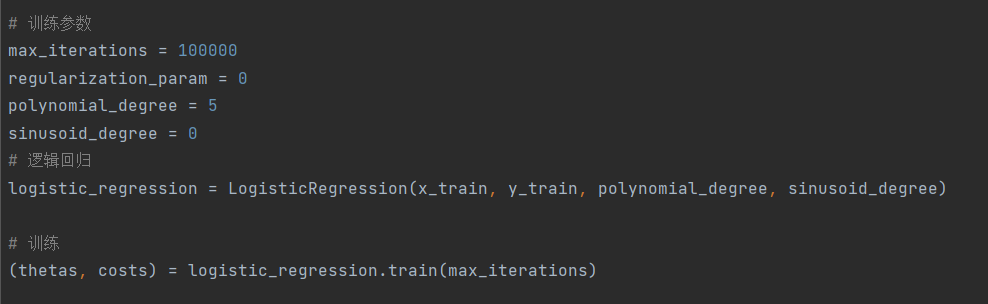
 2.训练数据
2.训练数据我们使用类中的train函数进行训练,代码及损失变化情况如下:
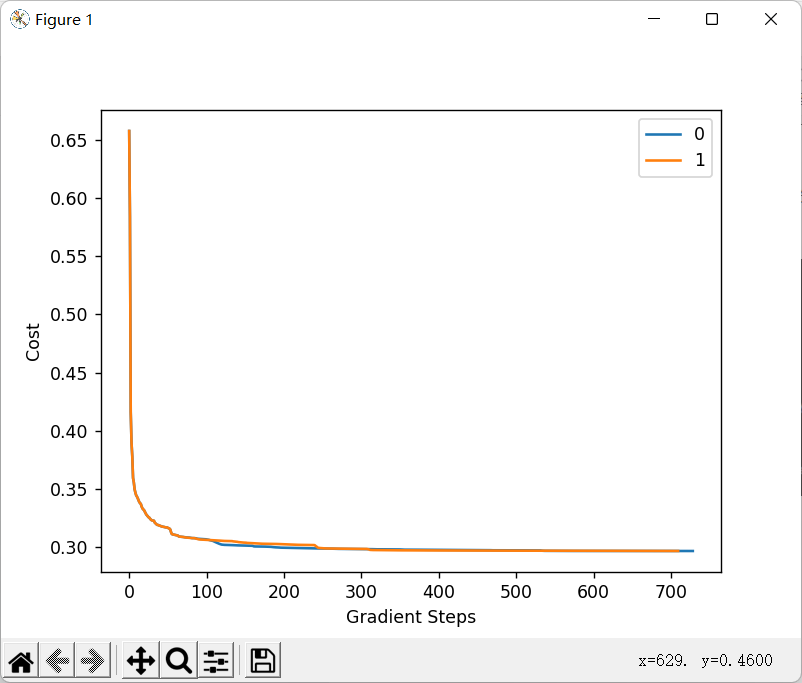
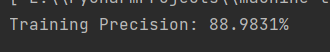
训练结果分类精度达到88.9831%,结果相当不错!!!
让我们绘制一下决策边界把!
-
相关阅读:
ZCMU--1431: Epic Game(C语言)
poetry执行报错 Reason: tried: ‘/opt/homebrew/Cellar/python@x.x
Argumentative structure for English essay
眨个眼就学会了PixiJS
SpringBoot与安全(Spring security)
Dubbo Admin修改注册中心为Nacos 以及Nacos整合Dubbo
WSL构建nRF5 SDK + ARM GCC开发环境 – RTT打印调试日志(二)
接口测试工具那么多,新公司用的自己没接触过怎么办?
1.安装 docker 容器并配置镜像加速器
postgresql中的stringtype=unspecified有什么作用?
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_52053775/article/details/126008864