-
【剑指offer系列】37. 序列化二叉树
这里是剑指offer系列的延续,作者将利用C++实现继续完成该系列的学习,剑指offer,喜欢的话可以点赞关注+收藏,加油更新中ing。
题目37. 序列化二叉树
请实现两个函数,分别用来序列化和反序列化二叉树。
您需要确保二叉树可以序列化为字符串,并且可以将此字符串反序列化为原始树结构。
数据范围
树中节点数量 [0,1000]。样例
你可以序列化如下的二叉树 8 / \ 12 2 / \ 6 4 为:"[8, 12, 2, null, null, 6, 4, null, null, null, null]"- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
【题解】-- BFS
- 树的中序前序后序遍历都可以访问到所有节点
但是无法得知节点在树的层级位置等信息,如图:
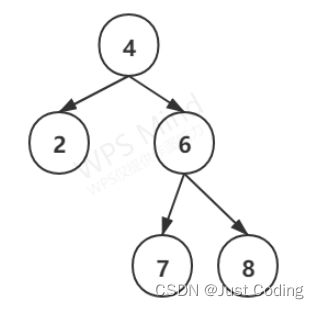
但是如果使用满二叉树的格式来看待这颗树,不足的位置使用NULL来填充。
所以按照次序的遍历,是可以定位出该节点在树的位置;
故思路就在于:我们使用队列,从根节点开始,层层去构建二叉树的结点。复杂度分析:
层序遍历,时间复杂度为O(n)。- 1
C++代码实现:
// 使用层序遍历的方式序列化二叉树(bfs 版本) /** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode *left; * TreeNode *right; * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: string str; // Encodes a tree to a single string. string serialize(TreeNode* root) { if(!root) // 空树的情况 { str += "null "; return str; } queue<TreeNode*> q; q.push(root); while(q.size()) { auto node = q.front(); q.pop(); if(node == nullptr) str += "null "; else { str += (to_string(node->val) + ' '); q.push(node->left); q.push(node->right); } } return str; } int getval(string& data, int cur, int next) { int val = 0; if(data[cur] != '-') for(int i = cur; i < next; ++i) val = val * 10 + data[i] - '0'; else { for(int i = cur + 1; i < next; ++i) val = val * 10 + data[i] - '0'; val = -val; } return val; } // Decodes your encoded data to tree. // 思路:使用队列,从根节点开始,层层去构建二叉树的结点。 TreeNode* deserialize(string data) { // 1. 先构建根节点 queue<TreeNode*> q; auto root = new TreeNode(-1); int cur = 0, next = 0; while(next < data.size() && data[next] != ' ') next++; // 此时 next 是第一个空格的位置 if(data[cur] == 'n') return nullptr; else { int val = getval(data, cur, next); root->val = val; q.push(root); } // 2. 使用队列逐步向下一层扩展(bfs) cur = next + 1; next = cur; while(q.size()) { auto node = q.front(); q.pop(); if(node == nullptr) continue; // 解析左节点,解析后链接 TreeNode* left = nullptr; while(next < data.size() && data[next] != ' ') next++; if(data[cur] != 'n') { int val = getval(data, cur, next); left = new TreeNode(val); } node->left = left; q.push(left); cur = next + 1; next = cur; // 解析右结点,解析后链接 TreeNode* right = nullptr; while(next < data.size() && data[next] != ' ') next++; if(data[cur] != 'n') { int val = getval(data, cur, next); right = new TreeNode(val); } node->right = right; q.push(right); cur = next + 1; next = cur; } return root; } };- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108

剑指offer系列将后续持续更新,有帮助的话,欢迎点赞👍、收藏⭐️+关注✌️哟~
-
相关阅读:
10分钟搞定Mysql主从部署配置
Maven 构建&项目测试
谷粒学苑 —— 9、课程管理:课程列表
git远程仓库限额的解决方法——大文件瘦身
9月有哪些程序员新书与您相约?
喜马拉雅 Redis 与 Pika 缓存使用军规
每天5分钟快速玩转机器学习算法:带有核函数的支持向量机模型
SpringBoot 集成 kaptcha 验证码
手写小程序摇树优化工具(七)——生成依赖图
每日刷题-5
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_46020266/article/details/126005586
