-
Netty——ByteBuffer消息粘包、半包示例
一、 ByteBuffer消息粘包、消息半包的概述
- NIO是面向缓冲区进行通信的,不是面向流的。既然是缓冲区,那它一定存在一个固定大小。这样一来通常会遇到两个问题:
- 消息粘包:当缓冲区足够大,由于网络不稳定种种原因,可能会有多条消息从通道读入缓冲区,此时如果无法分清数据包之间的界限,就会导致粘包问题;
- 消息半包:若消息没有接收完,缓冲区就被填满了,会导致从缓冲区取出的消息不完整,即半包的现象。
二、示例需求
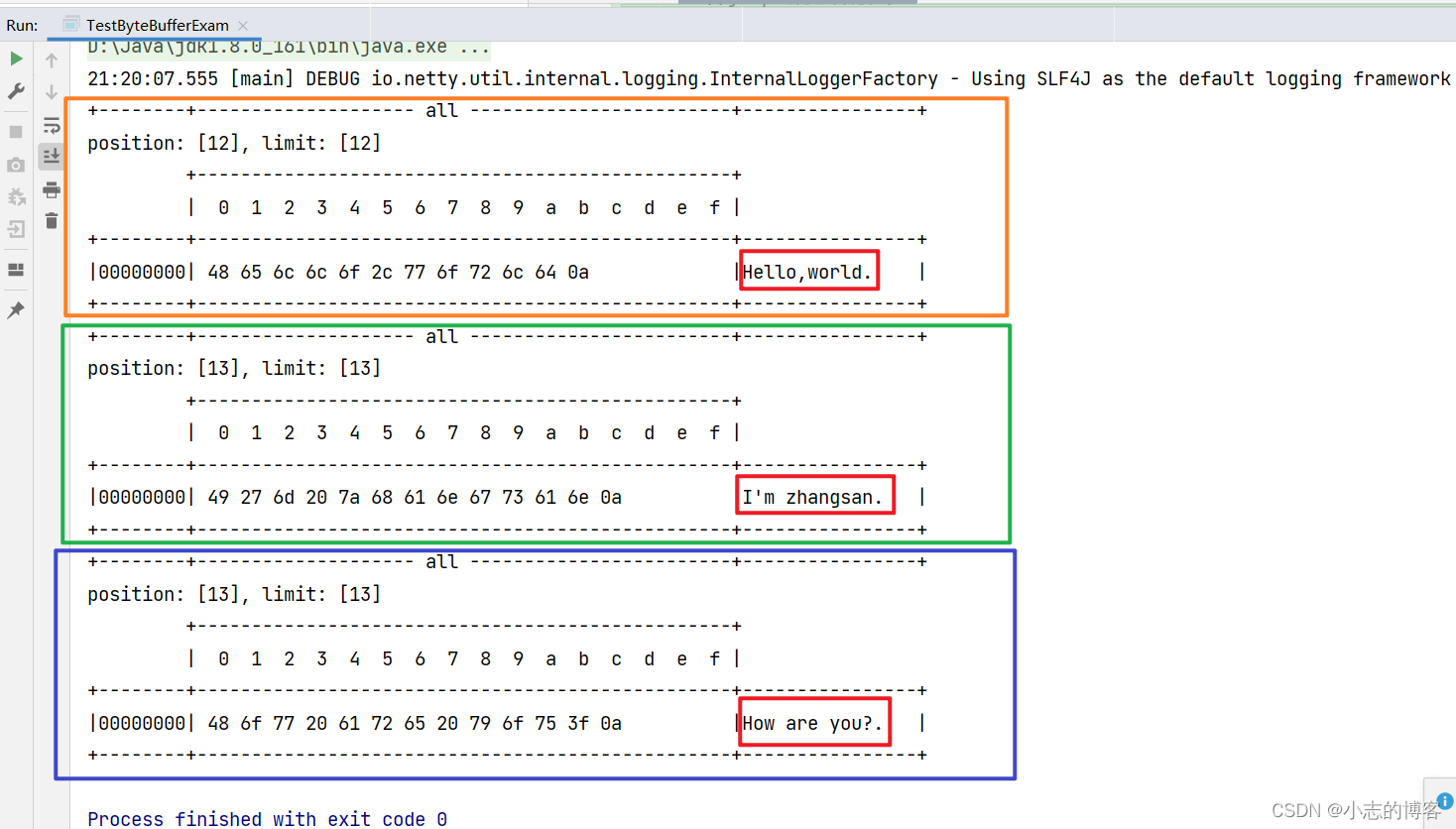
网络上有多条数据发送给服务端,数据之间使用 \n 进行分隔,但由于某种原因这些数据在接收时,被进行了重新组合,例如原始数据有3条:
- Hello,world\n
- I’m zhangsan\n
- How are you?\n
变成了下面的两个 byteBuffer (黏包,半包)
- Hello,world\nI’m zhangsan\nHo
- w are you?\n
现在要求你编写程序,将错乱的数据恢复成原始的按 \n 分隔的数据
三、示例代码
-
需求代码
package com.example.nettytest.nio.day1; import java.nio.ByteBuffer; import static com.example.nettytest.nio.day1.ByteBufferUtil.debugAll; /** * @description: * @author: xz * @create: 2022-07-26 21:10 */ public class TestByteBufferExam { public static void main(String[] args) { //分配一个新的字节缓冲区,容量为50 ByteBuffer sourceByteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(50); //写入数据 sourceByteBuffer.put("Hello,world\nI'm zhangsan\nHo".getBytes()); split(sourceByteBuffer); //再次写入数据 sourceByteBuffer.put("w are you?\n".getBytes()); split(sourceByteBuffer); } /** * 将错乱的数据恢复成原始的按 \n 分隔的数据方法 * */ public static void split(ByteBuffer sourceByteBuffer){ //flip 切换到读模式 sourceByteBuffer.flip(); for(int i = 0; i < sourceByteBuffer.limit(); i++){ if(sourceByteBuffer.get(i) =='\n'){//找到一条完整消息 //换行符索引+1-起始位置 int length =i + 1- sourceByteBuffer.position(); // 把此条完整消息存入新的 ByteBuffer ByteBuffer targetByteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(length); for(int j=0;j<length;j++){ targetByteBuffer.put(sourceByteBuffer.get()); } //打印byteBuffer中所有内容 debugAll(targetByteBuffer); } } //compact 把未读完的部分向前压缩,然后切换至写模式 sourceByteBuffer.compact(); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
-
输出ByteBuffer结构的工具类
package com.example.nettytest.nio.day1; import io.netty.util.internal.StringUtil; import java.nio.ByteBuffer; import static io.netty.util.internal.MathUtil.isOutOfBounds; import static io.netty.util.internal.StringUtil.NEWLINE; public class ByteBufferUtil { private static final char[] BYTE2CHAR = new char[256]; private static final char[] HEXDUMP_TABLE = new char[256 * 4]; private static final String[] HEXPADDING = new String[16]; private static final String[] HEXDUMP_ROWPREFIXES = new String[65536 >>> 4]; private static final String[] BYTE2HEX = new String[256]; private static final String[] BYTEPADDING = new String[16]; static { final char[] DIGITS = "0123456789abcdef".toCharArray(); for (int i = 0; i < 256; i++) { HEXDUMP_TABLE[i << 1] = DIGITS[i >>> 4 & 0x0F]; HEXDUMP_TABLE[(i << 1) + 1] = DIGITS[i & 0x0F]; } int i; // Generate the lookup table for hex dump paddings for (i = 0; i < HEXPADDING.length; i++) { int padding = HEXPADDING.length - i; StringBuilder buf = new StringBuilder(padding * 3); for (int j = 0; j < padding; j++) { buf.append(" "); } HEXPADDING[i] = buf.toString(); } // Generate the lookup table for the start-offset header in each row (up to 64KiB). for (i = 0; i < HEXDUMP_ROWPREFIXES.length; i++) { StringBuilder buf = new StringBuilder(12); buf.append(NEWLINE); buf.append(Long.toHexString(i << 4 & 0xFFFFFFFFL | 0x100000000L)); buf.setCharAt(buf.length() - 9, '|'); buf.append('|'); HEXDUMP_ROWPREFIXES[i] = buf.toString(); } // Generate the lookup table for byte-to-hex-dump conversion for (i = 0; i < BYTE2HEX.length; i++) { BYTE2HEX[i] = ' ' + StringUtil.byteToHexStringPadded(i); } // Generate the lookup table for byte dump paddings for (i = 0; i < BYTEPADDING.length; i++) { int padding = BYTEPADDING.length - i; StringBuilder buf = new StringBuilder(padding); for (int j = 0; j < padding; j++) { buf.append(' '); } BYTEPADDING[i] = buf.toString(); } // Generate the lookup table for byte-to-char conversion for (i = 0; i < BYTE2CHAR.length; i++) { if (i <= 0x1f || i >= 0x7f) { BYTE2CHAR[i] = '.'; } else { BYTE2CHAR[i] = (char) i; } } } /** * 打印所有内容 * @param buffer */ public static void debugAll(ByteBuffer buffer) { int oldlimit = buffer.limit(); buffer.limit(buffer.capacity()); StringBuilder origin = new StringBuilder(256); appendPrettyHexDump(origin, buffer, 0, buffer.capacity()); System.out.println("+--------+-------------------- all ------------------------+----------------+"); System.out.printf("position: [%d], limit: [%d]\n", buffer.position(), oldlimit); System.out.println(origin); buffer.limit(oldlimit); } /** * 打印可读取内容 * @param buffer */ public static void debugRead(ByteBuffer buffer) { StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder(256); appendPrettyHexDump(builder, buffer, buffer.position(), buffer.limit() - buffer.position()); System.out.println("+--------+-------------------- read -----------------------+----------------+"); System.out.printf("position: [%d], limit: [%d]\n", buffer.position(), buffer.limit()); System.out.println(builder); } public static void main(String[] args) { ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(10); buffer.put(new byte[]{97, 98, 99, 100}); debugAll(buffer); } private static void appendPrettyHexDump(StringBuilder dump, ByteBuffer buf, int offset, int length) { if (isOutOfBounds(offset, length, buf.capacity())) { throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException( "expected: " + "0 <= offset(" + offset + ") <= offset + length(" + length + ") <= " + "buf.capacity(" + buf.capacity() + ')'); } if (length == 0) { return; } dump.append( " +-------------------------------------------------+" + NEWLINE + " | 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f |" + NEWLINE + "+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+"); final int startIndex = offset; final int fullRows = length >>> 4; final int remainder = length & 0xF; // Dump the rows which have 16 bytes. for (int row = 0; row < fullRows; row++) { int rowStartIndex = (row << 4) + startIndex; // Per-row prefix. appendHexDumpRowPrefix(dump, row, rowStartIndex); // Hex dump int rowEndIndex = rowStartIndex + 16; for (int j = rowStartIndex; j < rowEndIndex; j++) { dump.append(BYTE2HEX[getUnsignedByte(buf, j)]); } dump.append(" |"); // ASCII dump for (int j = rowStartIndex; j < rowEndIndex; j++) { dump.append(BYTE2CHAR[getUnsignedByte(buf, j)]); } dump.append('|'); } // Dump the last row which has less than 16 bytes. if (remainder != 0) { int rowStartIndex = (fullRows << 4) + startIndex; appendHexDumpRowPrefix(dump, fullRows, rowStartIndex); // Hex dump int rowEndIndex = rowStartIndex + remainder; for (int j = rowStartIndex; j < rowEndIndex; j++) { dump.append(BYTE2HEX[getUnsignedByte(buf, j)]); } dump.append(HEXPADDING[remainder]); dump.append(" |"); // Ascii dump for (int j = rowStartIndex; j < rowEndIndex; j++) { dump.append(BYTE2CHAR[getUnsignedByte(buf, j)]); } dump.append(BYTEPADDING[remainder]); dump.append('|'); } dump.append(NEWLINE + "+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+"); } private static void appendHexDumpRowPrefix(StringBuilder dump, int row, int rowStartIndex) { if (row < HEXDUMP_ROWPREFIXES.length) { dump.append(HEXDUMP_ROWPREFIXES[row]); } else { dump.append(NEWLINE); dump.append(Long.toHexString(rowStartIndex & 0xFFFFFFFFL | 0x100000000L)); dump.setCharAt(dump.length() - 9, '|'); dump.append('|'); } } public static short getUnsignedByte(ByteBuffer buffer, int index) { return (short) (buffer.get(index) & 0xFF); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
- 134
- 135
- 136
- 137
- 138
- 139
- 140
- 141
- 142
- 143
- 144
- 145
- 146
- 147
- 148
- 149
- 150
- 151
- 152
- 153
- 154
- 155
- 156
- 157
- 158
- 159
- 160
- 161
- 162
- 163
- 164
- 165
- 166
- 167
- 168
- 169
- 170
- 171
- 172
- 173
- 174
- 175
- 176
- 177
- 178
- 179
- 180
- 181
- 182
- 183
-
输出结果
-
相关阅读:
《前端开发实战 · videojs 视频需求开发》
1、代理模式
WPF 02
2023年【A特种设备相关管理(锅炉压力容器压力管道)】考试内容及A特种设备相关管理(锅炉压力容器压力管道)考试技巧
《好代码 坏代码》阅读
Cobalt Strike
【java】ArrayList和LInkedList的区别
蓝桥杯嵌入式基础模块——GPIO的使用(新板)STM32G431(HAL库开发)
SpringBoot集成security
智能汽车能否真正实现无人驾驶,为什么?
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/li1325169021/article/details/126003430