-
C#让程序运行更稳健——异常、调试和测试(代码没看懂)
异常是一种封装了反常程序事件信息的对象。在C#中用异常来处理错误和反常情况,当异常抛出时,当前函数的执行会停止,堆栈展开,直到找到正确的异常处理代码。如果异常得到处理,程序会解决问题并继续执行。即使程序不能继续执行,捕获异常也能使程序输出错误信息并安全地终止程序。
一、异常处理语句
异常就是程序运行中发生的错误,异常处理是程序设计的一部分。错误的出现并不总是编写应用程序者的原因,有时应用程序会因为终端用户的操作而发生错误。无论如何,在编写程序前,都应预测应用程序和代码中出现的错误。
1、异常处理
导常提供了一种把程序控制权从某个部分转移到另一个部分的方式。C#异常处理是建立在四个关键词之上的:try、catch、finally和throw。
try:一个try块标识了一个将被激活的特定的异常的代码块。后跟一个或多个catch块。
catch:程序通过异常处理程序捕获异常。catch关键字表示异常的捕获。
finally:finally块用于执行给定的语句,不管异常是否被抛出都会执行。
throw:当问题出现时,程序抛出一个异常。使用throw关键字来完成。
2、捕获异常
捕获异常是通过try…catch语句实现的,语法格式如下:
- try
- {
- //引起异常的语句
- }
- catch( ExceptionName e1 )
- {
- //错误处理代码
- }
其中,try关键字标识了一个有异常的代码块,后跟一个或多个catch块。而catch关键字表示异常的捕获。
编写程序,利用try…catch语句捕获数据的越界问题。
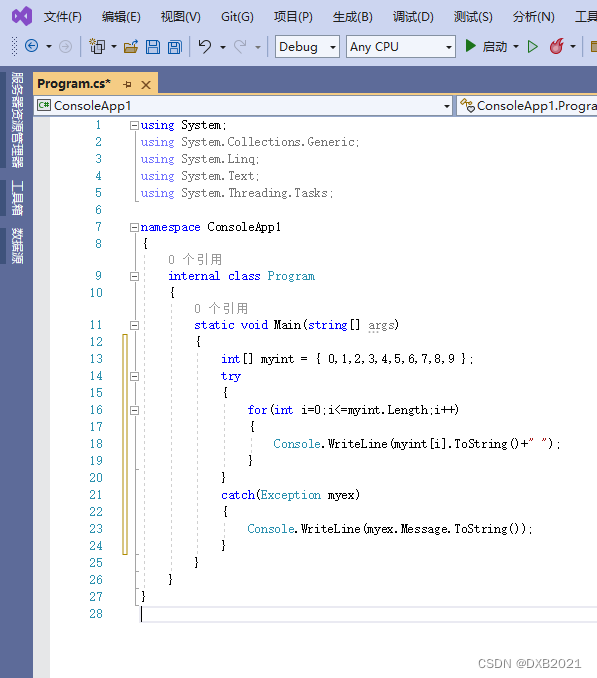
- using System;
- using System.Collections.Generic;
- using System.Linq;
- using System.Text;
- using System.Threading.Tasks;
- namespace ConsoleApp1
- {
- internal class Program
- {
- static void Main(string[] args)
- {
- int[] myint = { 0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9 };
- try
- {
- for(int i=0;i<=myint.Length;i++)
- {
- Console.WriteLine(myint[i].ToString()+" ");
- }
- }
- catch(Exception myex)
- {
- Console.WriteLine(myex.Message.ToString());
- }
- }
- }
- }
在代码中,首先定义一个数组myint,并为其赋值;然后通过for循环进行遍历,需要注意的是,由于循环变量i应该小于数组myint中所有元素的总数,但是当书写为“i<=myint.Length;”时,就会造成数组的越界问题;接着,再将这段有异常的for循环语句放入到try语句中,并通过catch语句捕获异常,描述出造成异常的原因。
运行结果以后,打开就马上关闭,没看完。所以,最后一句话增加Console.ReadLine();
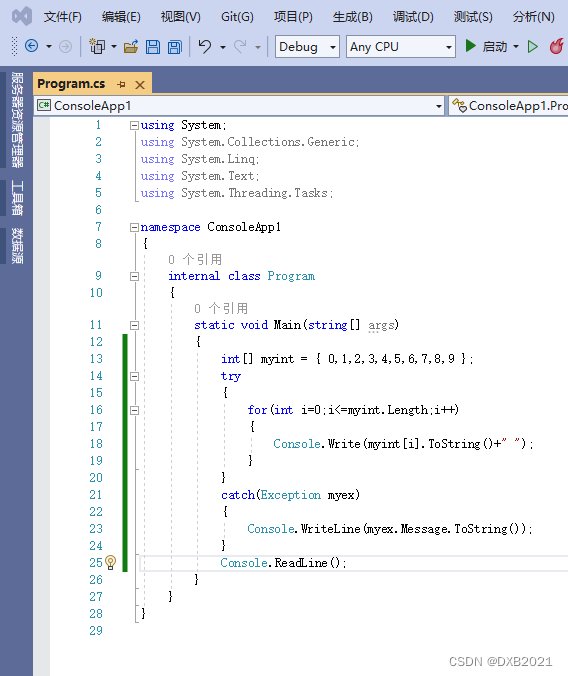
完整代码:
- using System;
- using System.Collections.Generic;
- using System.Linq;
- using System.Text;
- using System.Threading.Tasks;
- namespace ConsoleApp1
- {
- internal class Program
- {
- static void Main(string[] args)
- {
- int[] myint = { 0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9 };
- try
- {
- for(int i=0;i<=myint.Length;i++)
- {
- Console.Write(myint[i].ToString()+" ");
- }
- }
- catch(Exception myex)
- {
- Console.WriteLine(myex.Message.ToString());
- }
- Console.ReadLine();
- }
- }
- }
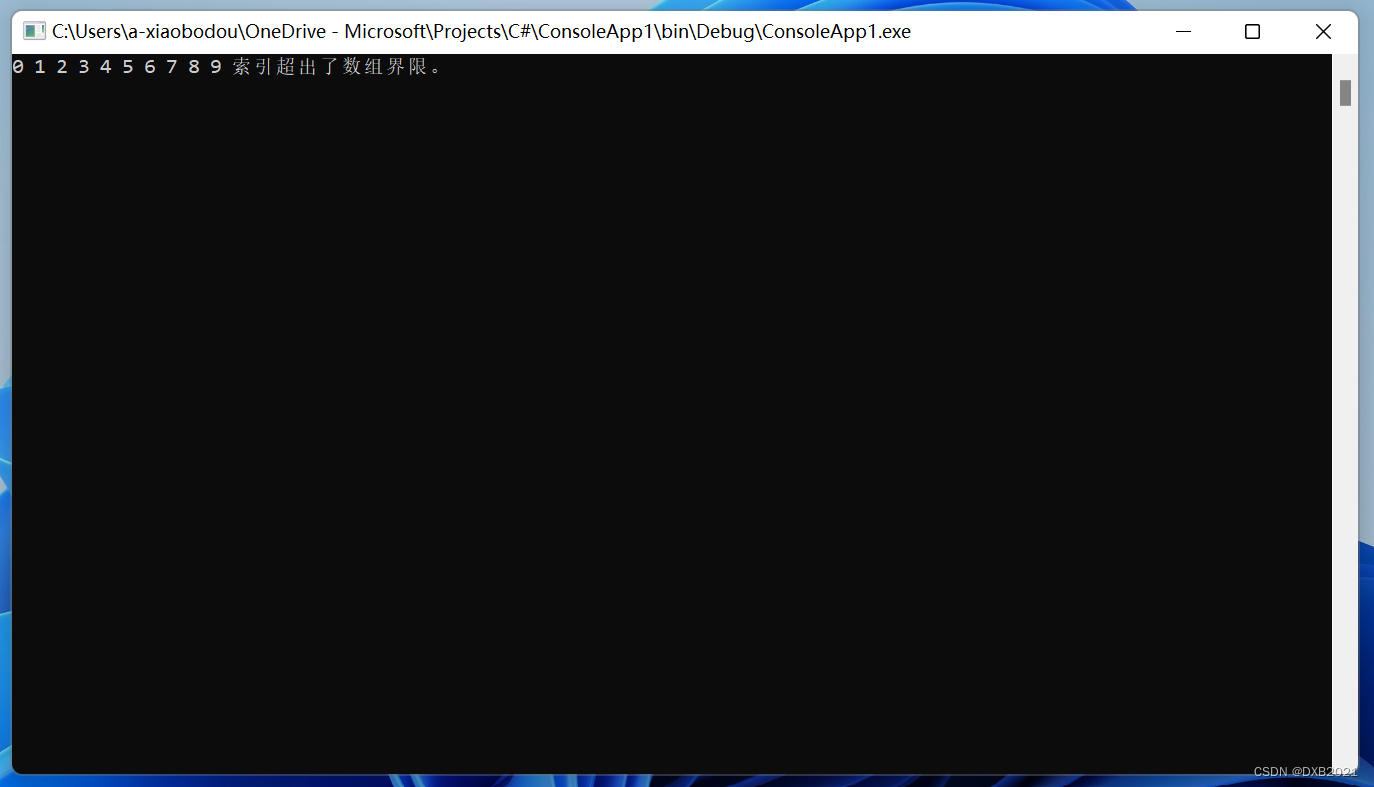
运行结果如下:
3、清除、处理异常
如果用户对产生的异常不进行处理,只能通过catch语句进行捕获,则仍然无法消除为错误所分配的资源 。所以需要使用try...finally语句清除异常,语法格式如下:
try
{
//包含容易产生异常的代码
}
finally
{
//要执行的语句
}
finilly语句虽然可以消除try语句块中分配的任何资源,但是它不管异常是否被抛出,程序都会执行。因此增加catch语句,就可以完美地合并两种错误处理技术,即捕获异常、消除并执行应用程序 。语法格式如下:
try
{
//包含容易产生异常的代码
}
catch(异常类 异常实例对象)
{
//异常处理代码
}
finally
{
//要执行的语句
}
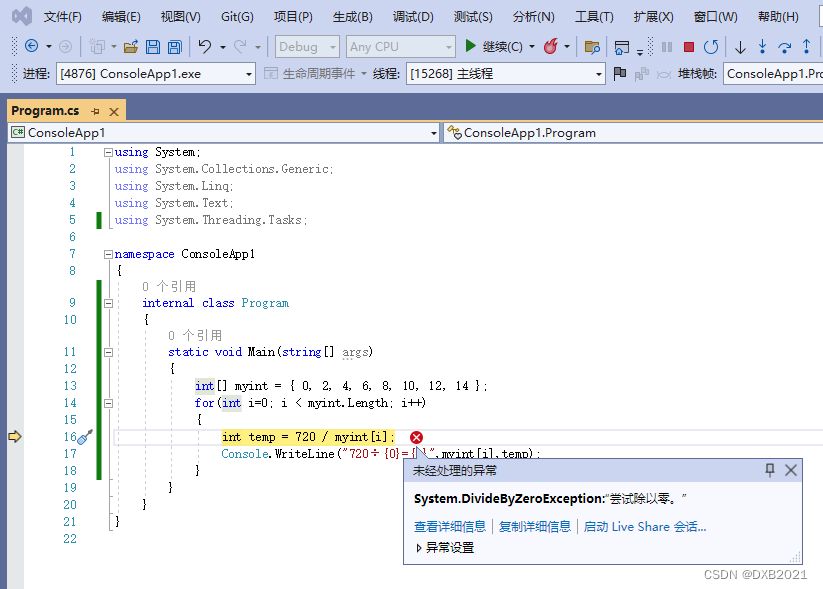
编程程序,输出尝试除以零所引发的异常。
代码如下:
- using System;
- using System.Collections.Generic;
- using System.Linq;
- using System.Text;
- using System.Threading.Tasks;
- namespace ConsoleApp1
- {
- internal class Program
- {
- static void Main(string[] args)
- {
- int[] myint = { 0, 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14 };
- for(int i=0; i < myint.Length; i++)
- {
- int temp = 720 / myint[i];
- Console.WriteLine("720÷{0}={1}",myint[i],temp);
- }
- }
- }
- }
运行结果如下:
编写程序,利用try...catch...finall语句清除除以零所引发的异常,确保程序正常运行。
代码如下:
- using System;
- using System.Collections.Generic;
- using System.Linq;
- using System.Text;
- using System.Threading.Tasks;
- namespace ConsoleApp1
- {
- internal class Program
- {
- static void Main(string[] args)
- {
- int[] myint = { 0, 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14 };
- try
- {
- for (int i = 0; i < myint.Length; i++)
- {
- int temp = 720 / myint[i];
- Console.WriteLine("720÷{0}={1}", myint[i], temp);
- }
- }
- catch(Exception myex)
- {
- Console.WriteLine(myex.Message.ToString());
- }
- finally
- {
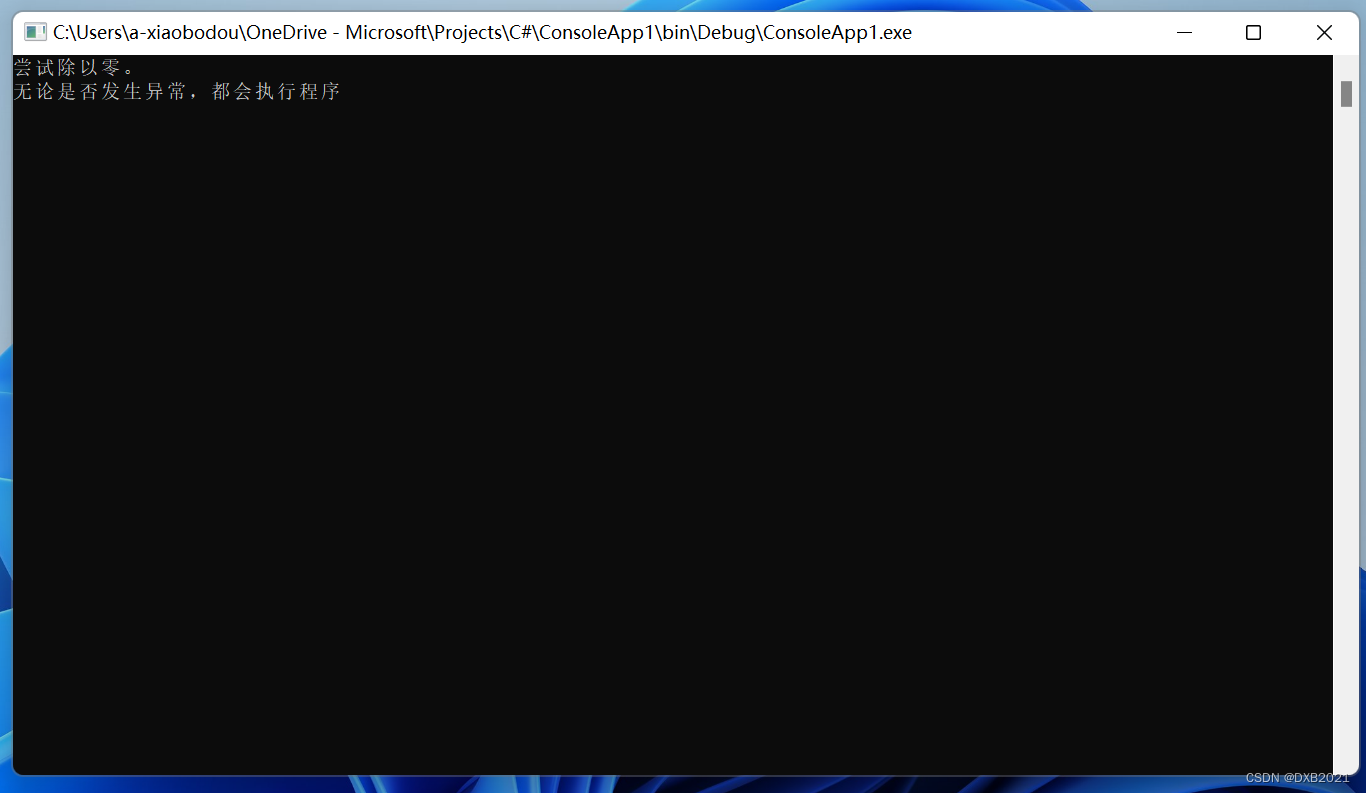
- Console.WriteLine("无论是否发生异常,都会执行程序");
- }
- Console.ReadLine();
- }
- }
- }
运行结果如下:
4、引发异常
有时在编写程序时,需要故意引发异常,以便捕获到异常的信息。而throw语句就是用于主动引发一个异常。
引发异常的语法格式:
throw new 异常类(异常信息);
异常类可以是系统预定义的类,也可以是用户自定义的类,而异常信息通常都表现为一个字符串。
编写程序,在Program类中定义一个整形的私有静态方法,该方法含有一个字符串类型的参数。然后通过该方法将一个不能转换成整数的字符串转换成整数,并引发异常。
代码如下:
- using System;
- using System.Collections.Generic;
- using System.Linq;
- using System.Text;
- using System.Threading.Tasks;
- using System.IO;
- using System.Threading;
- namespace ConsoleApp1
- {
- internal class Program
- {
- //用户自定义一个整形的静态私有成员函数ConvertStringToInt
- private static int ConvertStringToInt(string mystr)
- {
- int outnum = 0;
- //在格式转换时可能发生的异常
- try
- {
- //将字符串转换为整形
- outnum= Convert.ToInt32(mystr);
- return outnum;
- }//如果outnum发生了异常,那么就在catch中抛出异常
- catch
- {
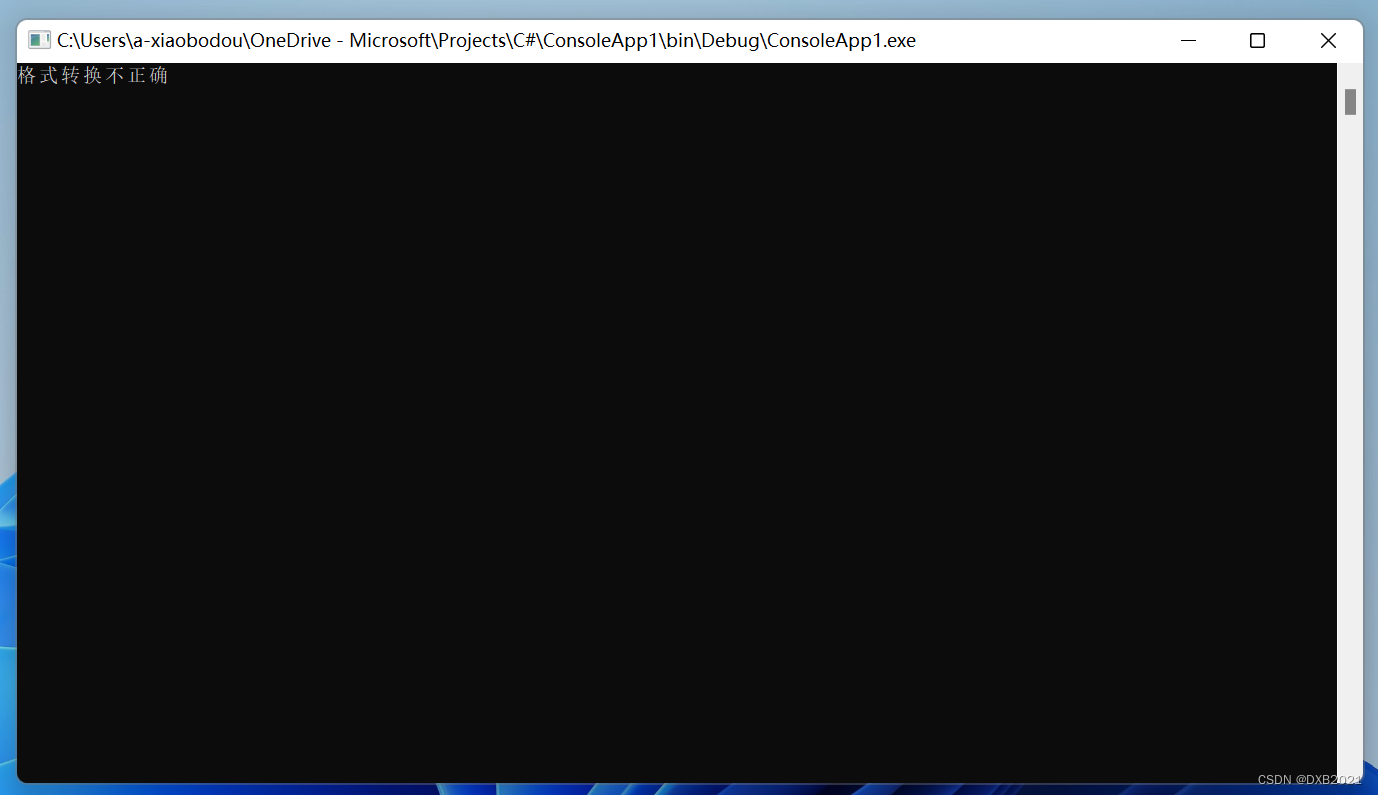
- throw new FormatException("格式转换不正确");
- }
- }
- static void Main(string[] args)
- {
- //在Main方法中调用ConvertStringToInt方法
- string mystr = "hao123";
- //在调用方法值时也会引发一个异常
- try
- {
- int myint = ConvertStringToInt(mystr);
- Console.WriteLine(myint);
- }
- catch(FormatException exf)
- {
- Console.WriteLine(exf.Message.ToString());
- }
- Console.ReadLine();
- }
- }
- }
运行结果如下:
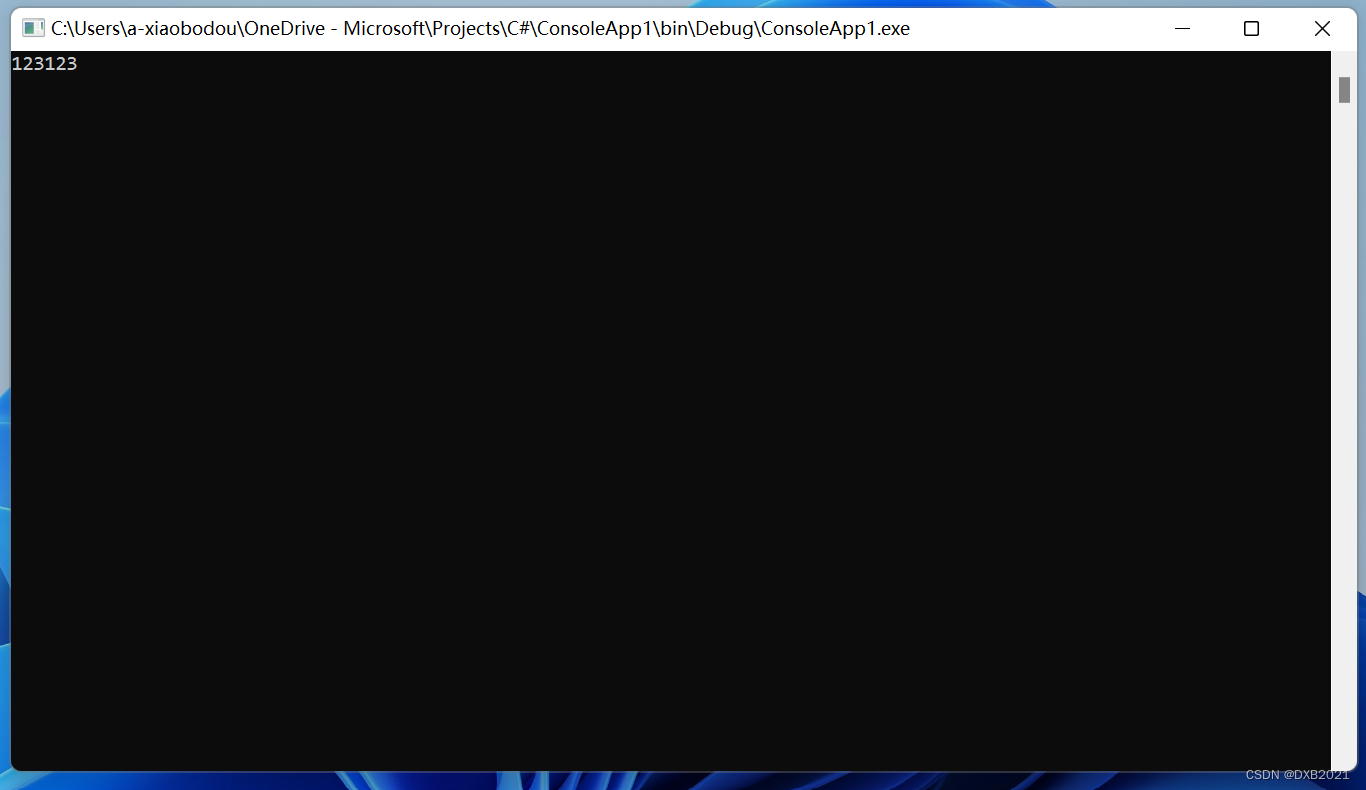
有一个语句修改为:“string mystr = "123123";”运行结果如下:
 代码不是很明白。
代码不是很明白。二、C#中的异常类
在C#中的异常,就是为了处理错误情况而提供的一种机制。它为每种错误情况提供了定制的处理方式,并且把标识错误的代码和预处理错误的代码分离开来。C#中的异常类主要是直接或间接地派生于System.Exception类,其中,System.ApplicationException类则是第三方定义的异常类,如果用户要自定义异常类,那么就从该类派生。
预定义的异常类 异常类 说明 Exception 所有异常对象的基类 SystemException 运行时产生的所有错误的基类 IndexOutofRangeException 当一个数组的下标超出范围时运行时引发 NullReferenceException 当一个空对象被引用时运行时引发 ArgumentException 所有参数异常的基类 FormatException 该类用于处理参数格式错误的异常。
1、IndexOutofRangeException类的使用
IndexOutofRangeException类用于描述试图访问索引超出界限的数组或集合的元素时引发的异常。
编写程序,定义一个数组,在遍历该数组时,超出该数组索引值的界限。
代码如下:
- using System;
- using System.Collections.Generic;
- using System.Linq;
- using System.Text;
- using System.Threading.Tasks;
- using System.IO;
- using System.Threading;
- namespace ConsoleApp1
- {
- internal class Program
- {
- static void Main(string[] args)
- {
- int[] myint = { 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 };
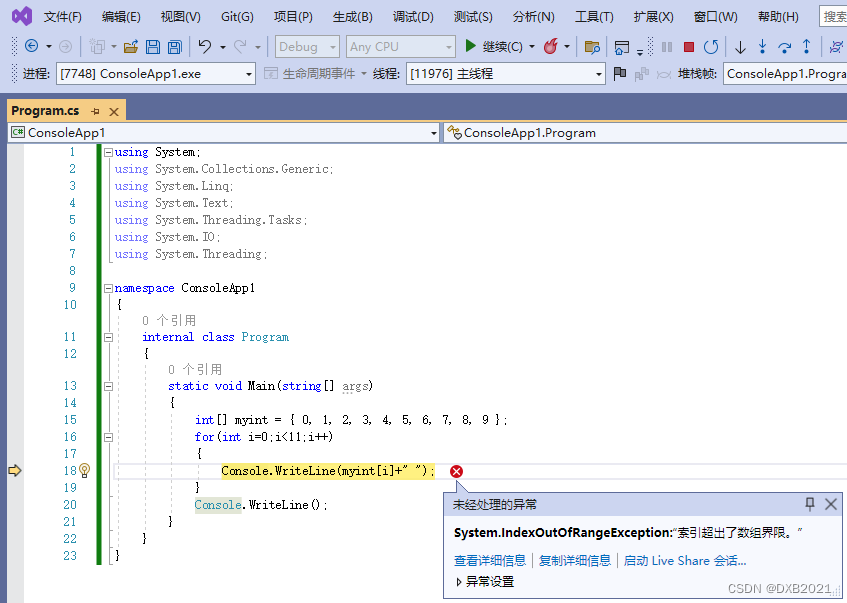
- for(int i=0;i<11;i++)
- {
- Console.WriteLine(myint[i]+" ");
- }
- Console.WriteLine();
- }
- }
- }
运行结果如下:
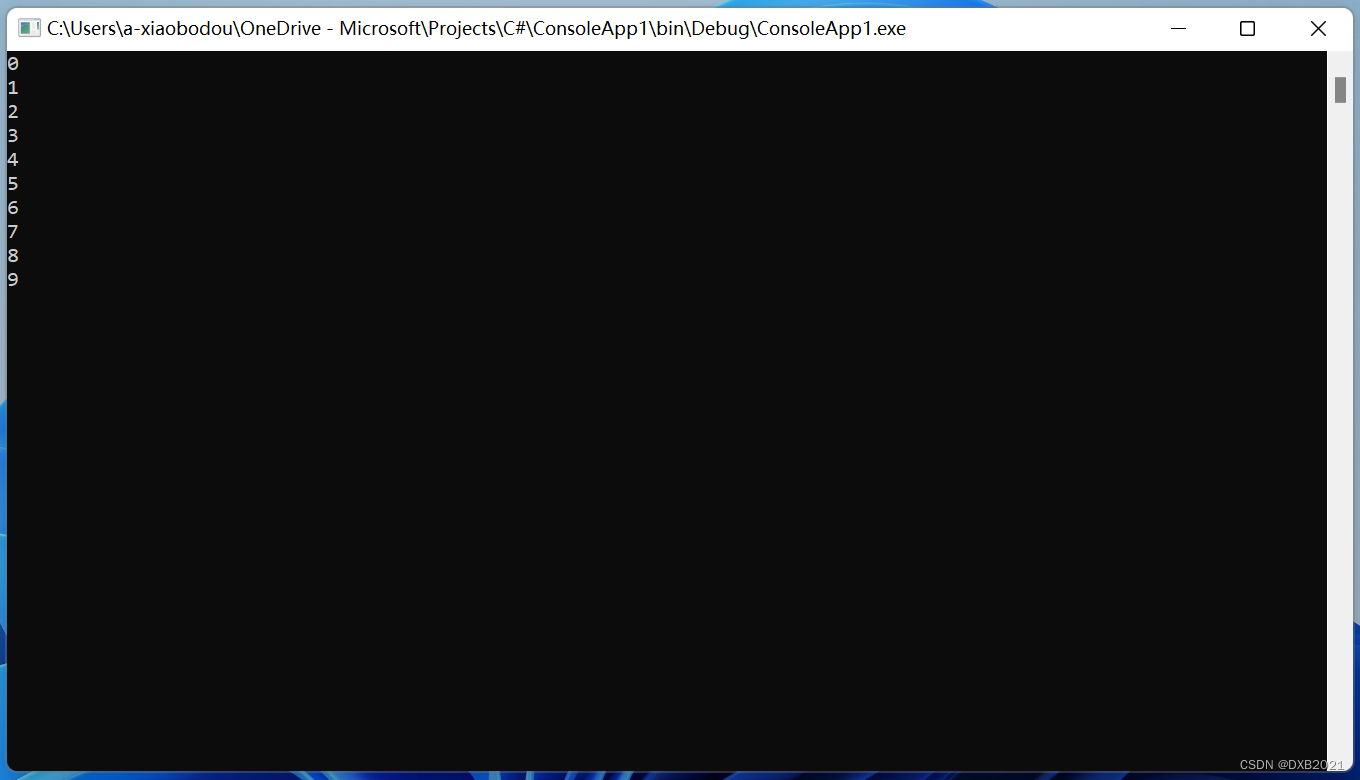
编写程序,使用IndexOutofRangeException类,捕获异常。
代码如下:
- using System;
- using System.Collections.Generic;
- using System.Linq;
- using System.Text;
- using System.Threading.Tasks;
- using System.IO;
- using System.Threading;
- namespace ConsoleApp1
- {
- internal class Program
- {
- static void Main(string[] args)
- {
- int[] myint = { 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 };
- try
- {
- for (int i = 0; i < 11; i++)
- {
- Console.WriteLine(myint[i] + " ");
- }
- }
- catch(IndexOutOfRangeException exIOR)
- {
- Console.WriteLine(exIOR.Message.ToString());
- }
- Console.ReadLine();
- }
- }
- }
运行结果如下:
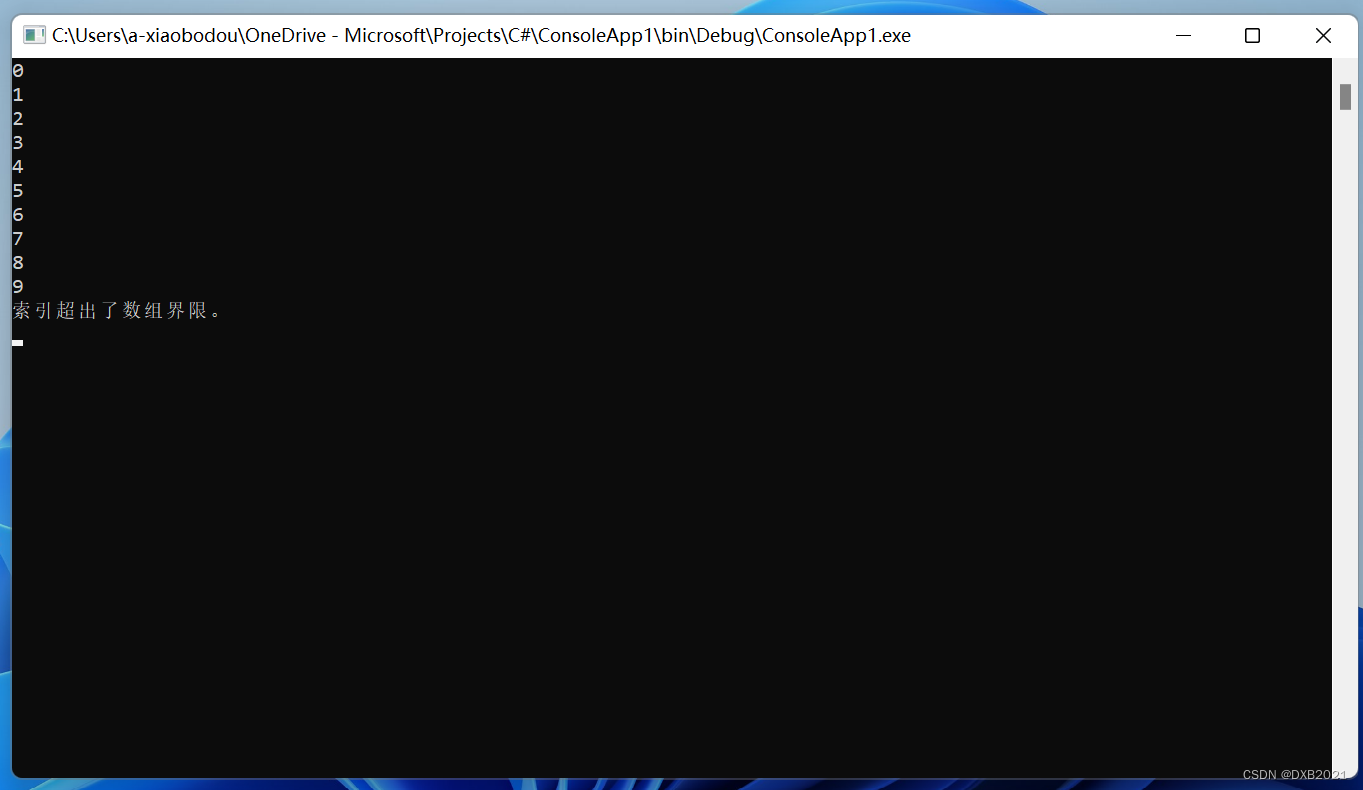
2、NullReferenceException的使用
NullReferenceException类用于描述尝试取消引用空对象,引用时所引发的异常。
编写程序,引用一个空值。
代码如下:
- using System;
- using System.Collections.Generic;
- using System.Linq;
- using System.Text;
- using System.Threading.Tasks;
- using System.IO;
- using System.Threading;
- namespace ConsoleApp1
- {
- internal class Program
- {
- static void Main(string[] args)
- {
- string mystr = null;
- try
- {
- Console.WriteLine(mystr.ToString());
- }
- catch(NullReferenceException exNR)
- {
- Console.WriteLine(exNR.Message.ToString());
- }
- Console.ReadLine();
- }
- }
- }
运行结果如下:
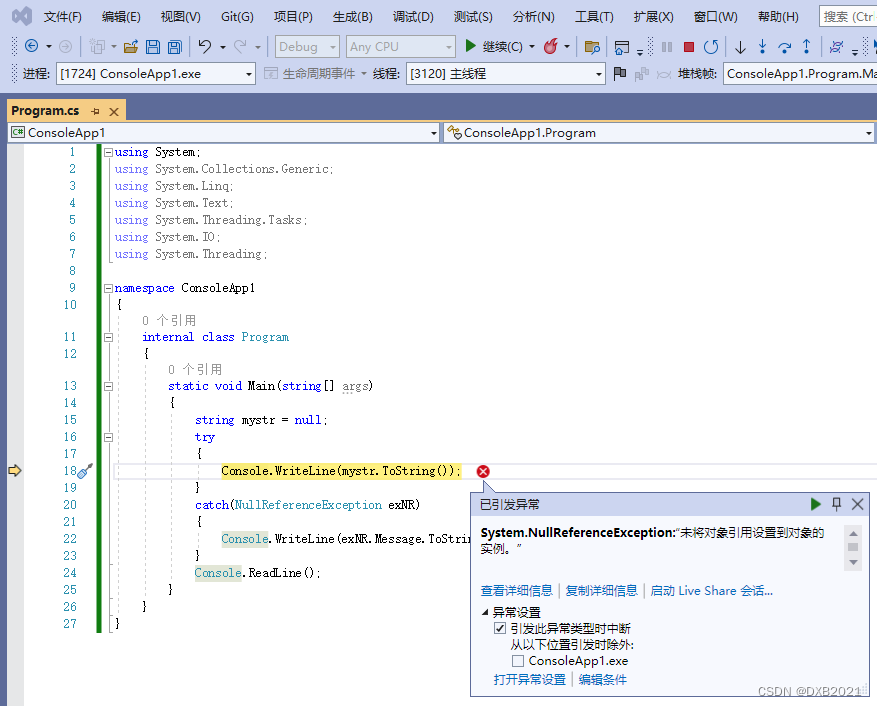
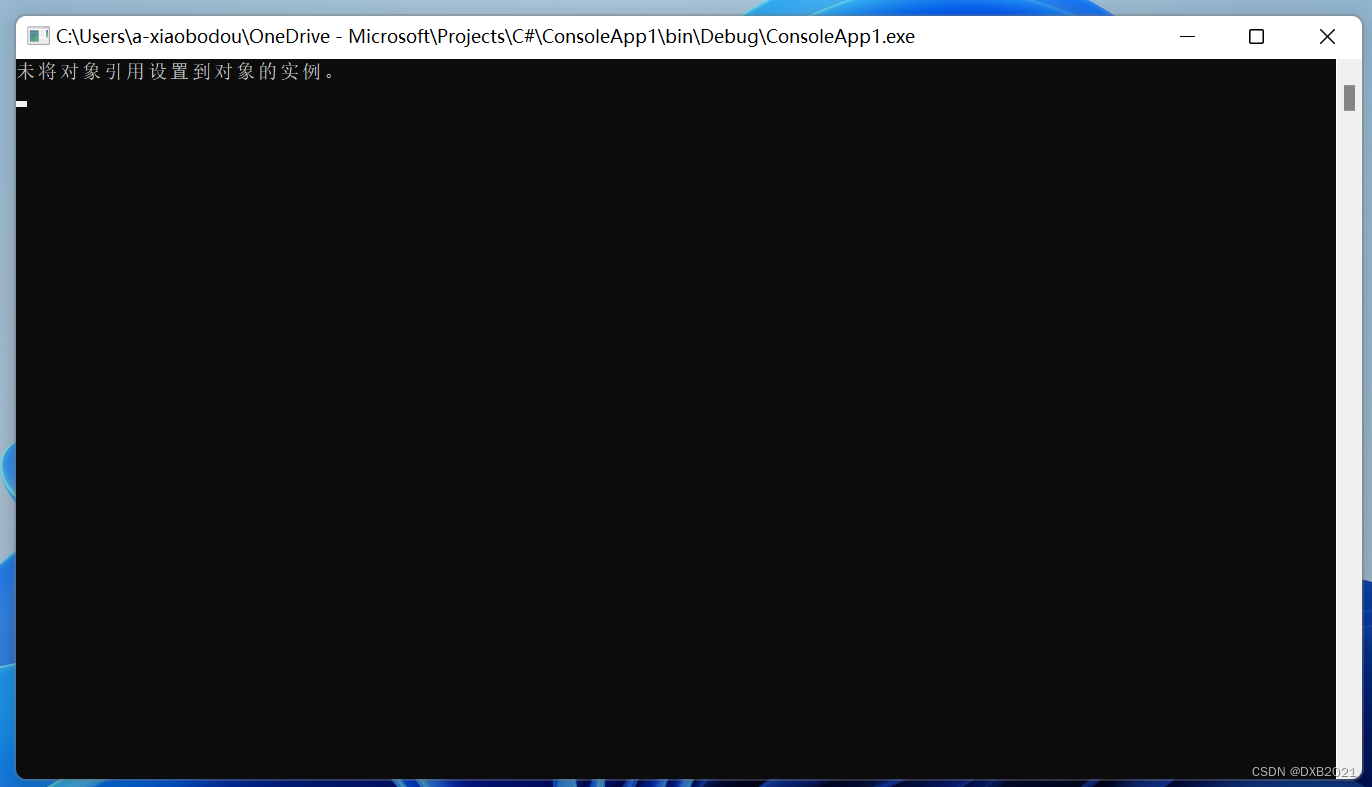
在代码中,定义了一个string类型的变量str,并赋予null值。由于访问一个变量的空值是没有任何意义的,所以try...catch捕获了NullReferenceException类描述的一个异常。
三、程序调试
每个人不可能一下就能写出完美的程序,所以需要不断地对代码进行高度,即在代码运行时检查代码并验证其执行路径和数据是否正确。常用的程序调试操作包括设置断点、开始、中断和停止程序的执行、单步执行程序以及使程序运行到指定的位置。
1、断点调试
2、开始、中断和停止程序的执行
3、逐过程执行和逐语句执行
-
相关阅读:
北京已收录2023开学了《乡村振兴战略下传统村落文化旅游设计》中国建筑出版传媒许少辉八一新书
Java0基础入门,看完这篇就够了
【K8S专栏】Kubernetes应用质量管理
一文搞懂EMAS Serverless小程序开发|电子书免费下载
2140. 解决智力问题;1401. 圆和矩形是否有重叠;901. 股票价格跨度
白嫖阿里云服务器,速看!数量不多
Oracle11g在红帽Linux上的安装教程
情绪感受一点分享
SCA Nacos 服务注册和配置中心(一)
计算机网络学习笔记(Ⅱ):物理层
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/DXB2021/article/details/125766942
