-
实体注解-批量生成10000条测试数据
提示:文章写完后,目录可以自动生成,如何生成可参考右边的帮助文档
一、 前言
最近收到一个需求,给多张表生成测试数据来测试前端的统计页面 部分字段要求从固定值中选择 部门,人员等要求是中文 日期要求在某些时间段 …等等
最先想到的当然是写工具类,再去生成对应的数据。但是下次如果还有这样的需求,我还要一个个写吗,能不能简化一下。
该方式可以解决快速单表生成测试数据,多表关联生成数据还需要在研究一下最后,就想到了写一个实体类的测试数据批量生成工具,演示如下
二、效果
先创建实体类
实体类
public class TestEntity { private String name; private Integer age; private String tel; private String dept; private Date date; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
生成数据的SQL并执行
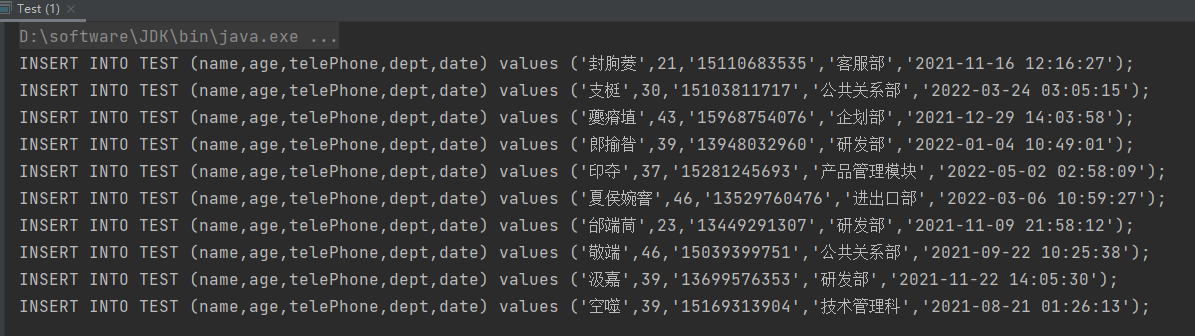
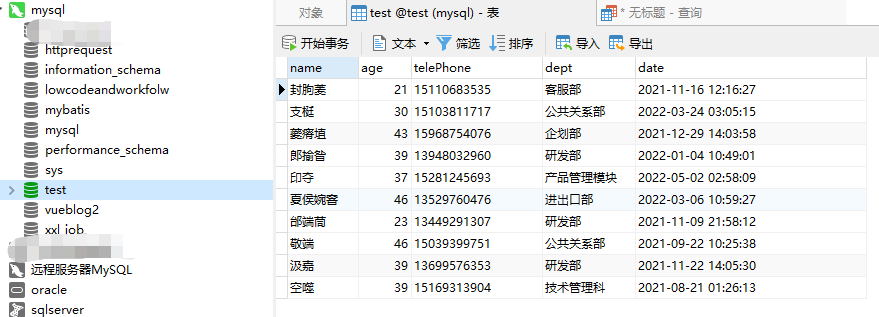
三、实现原理
根据实体类生成测试数据,实现的核心原理是注解和反射,主要经过以下三步
获取实体的注解属性及其参数
目前支持的数据类型只有String,int Date类型
首先获取传入类的属性和属性上注解的参数
Field[] fields = aClass.getDeclaredFields();
StringConfigure stringConfigure = field.getAnnotation(StringConfigure.class);
其中,String类型的数据支持的生成方式最多,为例进行说明,以下是String类型的注解的详细参数@Documented @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Target(ElementType.FIELD) public @interface StringConfigure { //在数据库中的该属性的列名 String fieldName() default ""; //生成测试数据的规则,NAME,TELNUMBER,UUID16,UUID,METHOD StringRule createRule() default StringRule.UUID16; //当createRule 为METHOD以下两个参数才生效 //用来指明自定义的参数生成规则 Class aClass() default Class.class; String method() default ""; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
根据实体的属性执行方法获取测试数据
反射方法内部调用了RandUtils方法中的一些生成工具,如:
String s = RandUtils.uuId();
RandUtils.uuId16();
RandUtils.name();
当然可以使用自定义的工具来生成数据当内置的字符串生成方法无法满足需求,需要指定自定义的方法来生成字符串,可以使用StringConfigure注解如下参数进行指明
下面的例子指明了用DefaultList类的getDept方法生成字符串
注意:
方法必须的无参,返回值为String类型@StringConfigure(createRule = StringRule.METHOD,aClass = DefaultList.class, method = "getDept") private String dept; //以下是 public class DefaultList { private static String[] deptList=new String[]{"产品管理模块","天猫信息服务有限","技术管理科","研发部","制造部","产品开发部","资材部" ,"设备部","客服部","进出口部","资讯部","企划部","公共关系部","人事部","金融业务模块"}; public DefaultList() { } public static String getDept() { return deptList[RandUtils.num(0,deptList.length-1)]; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
组装测试数据为SQL
StringBuffer sql = new StringBuffer("INSERT INTO " + tableName + " ("); for (int i = 0; i < fields.length; i++) { Field field=fields[i]; sql=sql.append(fieldName+") values ("); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
核心源码
public static String createSql(Class aClass, String tableName) throws Exception { Field[] fields = aClass.getDeclaredFields(); Class<DefaultList> randListClass = DefaultList.class; Method[] randListClassDeclaredMethods = randListClass.getDeclaredMethods(); StringBuffer sql = new StringBuffer("INSERT INTO " + tableName + " ("); for (int i = 0; i < fields.length; i++) { Field field=fields[i]; StringConfigure stringConfigure = field.getAnnotation(StringConfigure.class); DateConfigure dateConfigure = field.getAnnotation(DateConfigure.class); IntConfigure intConfigure = field.getAnnotation(IntConfigure.class); String fieldName=null; if (intConfigure != null) { fieldName=intConfigure.fieldName(); } else if (dateConfigure != null) { fieldName=dateConfigure.fieldName(); } else if (stringConfigure != null) { fieldName=stringConfigure.fieldName(); } if (fieldName.equals("")){ fieldName=field.getName(); } if (i!= fields.length-1){ sql=sql.append(fieldName+","); }else { sql=sql.append(fieldName+") values ("); } } for (int i = 0; i < fields.length; i++) { Field field=fields[i]; String appendS=null; StringConfigure stringConfigure = field.getAnnotation(StringConfigure.class); DateConfigure dateConfigure = field.getAnnotation(DateConfigure.class); IntConfigure intConfigure = field.getAnnotation(IntConfigure.class); if (intConfigure!=null){ int min = intConfigure.min(); int max = intConfigure.max(); int num = RandUtils.num(min, max); appendS=String.valueOf(num); }else if(dateConfigure!=null){ String end = dateConfigure.end(); String start = dateConfigure.start(); Date date = RandUtils.date(start, end,"yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss"); appendS="'"+date2String(date)+"'"; } else if(stringConfigure!=null){ StringRule rule = stringConfigure.createRule(); if (rule.equals(StringRule.UUID)){ String s = RandUtils.uuId(); appendS="'"+s+"'"; } else if (rule.equals(StringRule.UUID16)){ appendS="'"+RandUtils.uuId16()+"'"; } else if (rule.equals(StringRule.NAME)){ appendS="'"+RandUtils.name()+"'"; } else if (rule.equals(StringRule.TELNUMBER)){ appendS="'"+RandUtils.telNum()+"'"; } else if (rule.equals(StringRule.METHOD)){ Class arrayClass = stringConfigure.aClass(); if (!arrayClass.equals(Class.class)){ aClass=arrayClass; } else { aClass= DefaultList.class; } String arrayName = stringConfigure.method(); for (Method method : randListClassDeclaredMethods) { String name = method.getName(); if (arrayName.equals(name)){ Object o = aClass.newInstance(); String strings = (String) method.invoke(o); appendS="'"+strings+"'"; break; } } } } if (i!= fields.length-1){ sql=sql.append(appendS+","); }else { sql=sql.append(appendS+");"); } } return sql.toString(); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
四、如何使用
1、编写实体
package com.mabo.example.entity; import com.mabo.sql.DefaultList; import com.mabo.sql.StringRule; import com.mabo.sql.annotation.DateConfigure; import com.mabo.sql.annotation.IntConfigure; import com.mabo.sql.annotation.StringConfigure; import java.util.Date; public class TestEntity { @StringConfigure(createRule = StringRule.NAME) private String name; @IntConfigure(max = 50,min=20) private Integer age; @StringConfigure(fieldName = "telePhone",createRule = StringRule.TELNUMBER) private String tel; @StringConfigure(createRule = StringRule.METHOD,aClass = DefaultList.class, method = "getDept") private String dept; @DateConfigure(start = "2021-07-19 00:00:00",end = "2022-07-19 00:00:00") private Date date; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
2、引入相关依赖
私服,服务器下载速度非常快,里面有演示demo
私服下载地址: http://47.103.194.1:8081/download/demo?fileName=AutoData.zip
github下载地址: https://github.com/MaBo2420935619/AutoData3、执行反射方法生成SQL
package com.mabo.example; import com.mabo.example.entity.TestEntity; import com.mabo.sql.CreateSqlReflect; public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { String test = CreateSqlReflect.createSql(TestEntity.class, "TEST", 10); System.out.println(test); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
-
相关阅读:
Docker-安装(Linux,Windows)
leetcode:1203. 项目管理【双topo:组间topo + 组内topo】
mysqldump --where参数的变化
《算法导论》学习(十六)----一文讲懂红黑树
15:00面试,15:06就出来了,问的问题有点变态。。。
22.12.1打卡 漫步校园 记忆化搜索
忆享科技戟星安全实验室|互联网资产搜集平台大全
常用PCB接插件
涨姿势了,殊途同归的图片交互动效制作!
邯郸百亿斤粮食生产 国稻种芯·中国水稻节:河北大市粮食经
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_47053123/article/details/125880884
