-
数据结构与算法笔记五(哈希函数和哈希表,有序表并查集,KMP)
1. 与哈希函数有关的结构
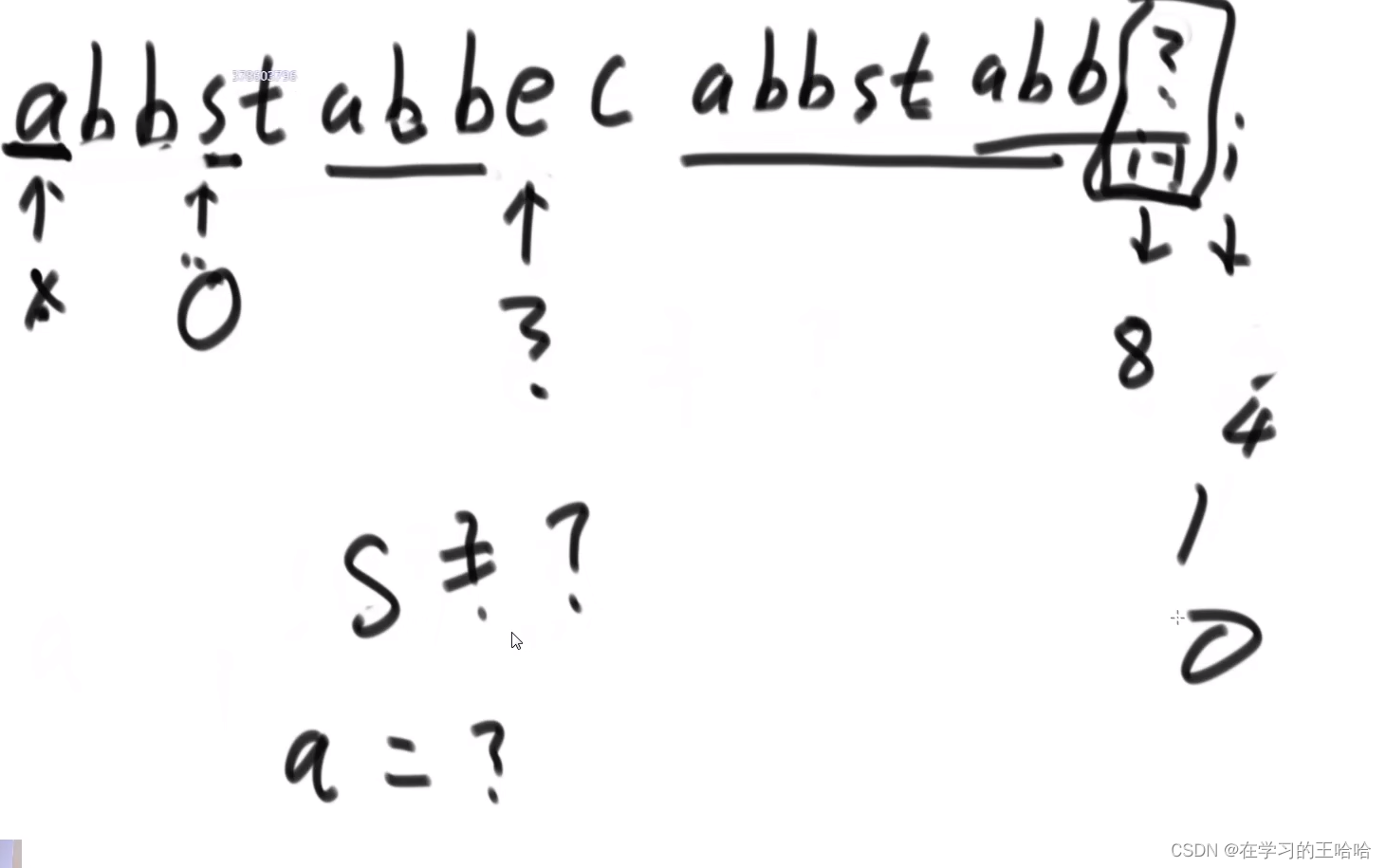
哈希函数和哈希表
1.1 哈希函数的特征:
- 哈希函数:输入域无穷,输出域有限,
MD5 返回值 0~ 2 64 − 1 2^{64}-1 264−1,返回值长度为16的字符串
sha1 返回值 128 - 相同的输入参数一定会返回相同的输出值,哈希函数没有任何的随机成分。
- 不同的输入也有可能导致相同的输出 (哈希碰撞)
- 具有均匀性和离散性
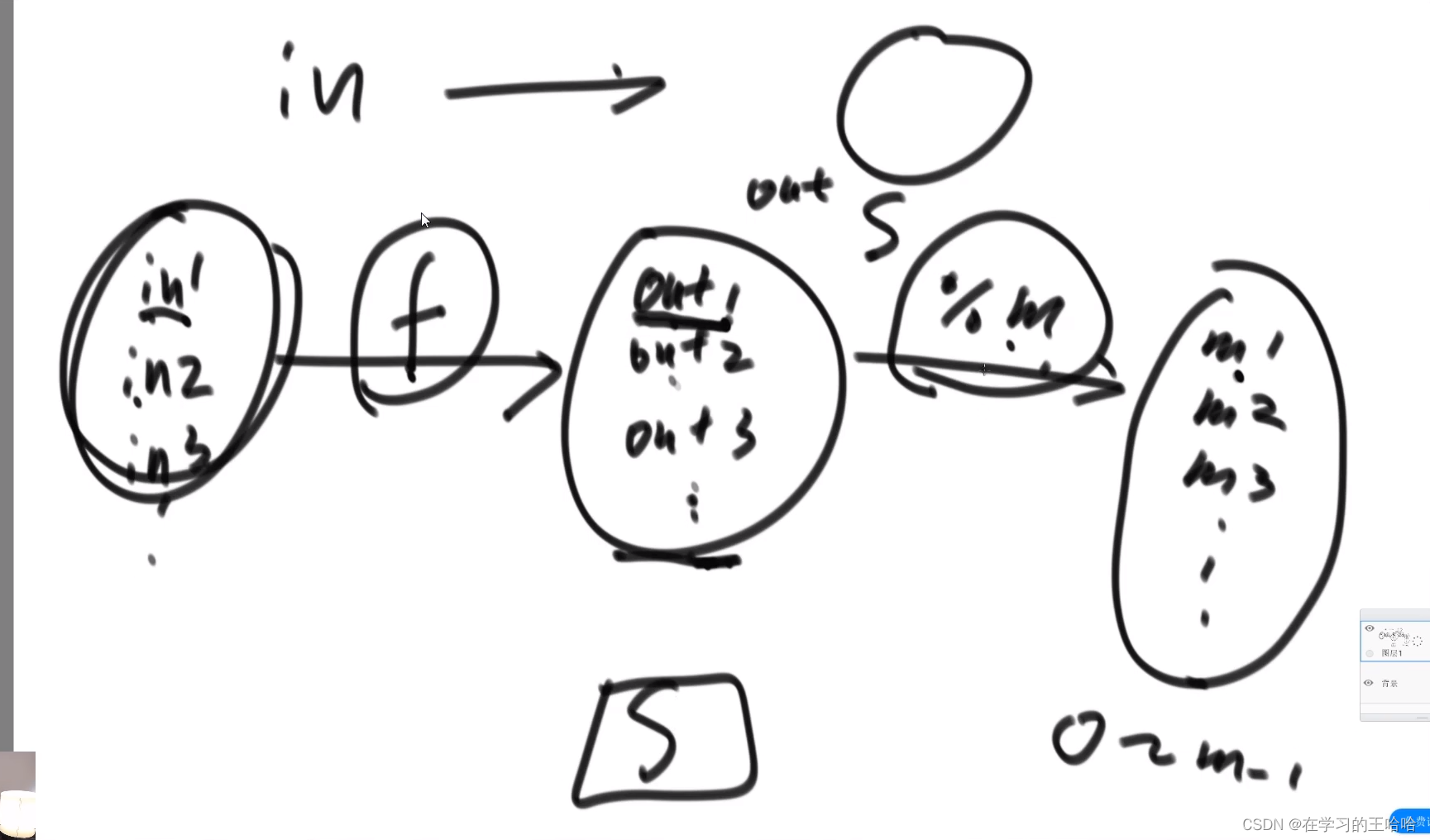
1.1 出现次数最多的数是哪个
有40亿个无符号整数, 其范围为:0~ 2 32 − 1 2^{32}-1 232−1,0 ~ 42亿,在1G内存中计算出现次数最多的数是哪个?
int:4字节,
value:4字节
哈希表至少需要8字节,
40亿 * 8 字节 需要320亿字节,也就是32G空间同样的数就是一条数据。
我们就可以使用哈希函数,针对40亿个无符号整数调哈希函数,然后100去余。放到对应的文件中,然后针对文件中的数放入各自的哈希表中,32G/100,
利用了哈希函数在种类上均分了,小文件放在了硬盘上,使用完一个文件就释放了
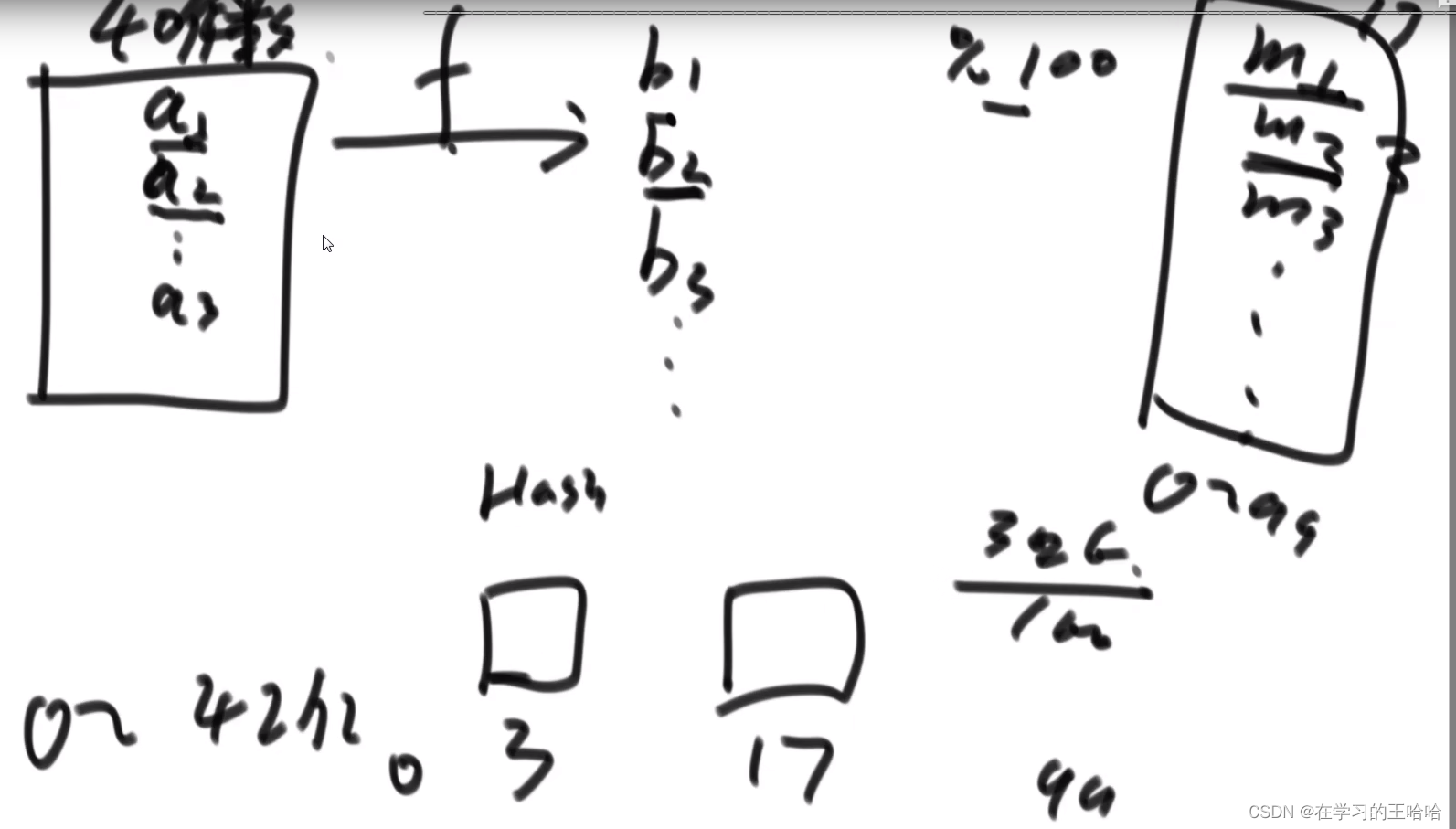
1.2 哈希表的具体实现
增删改查都是o(1)的
链地址法
字符串经过哈希函数,然后进行模运算

怎么加进去的就怎么找。
由于哈希函数的均匀性,所有链表长度都是均匀增长的。
链表长度一旦超过6,就扩容。
模17增加为模34。如果加入了N个字符串,经历了 logN次(最差情况,长度超过2就扩容)的扩容。总的代价是 O(N * logN)
离线扩容技术:不占用户的在线时间,jvm中进行扩容。
1.3 设计RandomPool结构

准备两张hash表,一张str->index , 另一张index->str。
package class01; import java.util.HashMap; public class Code02_RandomPool { public static class Pool<K> { private HashMap<K, Integer> keyIndexMap; private HashMap<Integer, K> indexKeyMap; private int size; public Pool() { this.keyIndexMap = new HashMap<K, Integer>(); this.indexKeyMap = new HashMap<Integer, K>(); this.size = 0; } public void insert(K key) { if (!this.keyIndexMap.containsKey(key)) { this.keyIndexMap.put(key, this.size); this.indexKeyMap.put(this.size++, key); } } public void delete(K key) { if (this.keyIndexMap.containsKey(key)) { int deleteIndex = this.keyIndexMap.get(key); int lastIndex = --this.size; K lastKey = this.indexKeyMap.get(lastIndex); this.keyIndexMap.put(lastKey, deleteIndex); this.indexKeyMap.put(deleteIndex, lastKey); this.keyIndexMap.remove(key); this.indexKeyMap.remove(lastIndex); } } public K getRandom() { if (this.size == 0) { return null; } int randomIndex = (int) (Math.random() * this.size); // 0 ~ size -1 return this.indexKeyMap.get(randomIndex); } } public static void main(String[] args) { Pool<String> pool = new Pool<String>(); pool.insert("zuo"); pool.insert("cheng"); pool.insert("yun"); System.out.println(pool.getRandom()); System.out.println(pool.getRandom()); System.out.println(pool.getRandom()); System.out.println(pool.getRandom()); System.out.println(pool.getRandom()); System.out.println(pool.getRandom()); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
1.4 布隆过滤器
100亿url黑名单,每个url 64字节,目的:方便查询,不支持删。
布隆过滤器:只有加入和查询,接受一定程度的失误率(允许错杀,不会放过)。
1.4.1 位图bitmap
4 bytes = 32bit
package com.wanghaha.algorithm; public class Day6_30_44BitMap { public static void main(String[] args) { int[] arr = new int[10]; // 32 * bit * 10 -> 320 bits // arr[0] int 0 ~ 31 // arr[1] int 32 ~ 63 // arr[2] int 64 ~ 95 int i = 178; //想取得178个bit的状态 int numIndex = 178 / 32; int bitIndex = 178 % 32; // int中的第几位 int s = (( arr[numIndex] >> (bitIndex)) & 1); // 请把178位的状态 改成1; arr[numIndex] = arr[numIndex] | ( 1<< (bitIndex)); // 请把178位的状态改成 0 i = 178; arr[numIndex] = arr[numIndex] & (~(1 << bitIndex)); // 请把178位的状态拿出来 i = 178; int bit = (arr[i / 32] >> (i%32)) & 1; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
1.4.2 布隆过滤器的实现
就是一个大的位图,m个bit
u1 通过哈希函数f1 然后模m 将对应的位图上的格子置位1。
经过k个哈希函数,对应的格子置为1。然后u2, u3等,一直到 第100亿个u。
最后布隆过滤器版本的黑名单做好了。
然后查url,经过k个哈希函数,只有全是1的时候,该url就在黑名单里。
需要条件: n样本量,p失误率
单样本大小无关。确定空间(向上取整):
m = − ( n ∗ l n P ) ( I n 2 ) 2 m=-\dfrac{(n*lnP)}{(In2)^2 } m=−(In2)2(n∗lnP)
算出哈希函数个数(向上取整):
k = l n 2 ∗ m n ≈ 0.7 ∗ m n k=ln2*\dfrac{m}{n}\thickapprox 0.7*\dfrac{m}{n} k=ln2∗nm≈0.7∗nm
实际的失误率
P 真 = ( 1 − e − ( n ∗ k 真 ) m 真 ) k 真 P_真 = (1 - e^{-\dfrac{(n*k_真)}{m_真} })^{k真} P真=(1−e−m真(n∗k真))k真1.5 一致性哈希原理
讨论数据服务器组织的问题。
1.5.1 实现
key要设计很多,且中高低频都有一定的数量。

如果增加机器,重新模,数据迁移的代价是全量的。使用一致性哈希可以解决这个问题。
一致性哈希没有模。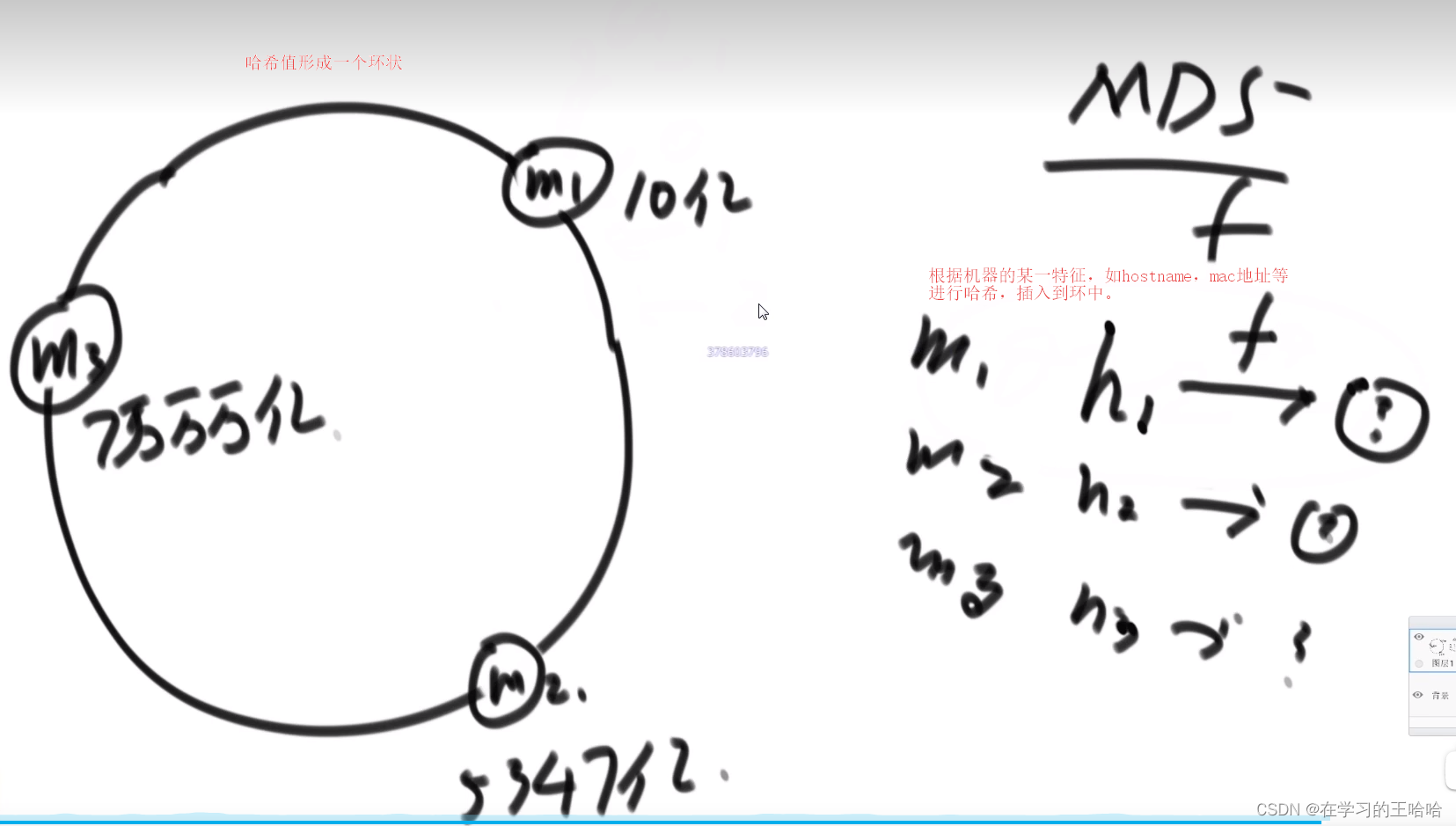
插入数据通过哈希函数找顺时针走第一个机器。
底层实现:
逻辑端存储机器的哈希值(数组),并且有序排列。
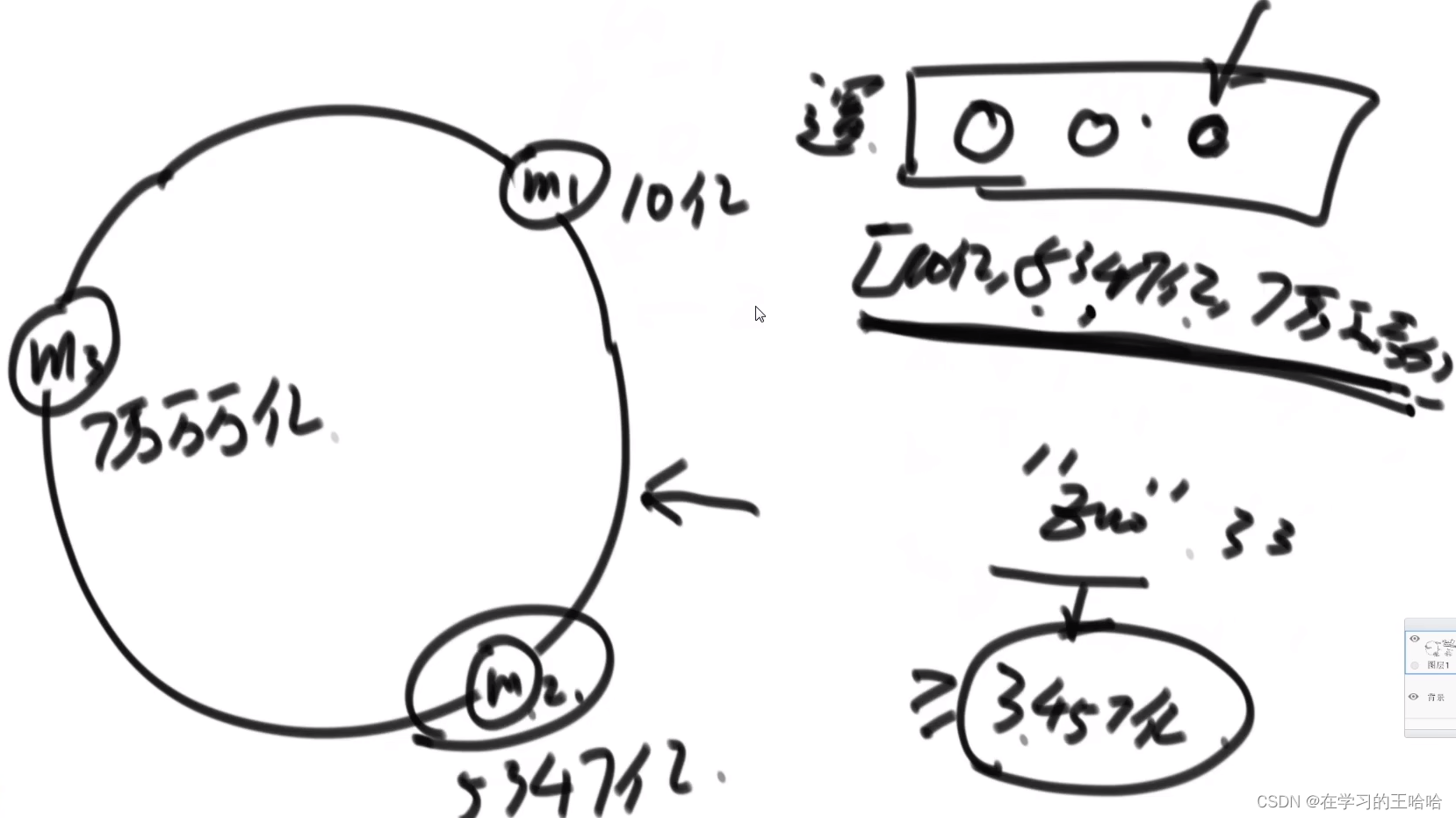
增加机器
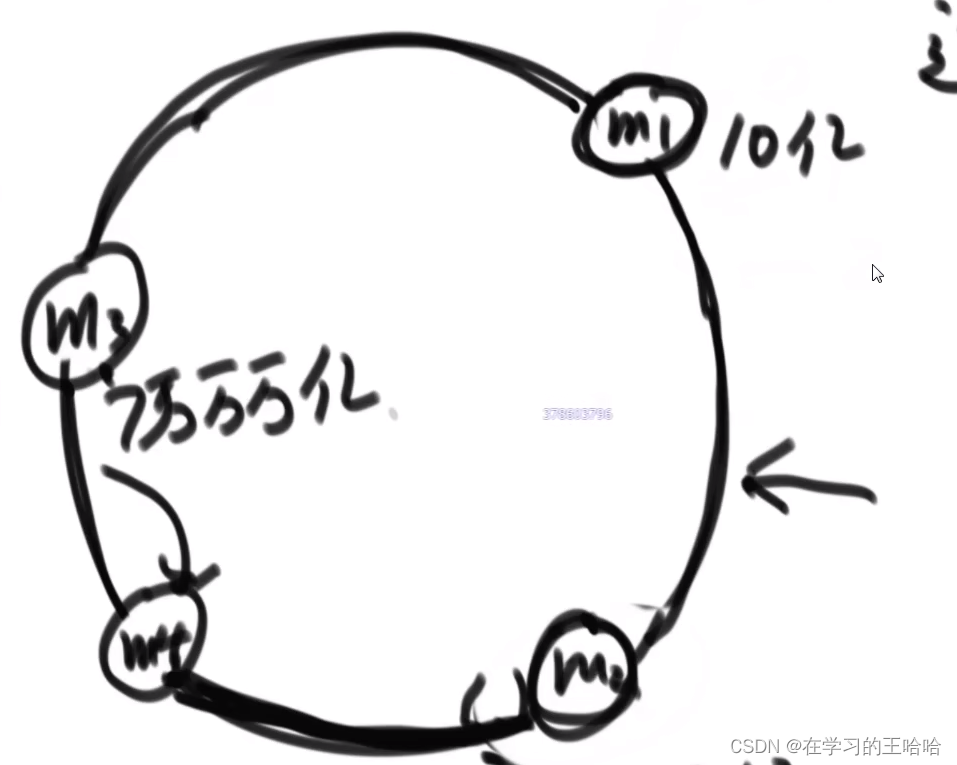
存在问题:- 机器数量很少的时候,做不到环的均分
- 即便可以均分,一旦均分后 减少或者增加机器,负载就不均衡
1.5.2 解决方法
虚假节点技术
m1,m2,m3都有一千个虚拟节点(字符串),都算哈希值然后去抢环。
环上就有3000个节点。相同一段上的m1,m2,m3的虚拟节点数据都差不多,超均衡。
增加机器m4,增加1000个节点,从m1,m2,m3上夺等量的数据。
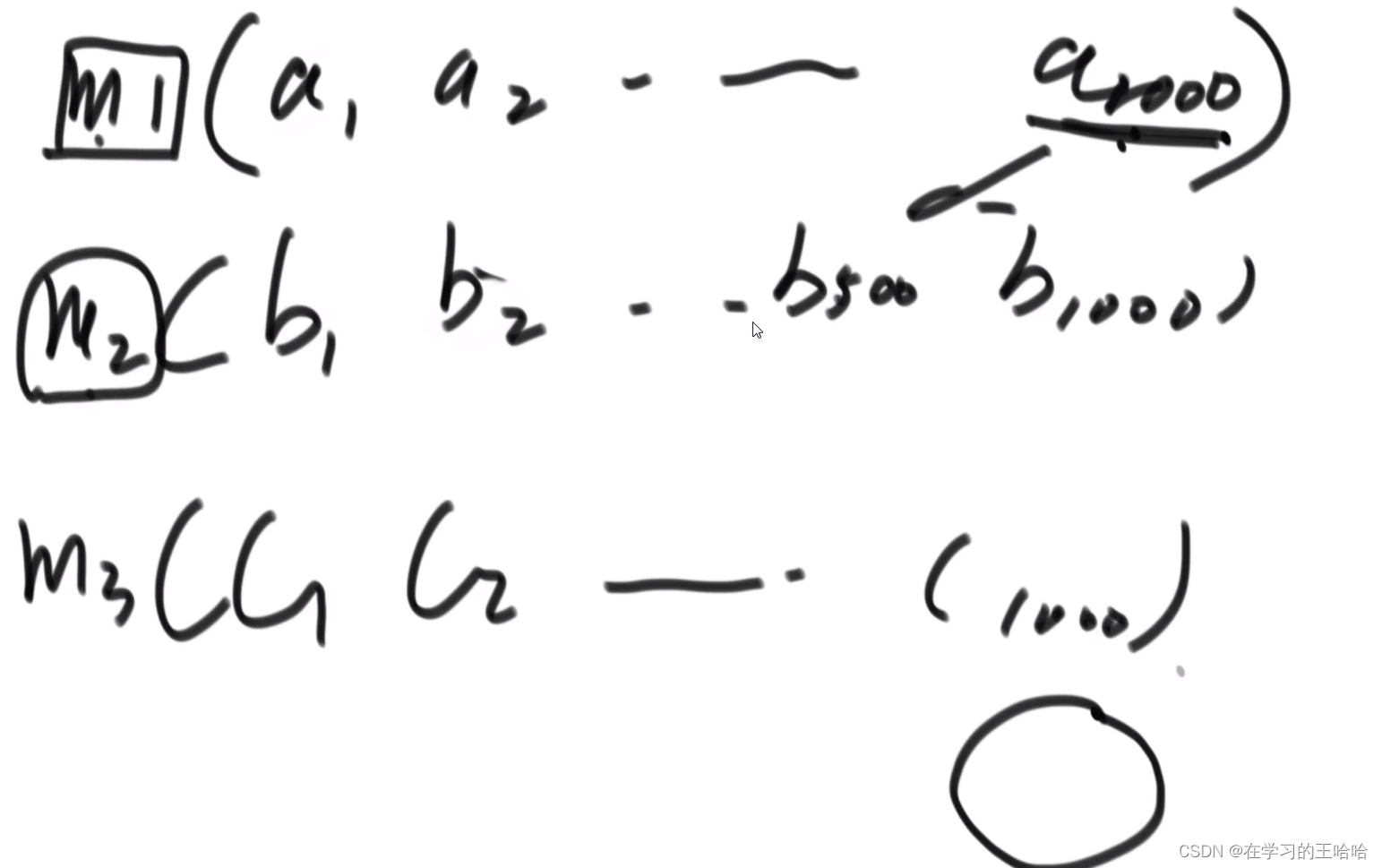
一致性哈希还可以管理负载,根据实际机器的状况增加或者减少虚拟节点1.6 练习题目:岛问题

时间复杂度: o(N*M)
package com.wanghaha.algorithm; public class Day7_4_45IsIands { public static int isIands(int[][] m){ if(m==null || m[0] == null) { return 0; } int length = m.length; int weight = m[0].length; int res = 0; for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < weight; j++) { if( m[i][j] == 1){ res ++; infect(m, i, j, length, weight); } } } return res; } private static void infect(int[][] m, int i, int j, int length, int weight) { if(i < 0 || i>= length || j< 0 || j>=weight || m[i][j] != 1){ return; } m[i][j] = 2; infect(m, i+1, j, length, weight); infect(m, i, j+1, length, weight); infect(m, i-1, j, length, weight); infect(m, i, j-1, length, weight); } public static void main(String[] args) { int[][] m1 = { { 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 }, { 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0 }, { 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0 }, { 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 }, { 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0 }, { 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0 }, { 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 }, }; System.out.println(isIands(m1)); int[][] m2 = { { 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 }, { 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0 }, { 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0 }, { 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0 }, { 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0 }, { 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0 }, { 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 }, }; System.out.println(isIands(m2)); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
1.7 如何设计一个并行算法解决这个问题?
2. 并查集
支持集合快速合并。
两个方法
是否属于同一个集合:issameset
合并两个集合:union链表:union时间复杂度o(1)
哈希表:issameset时间复杂度o(1)
并查集:都能做到o(1)
2.1 并查集的实现
往上指的图结构
issameset:通过往上指的指针,一直指到不能再往上指的找到的代表元素,判断是否时同一个元素
union: 先看是否是一个集合,不是的话,判断集合的大小 ,把少的所在集合的顶挂在另外一个集合的顶上。优化: 将过长的路径上的每个元素直接指向顶元素。
package class01; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.List; import java.util.Stack; public class Code04_UnionFind { public static class Element<V> { // 相当于给元素上面 画了个圈,包装一下 public V value; public Element(V value) { this.value = value; } } public static class UnionFindSet<V> { // 能够通过 原始元素找到 包装后的元素 public HashMap<V, Element<V>> elementMap; // key 某个元素 vlaue 该元素的父 public HashMap<Element<V>, Element<V>> fatherMap; // key 某个集合的代表元素, value 该集合的大小 public HashMap<Element<V>, Integer> rankMap; public UnionFindSet(List<V> list) { elementMap = new HashMap<>(); fatherMap = new HashMap<>(); rankMap = new HashMap<>(); for (V value : list) { Element<V> element = new Element<V>(value); elementMap.put(value, element); fatherMap.put(element, element); rankMap.put(element, 1); } } private Element<V> findHead(Element<V> element) { Stack<Element<V>> path = new Stack<>(); while (element != fatherMap.get(element)) { path.push(element); element = fatherMap.get(element); } while (!path.isEmpty()) { fatherMap.put(path.pop(), element); } return element; } public boolean isSameSet(V a, V b) { if (elementMap.containsKey(a) && elementMap.containsKey(b)) { return findHead(elementMap.get(a)) == findHead(elementMap.get(b)); } return false; } public void union(V a, V b) { if (elementMap.containsKey(a) && elementMap.containsKey(b)) { Element<V> aF = findHead(elementMap.get(a)); Element<V> bF = findHead(elementMap.get(b)); if (aF != bF) { Element<V> big = rankMap.get(aF) >= rankMap.get(bF) ? aF : bF; Element<V> small = big == aF ? bF : aF; fatherMap.put(small, big); rankMap.put(big, rankMap.get(aF) + rankMap.get(bF)); rankMap.remove(small); } } } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
1.7 如何设计一个并行算法解决这个问题?
3. KMP
3.1 KMP的实现
leetcode 28

最长的前缀和后缀的匹配长度,不能取到整体。
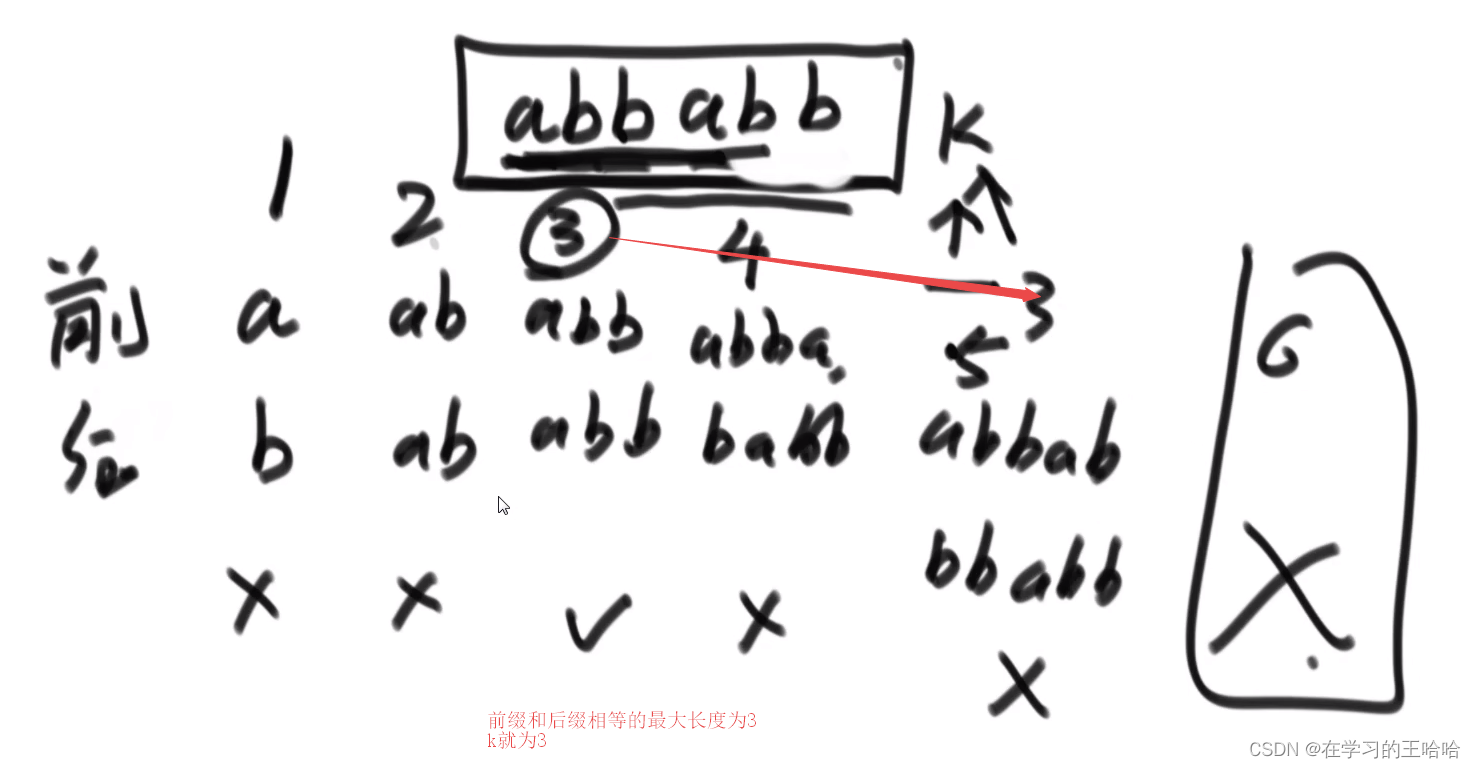
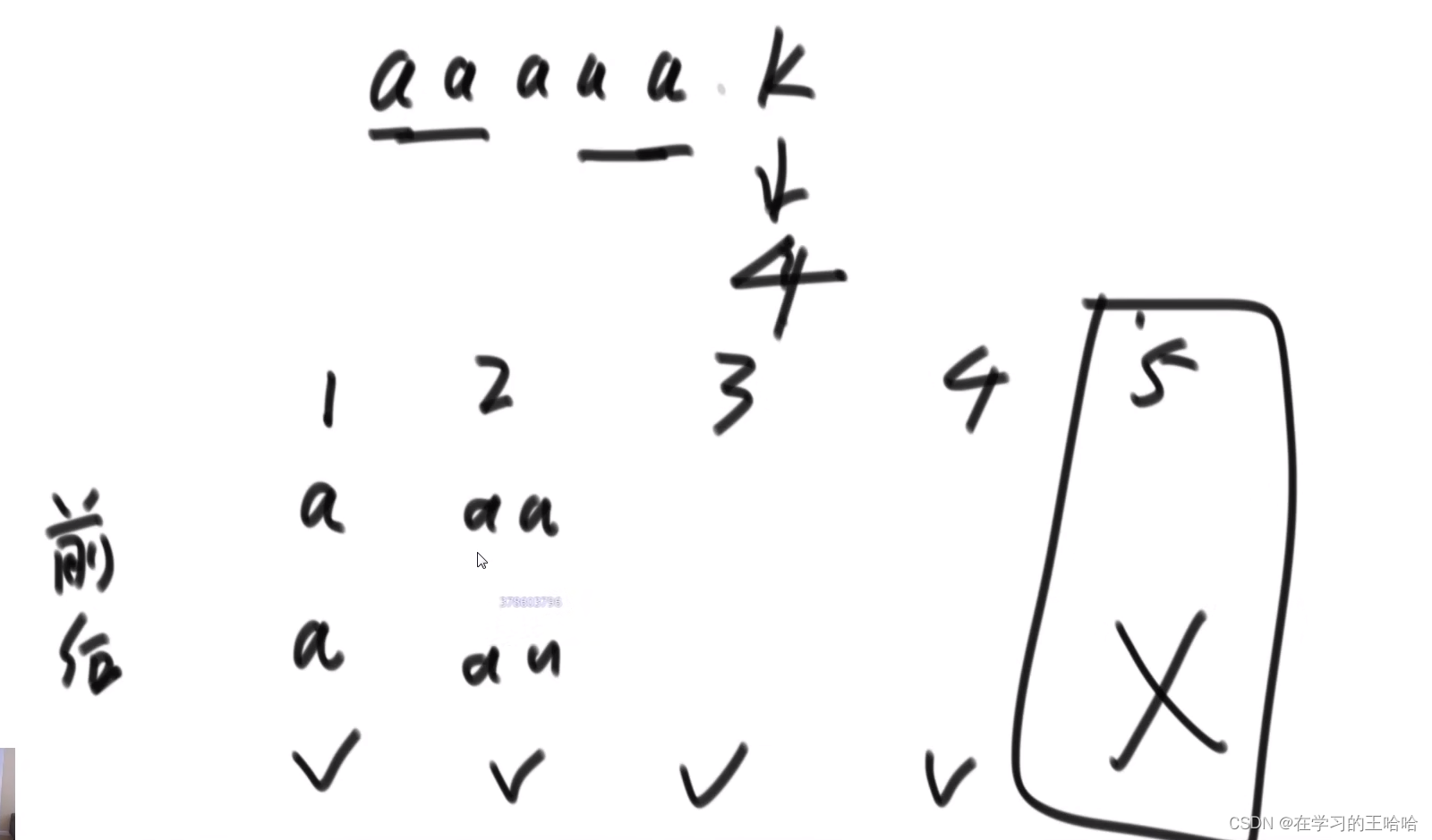
这个信息对str2中的每个字符求的。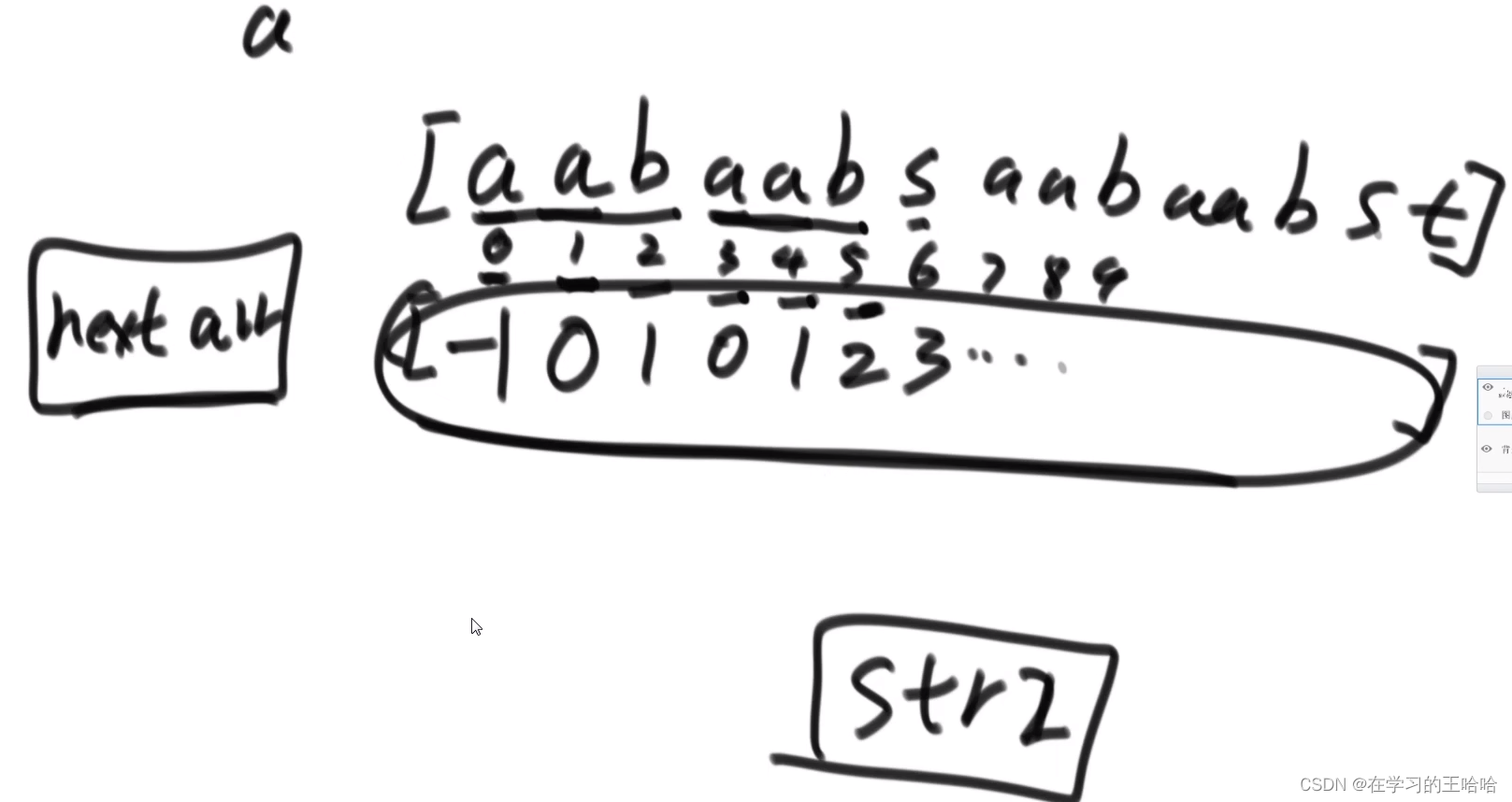 经典做法
经典做法

KMP
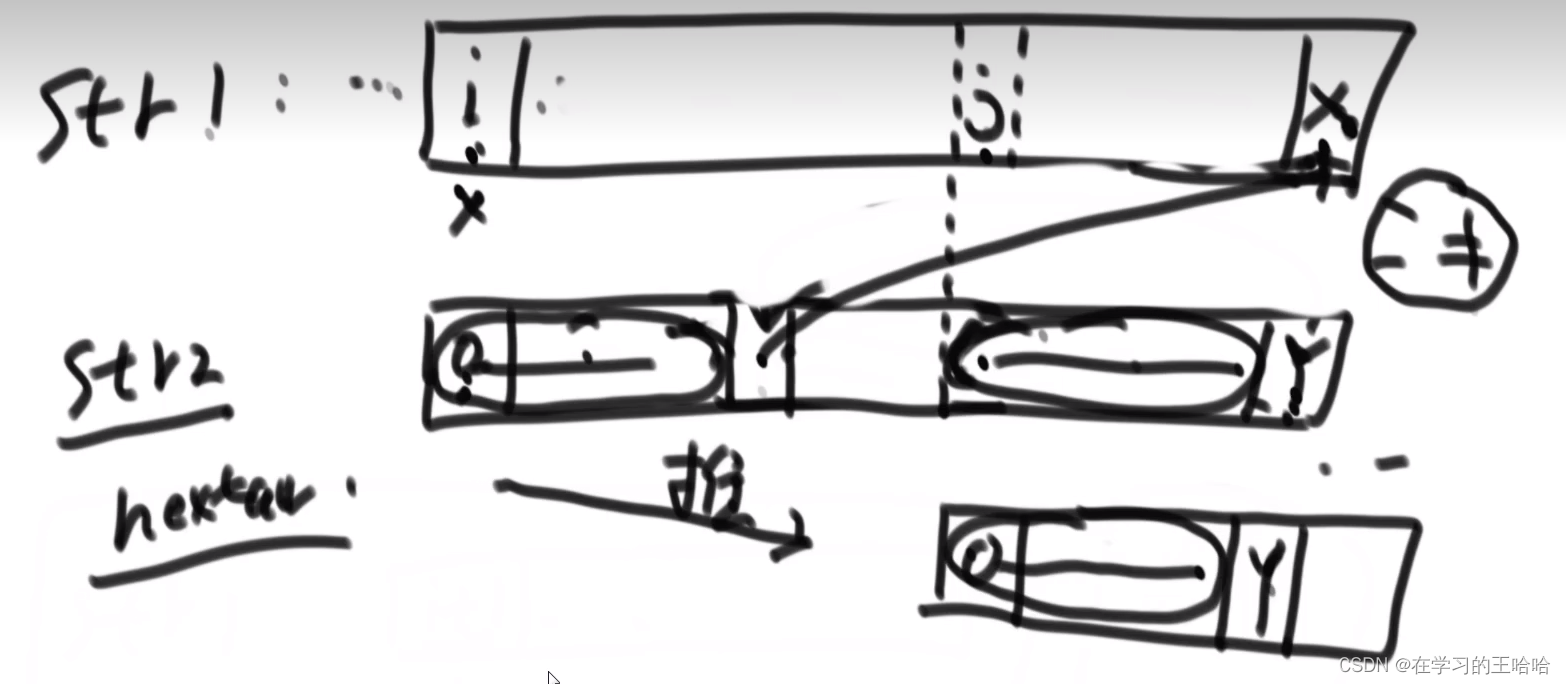
当x和y位置不一样的时候,然后找Y之前的最大前缀和后缀的匹配字段。
接下来:比对的位置x不变,比对的y位置回跳到到最大前缀的后一位。
1)检查以j开头能不能配出str2
2)我已经知道i到j位置都一定配不出str2,所以把检查的位置直接挪到了j
3.2 KMP的代码实现
package class03; public class Code01_KMP { public static int getIndexOf(String s, String m) { if (s == null || m == null || m.length() < 1 || s.length() < m.length()) { return -1; } char[] str1 = s.toCharArray(); char[] str2 = m.toCharArray(); int i1 = 0; int i2 = 0; int[] next = getNextArray(str2); //o(M) // o(N) while (i1 < str1.length && i2 < str2.length) { if (str1[i1] == str2[i2]) { i1++; i2++; } else if (next[i2] == -1) { // str2中比对的位置 无法再往前跳了 i1++; } else { i2 = next[i2]; } } // i1 或者 i2 越界了 return i2 == str2.length ? i1 - i2 : -1; } public static int[] getNextArray(char[] ms) { if (ms.length == 1) { return new int[] { -1 }; } int[] next = new int[ms.length]; next[0] = -1; next[1] = 0; int i = 2;// next数组的位置 int cn = 0; //拿哪个位置的字符和i-1的字符进行比较 // 也代表当前使用的信息是多少 while (i < next.length) { if (ms[i - 1] == ms[cn]) { next[i++] = ++cn; } else if (cn > 0) { cn = next[cn]; } else { // 没法往前跳了 next[i++] = 0; } } return next; } public static void main(String[] args) { String str = "abcabcababaccc"; String match = "ababa"; System.out.println(getIndexOf(str, match)); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
3.3 KMP复杂度计算
while (i1 < str1.length && i2 < str2.length) { if (str1[i1] == str2[i2]) { i1++; i2++; } else if (next[i2] == -1) { // str2中比对的位置 无法再往前跳了 i1++; } else { i2 = next[i2]; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
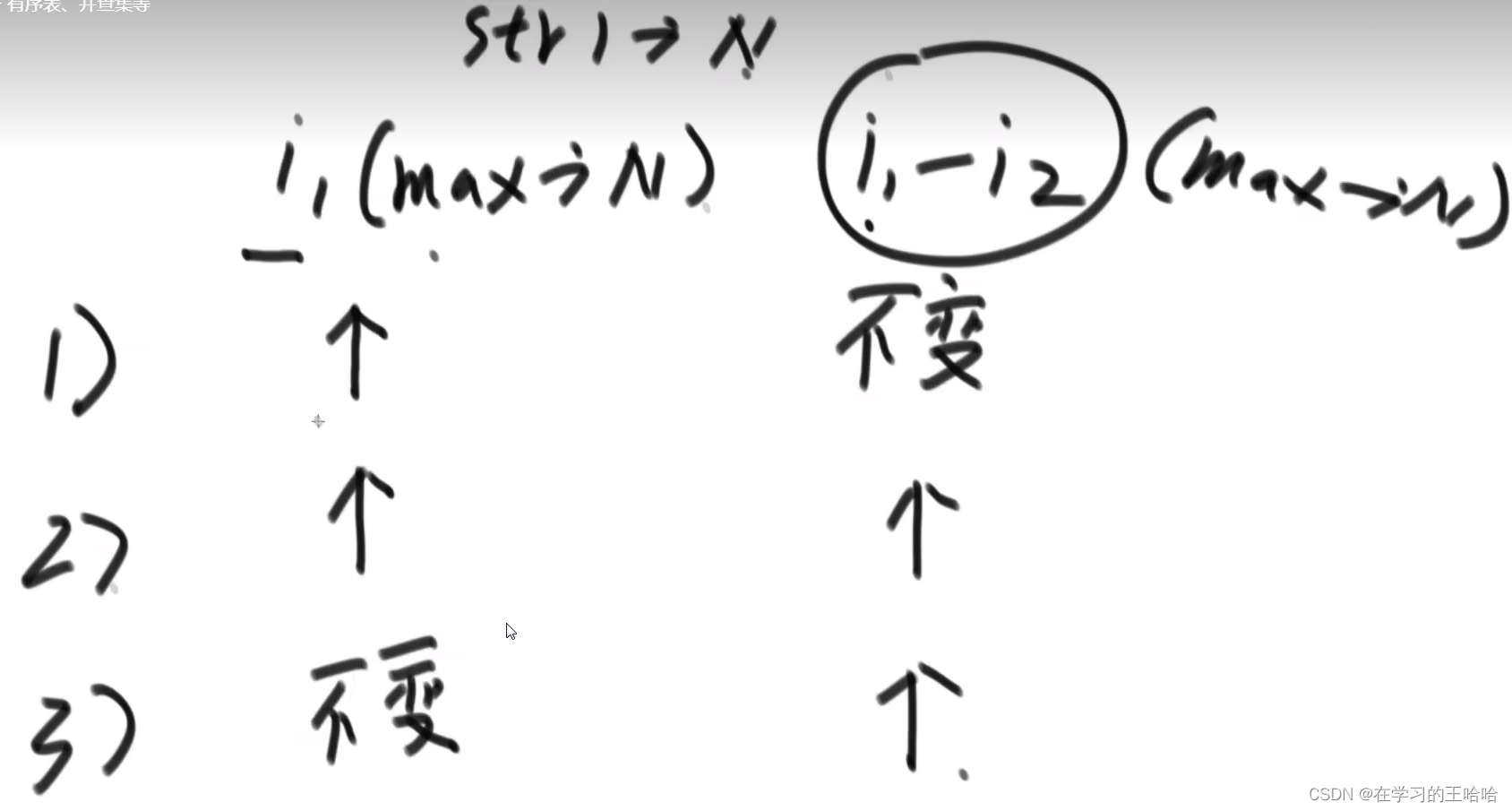
两个量,三个分支, 不会超过2N次,所以while是线性的
3.4 nextArr的实现
if (ms[i - 1] == ms[cn]) { next[i++] = ++cn;- 1
- 2
代表三个操作:
- 因为比较字符相等了,所有next[i] = cn + 1
- 因为i位置的cn求出来了,所有i++
- 因为i位置要使用i-1上位置的信息的,因为更新过后的i-1位置的信息是cn+1,所以cn要更新,++cn
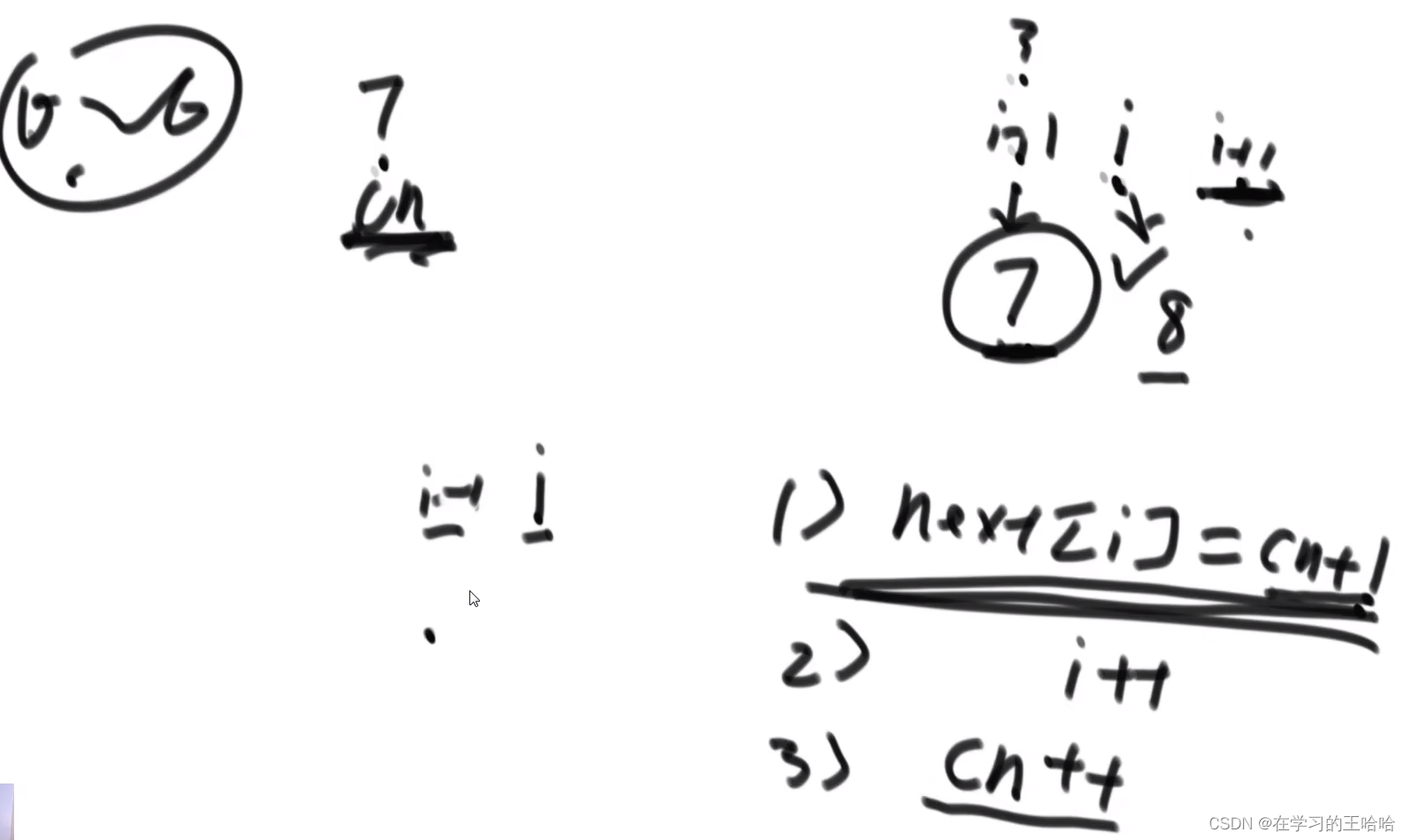
3.4 nextArr复杂度
o(M)
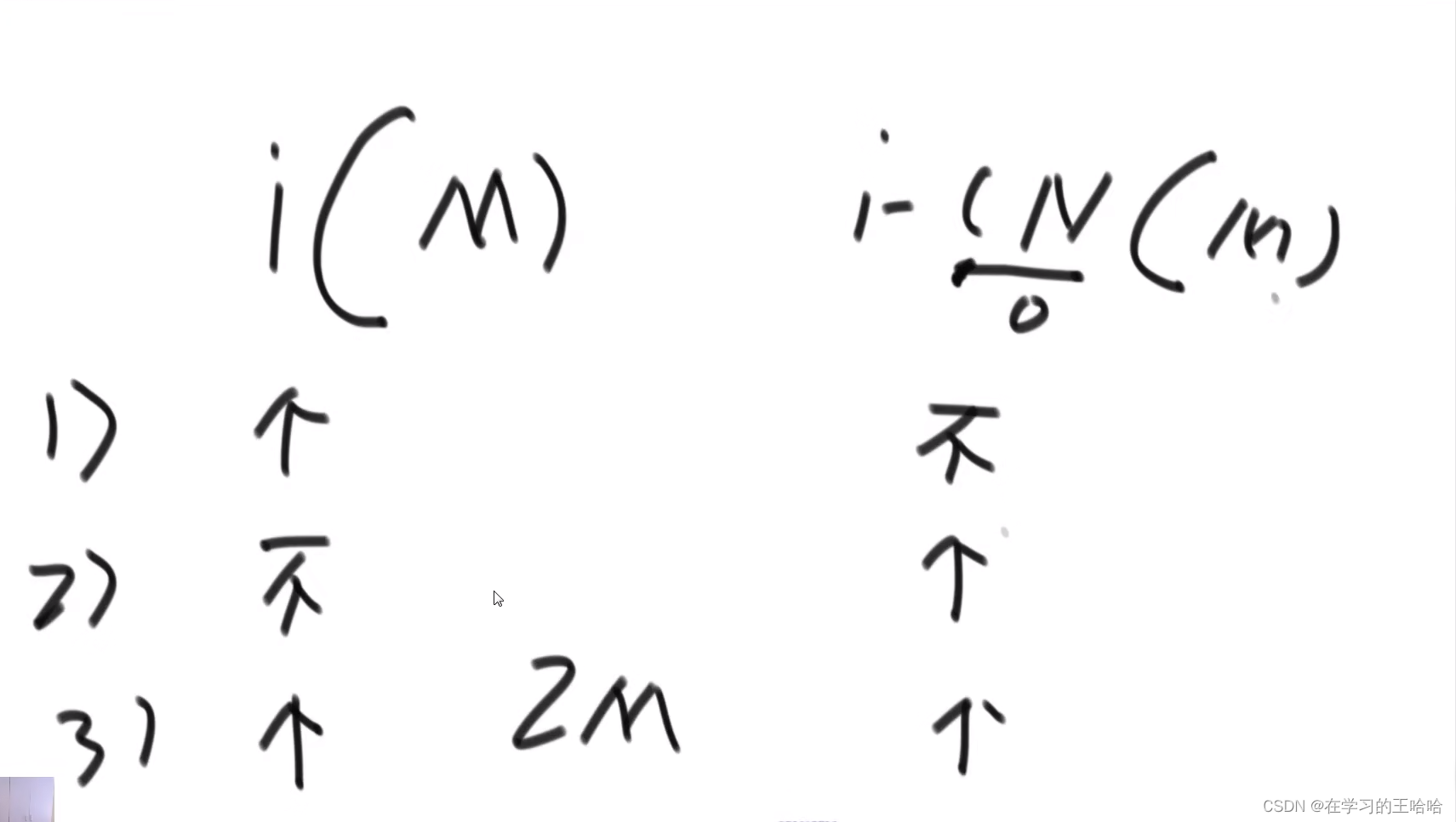
- 哈希函数:输入域无穷,输出域有限,
-
相关阅读:
[阶段4 企业开发进阶] 2. Redis--实战篇
论文阅读笔记 | 三维目标检测——SECOND算法
ACWSpring1.3
如何实现接口认证的设计(架构设计)
[移动通讯]【Carrier Aggregation-4】【LTE-1】
【Windows Server 2019】路由服务的配置和管理
互联网Java工程师面试题·Java 总结篇·第十弹
如何安装nvm管理node版本
人工智能大模型专题报告:方兴未艾,并驱争先
【爬虫】7.1. JavaScript动态渲染界面爬取-Selenium
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/prague6695/article/details/125515253