-
科学计算三维可视化笔记(第五周 交互界面)
内容来自中国大学MOOC,北京理工大学,python数据分析与展示课程,侵删。
如有错误,烦请指出。
python 科学计算三维可视化笔记 第五周 交互界面
一、Traits 基础
1. Traits 介绍
- Traits 库可以为 python 添加类型定义
- Traits 属性解决 color 类型问题
- 接受能表示颜色的各种类型的值
- 赋值为不能表达颜色的值时,能够立即捕捉到错误,提供一个错误报告,高速用户能够接受什么值
- 提供一个内部、标准的颜色表达方式
Traits 属性表示颜色的例子,Color 是一个 Trait 类型,在 Circle 类中用它定义了一个 color 属性:
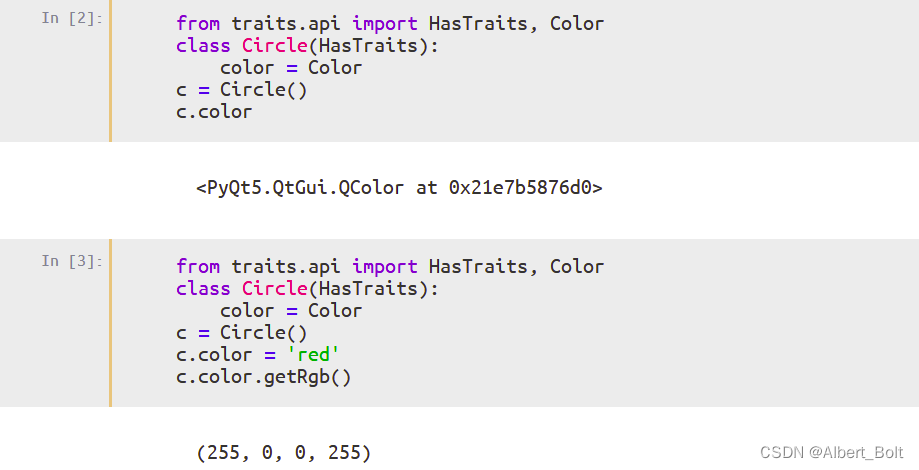
用c.configure_traits()实现交互选择颜色,确定新颜色后返回 True: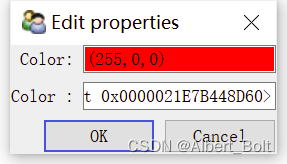
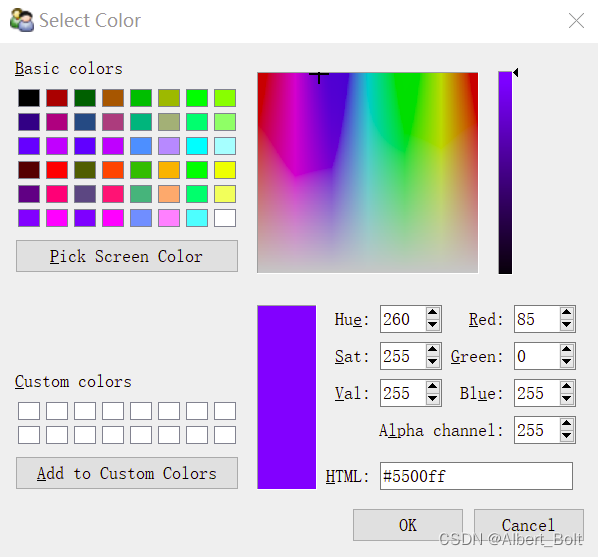
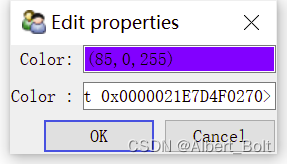
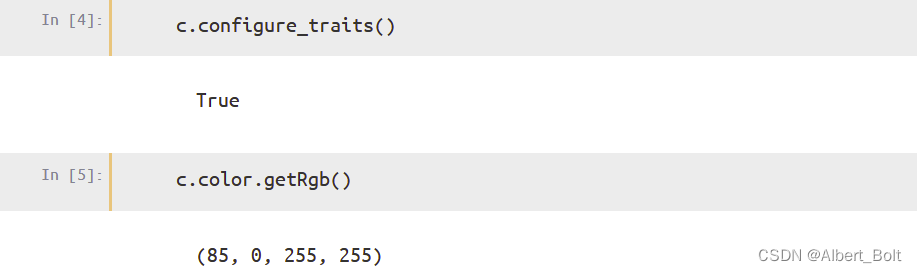
2. Traits 属性的功能
- Trait 库为 python 对象的属性增加了类型定义功能
- 还提供了功能:
- 初始化:每个 Trait 属性都有自己的默认值
- 验证:Trait 属性有明确的类型定义,满足定义的值才能赋值给属性
- 代理:Trait 属性值可以代理给其他对象的属性。
- 监听:Trait 属性值发生变化时,运行事先指定的函数
- 可视化:拥有 Trait 属性的对象,可生成编辑 Trait 属性的界面
一个实例:
from traits.api import Delegate, HasTraits, Instance, Int, Str class Parent(HasTraits): # 初始化:last_name为'Zhang' last_name = Str('Zhang') class Child(HasTraits): age = Int # 验证:father属性的值必须是Parent类的实例 father = Instance(Parent) # 代理:Child实例的last_name属性代理给其father属性的last_name last_name = Delegate('father') # 监听:当age属性点值被修改时,下面的函数将被运行 def _age_changed(self, old, new): print('Age changed from %s to %s' % (old,new))- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
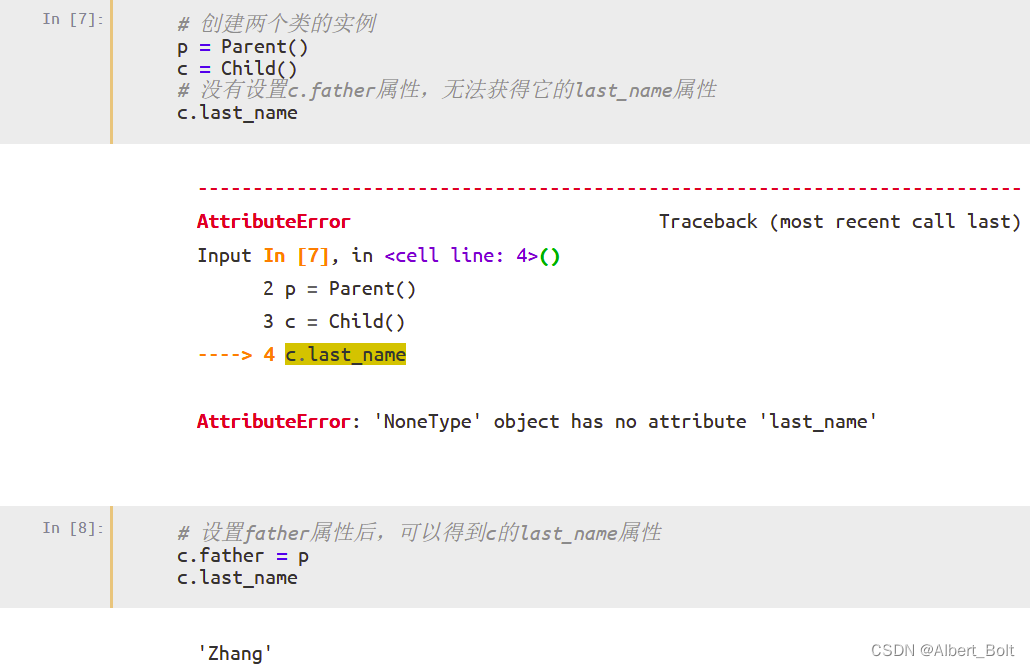

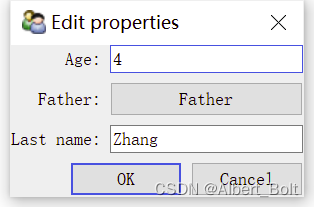
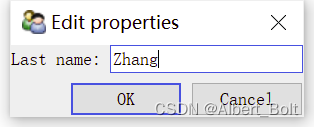
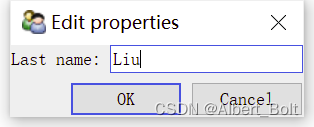
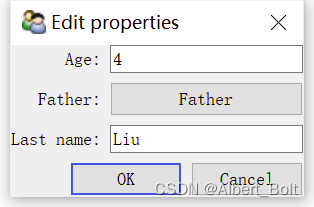
调用configure_traits()显示一个修改属性值的对话框,点击并修改 Father 后,Last name 也会随之变化:
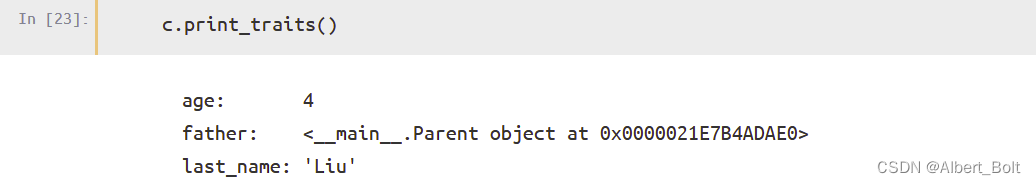
调用print_traits()方法输出所有 trait 属性与其值:
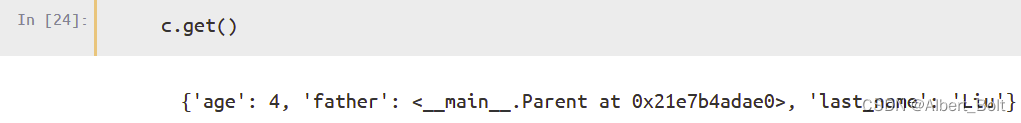
调用get()方法获得描述对象所有 trait 属性的字典:
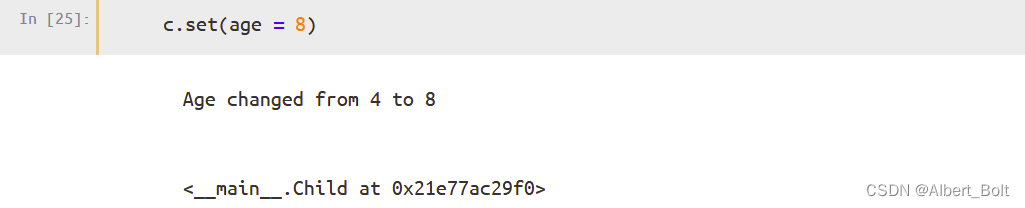
调用set()方法设置 trait 属性的值:
3. Traits 属性监听
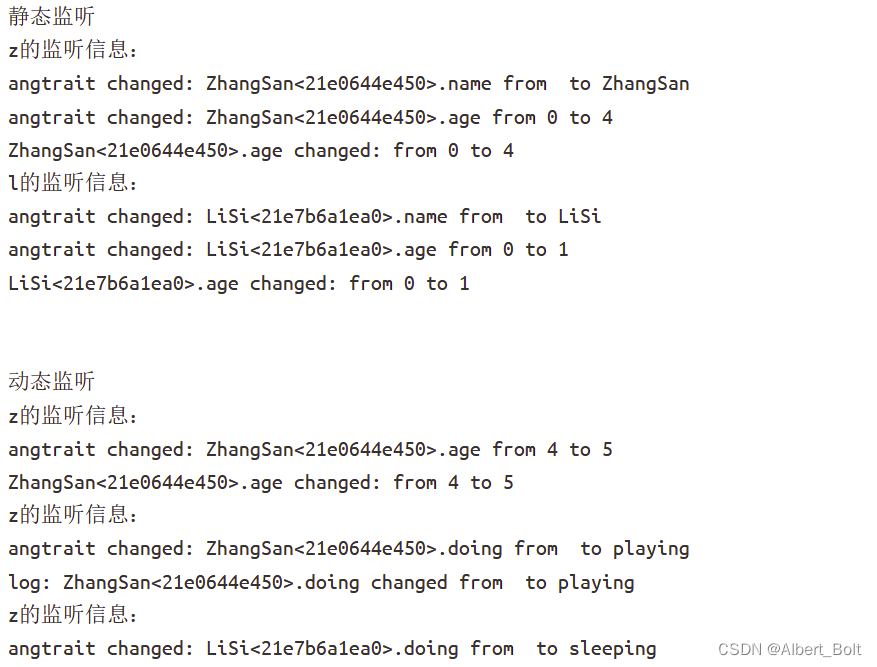
两种监听模式:动态监听、静态监听
(1) 一个实例from traits.api import HasTraits class Child(HasTraits): name = Str age = Int doing = Str def __str__(self): return '%s<%x>' % (self.name, id(self)) # 静态监听age属性的变化 def _age_changed(self, old, new): print('%s.age changed: from %s to %s' % (self, old, new)) # 静态监听任何Trait属性的变化 def _anytrait_changed(self, name, old, new): print('angtrait changed: %s.%s from %s to %s' % (self, name, old, new)) def log_trait_changed(obj, name, old, new): print('log: %s.%s changed from %s to %s' % (obj, name, old, new)) # 静态监听 print('静态监听') print('z的监听信息:') z = Child(name = 'ZhangSan', age=4) print('l的监听信息:') l = Child(name = 'LiSi', age=1) print('\n') # 动态监听doing属性的变化 z.on_trait_change(log_trait_changed, name='doing') print('动态监听') print('z的监听信息:') # 未改变z的doing,因此未调用log_trait_changed z.age = 5 print('z的监听信息:') z.doing = 'playing' print('z的监听信息:') # 未改变z的doing,因此未调用log_trait_changed l.doing = 'sleeping'- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
输出为:
(2) Trait 属性的监听函数调用顺序
(3) 静态监听函数的几种形式_age_changed(self)_age_changed(self, new)_age_changed(self, old, new)_age_changed(self, name, old, new)
(4) 动态监听函数的几种形式
observer()observer(new)observer(name, new)observer(obj, name, new)observer(obj, name, old, new)
(5) 对多个 trait 属性使用同一个监听函数
@on_trait_change(names) def any_method_name(self, ...) ...- 1
- 2
- 3
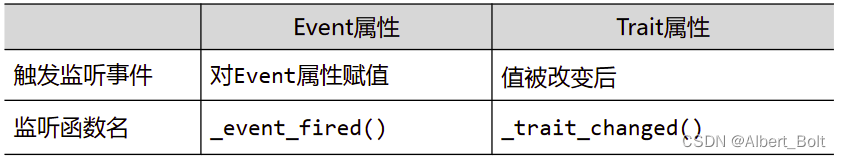
4. Event 和 Button 属性
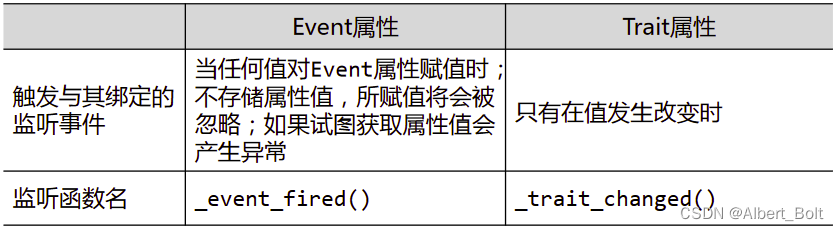
Event 属性与其他 Trait 属性的区别:
Botton 属性:- 具备 Event 事件处理功能
- 通过 TraitsUI 库,自动生成界面中的按钮控件
一个实例:
from traits.api import HasTraits, Str, Int, Event, on_trait_change class Child(HasTraits): name = Str('ZhangSan') age = Int(4) InfoUpdated = Event # 对_info_changed()方法进行修饰 @on_trait_change('name, age') def _info_changed(self): self.InfoUpdated = True # info_updated事件处理方法 def _InfoUpdated_fired(self): self.reprint() def reprint(self): print('reprint information %s, %s' % (self.name, self.age)) child = Child() print('第1轮监听结果:') child.name = 'LiSi' print('第2轮监听结果:') child.age = 1 print('第3轮监听结果:') child.name = "LiSi" # 未改变值,因此无监听结果 print('第4轮监听结果:') child.InfoUpdated = 0- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
输出结果:

5. Property 属性
一个实例:
from traits.api import HasTraits, Float, Property, cached_property class rectangle(HasTraits): w = Float(1.0) h = Float(2.0) area = Property(depends_on = ['w', 'h']) @cached_property def _get_area(self): print("computing...") return (self.w * self.h)- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
测试过程:
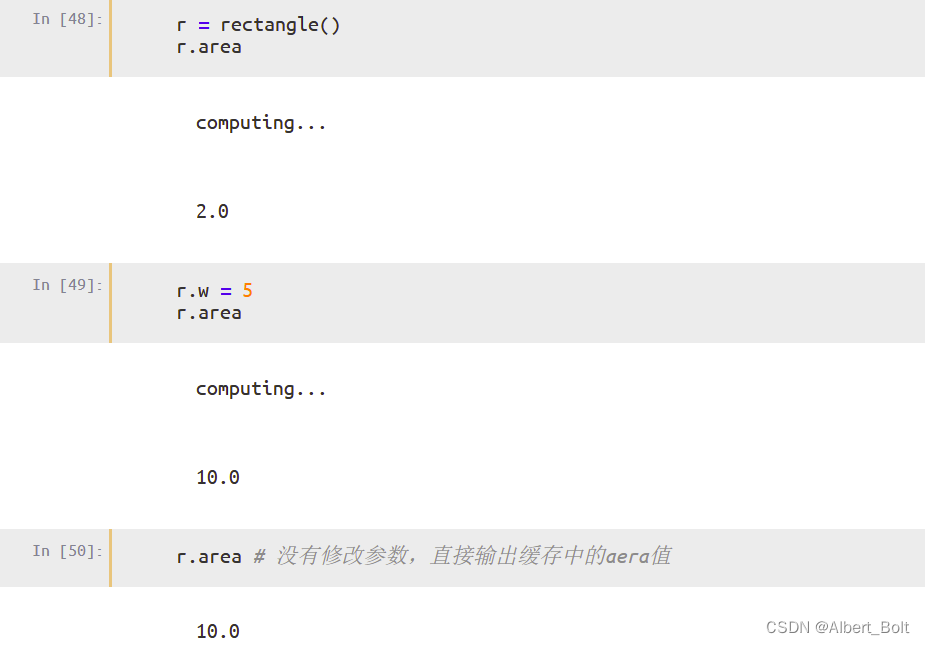
调用configure_traits()在可交互窗口改变 property 属性,每更改一次,会重新调用一次_get_area(),输出一个 computing…
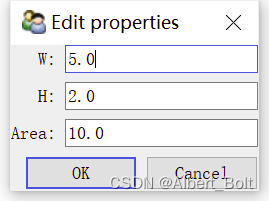
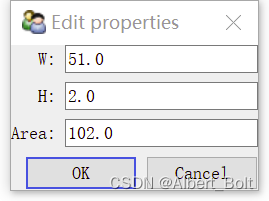

二、TraitsUI 入门
1. TraitsUI 介绍
python 界面开发库:
- Tkinter
- wxPython
- pyQt4
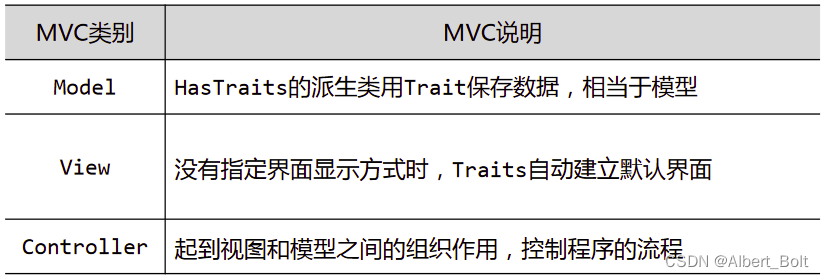
- TraitsUI:以 traits 为基础,以 MVC 为设计思想
Model - View - Controller
- Model:程序中存储数据以及对数据进行处理
- View:程序的界面实现数据的可视化/显示
- Controller:控制程序流程,M/V 之间组织作用
一个实例:
from traits.api import HasTraits, Str, Int class ModelManager(HasTraits): model_name = Str category = Str model_file = Str model_number = Int model = ModelManager() model.configure_traits()- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
生成model 对话框:
- 文字标签根据 trait 属性名自动生成:第一个字母都会自动大写,下划线用空格替代
- 当输入不符合类型的内容时,对话框会变为红色,OK按钮变为无效
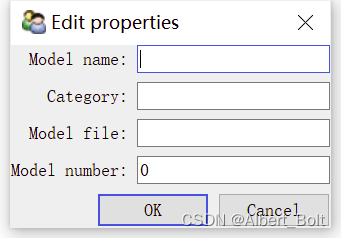
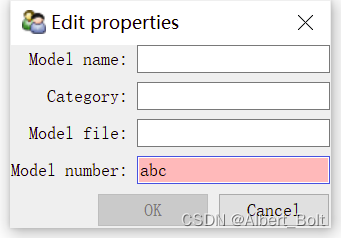
2. View 定义界面
traits.ui 支持的后台界面库:
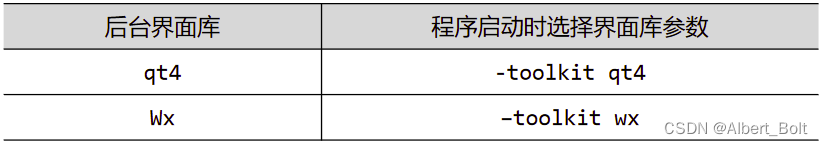
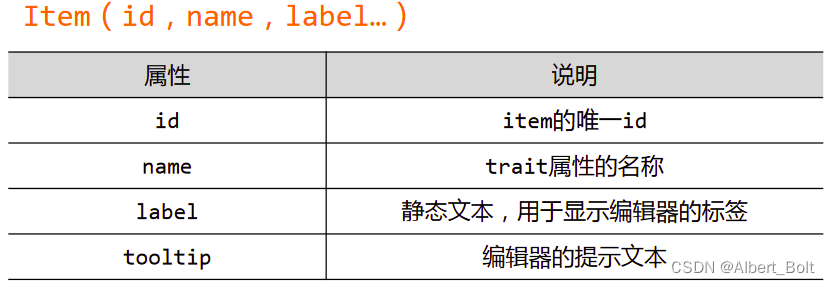
Item 对象属性:
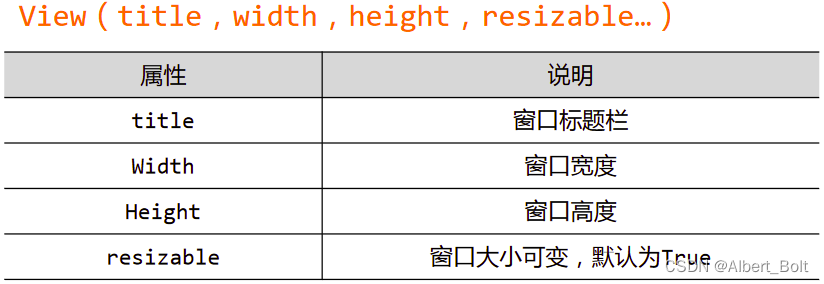
View 对象属性:
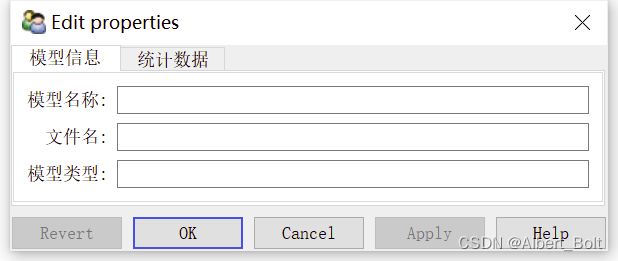
一个实例:from traits.api import HasTraits, Str, Int from traitsui.api import View, Item class ModelManager(HasTraits): model_name = Str category = Str model_file = Str model_number = Int view = View( Item('model_name', label=u"模型名称"), Item('model_file', label=u"文件名"), Item('category', label=u"模型类型"), Item('model_number',label=u"模型数量"), title = u"模型资料", width=220, resizable = True) model = ModelManager() model.configure_traits()- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
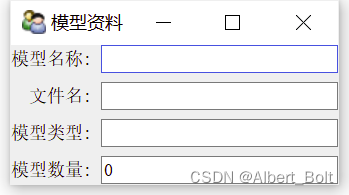
3. Group 对象组织界面
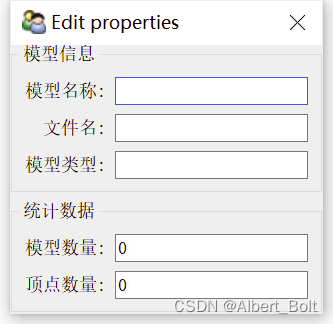
(1) 实例1:不在同一界面,Group 对象并列from traits.api import HasTraits, Str, Int from traitsui.api import View, Item, Group class ModelManager(HasTraits): model_name = Str category = Str model_file = Str model_number = Int vertices = Int view1 = View( Group( Item('model_name', label=u"模型名称"), Item('model_file', label=u"文件名"), Item('category', label=u"模型类型"), label = u'模型信息', show_border = True), Group( Item('model_number', label=u"模型数量"), Item('vertices', label=u"顶点数量"), label = u'统计数据', show_border = True), ) model = ModelManager() model.configure_traits(view=view1)- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26


(2) 实例2:在同一界面,Group 对象嵌套。默认竖直排列,使用
orientation = 'horizontal'水平排列from traits.api import HasTraits, Str, Int from traitsui.api import View, Item, Group class ModelManager(HasTraits): model_name = Str category = Str model_file = Str model_number = Int vertices = Int view1 = View( Group( Group( Item('model_name', label=u"模型名称"), Item('model_file', label=u"文件名"), Item('category', label=u"模型类型"), label = u'模型信息', show_border = True), Group( Item('model_number', label=u"模型数量"), Item('vertices', label=u"顶点数量"), label = u'统计数据', show_border = True), # 两个界面水平排列 orientation = 'horizontal', ) ) model = ModelManager() model.configure_traits(view=view1)- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
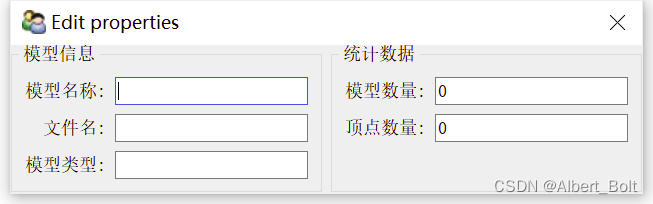
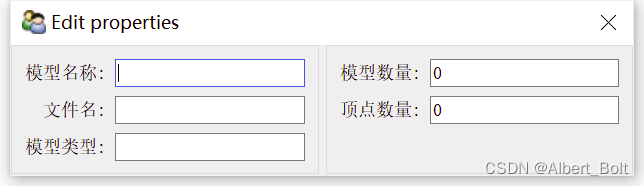
(3) 实例3:使用 HSplit 类
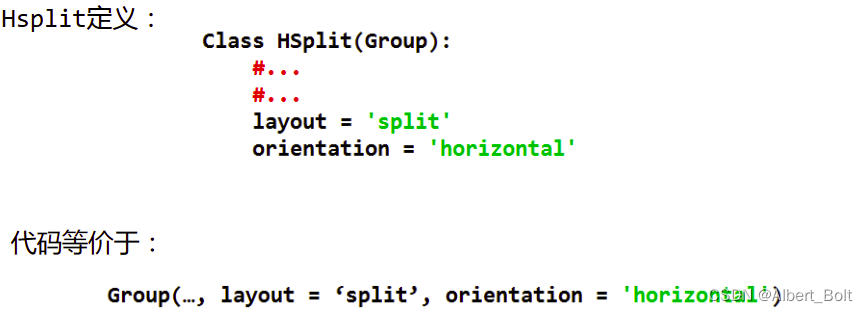
from traits.api import HasTraits, Str, Int from traitsui.api import View, Item, Group from traitsui.api import HSplit, VGroup class ModelManager(HasTraits): model_name = Str category = Str model_file = Str model_number = Int vertices = Int view1 = View( HSplit( VGroup( Item('model_name', label=u"模型名称"), Item('model_file', label=u"文件名"), Item('category', label=u"模型类型"), label = u'模型信息', show_border = True), VGroup( Item('model_number', label=u"模型数量"), Item('vertices', label=u"顶点数量"), label = u'统计数据', show_border = True), ) ) model = ModelManager() model.configure_traits(view=view1)- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
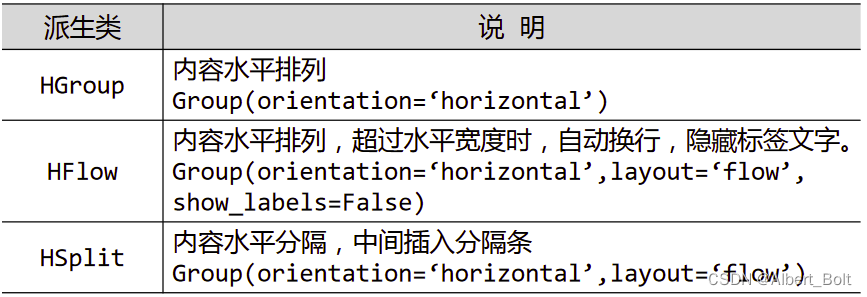
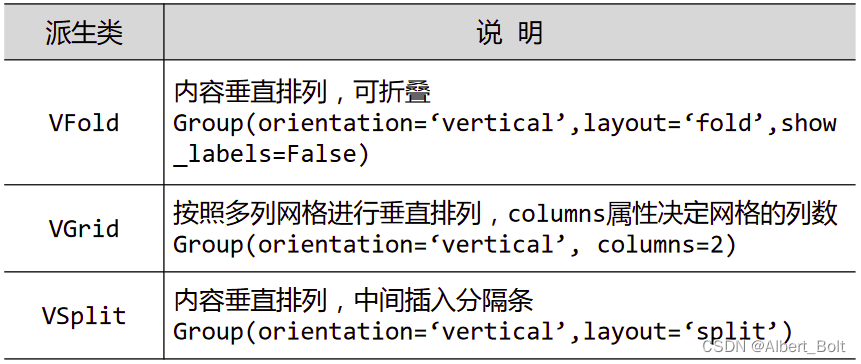
(4) Group的各种派生类

(5) 实例4:使用多个视图对象from traits.api import HasTraits, Str, Int from traitsui.api import View, Item, Group from traitsui.api import HSplit, VGroup g1 = [Item('model_name', label=u'模型名称'), Item('category', label=u'模型类型')] g2 = [Item('model_number', label=u'模型数量'), Item('vertices', label=u'顶点数量')] class ModelManager(HasTraits): model_name = Str category = Str model_number = Int vertices = Int traits_view = View( Group(*g1, label=u'模型信息', show_border=True), Group(*g2, label=u'统计数据', show_border=True), title = u'内部视图' ) global_view = View( Group(*g1, label=u'模型信息', show_border=True), Group(*g2, label=u'统计数据', show_border=True), title = u'外部视图' ) model = ModelManager() model.configure_traits() # 默认为内部视图 #model.configure_traits(view='traits_view') # 内部视图 #model.configure_traits(view=global_view) # 外部视图- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
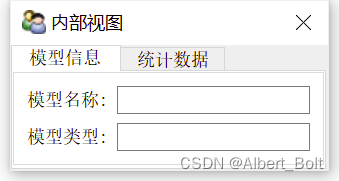

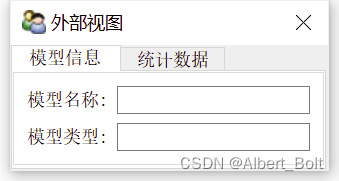
4. 视图配置
- 通过 kind 属性设置 View 显示类型:
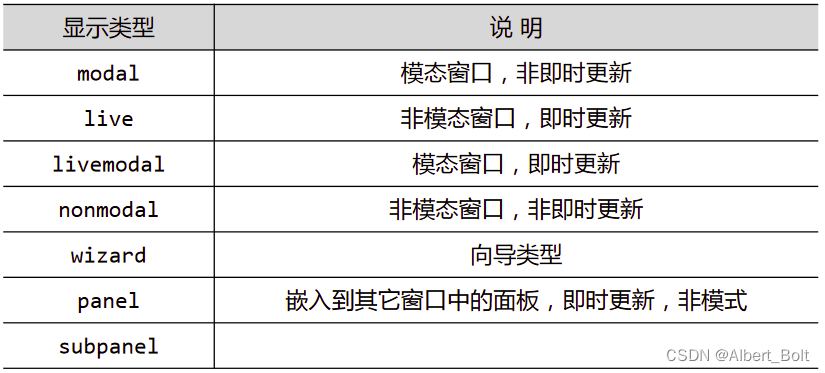
- 模态窗口:在此窗口关闭之前,其他窗口不能激活
- 即时更新:修改控件内容,立即反应到模型数据上
- wizard 是向导窗口、模态窗口、即时更新
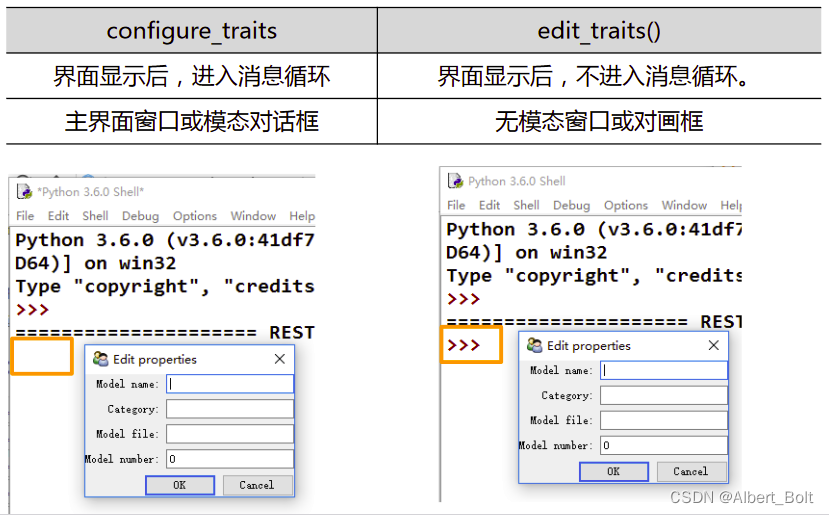
模态与非模态的实例:

TraitsUI 按钮配置:- 标准命令按钮:UndoButton, ApplyButton, RevertButton, OKButton, CancelButton, HelpButto
- traitsui.menu 预定义命令按钮:
- OKCancelButtons = [OKButton, CancelButton]
- ModelButtons = [ApplyButton, RevertButton, OKButton, CancelButton, HelpButton]
- LiveButtons = [UndoButton, RevertButton, OkButton, Cancel]
一个实例:
from traits.api import HasTraits, Str, Int from traitsui.api import View, Item, Group from traitsui.menu import ModalButtons class ModelManager(HasTraits): model_name = Str category = Str model_file = Str model_number = Int vertices = Int view1 = View( Group( Item('model_name', label=u"模型名称"), Item('model_file', label=u"文件名"), Item('category', label=u"模型类型"), label = u'模型信息', show_border = True), Group( Item('model_number', label=u"模型数量"), Item('vertices', label=u"顶点数量"), label = u'统计数据', show_border = True), kind = 'modal', buttons = ModalButtons ) model = ModelManager() model.configure_traits(view=view1)- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
5. TraitsUI 控件
(1) 文本编辑器 TextEditor
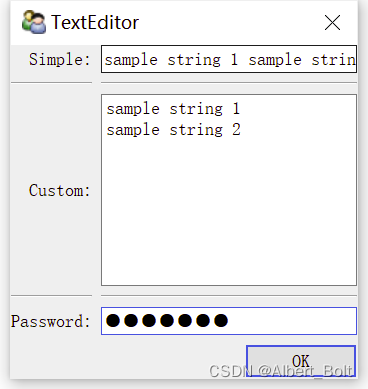
from traits.api import HasTraits, Str, Password from traitsui.api import Item, Group, View class TextEditor(HasTraits): # 定义文本编辑器的变量 string_trait = Str("sample string") password = Password # 定义布局,设置文本编辑器的风格 text_str_group = Group( Item('string_trait', style='simple', label='Simple'), Item('_'), Item('string_trait', style='custom', label='Custom'), Item('_'), Item('password', style='simple', label='Password') ) # 定义视图 traits_view = View( text_str_group, title = 'TextEditor', buttons = ['OK'] ) text = TextEditor() text.configure_traits()- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
Simple 为单行文本输入,Custom 为多行文本输入,Password 为密码样式:
(2) 按钮 Button
监听方法:
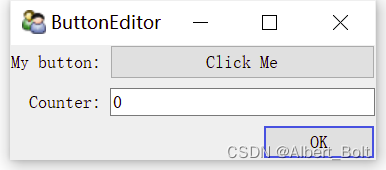
一个实例:'''按钮''' from traits.api import HasTraits, Button, Int from traitsui.api import View class ButtonEditor(HasTraits): # 定义按钮变量: my_button = Button('Click Me') counter = Int # 定义监听函数:按钮点击后触发事件 def _my_button_fired(self): self.counter += 1 # 定义视图 traits_view = View( 'my_button', 'counter', title = 'ButtonEditor', buttons = [ 'OK' ], resizable = True) button = ButtonEditor() button.configure_traits()- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
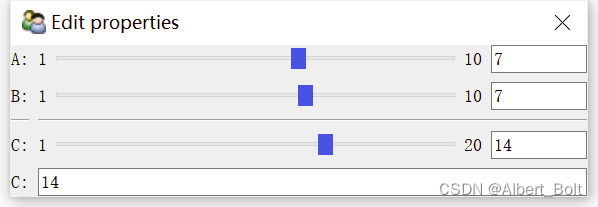
(3) 滑动条 Range'''滑动条''' from traits.api import HasTraits, Int, Range, Property, property_depends_on from traitsui.api import View, Item, RangeEditor class RangeDemo(HasTraits): a = Range(1, 10) b = Range(1, 10) c = Property(Int) view = View( Item('a'), Item('b'), '_', Item('c', editor=RangeEditor(low=1, high=20, mode='slider')), Item('c'), width = 0.3 ) @property_depends_on('a,b', settable=True) def _get_c(self): print("computing ...") return (self.a + self.b) range_ = RangeDemo() range_.configure_traits()- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
(4) 菜单、工具栏from traitsui.menu import Action- 1
控件列表:
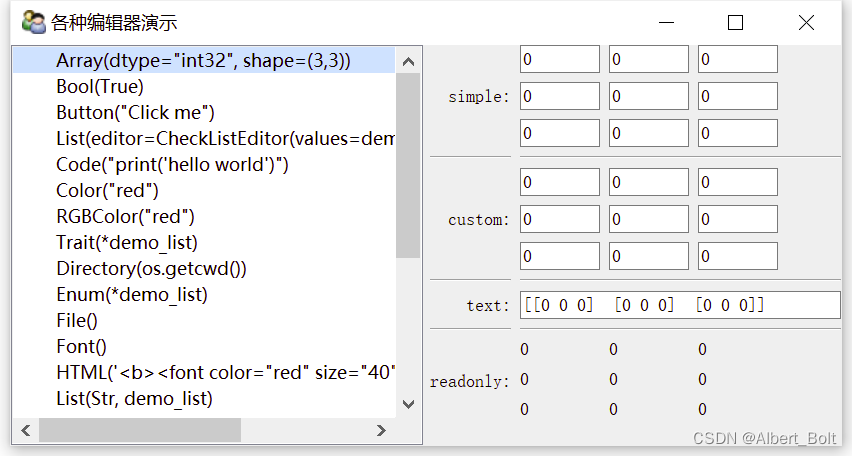
各种编辑器演示:'''演示TraitsUI的各种编辑器''' import os from datetime import time from traits.api import * from traitsui.api import * class EditorDemoItem(HasTraits): '''界面右半部分,对于选中的某个Trait属性,使用4种样式创建属性编辑器''' code = Code() view = View( Group( # 使用simple编辑器,可尽量减少界面占用空间,width属性可指定编辑器宽度,负数表示强制设置宽度 Item("item", style="simple", label="simple", width=-300), # 下划线字符串表示创建分隔线 "_", # 使用custom编辑器,可尽量呈现更多内容 Item("item", style="custom", label="custom"), "_", # 使用text编辑器,只呈现文本内容 Item("item", style="text", label="text"), "_", # 使用readonly编辑器,呈现只读文本 Item("item", style="readonly", label="readonly"), ), ) class EditorDemo(HasTraits): '''创建主界面''' # 创建List界面,用来展示各种Trait属性的字符串 codes = List(Str) # 初始化selected_item界面,用来存储被选项的编辑界面 selected_item = Instance(EditorDemoItem) # 初始化selected_code变量,用来存储被选项名称 selected_code = Str view = View( # 使用HSplite水平分隔两个界面 HSplit( # 界面左半部分,用来创建各种Trait属性的源程序列表 Item("codes", style="custom", show_label=False, # 将editor属性设置为ListStrEditor(列表选择框控件),并更新selected_code变量 editor=ListStrEditor(editable=False, selected="selected_code")), # 界面右半部分 Item("selected_item", style="custom", show_label=False), ), resizable = True, width = 800, height = 400, title = u"各种编辑器演示" ) def _selected_code_changed(self): '''当selected_code变量改变时触发,更新selected_item界面''' item = EditorDemoItem(code=self.selected_code) # 使用eval对selected_code字符串进行求值,并将值存储到item中 item.add_trait("item", eval(str(self.selected_code))) self.selected_item = item class Employee(HasTraits): '''创建Employee类,该类为包含四个属性的界面''' name = Unicode(label = u"姓名") department = Unicode(label = u"部门") salary = Int(label = u"薪水") bonus = Int(label = u"奖金") view = View("name", "department", "salary", "bonus") if __name__ == '__main__': employee = Employee() demo_list = [u"低通", u"高通", u"带通", u"带阻"] trait_defines = """ Array(dtype="int32", shape=(3,3)) # {1}fadsfa Bool(True) Button("Click me") List(editor=CheckListEditor(values=demo_list)) Code("print('hello world')") Color("red") RGBColor("red") Trait(*demo_list) # 无法用于custom编辑器 Directory(os.getcwd()) Enum(*demo_list) # 无法用于custom编辑器 File() Font() HTML('<b><font color="red" size="40">hello world</font></b>') List(Str, demo_list) Range(1, 10, 5) # 无法用于custom编辑器 List(editor=SetEditor(values=demo_list)) List(demo_list, editor=ListStrEditor()) Str("hello") Password("hello") Str("Hello", editor=TitleEditor()) Tuple(Color("red"), Range(1,4), Str("hello")) Instance(EditorDemoItem, employee) Instance(EditorDemoItem, employee, editor=ValueEditor()) Instance(time, time(), editor=TimeEditor()) """ demo = EditorDemo() trait_list = [] # 按行分割字符串 for s in trait_defines.split('\n'): # 判断s中是否存在可执行函数 if s.split('#')[0].strip(): # 去掉注释 trait_list.append(s.split('#')[0]) demo.codes = trait_list # 简洁写法 # demo.codes = [s.split("#")[0] for s in trait_defines.split("\n") if s.split('#')[0].strip()] demo.configure_traits()- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
-
相关阅读:
串口转HID键鼠功能芯片CH9329应用指南
Leetcode236 二叉树两节点的最近公共祖先
URI和URL的区别
计算机网络——物理层(传输方式)
hive数据倾斜(超详细)
11.12 - 每日一题 - 408
330. 按要求补齐数组
math_极限&微分&导数&微商/对数函数的导数推导(导数定义极限法)
【物理应用】大气辐射和透射率模型及太阳和月亮模型(Matlab代码实现)
C#WPF数字大屏项目实战08--生产量/良品统计
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/Albert_Bolt/article/details/125575419