-
C# 语言的高级应用
C# 语言的高级应用
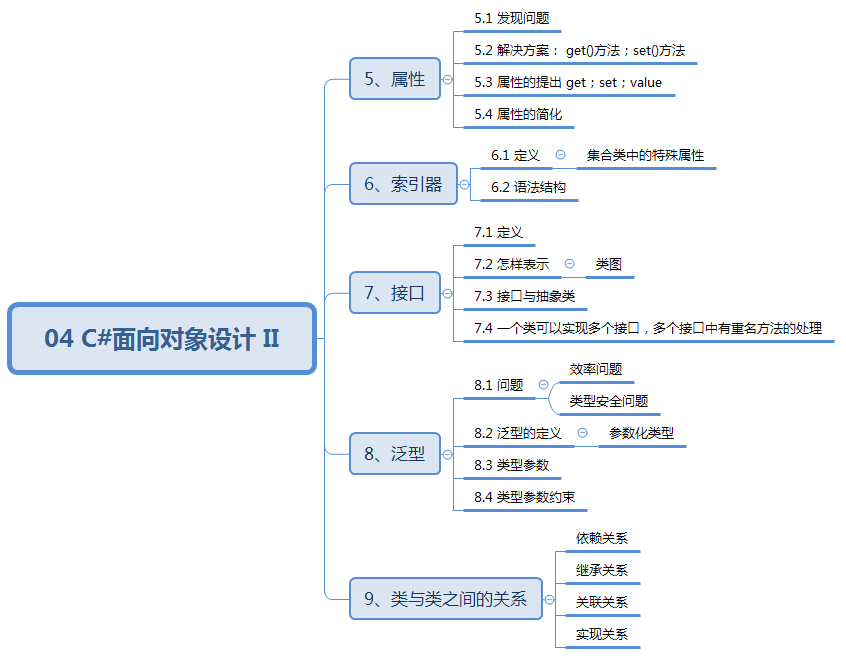
1、属性
例1:属性概念的引入(问题)
public class Animal { public int Age; public double Weight; public bool Sex; public Animal(int age, double weight, bool sex) { Age = age; Weight = weight; Sex = sex; } public void Eat() { Console.WriteLine("Animal Eat."); } public void Sleep() { Console.WriteLine("Animal Sleep."); } public override string ToString() { return string.Format("Animal Age:{0}, Weight:{1}, Sex:{2}", Age, Weight, Sex); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { Animal al = new Animal(1, 1.2, false); Console.WriteLine("Animal Age:{0}, Weight:{1}, Sex:{2}", al.Age, al.Weight, al.Sex); al.Age = -1; al.Weight = -0.5; Console.WriteLine(al); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
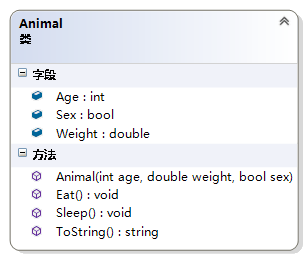
例2:问题的解决(Java语言解决该问题的方案)
public class Animal { private int _age; private double _weight; private readonly bool _sex; public int GetAge() { return _age; } public void SetAge(int value) { _age = (value > 0) ? value : 0; } public double GetWeight() { return _weight; } public void SetWeight(double value) { _weight = (value > 0) ? value : 0; } public bool GetSex() { return _sex; } public Animal(int age, double weight, bool sex) { _age = (age > 0) ? age : 0; _weight = (weight > 0) ? weight : 0; _sex = sex; } public void Eat() { Console.WriteLine("Animal Eat."); } public void Sleep() { Console.WriteLine("Animal Sleep."); } public override string ToString() { return string.Format("Animal Age:{0}, Weight:{1}, Sex:{2}", _age, _weight, _sex); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { Animal al = new Animal(1, 1.2, false); Console.WriteLine("Animal Age:{0},Weight:{1},Sex:{2}", al.GetAge(), al.GetWeight(), al.GetSex()); al.SetAge(-1); al.SetWeight(-0.5); Console.WriteLine(al); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
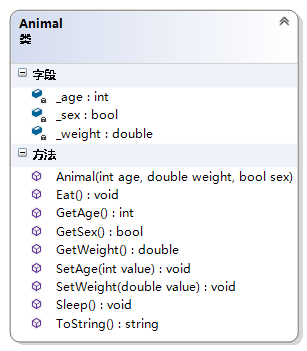
例3:属性的提出
public class Animal { private int _age; private double _weight; private readonly bool _sex; public int Age { get { return _age; } set { _age = (value > 0) ? value : 0; } } public double Weight { get { return _weight; } set { _weight = (value > 0) ? value : 0; } } public bool Sex { get { return _sex; } } public Animal(int age, double weight, bool sex) { _age = (age > 0) ? age : 0; _weight = (weight > 0) ? weight : 0; _sex = sex; } public void Eat() { Console.WriteLine("Animal Eat."); } public void Sleep() { Console.WriteLine("Animal Sleep."); } public override string ToString() { return string.Format("Animal Age:{0}, Weight:{1}, Sex:{2}", Age, Weight, Sex); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { Animal al = new Animal(1, 1.2, false); Console.WriteLine("Animal Age:{0}, Weight:{1}, Sex:{2}", al.Age, al.Weight, al.Sex); al.Age = -1; al.Weight = -0.5; Console.WriteLine(al); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
说明:C#在声明data时就可以定义
set、get方法。get:定义读取操作。set:定义赋值操作,value表示传入的参数值。
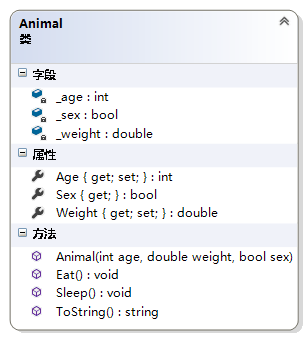
例4:属性的简化
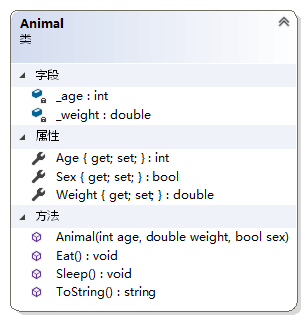
public class Animal { private int _age; private double _weight; public int Age { get { return _age; } set { _age = (value > 0) ? value : 0; } } public double Weight { get { return _weight; } set { _weight = (value > 0) ? value : 0; } } public bool Sex { get; private set; } public Animal(int age, double weight, bool sex) { _age = (age > 0) ? age : 0; _weight = (weight > 0) ? weight : 0; Sex = sex; } public void Eat() { Console.WriteLine("Animal Eat."); } public void Sleep() { Console.WriteLine("Animal Sleep."); } public override string ToString() { return string.Format("Animal Age:{0},Weight:{1},Sex:{2}", Age, Weight, Sex); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { Animal al = new Animal(1, 1.2, false); Console.WriteLine("Animal Age:{0}, Weight:{1}, Sex:{2}", al.Age, al.Weight, al.Sex); al.Age = -1; al.Weight = -0.5; Console.WriteLine(al); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
说明:属性可以看作是对私有数据部分增加的一层隔离。
2、索引器
2.1 定义
是集合类中的一种特殊属性,可使得集合类中的元素像数组元素一样访问。
2.2 语法结构
public 元素类型 this[int index] { get { ... } set { ... } } public 元素类型 this[string name] { get { ... } set { ... } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
例5:利用索引器实现对集合类
StudentSet中元素Student的访问。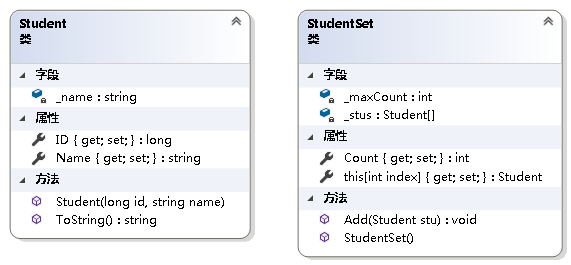
public class Student { private string _name; public string Name { get { return _name; } set { _name = string.IsNullOrEmpty(value) ? "NULL" : value; } } public long ID { get; set; } public Student(long id, string name) { ID = id; _name = name; } public override string ToString() { return string.Format("ID:{0},Name:{1}", ID, Name); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
public class StudentSet { private readonly int _maxCount = 500; private readonly Student[] _stus; public int Count { get; private set; } public StudentSet() { Count = 0; _stus = new Student[_maxCount]; } public void Add(Student stu) { if (stu == null) throw new ArgumentNullException(); if (Count == _maxCount) throw new IndexOutOfRangeException(); _stus[Count] = stu; Count++; } public Student this[int index] { get { if (index < 0 || index > Count - 1) throw new IndexOutOfRangeException(); return _stus[index]; } set { if (index < 0 || index > Count - 1) throw new IndexOutOfRangeException(); if (value == null) throw new ArgumentNullException(); _stus[index] = value; } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { StudentSet stuSet = new StudentSet(); stuSet.Add(new Student(10086, "张三")); stuSet.Add(new Student(95988, "李四")); stuSet[1].Name = string.Empty; Console.WriteLine(stuSet.Count); Console.WriteLine(stuSet[0]); Console.WriteLine(stuSet[1]); Console.WriteLine(stuSet[2]); //未处理的异常: System.IndexOutOfRangeException: 索引超出了数组界限。 } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
3、接口
3.1 概念
- 接口是类设计的蓝图,即只提供声明而没有实现。
- 接口不可以直接实例化对象(与抽象类相同)。
- C#允许一个类实现多个接口(注意与继承的区别)。
- 接口就是包含一系列不被实现的方法,而把这些方法的实现交给继承它的类。
3.2 表示
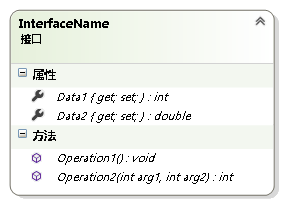
例6:根据类图利用
Dog实现IAnimal接口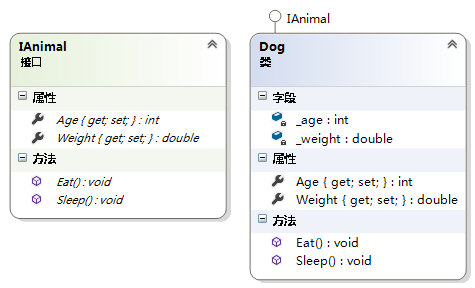
public interface IAnimal { int Age { get; set; } double Weight { get; set; } void Eat(); void Sleep(); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
public class Dog : IAnimal { private int _age; private double _weight; public int Age { get { return _age; } set { _age = (value >= 0) ? value : 0; } } public double Weight { get { return _weight; } set { _weight = (value >= 0) ? value : 0; } } public void Eat() { Console.WriteLine("Dog Eat"); } public void Sleep() { Console.WriteLine("Dog Sleep"); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { IAnimal al = new Dog(); al.Age = 1; al.Weight = 2.5; Console.WriteLine("Dog:Age={0}, Weight={1}", al.Age, al.Weight); al.Eat(); al.Sleep(); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
例7:利用接口实现“饲养系统”
某饲养员(Raiser)在目前状态下需要饲养三种动物:狗(Dog)、鸟(Bird)和鱼(Fish),该三种动物只需要让其睡觉(Sleep)和吃饭(Eat)即可。请设计该饲养系统,要求满足软件设计的“开闭原则”。
方案一:(在抽象类部分已经给出)
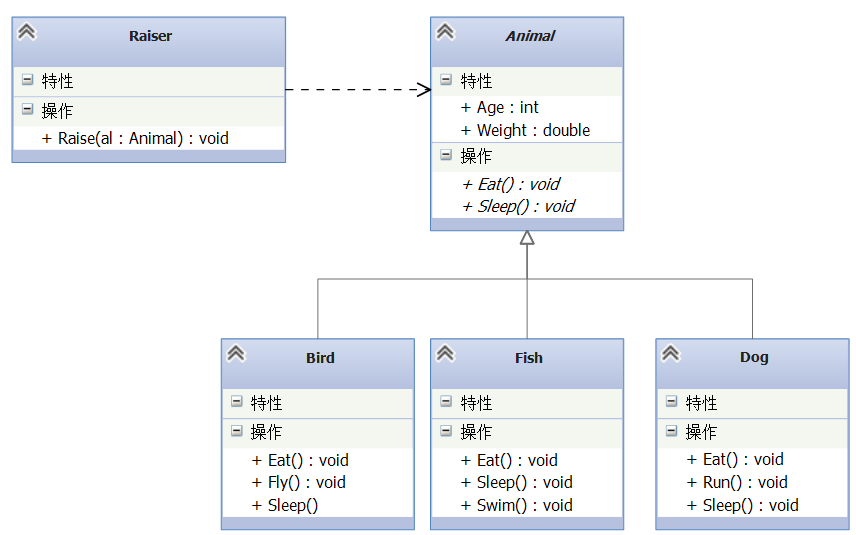
方案二:
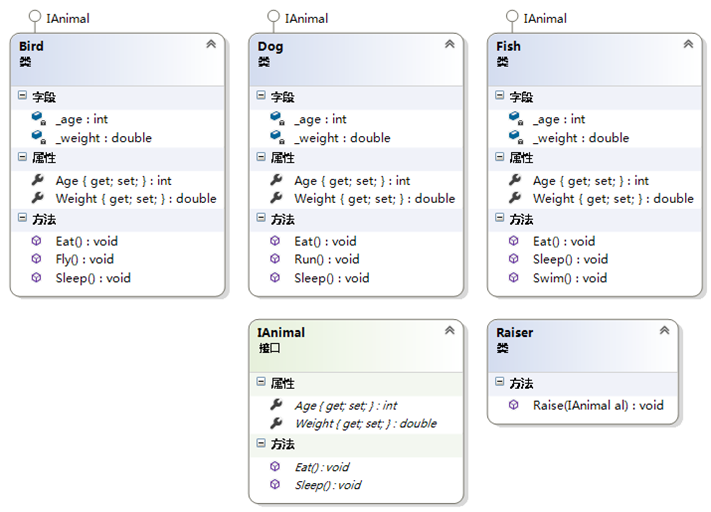
public interface IAnimal { int Age { get; set; } double Weight { get; set; } void Eat(); void Sleep(); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
public class Bird : IAnimal { private int _age; private double _weight; public int Age { get { return _age; } set { _age = (value >= 0) ? value : 0; } } public double Weight { get { return _weight; } set { _weight = (value >= 0) ? value : 0; } } public void Eat() { Console.WriteLine("Bird Eat."); } public void Sleep() { Console.WriteLine("Bird Sleep."); } public void Fly() { Console.WriteLine("Bird Fly."); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
public class Dog : IAnimal { private int _age; private double _weight; public int Age { get { return _age; } set { _age = (value >= 0) ? value : 0; } } public double Weight { get { return _weight; } set { _weight = (value >= 0) ? value : 0; } } public void Eat() { Console.WriteLine("Dog Eat."); } public void Sleep() { Console.WriteLine("Dog Sleep."); } public void Run() { Console.WriteLine("Dog Run."); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
public class Fish : IAnimal { private int _age; private double _weight; public int Age { get { return _age; } set { _age = (value >= 0) ? value : 0; } } public double Weight { get { return _weight; } set { _weight = (value >= 0) ? value : 0; } } public void Eat() { Console.WriteLine("Fish Eat."); } public void Sleep() { Console.WriteLine("Fish Sleep."); } public void Swim() { Console.WriteLine("Fish Swim."); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
public class Raiser { public void Raise(IAnimal al) { al.Eat(); al.Sleep(); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { Raiser rsr = new Raiser(); rsr.Raise(new Dog()); rsr.Raise(new Bird()); rsr.Raise(new Fish()); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
3.3 接口(interface)与抽象类(abstract class)
(1)相同点:
- 接口与抽象类都不可以直接实例化对象。
(2)不同点:
- 抽象类中的数据和操作必须有限制修饰符,而接口中的数据和操作不可以有限制修饰符。
- 抽象类中可以有带实现体的方法(非abstract方法),而接口只能有方法的声明。
- 抽象类在子类中通过override关键字覆写抽象方法,而接口被子类直接实现。
例8:一个类可以实现多个接口,但要注意多个接口中有重名方法的处理。
方式一:
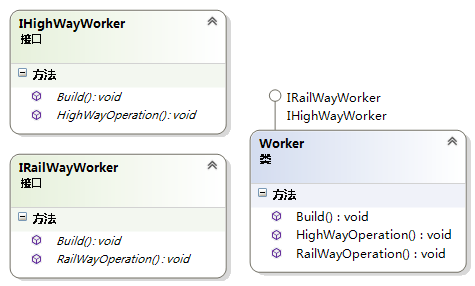
public interface IHighWayWorker { void HighWayOperation(); void Build(); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
public interface IRailWayWorker { void RailWayOperation(); void Build(); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
public class Worker : IRailWayWorker, IHighWayWorker { public void HighWayOperation() { Console.WriteLine("HighWayOperation."); } public void RailWayOperation() { Console.WriteLine("RailWayOperation"); } public void Build() { Console.WriteLine("HighWay,RailWay,Build."); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { Worker wr = new Worker(); wr.Build(); // HighWay,RailWay,Build. IHighWayWorker hwr = new Worker(); hwr.Build(); // HighWay,RailWay,Build. hwr.HighWayOperation(); // HighWayOperation. IRailWayWorker rwr = new Worker(); rwr.Build(); // HighWay,RailWay,Build. rwr.RailWayOperation();// RailWayOperation } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
方式二:
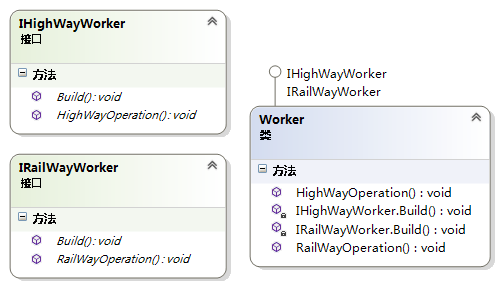
public interface IHighWayWorker { void HighWayOperation(); void Build(); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
public interface IRailWayWorker { void RailWayOperation(); void Build(); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
public class Worker : IHighWayWorker, IRailWayWorker { public void HighWayOperation() { Console.WriteLine("HighWayOperation."); } public void RailWayOperation() { Console.WriteLine("RailWayOperation"); } void IHighWayWorker.Build() { Console.WriteLine("HighWay Build."); } void IRailWayWorker.Build() { Console.WriteLine("RailWay Build."); } // 注意:void IHighWayWorker.Build()和void IRailWayWorker.Build() // 前面不能够加限制修饰符。 }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { Worker wr = new Worker(); //wr.Build(); 该语句错误 IHighWayWorker hwr = new Worker(); hwr.Build();//HighWay Build. hwr.HighWayOperation();//HighWayOperation. IRailWayWorker rwr = new Worker(); rwr.Build();//RailWay Build. rwr.RailWayOperation();//RailWayOperation } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
4、泛型
例9:存储
int数据类型的集合及操作。public class IntSet { private readonly int _maxSize; private readonly int[] _set; public IntSet() { _maxSize = 100; _set = new int[_maxSize]; //... } public void Insert(int k, int x) { //.... _set[k] = x; } public int Locate(int k) { //... return _set[k]; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { IntSet iSet = new IntSet(); iSet.Insert(0, 123); int i = iSet.Locate(0); Console.WriteLine(i); // 123 } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
例10:存储
string数据类型的集合及操作。public class StringSet { private readonly int _maxSize; private readonly string[] _set; public StringSet() { _maxSize = 100; _set = new string[_maxSize]; //... } public void Insert(int k, string x) { //.... _set[k] = x; } public string Locate(int k) { //... return _set[k]; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { StringSet strSet = new StringSet(); strSet.Insert(0, "abc"); string j = strSet.Locate(0); Console.WriteLine(j); // abc } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
例11:利用
object类存储通用数据类型的集合及操作。public class GSet { private readonly int maxSize; private readonly object[] _set; public GSet() { maxSize = 100; _set = new object[maxSize]; //... } public void Insert(int k, object x) { //.... _set[k] = x; } public object Locate(int k) { //... return _set[k]; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { GSet gSet1 = new GSet(); gSet1.Insert(0, 123); int k1 = (int)gSet1.Locate(0); Console.WriteLine(k1); // 123 GSet gSet2 = new GSet(); gSet2.Insert(0, "abc"); string k2 = (string)gSet2.Locate(0); Console.WriteLine(k2); // abc GSet gSet3 = new GSet(); gSet3.Insert(0, 123); gSet3.Insert(1, "abc");//编译时可以通过,运行时出现异常。 int k3 = (int)gSet3.Locate(1); //这样使用存在类型安全问题。 Console.WriteLine(k3); // 未处理的异常: System.InvalidCastException: 指定的转换无效。 } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
泛型定义:即参数化类型。
在编译时用一个具体类型代替该参数类型,可定义类型安全的类而不影响工作效率。
例12:利用泛型
T存储通用数据类型的集合及操作。public class GSet<T> { private readonly int _maxSize; private readonly T[] _set; public GSet() { _maxSize = 100; _set = new T[_maxSize]; //... } public void Insert(int k, T x) { //.... _set[k] = x; } public T Locate(int k) { //... return _set[k]; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { GSet<int> gSet1 = new GSet<int>(); gSet1.Insert(0, 123); int k1 = gSet1.Locate(0); Console.WriteLine(k1); // 123 GSet<string> gSet2 = new GSet<string>(); gSet2.Insert(0, "abc"); string k2 = gSet2.Locate(0); Console.WriteLine(k2); // abc } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
我们把
T称为类型参数,当然我们也可以对T进行约束。例13:为类型参数
T增加约束,比如T只能是值类型。public class GSet<T> where T : struct { private readonly int _maxSize; private readonly T[] _set; public GSet() { _maxSize = 100; _set = new T[_maxSize]; //... } public void Insert(int k, T x) { //.... _set[k] = x; } public T Locate(int k) { //... return _set[k]; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { GSet<int> gSet1 = new GSet<int>(); gSet1.Insert(0, 123); int k1 = gSet1.Locate(0); Console.WriteLine(k1); // 123 // GSet<string> gSet2 = new GSet<string>(); // 编译错误 // 错误 CS0453 类型“string”必须是不可以为 null 值的类型, // 才能用作泛型类型或方法“GSet < T >”中的参数“T” } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
有关泛型约束可以查看以下图文:
5、类与类之间的关系
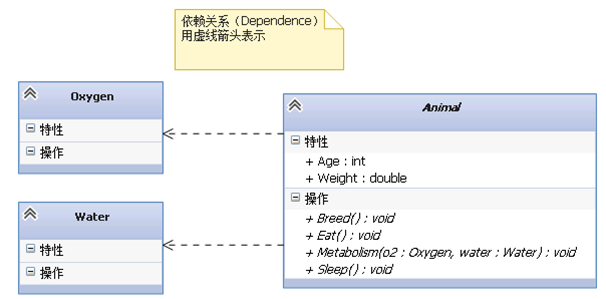
public class Oxygen { //... }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
public class Water { //... }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
public abstract class Animal { public int Age; public double Weight; public abstract void Eat(); public abstract void Sleep(); public abstract void Breed(); public abstract void Metabolism(Oxygen o2, Water water); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
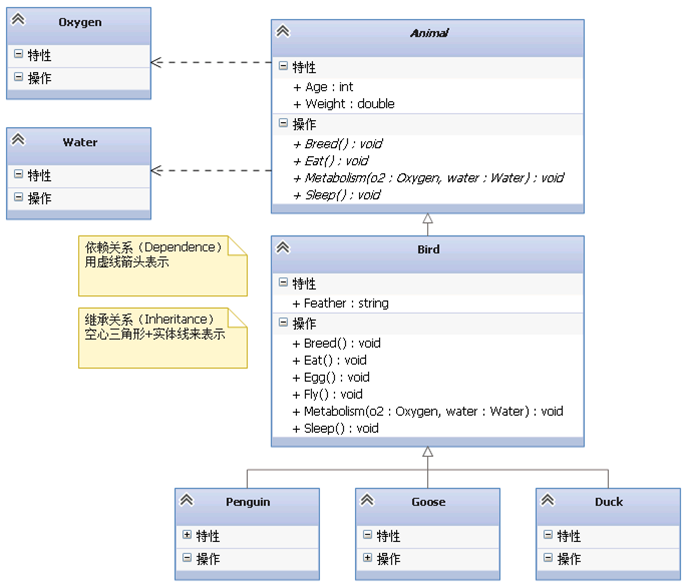
public class Bird : Animal { public string Feather; public void Fly() { //... } public void Egg() { //... } public override void Eat() { //... } public override void Sleep() { //... } public override void Breed() { //... } public override void Metabolism(Oxygen o2, Water water) { //... } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
public class Penguin : Bird { //... }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
public class Goose : Bird { //... }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
public class Duck : Bird { //... }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
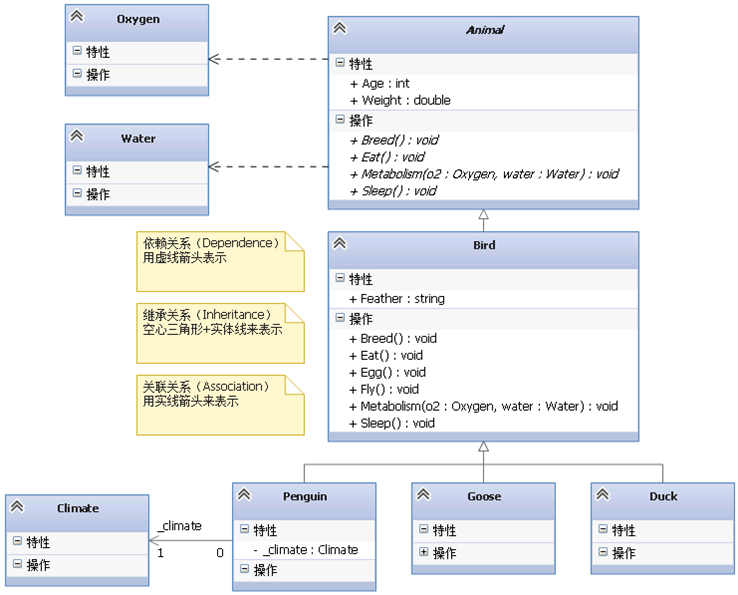
public class Climate { //... }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
public class Penguin : Bird { private Climate _climate; //... }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
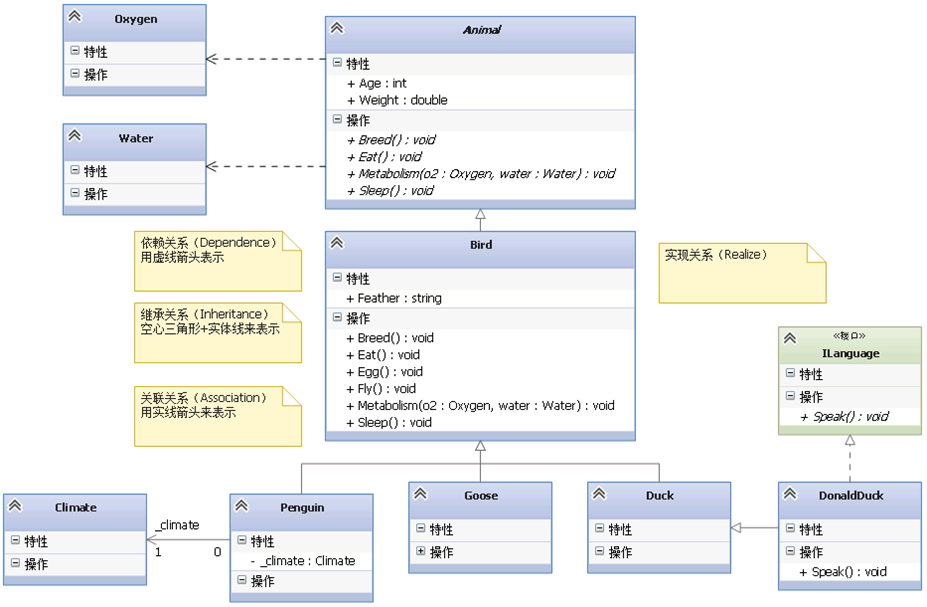
public interface ILanguage { void Speak(); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
public class DonaldDuck : Duck, ILanguage { public void Speak() { //... } //... }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
-
相关阅读:
传奇单机架设教程,五分钟完成单机架设
C#基础知识
[CMake] CMake 基础命令
【AGC】集成华为AGC崩溃服务实用教程
元宇宙的核心技术之我见
Hive之grouping sets用法详解
恒合仓库 - 商品管理模块、上传照片、添加采购单、添加出库单、商品分类
Arduino程序设计(三) 光照采集 + 温度采集
第十九章 文件操作
操作系统课设
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/LSGO_MYP/article/details/125621559