-
【手撕STL】AVL树
AVL树的概念
二叉搜索树虽可以缩短查找的效率,但如果数据有序或接近有序二叉搜索树将退化为单支树,查找元素相当于在顺序表中搜索元素,效率低下。因此,找到了解决上述问题的方法:当向二叉搜索树中插入新结点后,如果能保证每个结点的左右子树高度之差的绝对值不超过1(需要对树中的结点进行调整),即可降低树的高度,从而减少平均搜索长度。
AVL树的性质:
- 它的左右子树都是AVL树
- 左右子树高度之差(简称平衡因子)的绝对值不超过1(-1/0/1)
- 如果一棵二叉搜索树是高度平衡的,它就是AVL树。如果它有n个结点,其高度可保持在 O(logN),搜索时间复杂度O(logN)。
注:平衡因子=右子树的高度-左子树的高度
平衡因子更新规则:
- 插入更新的节点在父亲的左边,父亲平衡因子–;插入更新的节点在父亲的右边,父亲平衡因子++
- 父亲的平衡因子更新以后是-1或者1,说明父亲所在子树的高度变了,需要继续往上更新
- 父亲的平衡因子更新以后是0,说明父亲所在子树的高度没变,不需要继续往上更新
- 父亲的平衡因子更新以后是-2或者2,说明父亲所在子树已经不平衡了,需要旋转处理使它平衡
- 更新以后,更新到了根节点就不需要在更新了
AVL树的旋转
如果在一棵原本是平衡的AVL树中插入一个新节点,可能造成不平衡,此时必须调整树的结构,使之平衡化。根据节点插入位置的不同,AVL树的旋转分为四种:
新节点插入较高左子树的左侧—左左:右单旋
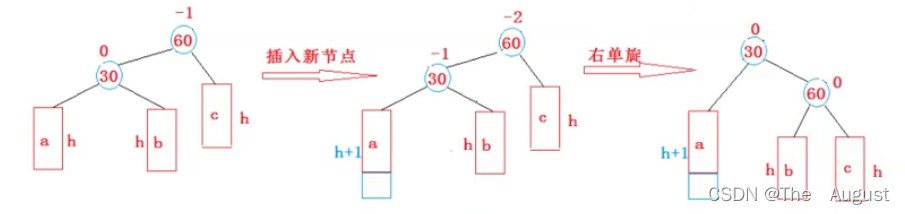
a,b,c是高度为h的AVL子树,他们有无数种情况,只要在a中插入节点,a的高度变为h+1,就会引发右单旋(h>=0)
右单旋操作:
- b子树变成60的左子树
- 60成为30的右子树,30成为这棵树的根
- 30和60的平衡因子变为0
新节点插入较高右子树的右侧—右右:左单旋

a,b,c是高度为h的AVL子树,只要c这棵子树的高度变为h+1,就会引发左单旋左单旋操作:
- b子树变成30的右子树
- 30成为60的左子树,60成为这棵树的根
- 30和60的平衡因子变为0
新节点插入较高左子树的右侧—左右:先左单旋再右单旋
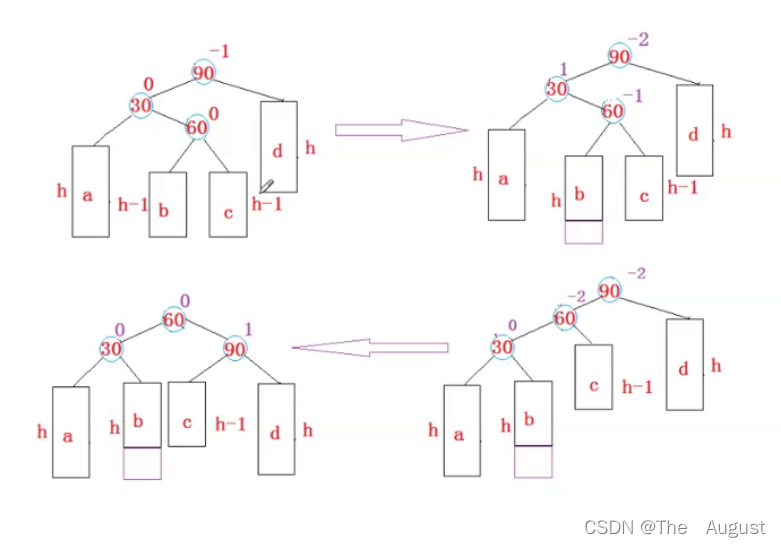
操作:- 先以30为旋转点,进行左单旋
- 以90作为旋转点进行右单旋
新节点插入较高右子树的左侧—右左:先右单旋再左单旋
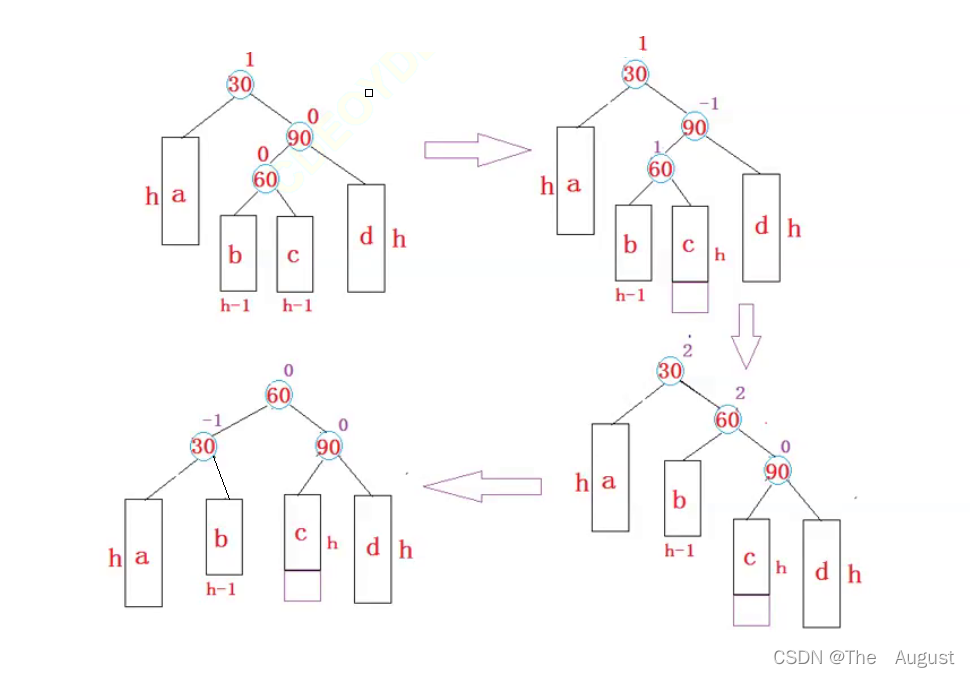
操作:
- 先以90为旋转点,进行右单旋
- 以30作为旋转点进行左单旋
双旋平衡因子更新问题:

双旋以后的结果:- b变成30的右边
- c变成60的左边
- 30和90分别变成60的左边和右边,60成为新的根
总结:
- 旋转的本质:在遵循搜索树的规则情况,让左右均衡,并且降低整棵树的高度
- 更新平衡因子的过程中,引发旋转的路径是直线就是单旋,如果是折线就是双旋
总结:
假如以pParent为根的子树不平衡,即pParent的平衡因子为2或者-2,分以下情况考虑- pParent的平衡因子为2,说明pParent的右子树高,设pParent的右子树的根为pSubR
- 当pSubR的平衡因子为1时,执行左单旋
- 当pSubR的平衡因子为-1时,执行右左双旋
- pParent的平衡因子为-2,说明pParent的左子树高,设pParent的左子树的根为pSubL
- 当pSubL的平衡因子为-1是,执行右单旋
- 当pSubL的平衡因子为1时,执行左右双旋
旋转完成后,原pParent为根的子树个高度降低,已经平衡,不需要再向上更新。
AVL树的实现
#pragma once #define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1 #include<assert.h> #include<iostream> using namespace std; template<class K,class V> struct AVLTreeNode { AVLTreeNode(const pair<K, V>& kv) :_left(nullptr) , _right(nullptr) , _parent(nullptr) , _kv(kv) , _bf(0) {} AVLTreeNode<K, V>* _left; AVLTreeNode<K, V>* _right; AVLTreeNode<K, V>* _parent; pair<K, V> _kv; int _bf; //balance factor= 右树的高度-左树的高度 }; template<class K,class V> class AVLTree { typedef AVLTreeNode<K, V> Node; public: AVLTree() :_root(nullptr) {} bool Insert(const pair<K, V>& kv) { if (_root == nullptr) { _root = new Node(kv); return true; } Node* parent = nullptr; Node* cur = _root; while (cur) { if (cur->_kv.first < kv.first) { parent = cur; cur = cur->_right; } else if (cur->_kv.first > kv.first) { parent = cur; cur = cur->_left; } else { return false; } } cur = new Node(kv); if (parent->_kv.first > kv.first) { parent->_left = cur; cur->_parent = parent; } else { parent->_right = cur; cur->_parent = parent; } //控制树的平衡 while (parent) { //更新平衡因子 if (parent->_left == cur) parent->_bf--; else parent->_bf++; //检查父亲的平衡因子 //父亲所在子树的高度不变,不影响祖先,跟新结束 if (parent->_bf == 0) break; //父亲所在子树高度变了,继续往上更新 else if (parent->_bf == -1 || parent->_bf == 1) { cur = parent; parent = cur->_parent; } //父亲所在子树的出现了不平衡,需要旋转处理 else if (parent->_bf == -2 || parent->_bf == 2) { if (parent->_bf == -2 && cur->_bf == -1) { RotateR(parent); } else if (parent->_bf == 2 && cur->_bf == 1) { RotateL(parent); } else if (parent->_bf == -2 && cur->_bf == 1) { RotateLR(parent); } else if (parent->_bf == 2 && cur->_bf == -1) { RotateRL(parent); } else { assert(false); } break; } else { assert(false); } } return true; } void RotateR(Node* parent) { Node* subL = parent->_left; Node* subLR = subL->_right; parent->_left = subLR; if (subLR) { subLR->_parent = parent; } Node* ppNode = parent->_parent; subL->_right = parent; parent->_parent = subL; if (parent == _root) { _root = subL; subL->_parent = nullptr; } else { if (ppNode->_left == parent) ppNode->_left = subL; else ppNode->_right = subL; subL->_parent = ppNode; } subL->_bf = parent->_bf = 0; } void RotateL(Node* parent) { Node* subR = parent->_right; Node* subRL = subR->_left; parent->_right = subRL; if (subRL) { subRL->_parent = parent; } Node* ppNode = parent->_parent; subR->_left = parent; parent->_parent = subR; if (parent == _root) { _root = subR; subR->_parent = nullptr; } else { if (ppNode->_left == parent) ppNode->_left = subR; else ppNode->_right = subR; subR->_parent = ppNode; } subR->_bf = parent->_bf = 0; } void RotateLR(Node* parent) { Node* subL = parent->_left; Node* subLR = subL->_right; int bf = subLR->_bf; RotateL(parent->_left); RotateR(parent); if (bf == 1) { parent->_bf = 0; subL->_bf = -1; subLR->_bf = 0; } else if (bf == -1) { parent->_bf = 1; subL->_bf = 0; subLR->_bf = 0; } else if (bf == 0) { parent->_bf = 0; subL->_bf = 0; subLR->_bf = 0; } else { assert(false); } } void RotateRL(Node* parent) { Node* subR = parent->_right; Node* subRL = subR->_left; int bf = subRL->_bf; RotateR(parent->_right); RotateL(parent); if (bf == 1) { parent->_bf = -1; subR->_bf = 0; subRL->_bf = 0; } else if (bf == -1) { parent->_bf = 0; subR->_bf = 1; subRL->_bf = 0; } else if (bf == 0) { parent->_bf = 0; subR->_bf = 0; subRL->_bf = 0; } else { assert(false); } } int Height(Node* root) { if (root == nullptr) return 0; int leftHeight = Height(root->_left); int rightHeight = Height(root->_right); return leftHeight > rightHeight ? ++leftHeight : ++rightHeight; } bool IsBalance() { return _IsBalance(_root); } private: bool _IsBalance(Node* root) { if (root == nullptr) return true; int leftHeight = Height(root->_left); int rightHeight = Height(root->_right); if (rightHeight - leftHeight != root->_bf) cout << "平衡因子异常:" << root->_kv.first << endl; return abs(rightHeight - leftHeight) < 2 && _IsBalance(root->_left) && _IsBalance(root->_right); } Node* _root; };- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
- 134
- 135
- 136
- 137
- 138
- 139
- 140
- 141
- 142
- 143
- 144
- 145
- 146
- 147
- 148
- 149
- 150
- 151
- 152
- 153
- 154
- 155
- 156
- 157
- 158
- 159
- 160
- 161
- 162
- 163
- 164
- 165
- 166
- 167
- 168
- 169
- 170
- 171
- 172
- 173
- 174
- 175
- 176
- 177
- 178
- 179
- 180
- 181
- 182
- 183
- 184
- 185
- 186
- 187
- 188
- 189
- 190
- 191
- 192
- 193
- 194
- 195
- 196
- 197
- 198
- 199
- 200
- 201
- 202
- 203
- 204
- 205
- 206
- 207
- 208
- 209
- 210
- 211
- 212
- 213
- 214
- 215
- 216
- 217
- 218
- 219
- 220
- 221
- 222
- 223
- 224
- 225
- 226
- 227
- 228
- 229
- 230
- 231
- 232
- 233
- 234
- 235
- 236
- 237
- 238
- 239
- 240
- 241
- 242
- 243
- 244
- 245
- 246
- 247
- 248
- 249
- 250
- 251
- 252
- 253
- 254
- 255
- 256
- 257
- 258
- 259
- 260
- 261
- 262
- 263
- 264
- 265
- 266
- 267
- 268
- 269
- 270
- 271
- 272
- 273
- 274
- 275
- 276
- 277
- 278
- 279
- 280
- 281
- 282
- 283
AVL树的验证
AVL树是在二叉搜索树的基础上加入了平衡性的限制,因此要验证AVL树,可以分两步:
- 验证其为二叉搜索树
- 如果中序遍历可得到一个有序的序列,就说明为二叉搜索树
- 验证其为平衡树
- 每个节点子树高度差的绝对值不超过1(注意节点中如果没有平衡因子)
- 节点的平衡因子是否计算正确
- 验证用例
- 常规场景:{16, 3, 7, 11, 9, 26, 18, 14, 15}
- 特殊场景:{4, 2, 6, 1, 3, 5, 15, 7, 16, 14}
AVL树的删除:
- 按二叉搜索树的思路进行删除
- 更新平衡因子(删除左节点,该父亲节点++;删除右节点,该父亲节点–)
- 当父亲节点平衡因子为1或者-1时,不需要往上更新;当父亲节点平衡因子为0时,需要往上更新
- 如果出现不平衡,进行旋转(注意父节点的平衡因子(高度变了))
AVL树的性能
AVL树是一棵绝对平衡的二叉搜索树,其要求每个节点的左右子树高度差的绝对值都不超过1,这样可以保证查询时高效的时间复杂度,即logN 。但是如果要对AVL树做一些结构修改的操作,性能非常低下,比如:插入时要维护其绝对平衡,旋转的次数比较多,更差的是在删除时,有可能一直要让旋转持续到根的位置。因此:如果需要一种查询高效且有序的数据结构,而且数据的个数为静态的(即不会改变),可以考虑AVL树,但一个结构经常修改,就不太适合。
-
相关阅读:
补充:selenium操作已打开的浏览器窗口
esp32-rust-std-examples-blinky
C语言基本概念----类型
冰冰学习笔记:list的简单模拟
LeetCode78.子集
JAVA高级——lambda
SVM模型实现人脸识别
【小程序项目开发 -- 京东商城】uni-app 商品分类页面(下)
mellanox&nvidia 不带管理口IB交换机升级FW及基本管理
每日一题(两数相加)
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/AI_ELF/article/details/123042060