-
代码随想录1刷—二叉树篇(二)
代码随想录1刷—二叉树篇(二)
- 迭代法中究竟什么时候用队列,什么时候用栈?
- 递归函数什么时候要有返回值,什么时候不能有返回值?
- [222. 完全二叉树的节点个数](https://leetcode.cn/problems/count-complete-tree-nodes/)
- [110. 平衡二叉树](https://leetcode.cn/problems/balanced-binary-tree/)
- [257. 二叉树的所有路径](https://leetcode.cn/problems/binary-tree-paths/)(认真多看几次!总会做出来的!)
- [404. 左叶子之和](https://leetcode.cn/problems/sum-of-left-leaves/)
- [513. 找树左下角的值](https://leetcode.cn/problems/find-bottom-left-tree-value/)
- [112. 路径总和](https://leetcode.cn/problems/path-sum/)
- [113. 路径总和 II](https://leetcode.cn/problems/path-sum-ii/)
- [106. 从中序与后序遍历序列构造二叉树](https://leetcode.cn/problems/construct-binary-tree-from-inorder-and-postorder-traversal/)
- [105. 从前序与中序遍历序列构造二叉树](https://leetcode.cn/problems/construct-binary-tree-from-preorder-and-inorder-traversal/)
- [654. 最大二叉树](https://leetcode.cn/problems/maximum-binary-tree/)
- [617. 合并二叉树](https://leetcode.cn/problems/merge-two-binary-trees/)
- [700. 二叉搜索树中的搜索](https://leetcode.cn/problems/search-in-a-binary-search-tree/)
- [98. 验证二叉搜索树](https://leetcode.cn/problems/validate-binary-search-tree/)
- [530. 二叉搜索树的最小绝对差](https://leetcode.cn/problems/minimum-absolute-difference-in-bst/)
- [501. 二叉搜索树中的众数](https://leetcode.cn/problems/find-mode-in-binary-search-tree/)
迭代法中究竟什么时候用队列,什么时候用栈?
如果是模拟前中后序遍历就用栈,如果是适合层序遍历就用队列;
其他情况:先用队列试试行不行,不行就用栈。
递归函数什么时候要有返回值,什么时候不能有返回值?
- 如果需要搜索整棵二叉树且不用处理递归返回值,递归函数就不要返回值。(113. 路径总和 II)
- 如果需要搜索整棵二叉树且需要处理递归返回值,递归函数就需要返回值。 (236. 二叉树的最近公共祖先)
- 如果要搜索其中一条符合条件的路径,那么递归一定需要返回值,因为遇到符合条件的路径了就要及时返回。(112. 路径总和)
222. 完全二叉树的节点个数
普通二叉树的求法
遍历+记录遍历的节点数量就可以了。
//递归 class Solution { public: int countNodes(TreeNode* root) { if (root == NULL) return 0; return 1 + countNodes(root->left) + countNodes(root->right); } }; 时间复杂度:O(n) 空间复杂度:O(log n),算上了递归系统栈占用的空间- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
//迭代 class Solution { public: int countNodes(TreeNode* root) { queue<TreeNode*> que; if (root != NULL) que.push(root); int result = 0; while (!que.empty()) { int size = que.size(); for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) { TreeNode* node = que.front(); que.pop(); result++; // 记录节点数量 if (node->left) que.push(node->left); if (node->right) que.push(node->right); } } return result; } }; 时间复杂度:O(n) 空间复杂度:O(n)- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
利用完全二叉树性质的求法
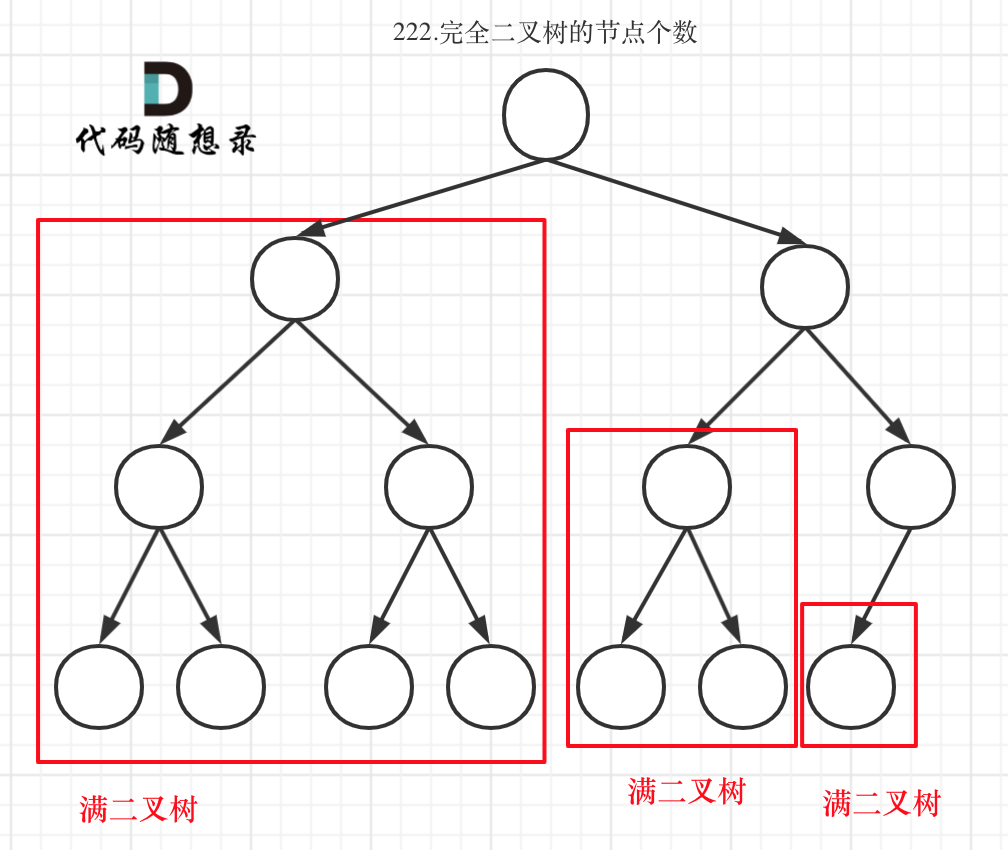
完全二叉树只有两种情况,情况一:就是满二叉树,情况二:最后一层叶子节点没有满。
对于情况一,可以直接用 2^树深度 - 1 来计算,注意这里根节点深度为1。
对于情况二,分别递归左孩子,和右孩子,递归到某一深度一定会有左孩子或者右孩子为满二叉树,然后依然可以按照情况1来计算。
完全二叉树(一)如图:
完全二叉树(二)如图:
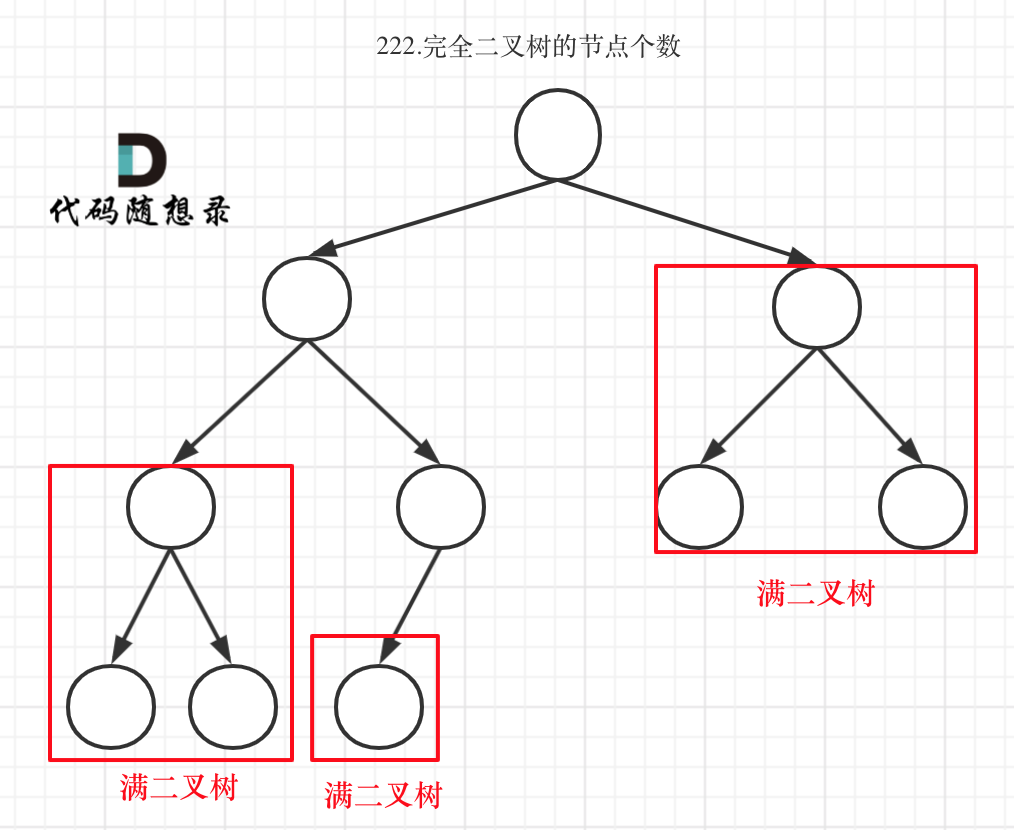
可以看出如果整个树不是满二叉树,就递归其左右孩子,直到遇到满二叉树为止,用公式计算这个子树(满二叉树)的节点数量。
class Solution { public: int countNodes(TreeNode* root) { if (root == nullptr) return 0; TreeNode* left = root->left; TreeNode* right = root->right; int leftHeight = 0, rightHeight = 0; // 这里初始为0是有目的的,为了下面求指数方便 while (left) { // 求左子树深度 left = left->left; leftHeight++; } while (right) { // 求右子树深度 right = right->right; rightHeight++; } if (leftHeight == rightHeight) { return (2 << leftHeight) - 1; // 注意(2<<1) 相当于2^2,所以leftHeight初始为0 } return countNodes(root->left) + countNodes(root->right) + 1; } }; 时间复杂度:O(log n × log n) 空间复杂度:O(log n)- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
110. 平衡二叉树
一个二叉树每个节点 的左右两个子树的高度差的绝对值不超过 1 。
强调一波概念:
- 二叉树节点的深度:指从根节点到该节点的最长简单路径边的条数。
- 二叉树节点的高度:指从该节点到叶子节点的最长简单路径边的条数。
关于根节点的深度究竟是1 还是 0:leetcode的题目中都是以节点为一度,即根节点深度是1。但维基百科上定义用边为一度,即根节点的深度是0,暂时以leetcode为准(毕竟在这上面刷题)。
class Solution { public: int getHeight(TreeNode* node) { if (node == nullptr) return 0; int leftHeight = getHeight(node->left); if (leftHeight == -1) return -1; int rightHeight = getHeight(node->right); if (rightHeight == -1) return -1; return abs(leftHeight - rightHeight) > 1 ? -1 : 1+max(leftHeight, rightHeight); //abs()绝对值 //返回以该节点为根节点的二叉树的高度 } bool isBalanced(TreeNode* root) { return getHeight(root) == -1 ? false : true; } };- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
迭代版本太复杂了干不明白,代码随想录链接:迭代版平衡二叉树解法 (programmercarl.com)
257. 二叉树的所有路径(认真多看几次!总会做出来的!)
递归
class Solution { public: vector<string> answer; vector<int> path; void traversal(TreeNode* cur,vector<int>& path,vector<string>& answer){ path.push_back(cur->val); if(cur->left == nullptr && cur->right == nullptr){ string sPath; for(int i = 0;i < path.size() - 1;i++){ sPath += to_string(path[i]); //to_string函数 : 将数值转化为字符串。返回对应的字符串 sPath += "->"; } sPath += to_string(path[path.size() - 1]); answer.push_back(sPath); return; } if(cur->left){ traversal(cur->left,path,answer); path.pop_back(); } if(cur->right){ traversal(cur->right,path,answer); path.pop_back(); } } vector<string> binaryTreePaths(TreeNode* root) { if(root == nullptr) return answer; traversal(root,path,answer); return answer; } };- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
精简版的递归我没看懂emm…点击跳转看吧:二叉树所有路径(递归版)—代码随想录 (programmercarl.com)
迭代
class Solution { public: vector<string> binaryTreePaths(TreeNode* root) { stack<TreeNode*> TreeSt; stack<string> pathSt; vector<string> result; if(root == nullptr) return result; TreeSt.push(root); pathSt.push(to_string(root->val)); while(!TreeSt.empty()){ TreeNode* node = TreeSt.top(); TreeSt.pop(); string path = pathSt.top(); pathSt.pop(); if(node->left == nullptr && node->right == nullptr){ result.push_back(path); } if(node->left){ TreeSt.push(node->left); pathSt.push(path + "->" + to_string(node->left->val)); } if(node->right){ TreeSt.push(node->right); pathSt.push(path + "->" + to_string(node->right->val)); } } return result; } };- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
404. 左叶子之和
class Solution { public: int sumOfLeftLeaves(TreeNode* root) { if (root == nullptr) return 0; int val = 0; if(root->left != nullptr && root->left->left == nullptr && root->left->right == nullptr){ val += root->left->val; } return val + sumOfLeftLeaves(root->right) + sumOfLeftLeaves(root->left); } };- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
class Solution { public: int sumOfLeftLeaves(TreeNode* root) { stack<TreeNode*> stack; if(root == nullptr) return 0; stack.push(root); int result = 0; while(!stack.empty()){ TreeNode* node = stack.top(); stack.pop(); if(node->left!=nullptr&&node->left->left==nullptr&&node->left->right==nullptr){ result += node->left->val; } if(node->right) stack.push(node->right); if(node->left) stack.push(node->left); } return result; } };- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
513. 找树左下角的值
注意!左下角!是最底层 最左边!所以用层序遍历到最底层!层序遍历的话要用队列!
class Solution { public: int findBottomLeftValue(TreeNode* root) { queue<TreeNode*> que; if(root != nullptr) que.push(root); int result = 0; while(!que.empty()){ int size = que.size(); for(int i = 0; i< size ;i++){ TreeNode* node = que.front(); que.pop(); if(i == 0) result = node->val; if(node->left) que.push(node->left); if(node->right) que.push(node->right); } } return result; } };- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
class Solution { public: int maxLen = INT_MIN; int leftval; void traversal(TreeNode* root,int leftLen){ if(root->left == nullptr && root->right == nullptr){ if(leftLen > maxLen){ maxLen = leftLen; leftval = root->val; } return; } if(root->left){ traversal(root->left, leftLen + 1); } if(root->right){ traversal(root->right, leftLen + 1); } return; } int findBottomLeftValue(TreeNode* root) { traversal(root,0); return leftval; } };- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
112. 路径总和
class Solution { public: bool traversal(TreeNode* cur, int sum){ if(!cur->left &&!cur->right && sum == 0) return true; if(!cur->left &&!cur->right && sum != 0 ) return false; if(cur->left){ if(traversal(cur->left,sum - cur->left->val)) return true; } if(cur->right){ if(traversal(cur->right,sum - cur->right->val)) return true; } return false; } bool hasPathSum(TreeNode* root, int targetSum) { if(root == nullptr) return false; return traversal(root,targetSum - root->val); } };- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
class Solution { public: bool hasPathSum(TreeNode* root, int targetSum) { if (root == nullptr) return false; if (!root->left && !root->right && targetSum == root->val) { return true; } return hasPathSum(root->left, targetSum - root->val) || hasPathSum(root->right, targetSum - root->val); } }; //超简版递归- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
//迭代版本 class Solution { public: bool hasPathSum(TreeNode* root, int targetSum) { if(root==nullptr) return false; stack<pair<TreeNode*,int>> st; st.push(pair<TreeNode*,int>(root,root->val)); while(!st.empty()){ pair<TreeNode*, int> node = st.top(); st.pop(); if (!node.first->left && !node.first->right && targetSum == node.second) return true; if (node.first->left){ st.push(pair<TreeNode*, int>(node.first->left, node.second + node.first->left->val)); } if (node.first->right){ st.push(pair<TreeNode*, int>(node.first->right, node.second + node.first->right->val)); } } return false; } };- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
113. 路径总和 II
class Solution { public: vector<vector<int>> result; vector<int> path; void traversal(TreeNode* cur, int count) { if (!cur->left && !cur->right && count == 0) { result.push_back(path); return; } if (!cur->left && !cur->right && count != 0) return ; if (cur->left) { // 左 (空节点不遍历) path.push_back(cur->left->val); traversal(cur->left, count - cur->left->val); // 递归 path.pop_back(); } if (cur->right) { // 右 (空节点不遍历) path.push_back(cur->right->val); traversal(cur->right, count - cur->right->val); // 递归 path.pop_back(); } return ; } vector<vector<int>> pathSum(TreeNode* root, int targetSum) { result.clear(); path.clear(); if (root == nullptr) return result; path.push_back(root->val); // 把根节点放进路径 traversal(root, targetSum - root->val); return result; } };- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
106. 从中序与后序遍历序列构造二叉树
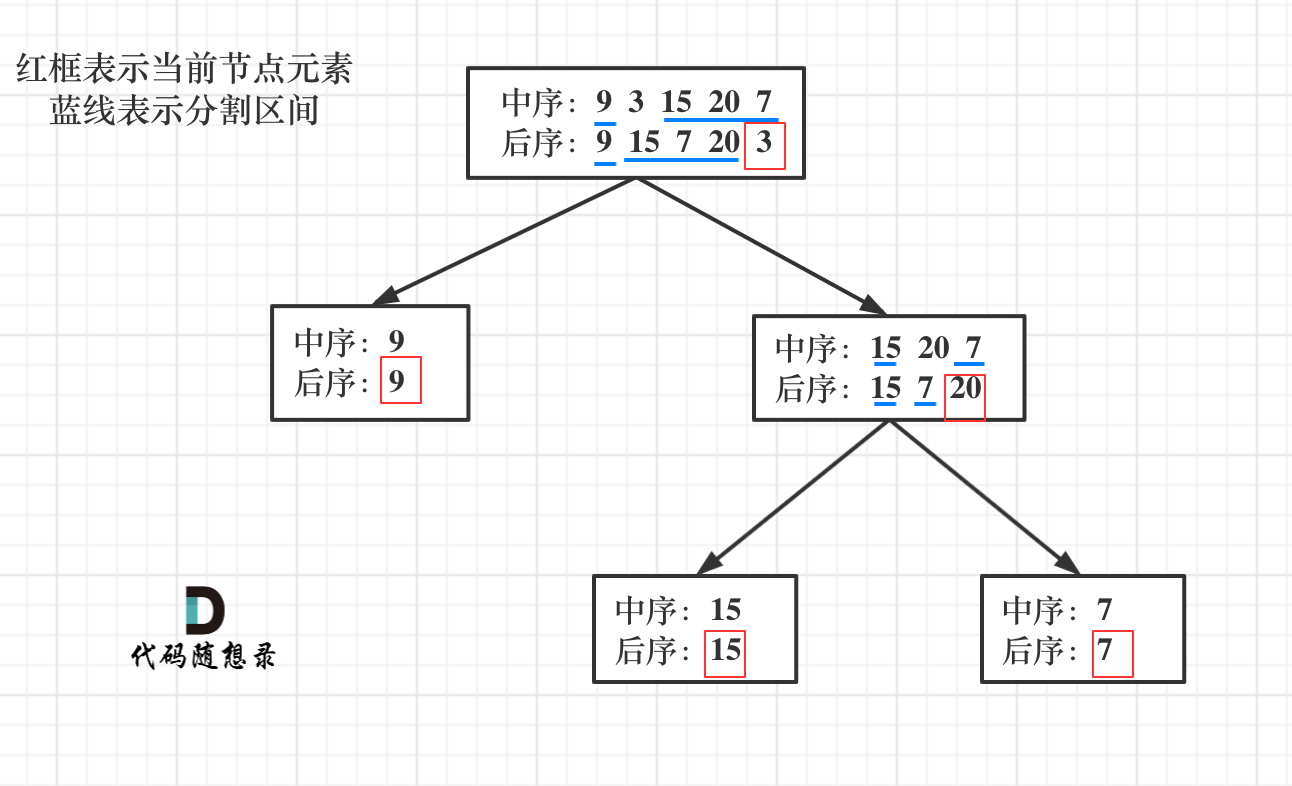
//数组版本,每层递归定定义了新的vector(就是数组),既耗时又耗空间 class Solution { public: TreeNode* traversal(vector<int>& inorder,vector<int>& postorder){ if(postorder.size() == 0) return nullptr; int rootvalue = postorder[postorder.size() - 1]; TreeNode* Root = new TreeNode(rootvalue); if(postorder.size() == 1) return Root; int CutIndex; for(CutIndex = 0;CutIndex < inorder.size();CutIndex++){ if(inorder[CutIndex] == rootvalue) break; } vector<int> leftInorder(inorder.begin(),inorder.begin() + CutIndex); vector<int> rightInorder(inorder.begin() + CutIndex + 1,inorder.end()); postorder.resize(postorder.size() - 1); vector<int> leftPostorder(postorder.begin(),postorder.begin() + leftInorder.size()); vector<int> rightPostorder(postorder.begin() + leftInorder.size(),postorder.end()); Root->left = traversal(leftInorder,leftPostorder); Root->right = traversal(rightInorder,rightPostorder); return Root; } TreeNode* buildTree(vector<int>& inorder, vector<int>& postorder) { if(inorder.size() == 0 || postorder.size() == 0) return nullptr; return traversal(inorder,postorder); } };- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
//索引下标版本 思路和前面一样 但是不用重复定义vector了 class Solution { public: TreeNode* traversal(vector<int>& inorder, int inorderBegin, int inorderEnd, vector<int>& postorder, int postorderBegin, int postorderEnd) { if(postorderBegin == postorderEnd) return nullptr; int rootvalue = postorder[postorderEnd - 1]; TreeNode* Root = new TreeNode(rootvalue); if(postorderEnd - postorderBegin == 1) return Root; int CutIndex; for(CutIndex = 0;CutIndex < inorder.size();CutIndex++){ if(inorder[CutIndex] == rootvalue) break; } int leftInorderBegin = inorderBegin; int leftInorderEnd = CutIndex; int rightInorderBegin = CutIndex + 1; int rightInorderEnd = inorderEnd; int leftPostorderBegin = postorderBegin; int leftPostorderEnd = postorderBegin + CutIndex - inorderBegin; int rightPostorderBegin = postorderBegin + CutIndex - inorderBegin; int rightPostorderEnd = postorderEnd - 1; Root->left = traversal(inorder, leftInorderBegin, leftInorderEnd, postorder, leftPostorderBegin, leftPostorderEnd); Root->right = traversal(inorder, rightInorderBegin, rightInorderEnd, postorder, rightPostorderBegin, rightPostorderEnd); return Root; } TreeNode* buildTree(vector<int>& inorder, vector<int>& postorder) { if(inorder.size() == 0 || postorder.size() == 0) return nullptr; return traversal(inorder,0,inorder.size(),postorder,0,postorder.size()); } };- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
105. 从前序与中序遍历序列构造二叉树
class Solution { public: TreeNode* traversal(vector<int>& inorder, int inorderBegin, int inorderEnd, vector<int>& postorder, int postorderBegin, int postorderEnd) { if(postorderBegin == postorderEnd) return nullptr; int rootvalue = postorder[postorderBegin]; TreeNode* Root = new TreeNode(rootvalue); if(postorderEnd - postorderBegin == 1) return Root; int CutIndex; for(CutIndex = 0;CutIndex < inorder.size();CutIndex++){ if(inorder[CutIndex] == rootvalue) break; } int leftInorderBegin = inorderBegin; int leftInorderEnd = CutIndex; int rightInorderBegin = CutIndex + 1; int rightInorderEnd = inorderEnd; int leftPostorderBegin = postorderBegin + 1; int leftPostorderEnd = postorderBegin + 1 + CutIndex - inorderBegin; int rightPostorderBegin = postorderBegin + 1 + CutIndex - inorderBegin; int rightPostorderEnd = postorderEnd; Root->left = traversal(inorder, leftInorderBegin, leftInorderEnd, postorder, leftPostorderBegin, leftPostorderEnd); Root->right = traversal(inorder, rightInorderBegin, rightInorderEnd, postorder, rightPostorderBegin, rightPostorderEnd); return Root; } TreeNode* buildTree(vector<int>& preorder, vector<int>& inorder) { if (inorder.size() == 0 || preorder.size() == 0) return NULL; return traversal(inorder, 0, inorder.size(), preorder, 0, preorder.size()); } };- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
654. 最大二叉树
//也是每层递归定定义了新的vector(就是数组),既耗时又耗空间 class Solution { public: TreeNode* constructMaximumBinaryTree(vector<int>& nums) { //题干说了1 <= nums.length <= 1000 所以不会是空 //当递归遍历的时候,如果传入的数组大小为1,说明遍历到了叶子节点了,那么应该定义一个新的节点,并把这个数组的数值赋给新的节点,然后返回这个节点。 这表示一个数组大小是1的时候,构造了一个新的节点,并返回。 TreeNode* node = new TreeNode(0); if(nums.size() == 1){ node->val = nums[0]; return node; } //找到最大值和其对应的下标 int MaxValue = 0; int MaxValueIndex = 0; for(int i = 0 ;i < nums.size();i++){ if(nums[i] > MaxValue){ MaxValue = nums[i]; MaxValueIndex = i; } } node->val = MaxValue; //最大值所在的下标左区间 构造左子树 if(MaxValueIndex > 0){ vector<int> newVector(nums.begin(), nums.begin() + MaxValueIndex); node->left = constructMaximumBinaryTree(newVector); } //最大值所在的下标左区间 构造左子树 if(MaxValueIndex < (nums.size() - 1)){ vector<int> newVector(nums.begin() + MaxValueIndex + 1,nums.end()); node->right = constructMaximumBinaryTree(newVector); } return node; } };- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
class Solution { public: TreeNode* traversal(vector<int>& nums, int left, int right) { if (left >= right) return nullptr; int maxValueIndex = left; for (int i = left + 1; i < right; i++) { if (nums[i] > nums[maxValueIndex]){ maxValueIndex = i; } } TreeNode* root = new TreeNode(nums[maxValueIndex]); root->left = traversal(nums, left, maxValueIndex); root->right = traversal(nums, maxValueIndex + 1, right); return root; } TreeNode* constructMaximumBinaryTree(vector<int>& nums) { return traversal(nums, 0, nums.size()); } };- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
注意类似用数组构造二叉树的题目,每次分隔尽量不要定义新的数组,而是通过下标索引直接在原数组上操作,这样可以节约时间和空间上的开销。
什么时候递归函数前面加if,什么时候不加if?
其实就是不同代码风格的实现,一般情况来说:如果让空节点(空指针)进入递归,就不加if,如果不让空节点进入递归,就加if限制一下,相应的两者的终止条件也会有相应的调整。
在本题目中给的两个版本:
第一版递归过程:(加了if判断,为了不让空节点进入递归)
if (maxValueIndex > 0) { // 这里加了判断是为了不让空节点进入递归 vector<int> newVec(nums.begin(), nums.begin() + maxValueIndex); node->left = constructMaximumBinaryTree(newVec); } if (maxValueIndex < (nums.size() - 1)) { // 这里加了判断是为了不让空节点进入递归 vector<int> newVec(nums.begin() + maxValueIndex + 1, nums.end()); node->right = constructMaximumBinaryTree(newVec); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
第二版递归过程: (如下代码就没有加if判断)
root->left = traversal(nums, left, maxValueIndex); root->right = traversal(nums, maxValueIndex + 1, right);- 1
- 2
第二版代码是允许空节点进入递归,所以没有加if判断,当然终止条件也要有相应的改变。
第一版终止条件,是遇到叶子节点就终止,因为空节点不会进入递归。
第二版相应的终止条件,是遇到空节点,也就是数组区间为0,就终止了。
617. 合并二叉树
class Solution { public: TreeNode* mergeTrees(TreeNode* root1, TreeNode* root2) { if(root1 == nullptr) return root2; if(root2 == nullptr) return root1; TreeNode* node = new TreeNode(0); node->val = root1->val + root2->val; node->left = mergeTrees(root1->left,root2->left); node->right = mergeTrees(root1->right,root2->right); return node; } };- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
class Solution { public: TreeNode* mergeTrees(TreeNode* root1, TreeNode* root2) { if(root1 == nullptr) return root2; if(root2 == nullptr) return root1; queue<TreeNode*> que; que.push(root1); que.push(root2); while(!que.empty()){ TreeNode* node1 = que.front();que.pop(); TreeNode* node2 = que.front();que.pop(); node1->val += node2->val; if(node1->left != nullptr && node2->left != nullptr){ que.push(node1->left); que.push(node2->left); } if(node1->right != nullptr && node2->right != nullptr){ que.push(node1->right); que.push(node2->right); } if(node1->left == nullptr && node2->left != nullptr){ node1->left = node2->left; } if(node1->right == nullptr && node2->right != nullptr){ node1->right = node2->right; } } return root1; } };- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
700. 二叉搜索树中的搜索
二叉搜索树是一个有序树:
- 若它的左子树不空,则左子树上所有结点的值均小于它的根结点的值;
- 若它的右子树不空,则右子树上所有结点的值均大于它的根结点的值;
- 它的左、右子树也分别为二叉搜索树
class Solution { public: TreeNode* searchBST(TreeNode* root, int val) { if (root == nullptr || root->val == val) return root; if (root->val > val) return searchBST(root->left, val); if (root->val < val) return searchBST(root->right, val); return NULL; } };- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
迭代法
一提到二叉树遍历的迭代法,可能立刻想起使用栈来模拟深度遍历,使用队列来模拟广度遍历。对于二叉搜索树可就不一样了,因为二叉搜索树的特殊性,也就是节点的有序性,可以不使用辅助栈或者队列就可以写出迭代法。
对于一般二叉树,递归过程中还有回溯的过程,例如走一个左方向的分支走到头了,那么要调头,在走右分支。而对于二叉搜索树,不需要回溯的过程,因为节点的有序性就帮我们确定了搜索的方向。
class Solution { public: TreeNode* searchBST(TreeNode* root, int val) { while (root != nullptr) { if (root->val > val) root = root->left; else if (root->val < val) root = root->right; else return root; } return NULL; } };- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
98. 验证二叉搜索树
中序遍历下,输出的二叉搜索树节点的数值是有序序列。有了这个特性,验证二叉搜索树,就相当于变成了判断一个序列是不是递增的了。
class Solution { public: vector<int> vec; void tracersal(TreeNode* root){ if(root == nullptr) return; tracersal(root->left); vec.push_back(root->val); tracersal(root->right); } //前序遍历放入数组 bool isValidBST(TreeNode* root) { vec.clear(); tracersal(root); for(int i = 1;i < vec.size();i++){ if(vec[i] <= vec[i - 1]) return false; } return true; } };- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
class Solution { public: TreeNode* pre = nullptr; //用于记录前一个结点 bool isValidBST(TreeNode* root) { if(root == nullptr) return true; bool left = isValidBST(root->left); if(pre != nullptr && pre->val >= root->val) return false; pre = root; //记录结点~ bool right = isValidBST(root->right); return left && right; } };- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
530. 二叉搜索树的最小绝对差
class Solution { private: vector<int> vec; void traversal(TreeNode* root){ if(root == nullptr) return; traversal(root->left); vec.push_back(root->val); traversal(root->right); } public: int getMinimumDifference(TreeNode* root) { vec.clear(); traversal(root); if(vec.size() < 2) return 0; int result = INT_MAX; for(int i = 1; i < vec.size();i++){ result = min(result,vec[i] - vec[i-1]); } return result; } };- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
class Solution { private: int result = INT_MAX; TreeNode* pre; void traversal(TreeNode* cur){ if(cur == nullptr) return; traversal(cur->left); if(pre != nullptr){ result = min(result,cur->val - pre->val); } pre = cur; //在递归中记录前一个节点的指针 traversal(cur->right); } public: int getMinimumDifference(TreeNode* root) { traversal(root); return result; } };- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
//迭代法 class Solution { public: int getMinimumDifference(TreeNode* root) { stack<TreeNode*> st; TreeNode* cur = root; TreeNode* pre = nullptr; int result = INT_MAX; while(cur != nullptr || !st.empty()){ if(cur != nullptr){ st.push(cur); cur = cur->left; //左 }else{ cur = st.top(); st.pop(); if(pre != nullptr){ //中 result = min(result,cur->val - pre->val); } pre = cur; cur = cur->right; //右 } } return result; } };- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
501. 二叉搜索树中的众数
如果不是二叉搜索树
把这个树都遍历了,用map统计频率,把频率排个序,最后取前面高频的元素的集合。
class Solution { private: void searchBST(TreeNode* cur,unordered_map<int,int>& map){ if(cur == nullptr) return; map[cur->val]++; searchBST(cur->left,map); searchBST(cur->right,map); return; } bool static cmp (const pair<int, int>& a, const pair<int, int>& b) { return a.second > b.second; } public: vector<int> findMode(TreeNode* root) { unordered_map<int, int> map; // key:元素,value:出现频率 vector<int> result; if(root == nullptr) return result; searchBST(root, map); vector<pair<int,int>> vec(map.begin(),map.end()); sort(vec.begin(),vec.end(),cmp); result.push_back(vec[0].first); //最高的就是答案 for(int i = 1;i<vec.size();i++){ if(vec[i].second == vec[0].second) //可能最高的不止一个,继续放 result.push_back(vec[i].first); else break; } return result; } };- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
map中的value排序问题
注意:无法直接对map中的value排序,C++中如果使用std::map或者std::multimap,那么可以对key排序,但不能对value排序。
所以要把map转化数组即vector,再进行排序,当然vector里面放的也是
pair<int, int>类型的数据,第一个int为元素,第二个int为出现频率。bool static cmp (const pair<int, int>& a, const pair<int, int>& b) { return a.second > b.second; // 按照频率从大到小排序 } vector<pair<int, int>> vec(map.begin(), map.end()); sort(vec.begin(), vec.end(), cmp); // 给频率排个序- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
是二叉搜索树
递归法
class Solution { private: int maxCount; int count; TreeNode* pre; vector<int> result; void searchBST(TreeNode* cur){ if(cur == nullptr) return; searchBST(cur->left); if(pre == nullptr){ count = 1; }else if(pre->val == cur->val){ count++; }else{ count = 1; } pre = cur; if(count == maxCount){ result.push_back(cur->val); //由于众数不止一个所以需要二次遍历 //而直接将其加入数组中可以规避二次便利 } //但是并无法确定此时的maxCount为最大的,因此需要下面的步骤 if(count > maxCount){ maxCount = count; result.clear(); result.push_back(cur->val); } searchBST(cur->right); return; } public: vector<int> findMode(TreeNode* root) { count = 0; maxCount = 0; TreeNode* pre = nullptr; result.clear(); searchBST(root); return result; } };- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
迭代法
class Solution { public: vector<int> findMode(TreeNode* root) { stack<TreeNode*> st; TreeNode* cur = root; TreeNode* pre = nullptr; int maxCount = 0; int count = 0; vector<int> result; while (cur != nullptr || !st.empty()) { if (cur != nullptr) { st.push(cur); cur = cur->left; // 左 } else { cur = st.top(); st.pop(); // 中 if(pre == nullptr){ count = 1; }else if(pre->val == cur->val){ count++; }else{ count = 1; } pre = cur; if(count == maxCount){ result.push_back(cur->val); } if(count > maxCount){ maxCount = count; result.clear(); result.push_back(cur->val); } cur = cur->right; // 右 } } return result; } };- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
-
相关阅读:
I.MX6U-ALPHA开发板(高精度定时器)
【研发工具】Centos下搭建轻量级内网FTP服务器
HTML5 实现扑克翻牌游戏
【附源码】计算机毕业设计JAVA移动在线点菜系统服务端服务端
这些 git 高级命令你知道几个
TikTok视频播放量低,是被限流了吗?
MATLAB | MATLAB配色不够用 全网最全的colormap补充包来啦
python基础 | 类与继承
Pico,是要拯救还是带偏消费级VR?
ON1 Photo RAW 2024照片编辑器「Mac」
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/h0327x/article/details/125624134