-
python 笔记
目录
工具
创建文件夹
如果无指定文件夹则创建文件夹,有则打印文件夹已存在。
def mkdir(path): folder = os.path.exists(path) if not folder: os.makedirs(path) else: print("There is this folder!")- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
获取目录下所有文件名并排序
roots = "C:\\Users\\ps\\Desktop\\jupyter\\images\\imgs\\" names = os.listdir(roots) names.sort(key=lambda x:int(x[:-4])) print(names)- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
删除指定比例文件
获取目录下指定后缀文件名
def fileNames(root, suffix=None): names = os.listdir(root) result = [] if suffix: for name in names: if os.path.splitext(name)[1] == suffix: result.append(name) else: result = names return result- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
重命名
import os os.rename(old_path, new_path)- 1
- 2
读取图像
import cv2 import os def ImageRead(image_name, image_path): """ image_name: 图像名如(50.BMP) image_path: 图像所属路径 """ image = cv2.imread(os.path.join(image_path, image_name)) if image is None: print("%s read failed"%(image_name)) return image image_try = ImageRead('50.BMP') print(image_try.shape)- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
判读图像是否为RGB,是转为灰度,否则拷贝源图像
impot cv2 def Gray(image): if image.shape[2] == 3: gray = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY) else: gray = image.copy() return gray gray_try = Gray(image_try) print(gray_try.shape)- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
显示图像并按ESC退出
while(1): cv2.imshow('image', img) if cv2.waitKey(20) & 0xFF == 27: break cv2.destroyAllWindows()- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
鼠标窗口交互画矩形
import cv2 """ 鼠标左键按下返回此时坐标值并以此为矩形左上顶点 鼠标左键放开返回此时坐标值并以此为矩形右下顶点 鼠标移动时显示坐标点及对应图像灰度或RGB值 """ def draw_rectangle(event, x, y, flags, param): global ix, iy if event == cv2.EVENT_LBUTTONDOWN: ix, iy = x, y print("left up point:=", x, y) elif event == cv2.EVENT_LBUTTONUP: print("right down point:=", x, y) print("width=", x-ix) print("height=", y-iy) cv2.rectangle(img, (ix, iy), (x, y), (0, 255, 0), 2) elif event == cv2.EVENT_MOUSEMOVE: rint("点(%d,%d)图像灰度为:%s"%(x, y, img[y, x])) img = cv2.imread("...\\138.BMP") cv2.namedWindow('image') cv2.setMouseCallback('image', draw_rectangle) while(1): cv2.imshow('image', img) if cv2.waitKey(20) & 0xFF == 27: break cv2.destroyAllWindows()- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
高低阈值,之间保持不变,高于高阈值或低于低阈值都设为0
def Threshold(image, high_threshold, low_threshold): rows = image.shape[0] columns = image.shape[1] for row in range(rows): for column in range(columns): if image[row][column] < low_threshold or image[row][column] > high_threshold: image[row][column] = 0- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
检查包是否安装
from __future__ import print_function import importlib # check that all package are install required_packages = { ' ', ' ', } problem_packages = list() # Iterate over the required packages: If the package is not installed # Ignore the exception for package in required_packages: try: p = importlib.inport_module(package) except ImportError: probles_package.append(package) if len(problem_packages) is 0: print('All is well.') else: print('The following packages are required but not installed: + ','.join(problem_packages))- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
读写txt文件
with open(path, 'r') as txtFile: for line in txtFile:- 1
- 2
- ‘r’: 读;
- ‘w’: 写;
- ’a’: 追加
弧度转角度
radian = math.pi angle = math.degrees(radian)- 1
- 2
角度转弧度
angle = 27 radian = math.radians(angle)- 1
- 2
yolo txt 转xml
from xml.dom.minidom import Document import os import cv2 dic = {'0':"g", '1':"b", '2':"gc", '3':"cu"} def CreateElement(builder, element, content): ele = builder.createElement(element) cont = builder.createTextNode(content) ele.appendChild(cont) return ele def Txt2Xml(txt_path, xml_path, img_path): names = os.listdir(txt_path) for i, name in enumerate(names): xml_builder = Document() annotation = xml_builder.createElement("annotation") xml_builder.appendChild(annotation) img = cv2.imread(img_path+name[0:-4]+".bmp") num_height, num_width, num_depth = img.shape flag = 0 with open(os.path.join(txt_path, name), 'r') as txt_file: for txt_line in txt_file: flag += 1 txt_line_str = txt_line.strip().split(" ") folder = CreateElement(xml_builder, "folder","VOC2007" ) if 1 == flag: filename = CreateElement(xml_builder,"filename",name[0:-4]+".jpg" ) annotation.appendChild(filename) size = xml_builder.createElement("size") width = CreateElement(xml_builder, "width", str(num_width)) size.appendChild(width) height = CreateElement(xml_builder,"height",str(num_height)) size.appendChild(height) depth = CreateElement(xml_builder,"depth", str(num_depth)) size.appendChild(depth) annotation.appendChild(size) obj = xml_builder.createElement("object") img_name = CreateElement(xml_builder,"name", dic[txt_line_str[0]]) obj.appendChild(img_name) pose = CreateElement(xml_builder,"pose","Unspecified") obj.appendChild(pose) truncated = CreateElement(xml_builder,"truncated","0") obj.appendChild(truncated) difficult = CreateElement(xml_builder,"difficult","0") obj.appendChild(difficult) bndbox = xml_builder.createElement("bndbox") mathData=int(((float(txt_line_str[1]))*num_width+1)-(float(txt_line_str[3]))*0.5*num_width) xmin = CreateElement(xml_builder,"xmin",str(mathData)) bndbox.appendChild(xmin) mathData = int(((float(txt_line_str[2]))*num_height+1)-(float(txt_line_str[4]))*0.5*num_height) ymin = CreateElement(xml_builder,"ymin", str(mathData)) bndbox.appendChild(ymin) mathData = int(((float(txt_line_str[1]))*num_width+1)+(float(txt_line_str[3]))*0.5*num_width) xmax = CreateElement(xml_builder,"xmax", str(mathData)) bndbox.appendChild(xmax) mathData = int(((float(txt_line_str[2]))*num_height+1)+(float(txt_line_str[4]))*0.5*num_height) ymax = CreateElement(xml_builder,"ymax", str(mathData)) bndbox.appendChild(ymax) obj.appendChild(bndbox) annotation.appendChild(obj) with open(xml_path+name[0:-4]+".xml", 'w') as xml_file: xml_builder.writexml(xml_file, indent='\t', newl='\n', addindent='\t', encoding='utf-8') txt_path = ".\\txt\\" xml_path = ".\\xml\\" img_path = ".\\imgs\\" Txt2Xml(txt_path, xml_path, img_path)- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
创建exe程序
安装pyinstaller
pip install PyInstaller- 1
创建
- 将.py文件和.ico文件放在同一个文件夹下;
- 执行命令
Pyinstaller -F -i name.ico name.py- 1
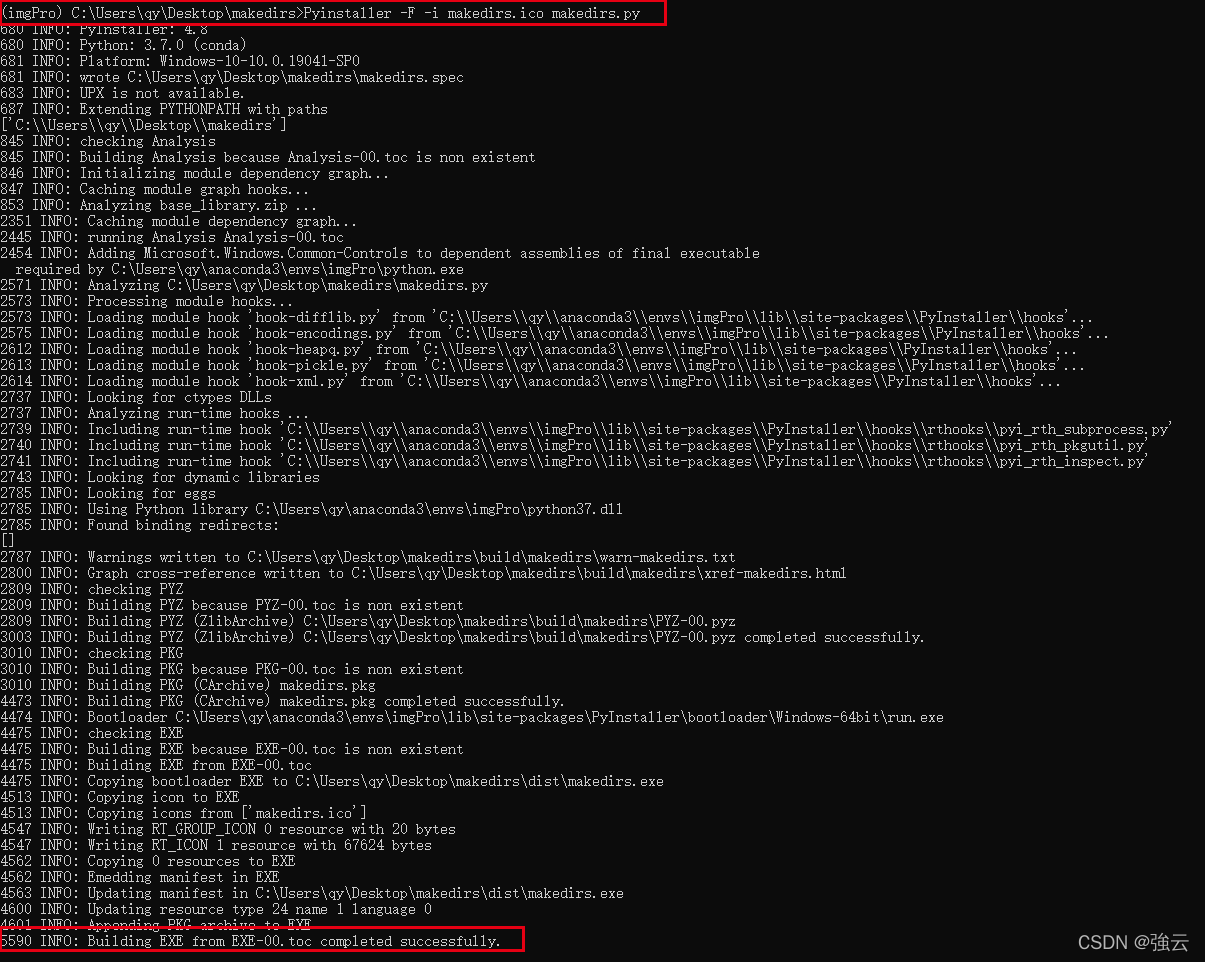
- 查看dis下的exe文件
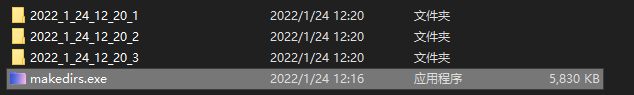
效果
python代码用的我另一篇博客python_文件夹操作
根据本地时间生成文件夹
需求
- 自动生成文件夹
- 名字为 年_月_日_时_分_序列号
- 序列号从1开始,升序排列。
源代码
""" 时间: 2022/01/24 作者: qiangyunLi, 深圳市宇瞳创新科技有限公司 需求描述: - 自动生成文件夹 - 名字为 **年_月_日_时_分_序列号** - 序列号从1开始,升序排列。 """ import os import time root = os.getcwd() t = time.localtime() path = str(t.tm_year)+"_"+str(t.tm_mon)+"_"+str(t.tm_mday)+"_"+str(t.tm_hour)+"_"+str(t.tm_min) names = os.listdir(root) i = 1 while(True): create_pat = path + "_" + str(i) folder = os.path.exists(create_pat) if folder: i = i+1 else: os.makedirs(create_pat) break- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
效果
我把这个代码封装成了exe文件,具体封装过程可看上述创建exe文件
exe文件已上传
语法
查看pythin 版本
python -V- 1
变量名
python3 中,可以用中文作为变量名,非ASCII标识码也是允许了。通常情况下不建议使用
关键字
我们不能将他们用作任何标识符名称。利用标准库提供的keyword模块,可以输出当前版本的所有关键字。
>>> import keyword >>> keyword.kwlist ['False','None','True','and', 'as','assert','async','await', 'break','class', 'continue','def','del','elif', 'else', 'except', 'finally', 'for', 'from','global', 'if', 'import','in', 'is', 'lambda', 'nonlocal', 'not', 'or', 'pass','raise', 'return', 'try', 'while', 'with','yield']- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
行与缩进
缩进的空格数是可变的,但是同一个代码快的语句必须包含相同的缩进空格数。
多行语句
语句很长,可以使用反斜杠 \ ;在[]、{}、()中不需要使用反斜杠。
字符串
- 使用三引号可以指定一个多行字符串;
- 使用r可以让反斜杠不发生转义;
- 字符串可以用+进行连接,用*运算符进行重复;
- 字符串索引,从左往右以0开始,从右往左以-1开始;
- 字符串不能改变;
- 无字符类型,一个字符就是长度为1的字符串;
- 字符串的截取语法:变量[头下标:尾下标:步长]。
同一行显示多条语句
语句间用(;)分隔。
print输出
print默认输出是换行的,要不换行在变量末尾加上end=“”。
变量
-
变量不需要声明,每个变量在使用前必须赋值,变量赋值后才会被创建。
-
变量没有类型,类型是指变量所指的内存中对象的类型。
-
允许同时为多个变量赋值
a = b = c = 1- 1
-
isinstance 和 type
- type()不会认为子类是一种父类类型;
- isinstance()会认为子类是一种父类类型。
-
del: 可以删除一些对象的引用和单个或多个对象。
-
一个变量可以通过赋值指向不同类型的对象。(注意变量在多次地方可能发生改变)
-
/ 返回一个浮点数,// 返回一个整数;
数据类型转换
将数据类型作为函数名即可。
- complex(real [,imag]):创建一个复数
- repr(x):将对象 x 转换为表达式字符串
- eval(str):用来计算在字符串中的有效Python表达式,并返回一个对象
- dict(d):创建一个字典。d 必须是一个 (key, value)元组序列。
- frozenset(s):转换为不可变集合
- chr(x):将一个整数转换为一个字符
- ord(x):将一个字符转换为它的整数值
- hex(x):将一个整数转换为一个十六进制字符串
- oct(x):将一个整数转换为一个八进制字符串
运算符
- ** :幂次
- := :海象运算符,可在表达式内部为变量赋值;python 3.8新增。
- 位运算符:把数字看作二进制进行计算。
- 身份运算符:
- is: 判断两个标识符是不是引用自一个对象;
- is not 判断两个标识符是不是引用不同对象。
- id(): 用于获取对象内存地址
数字
- ceil: 上取整
- exp(x): e的x次幂
- floor:向下取整
- log:对数
- modf(x):返回x的整数部分与小数部分
- round:四舍五入
随机数
- choice(seq):从序列的元素随机挑选一个元素;
- randrange(start, stop, step):从指定范围内,按指定的基数递增的集合中获取一个随机数;
- random()随机生成下一个实数吗【0,1)
- seed(x) : 改变随机数生成器的种子,
- shuffle(): 将序列中所有元素随机排列
- uniform(x, y) :随机生成下一个实数,在[X, Y]范围内。
三角函数
- acos(x) : 返回x的反余弦值;
- asin(x): 返回x的反正弦值;
- atan(x):返回x的反正切值;
- ata2(y,x):返回给定x,y坐标值的反正切值;
- hypot(x, y):返回欧几里得范数
- degrees(x):弧度转角度
- radians(x):角度转弧度。
常量
- pi
- e
字符串
- f-string: 格式化字符串以f开头,后面跟着字符串,字符串中的表达式用{}包起来,它会将变量或者表达式计算后的值替换进去;python 3.8中,可以使用=拼接运算表达式与结果。
字符串内建函数
- capitalize(): 第一个字符大写;
- center(width, fillchar): 返回一个指定的宽度width居中的字符串,fillchar为填充的字符,默认为空格。
- count(str, beg = 0, end=len(string)): 返回str在string里面出现的此时,可指定范围。
- bytes.decode(encoding=“utf-8”,errors=“strict”): 解码bytes对象
- encode(encoding="UTF-8:, errors=‘strict’): 编码;
- endswith(suffix, beg=0, end=len(string)):检查字符串是否以suffix结束;
- expandtabs(tabsize=8):将字符串string中的tab符合转为空格,默认空格数8;
- find(str, beg=0, end=len(string)):检查字符是否在字符串中;是返回索引,否走返回-1;
- isalnum(): 如果字符串至少有一个字符并且所有字符都是字母或者数字返回True;
- isalpha():如果字符串至少有一个字符并且所有字符都是字母或者中文则返回True;
- isdigit():如果字符串只包含数字则返回True;
- islower(): 如果字符串至少包含一个区分大小写的字符,这些字符都是小写返回True;
- isnumeric(): 是否为数字字符;
- isspace(): 只为空白
- istitle(): 是否为标题化的;
- isupper: 是否都是大写;
- join(seq): 以指定字符串作为分隔符,
- ljust(width, fillchar): 左对齐,填充指定长度;
- lower(): 转化为小写
- lstrip():截掉左边空格或指定字符;
- maketrans():创建字符映射的转换表,对于接受两个参数的最简单的调用方式,第一个参数为字符串,表示需要转换的字符,第二个参数也是字符串表示转换的目标。
- max(str) :返回str中最大的字母;
- min(str):返回str中最小的字母;
- replace(old, new, max): 将字符串中的old替换为new,max指定最多替换次数;
- rfind():右边开始查找;
- rjust(width, fillchar):右对齐,填充至width
- rstrip(): 删除字符串末尾的空格;
- startswith(substr, beg=0, end=len(string)): 检查字符串是否以指定的字串开头;
- swapcase():将字符串的大写转化为小写,小写转换为大写;
- title(): 所有单词大写开头,其余小写;
- translate(table, deletechars=“”):根据str给出的表转换string字符,过滤掉的字符放在deletechars参数中。
- upper(): 小写变大写;
- isdecimal():检查字符串只包含十进制字符。
列表
- list.count(obj): 统计某个元素在列表出现的次数;
- list.extend(seq):追加序列;
- list.index(obj): 第一个匹配的索引;
- list.insert(index, obj)
- list.pop(index=-1):移除并返回
- list.remove(obj):移除第一个匹配项;
- list.reverse()
- list.sort()
- list.clear()
- list.copy()
字典
键必须不可变;
集合
- 添加元素:s.add(); s.update()
- 移除元素:sremove(); s.discard()
- 随机删除:s.pop()
集合内置方法完整列表
- add() 为集合添加元素
- clear() 移除集合中的所有元素
- copy() 拷贝一个集合
- difference() 返回多个集合的差集
- difference_update() 移除集合中的元素,该元素在指定的集合也存在。
- discard() 删除集合中指定的元素
- intersection() 返回集合的交集
i- ntersection_update() 返回集合的交集。 - isdisjoint() 判断两个集合是否包含相同的元素,如果没有返回 True,否则返回 False。
- issubset() 判断指定集合是否为该方法参数集合的子集。
- issuperset() 判断该方法的参数集合是否为指定集合的子集
- pop() 随机移除元素
- remove() 移除指定元素
- symmetric_difference() 返回两个集合中不重复的元素集合。
- symmetric_difference_update() 移除当前集合中在另外一个指定集合相同的元素,并将另外一个指定集合中不同的元素插入到当前集合中。
- union() 返回两个集合的并集
- update() 给集合添加元素
迭代器 与 生成器
迭代器对象从集合的第一个元素开始访问,直到所有元素被访问结束,只往前;
iter(), next()yield
函数
不定参数
def functionname[args, var_args_tupe):
加了 * 号的参数会以元组的形式导入,存放所有未命名的参数变量;
加了 **的参数会以字典的形式导入;
使用单独号作为参数,*号后的参数必须使用关键字参数;匿名函数 lambda
- lambda 拥有自己的命名空间,且不能访问自己参数列表外或全局命名空间的参数;
- 语法:lambda arg1, arg2, …, argn: expression
python 3.8 中 / 指明/前必须使用位置参数。
模块
__name__属性
一个模块被另一个程序第一次引入时,其主程序将运行。如果我们想在模块被引入时,模块中的某一程序块不执行,我们可以用__name__属性来使该程序块仅在该模块自身运行时执行。
if name == ‘main’:
print(‘程序自身在运行’)
else:
print(‘我来自另一模块’)dir() 函数
内置的函数 dir() 可以找到模块内定义的所有名称。以一个字符串列表的形式返回:
Python 中只有模块(module),类(class)以及函数(def、lambda)才会引入新的作用域,其它的代码块(如 if/elif/else/、try/except、for/while等)是不会引入新的作用域的,也就是说这些语句内定义的变量,外部也可以访问,
len
len() 返回的长度是从1开始算的。
Iterator Protocol
- 迭代器是一个对象
- 迭代器可以被next()函数调用,并返回一个值
- 迭代器可以被iter()函数调用,并返回迭代器自己
- 连续被next()调用时依次返回一系列的值
- 如果到了迭代器的末尾,则抛出StopIteration异常
- 迭代器也可以没有末尾,只要被next()调用,就一定会返回一个值
- Python中,next()内置函数调用的是对象的__next__()方法
- 只要一个对象实现了__next__()方法,就可以被next()函数调用
- Python中, iter()内置函数调用的是对象的__iter__()方法
- 一个实现了迭代器协议的对象可以被for语句循环迭代直到终止
for
- for语句里用的是iterable,而非iterator
- for语句执行的第一个操作是从一个iterable生成一个iterator
- for语句的循环体其实是靠检测StopIteration异常来中断的
- 要想对for语句迭代需要三个条件:iter(), next(), StopIteration
生成器
- 迭代器协议很有用,但实现起来有些繁琐
- 生成器在保持代码简洁优雅的同时,自动实现了迭代器协议
yeild
- 和 return 不同,它只是暂停,第一次执行第一个yeild,第二次执行第二个yeild
- yeild返回生成对象,需要调用next()才会生成值
Generator Expression
[print(x) for x in (x ** 2 for x in range(5))] // 两个in,一个生成list,一个生成迭代器 sum([ x ** 2 for x in range(10000000)]) sum(x ** 2 for x in range(10000000)])- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 第一句生成一个list,然后再进行操作,占用内存大
- 第二句生成一个生成表达式,生成器本还要加上一个(), 但sum本就是()调用,故不需要两个(), 写一个
为什么需要生成器
- 相比迭代器协议,实现生成器的代码量小,可读性更高
- 相比在list中操作元素,直接使用生成器能节省大量内存
- 有时候我们需要写一个无法i再内存中存放的无限数据流
- 可以建成生成器管道(多个生成器链式调用)
- 只需要迭代使用,并不需要对其进行其他操作,最好使用生成器。
关于Python中的迭代器思维
- Python中有两类运算:
- 可以并行的是量化的运算:Numpy
- 必须一个个的操作的迭代式运算:Generator
- Python中有两类数据:
- 内存放得下的:数据量较小的数据
- 内存中放不下的:数据量较大或者无穷大的数据
- Python中有两种思维:
- Eager: 着急派,需要的话,必须全都准备好
- Lazy: 懒惰派, 需要的时候再说
- Python中处处是迭代器,缺的是发现迭代器的眼睛
-
相关阅读:
SuperMap iServer11i新功能----图例的发布和使用
将SpringBoot项目的jar包注册成service服务的方式启动
k8s集群中部署服务之部署描述文件准备
Mysql 表逻辑分区原理和应用
配电室电力监控系统:实时掌握电力运行状况
马尔可夫链
[SpringBoot] SpringBoot-03-配置文件格式
stm32 - 中断
3D怎么看模型内部结构---模大狮模型网
自动化运维机器人(RPA)在银行IT运维领域应用场景分析
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_42577742/article/details/125616272