-
【刷题】BFS题目精选
1.BFS使用场景
-
分层遍历
-
一层一层的遍历一个图、数、矩阵
-
简单图的最短路径
-
-
连通块问题
-
通过图的一个点找到其他所有连通的点
-
找到所有方案问题的一种非递归实现方式
-
-
拓扑排序
时间复杂度:
N个点,M条边,图上BFS时间复杂度 = O(N + M),说是 O(M)问题也不大,因为M一般都比N大。
M最大是 O(N^2) 的级别(任意两个点之间都有边), 所以最坏情况可能是 O(N^2)
1.1.关于最短路算法
1.1.1dijkstra算法
也叫做单源最短路径算法,解决一个点到其余个点顶点的最短路径
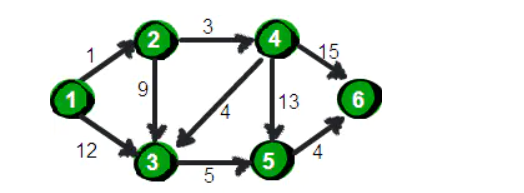
首先需要写出邻接矩阵

使用dis数组存储源顶点(1号顶点)到其余个顶点的距离
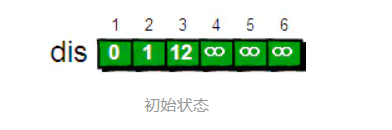
具体思路
-
从初始的dis数组中找到最小值为2,那么1->2顶点的最短路径就成为了确定值,值为1。
-
从顶点2开始出发,可以到达的顶点为2->3,2->4;其中如果中顶点2进行"中转",那么1->2->3的路径为1(1->2的最短路径)+9(2->3的路径)为10,小于1->3的距离12,所以将dis数组中1->3的值变为10;对2->4进行同样的处理1->4的最短路径更新为4。
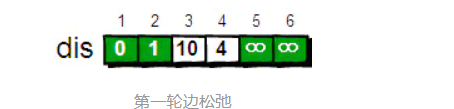
在现在的dis数组中,确定的顶点有2;而第一次松弛后除去到顶点2的最短路径为1->4(路径长度为4),顶点4为确定值。从4开始出发
- 可以到达的顶点有3,5,6;将顶点4作为"中转"进行第二轮的松弛
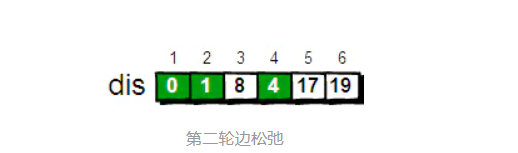
现在的确定的顶点为2,4;剩下顶点的最短路径为1->3,顶点3为最短路径,变为确定值;
进行下一轮的松弛

最终的松弛结果为:
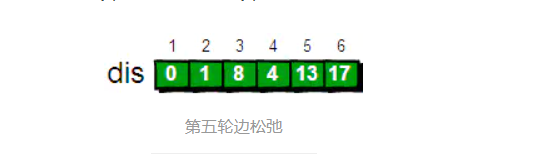
dis数组中存放了到各顶点的最短路径
//代码实现 const int INF=INT_MAX;//最大值 const int Maxsize=INT_MAX;//最大顶点数 int e[Maxsize][Maxsize];//邻接矩阵 int flag[Maxsize];//标记数组,记录顶点是否为 int dis[Maxsize];//距离表 int n,m;//n表示节点,m表示边 //初始化dis数组 void dijkstra(){ //邻接矩阵中的0位置不存数,为了方便都按照结点开始 for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){ dis[i]=e[1][i] } for(int i=2;i<=n;i++){ flag[i]=0; } book[i]=1; //对dis进行松弛处理 for(int i=1;i<=n-1;i++){ //对于n个节点需要进行n-1次松弛处理 //记录这一轮松弛的最短距离 int min_num=INT_MAX; //记录这一轮松弛的确定节点 int min_index=0; for(int k=1;k<=n;k++){ if(flag[k]==0&&dis[k]<min_num)//如果还不是确定结点 { min_num=dis[k]; min_index=k; } } //确定结点 flag[min_index]=1; //松弛处理 for(int j=1;j<=n;j++){ if(flag[j]==0&&e[min_index][j]<INT_MAX)//如果两个结点之间有路径 { dis[j]=min(dis[j],dis[min_index]+e[min_index][j]); } } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
dijkstra算法的优化
c edge { int d,v;// d:距离;v:节点(弧头) edge(){} edge(int a,int b)// 初始化 d 和 v { d=a,v=b; } // 重载"<"运算符,以便更改优先队列的排序规则 // 根据"最短距离"d来进行排序 bool operator < (const edge&x)const { if(d==x.d)return v<x.v; else return d>x.d; } }; vector<edge>G[Maxsize];// 图 G int dis[Maxsize];// 距离表 int n,m;// n:顶点个数 m:边数 int v1,v2,w;// v1->v2,weight==w // Dijkstra算法,源点为 s void dijkstra(int s) { // 初始化dis数组 for(int i=0;i<=n;i++)dis[i]=INF; dis[s]=0; priority_queue<edge>que;// 优先队列 que.push(edge(dis[s],s));// 将起点压入队列 // 队列非空 while(!que.empty()) { // get the min_index edge temp=que.top(); que.pop(); int v=temp.v;// 顶点 if(dis[v]<temp.d)continue;// // 遍历顶点v相连的所有边 for(int i=0;i<G[v].size();i++) { edge e=G[v][i]; if(dis[e.v]>dis[v]+e.d) { dis[e.v]=dis[v]+e.d; que.push(edge(dis[e.v],e.v)); } } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
1.1.2Floyd-Warshall算法
弗洛伊德算法的核心就是通过引入第三k个顶点进行中转,只需要判e[ i ] [ 1 ]+e[ 1 ] [ j ]是否会比e[ i ] [ j ]小即可。
//弗洛伊德算法最核心的部分只有几行代码,其中e表示邻接矩阵 for(int k=1;k<=n;k++){//中间媒介可能不止一个 for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){//遍历所有的结点 for(int j=1;j<=n;j++){ e[i][j]=min(e[i][j],e[i][k]+e[j][j];) } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
弗洛伊德算法的优点是可以处理负权问题
2.题目
题目1:
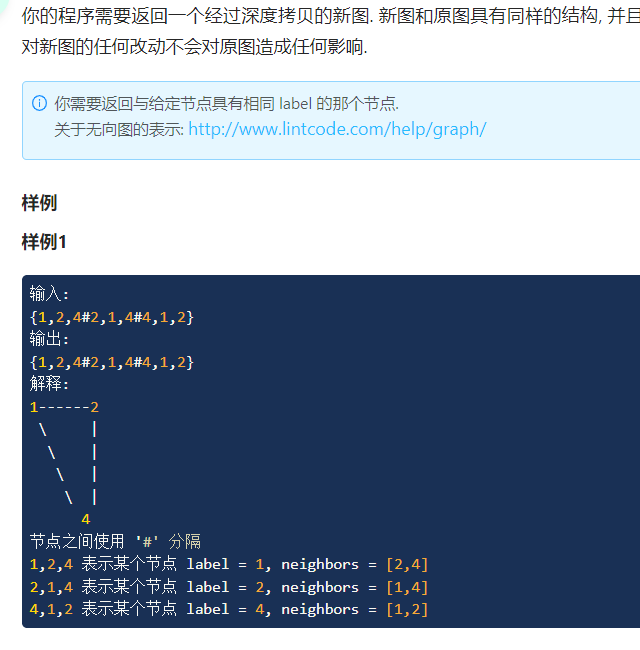
方法一:分治
class Solution { public: UndirectedGraphNode *clone(UndirectedGraphNode*node,map<int,UndirectedGraphNode *>&table){ if(node==NULL){ return NULL; } //如果当前的结点已经被复制 if(table.find(node->label)!=table.end()){ return table[node->label]; } //如果当前结点没有被复制 //调用构造函数 UndirectedGraphNode *newcode=new UndirectedGraphNode(node->label); table[node->label]=newcode; for(int i=0;i<(node->neighbors).size();i++){ UndirectedGraphNode *code=clone((node->neighbors)[i],table); (newcode->neighbors).push_back(code); } return newcode; } UndirectedGraphNode* cloneGraph(UndirectedGraphNode *node) { map<int,UndirectedGraphNode *>visittable; return clone(node,visittable); } };- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
方法二:BFS
//思路分为三步 //第一步:得到所有不重复的点 //第二步:将点与复制的点进行映射 //第三步:复制边 class Solution { public: UndirectedGraphNode* cloneGraph(UndirectedGraphNode *node) { if(node==nullptr){ return node; } //第一步:得到所有的点 vector<UndirectedGraphNode*>nodes=getnodes(node); //第二步:将得到的点和复制的点进行映射 unordered_map<UndirectedGraphNode*,UndirectedGraphNode*>mapping=clonenodes(nodes); //第三步:连接边 connectnodes(mapping,nodes); return mapping[node]; } vector<UndirectedGraphNode *>getnodes(UndirectedGraphNode *node){ queue<UndirectedGraphNode *>q; //不重复的Set unordered_set<UndirectedGraphNode *>s; vector<UndirectedGraphNode*>nodes; q.push(node); s.insert(node); nodes.push_back(node); while(!q.empty()){ UndirectedGraphNode*tmp=q.front(); q.pop(); for(auto neighbor:tmp->neighbors){ //如果在s中找到,表示已经被放入了则跳过 if(s.find(neighbor)!=s.end()){ continue; } q.push(neighbor); s.insert(neighbor); nodes.push_back(neighbor); } } return nodes; } unordered_map<UndirectedGraphNode *,UndirectedGraphNode *>clonenodes(vector<UndirectedGraphNode *>nodes){ unordered_map<UndirectedGraphNode *,UndirectedGraphNode *>mapping; for(auto node:nodes){ mapping.insert(make_pair(node,new UndirectedGraphNode(node->label))); } return mapping; } //连接复制好的边 void connectnodes(unordered_map<UndirectedGraphNode *,UndirectedGraphNode *>mapping,vector<UndirectedGraphNode *>nodes){ for(auto node:nodes){ for(auto neighbor:node->neighbors){ UndirectedGraphNode*newnode=mapping[node]; UndirectedGraphNode*newneighbor=mapping[neighbor]; newnode->neighbors.push_back(newneighbor); } } } };- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
(题目2)
思路:
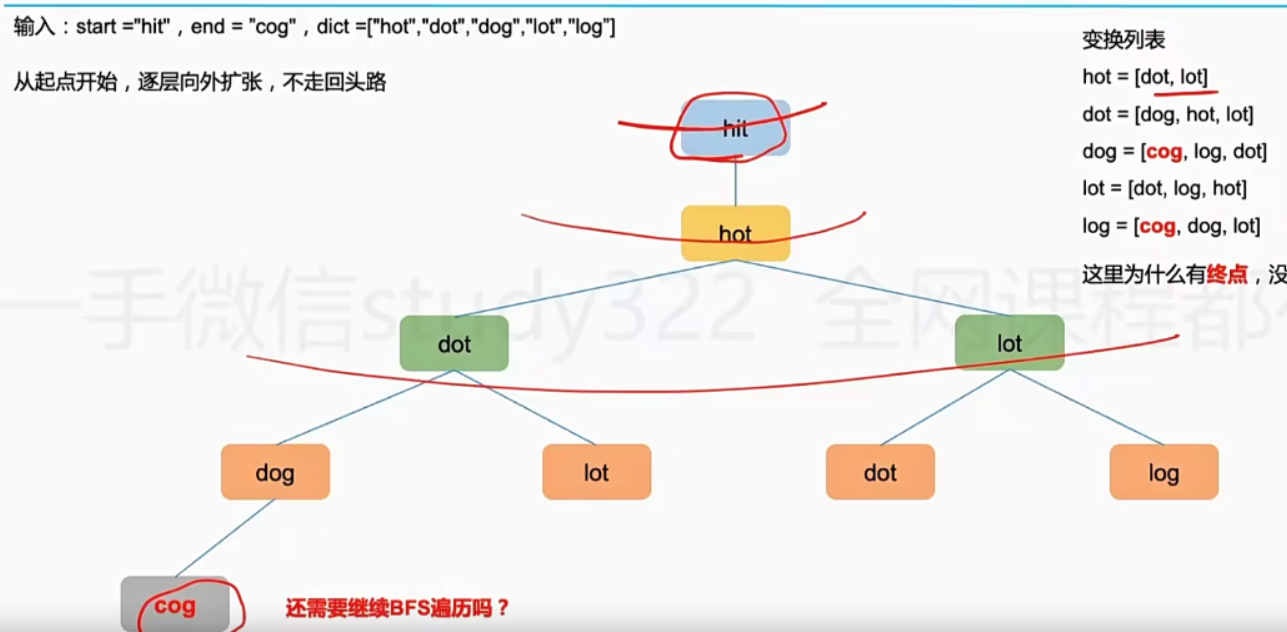
每个单词可以转换的单词形成了一棵树,所以可以使用BFS得到结果// version LintCode class Solution { public: int ladderLength(string &start, string &end, unordered_set<string> &dict) { int n=start.size(); if(start==end){ return 1; } if(n<1||n!=end.size()){ return -1; } queue<string>q; q.push(start); dict.erase(start); int step=2; while(!q.empty()){ //记录这一层的单词数量 int size=q.size(); for(int i=0;i<size;i++){ string tmp=q.front(); q.pop(); //替换字母 for(int j=0;j<tmp.size();j++){ char ch=tmp[j]; for(char c='a';c<='z';c++){ if(ch==c){ continue; } tmp[j]=c; if(tmp==end){ return step; } else if(dict.find(tmp)!=dict.end()){ q.push(tmp); dict.erase(tmp); } tmp[j]=ch; } } } //每遍历完一次就需要加1 step++; } return 0; } };- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
(题目3:连通块问题)
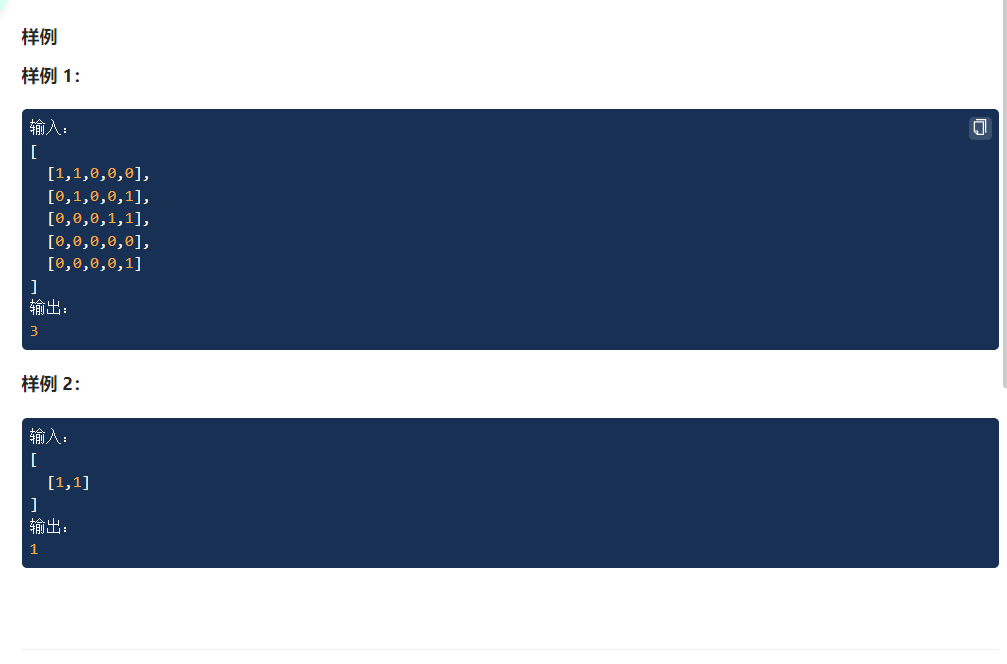

class Solution { public: int numIslands(vector<vector<bool>> &grid) { if(grid.size()==0||grid[0].size()==0){ return 0; } int m=grid.size(),n=grid[0].size(),num=0; //标记数组 vector<vector<bool>>flag(m,vector<bool>(n,false)); for(int i=0;i<m;i++){ for(int j=0;j<n;j++){ if(grid[i][j]&&!flag[i][j]){ dfs(grid,flag,i,j,m,n); num++; } } } return num; } void dfs(vector<vector<bool>>&grid,vector<vector<bool>>&flag,int i,int j,int m,int n){ if(i<0||i>=m||j<0||j>=n||!grid[i][j]||flag[i][j]){ return ; } flag[i][j]=true; dfs(grid,flag,i+1,j,m,n); dfs(grid,flag,i-1,j,m,n); dfs(grid,flag,i,j+1,m,n); dfs(grid,flag,i,j-1,m,n); } };- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
(题目5)
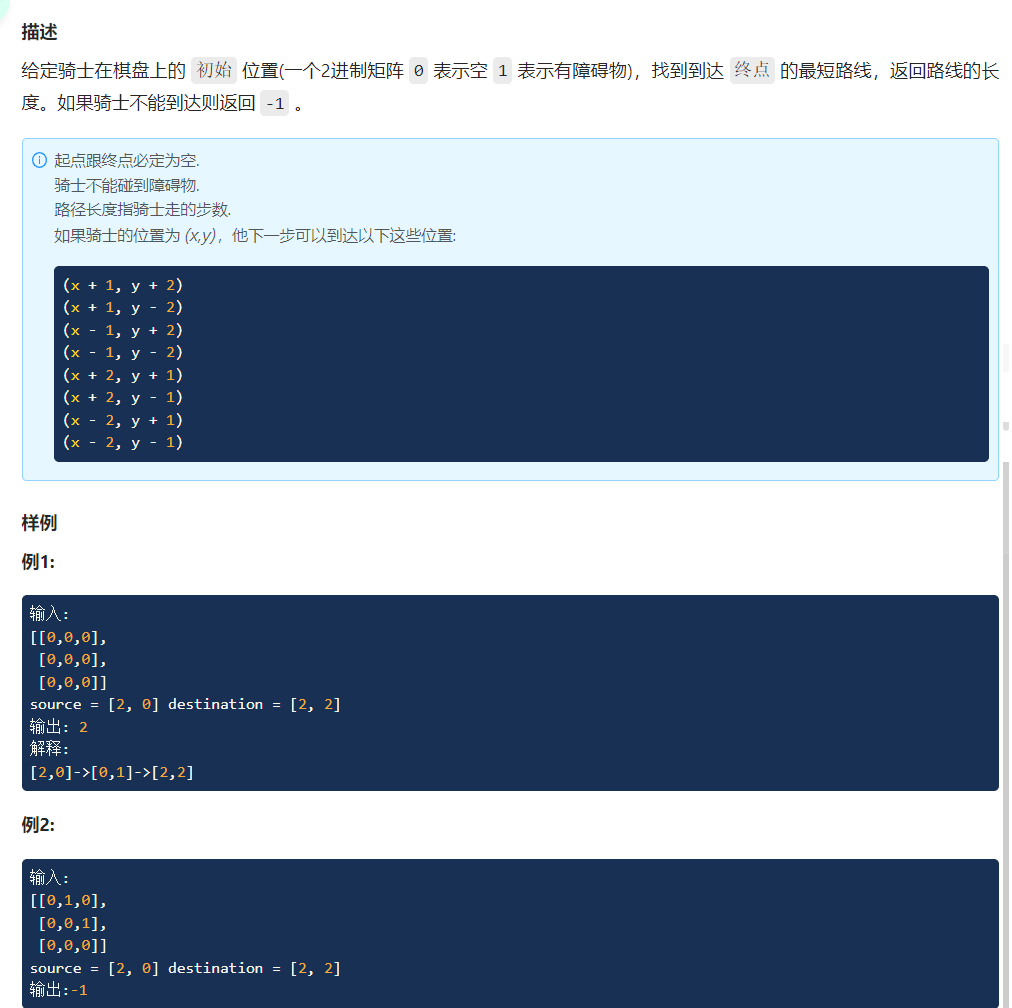
方法:BFS
BFS将达到的点按照路径转换为一棵树,模拟对树的层序遍历实现。
//朴素BFS class Solution { public: int shortestPath(vector<vector<bool>> &grid, Point source, Point destination) { int m=grid.size(),n=grid[0].size(); if(m==0||n==0){ return -1; } queue<Point>q; q.push(source); int ans=0; vector<vector<int>>direct={{1,2},{1,-2},{-1,2},{-1,-2},{2,1},{2,-1},{-2,1},{-2,-1}}; while(!q.empty()){ //记录这一层的数量 int size=q.size(); for(int i=0;i<size;i++){ Point tmp=q.front();q.pop(); if(tmp.x==destination.x&&tmp.y==destination.y){ return ans; } for(int k=0;k<8;k++){ Point node; node.x=tmp.x+direct[k][0]; node.y=tmp.y+direct[k][1]; if(node.x>=0&&node.x<m&&node.y>=0&&node.y<n){ if(!grid[node.x][node.y]){ q.push(node); } grid[node.x][node.y]=true; } } } ans++; } return -1; } };- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
(题目6)
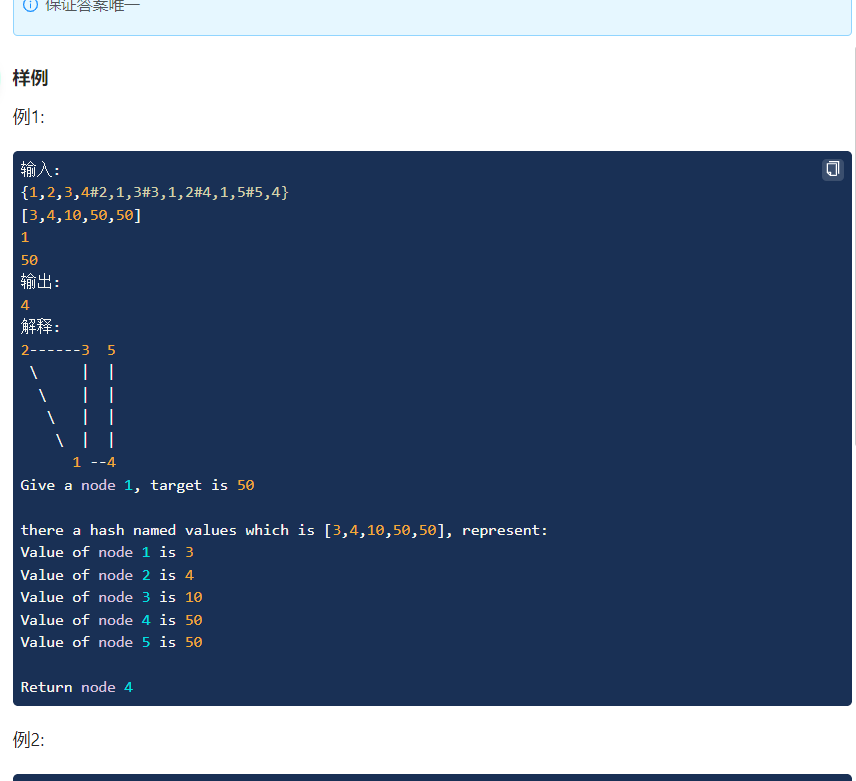
//朴素bfs class Solution { public: UndirectedGraphNode* searchNode(vector<UndirectedGraphNode*>& graph, map<UndirectedGraphNode*, int>& values, UndirectedGraphNode* node, int target) { queue<UndirectedGraphNode*>q; q.push(node); set<UndirectedGraphNode*>se; se.insert(node); while(!q.empty()){ UndirectedGraphNode* tmp=q.front();q.pop(); if(values[tmp]==target) { return tmp; } for(auto it=tmp->neighbors.begin();it!=tmp->neighbors.end();it++){ if(se.find(*it)==se.end()){ se.insert(*it); q.push(*it); } } } return NULL; } };- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
(题目7)
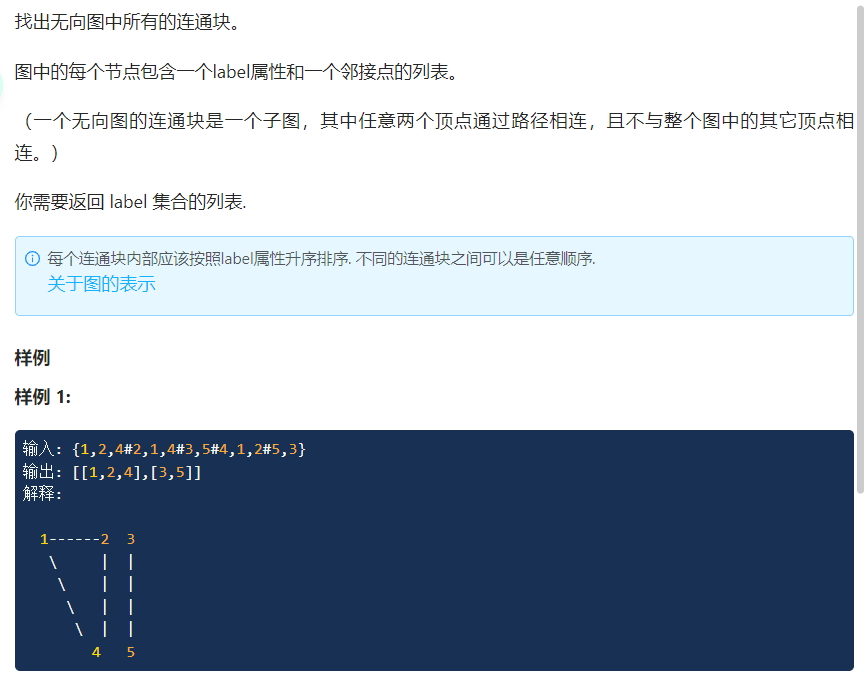
//考察点:并查集 //用map记录父亲节点 map<int,int>f; //寻找根节点 int find(int x){ return f[x]==x?x:f[x]=find(f[x]); } class Solution { public: vector<vector<int>> connectedSet(vector<UndirectedGraphNode*> nodes) { if(nodes.empty()){ return {}; } //初始化 for(int i=0;i<nodes.size();i++){ f[nodes[i]->label]=nodes[i]->label; } for(auto e:nodes){ //互为邻居的为同一块 for(auto i:e->neighbors){ if(find(e->label)!=find(i->label)){ f[find(i->label)]=f[find(e->label)]; } } } map<int,vector<int>>tmpres; for(auto e:nodes){ //将父节点相同的放在同一个vector中 tmpres[find(e->label)].push_back(e->label); } vector<vector<int>>res; for(auto i:tmpres){ //插入map中的vector<int>部分 res.push_back(i.second); } return res; } };- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
矩阵上的bfs
(题目8)
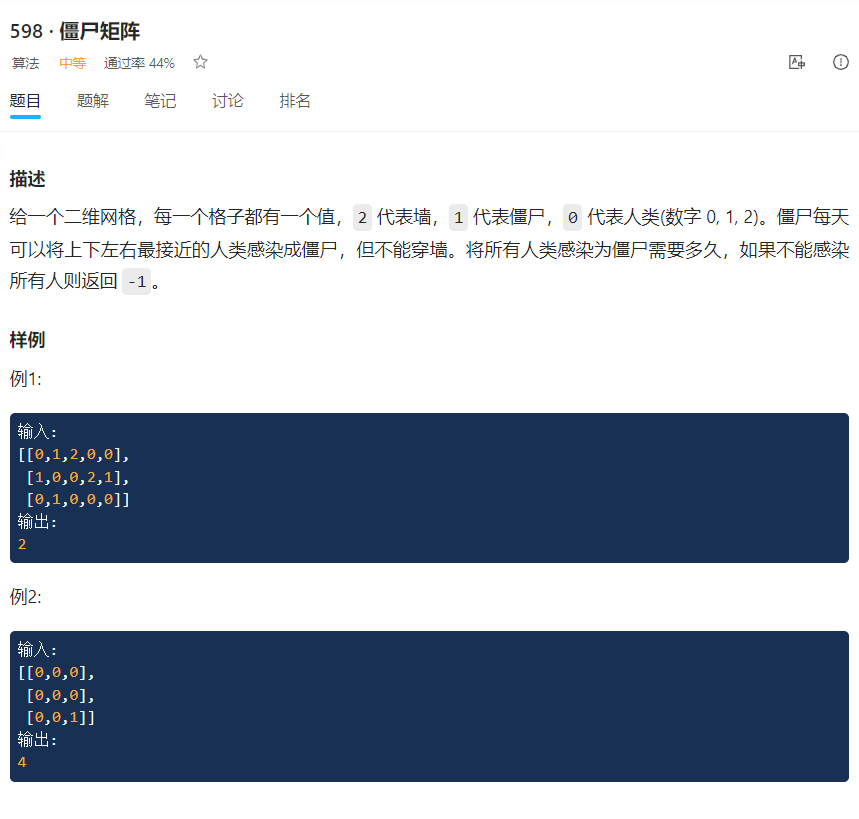
class point{ public: int x,y; point(int _x,int _y) :x(_x),y(_y) {} }; class Solution { public: int zombie(vector<vector<int>> &grid) { int cnt=0,n=grid.size(); if(n==0){ return 0; } int m=grid[0].size(); if(m==0){ return 0; } queue<point>q; for(int i=0;i<n;i++){ for(int j=0;j<m;j++){ if(grid[i][j]==1){ q.push(point(i,j)); } } } int day[4][2]={{1,0},{-1,0},{0,-1},{0,1}}; while(!q.empty()){ int size=q.size(); cnt++; //感染上下左右的点 for(int i=0;i<size;i++){ point head=q.front();q.pop(); for(int k=0;k<4;k++){ int x=head.x+day[k][0]; int y=head.y+day[k][1]; if(x>=0&&x<n&&y>=0&&y<m&&grid[x][y]==0){ grid[x][y]=1; q.push(point(x,y)); } } } } for(int i=0;i<n;i++){ for(int j=0;j<m;j++){ //如果还有0表示还有幸存者 if(grid[i][j]==0){ return -1; } } } //需要减一,在刚进入队列时多加了一次 return cnt-1; } };- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
(题目9)
这个题的解题思路和地图分析相似。
(地图分析)[573 · 邮局的建立 II - LintCode]
/* 直接思路: 1.遍历所有的空地点 2.对每个空地点用bfs到所有house的距离 3.用打擂台的方式求最短距离 */ class Solution { public: #define WALL 2 #define HOUSE 1 #define EMPT 0 const vector<vector<int>> direct= {{1,0}, {0,1}, {-1,0}, {0,-1}}; int minDis; int numHouse; class Coord { public: int x, y; Coord(int x, int y) : x(x), y(y) {}; }; int shortestDistance(vector<vector<int>> &grid) { // write your code here if (grid.size() == 0) { return -1; } minDis = -1; numOfHouse(grid); for (int i = 0; i < grid.size(); i++) { for (int j = 0; j < grid[0].size(); j++) { if (grid[i][j] == EMPT) { Coord pos(i, j); findDis(pos, grid); } } } return minDis; } void numOfHouse(vector<vector<int>> &grid) { for (int i = 0; i < grid.size(); i++) { for (int j = 0; j < grid[0].size(); j++) { if (grid[i][j] == HOUSE) { numHouse++; } } } } bool isInBound(vector<vector<int>> &grid, int x, int y) { if (x < 0 || x >= grid.size() || y < 0 || y >= grid[0].size()) { return 0; } else { return 1; } } void findDis(Coord &pos, vector<vector<int>> &grid) { vector<vector<bool>> visited(grid.size(), vector<bool>(grid[0].size())); queue<Coord> q; q.push(pos); visited[pos.x][pos.y] = 1; int dis = 0; int visitedHouse = 0; int step = 0; while (!q.empty()) { int qsize = q.size(); step++; for (int i = 0; i < qsize; i++) { Coord cd = q.front(); q.pop(); for (int j = 0; j < direct.size(); j++) { int x = cd.x + direct[j][0]; int y = cd.y + direct[j][1]; if (isInBound(grid, x, y) && visited[x][y] == 0) { if (grid[x][y] == HOUSE) { dis += step; if (minDis != -1 && dis >= minDis) { return; } visitedHouse++; if (visitedHouse == numHouse) { minDis = dis; return; } } if (grid[x][y] == EMPT) { q.push(Coord(x, y)); } visited[x][y] = 1; } } } } } };- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
class point{ public: int x,y; point(int _x,int _y) :x(_x),y(_y) {} }; class Solution { public: int dir[4][2]={{1,0},{-1,0},{0,1},{0,-1}}; //记录房子的数量 int mindis=INT_MAX,numhouse=0; int shortestDistance(vector<vector<int>> &grid) { int n=grid.size(),m=grid[0].size(); if(n==0||m==0){ return -1; } numofhouse(grid); for(int i=0;i<n;i++){ for(int j=0;j<m;j++){ //如果是一块空地,就找他的所有距离 if(grid[i][j]==0){ point pos(i,j); finddis(pos,grid); } } } return mindis; } void numofhouse(vector<vector<int>>&grid){ for(int i=0;i<grid.size();i++){ for(int j=0;j<grid[0].size();j++){ if(grid[i][j]==1){ numhouse++; } } } } bool isinfound(int x,int y,vector<vector<int>>&grid){ if(x<0||x>=grid.size()||y<0||y>=grid[0].size()){ return false; } return true; } void finddis(point&p,vector<vector<int>>&grid){ //记录该点是否被遍历 vector<vector<bool>>visit(grid.size(),vector<bool>(grid[0].size())); queue<point>q; q.push(p); //visit记录访问房子的数量,distance记录距离 visit[p.x][p.y]=1; int visithouse=0,step=0,distance=0; while(!q.empty()){ step++; int size=q.size(); for(int i=0;i<size;i++){ point head=q.front();q.pop(); for(int k=0;k<4;k++){ int x=head.x+dir[k][0]; int y=head.y+dir[k][1]; if(isinfound(x,y,grid)&&visit[x][y]==0) { if(grid[x][y]==1){ distance+=step; visithouse++; if(visithouse==numhouse){ mindis=min(distance,mindis); return ; } } //如果是没有被访问的空点,就加入队列中 if(grid[x][y]==0){ q.push(point(x,y)); } visit[x][y]==1; } } } } } };- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
-
-
相关阅读:
面向对象的设计(OOD)原则了解一下
研发效能的逻辑:填补软工鸿沟
嵌入式Linux驱动开发5---volatile变量
Docker 基本使用
02 | Spring Data Common 之 Repository 如何全面掌握?
1. Python 的 print( )输出函数
实习三个月的感悟
Isito 入门(九):安全认证
正大期货主账户留4行情软件用的什么?
molecular-graph-bert(一)
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_53893431/article/details/125610163
