-
【大数据离线开发】6.2 MapReduce的高级特性
6.2 MapReduce的高级特性
6.2.1 序列化Serializable
6.2.1.1 Java的序列化
Java的序列化:将对象写入到文件中
Student.java
//实现Java的序列化,必须实现Serializable public class Student implements Serializable { private int stuID; private String stuName; public int getStuID() { return stuID; } public void setStuID(int stuID) { this.stuID = stuID; } public String getStuName() { return stuName; } public void setStuName(String stuName) { this.stuName = stuName; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
TestStudent.java
public class TestStudent { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { //创建一个学生对象 Student student = new Student(); student.setStuID(1); student.setStuName("Tom"); //把这个对象保存到文件中------------>序列化 OutputStream out = new FileOutputStream("F:\\temp\\student.txt"); ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(out); oos.writeObject(student); oos.close(); out.close(); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
6.2.1.2 Mapreduce的序列化
核心:接口 Writable
如果一个类实现了的Hadoop的序列化机制(接口:Writable),这个类的对象就可以作为输入和输出的值。
案例1: 读取员工数据,生成员工的对象,直接输出到HDFS
Emp.java
//代表员工 //数据:7654,MARTIN,SALESMAN,7698,1998/9/29,1250,1400,30 public class Emp implements Writable { private int empno;//员工号 private String ename;//员工姓名 private String job;//职位 private int mgr;//经理的员工号 private String hiredate;//加入时间 private int sal;//月薪 private int comm;//奖金 private int deptno;//部门编号 @Override public String toString() { return "Emp{" + "empno=" + empno + ", ename='" + ename + '\'' + ", sal=" + sal + ", deptno=" + deptno + '}'; } @Override public void write(DataOutput dataOutput) throws IOException { //实现序列化,把对象输出到输出流 dataOutput.writeInt(this.empno); dataOutput.writeUTF(this.ename); dataOutput.writeUTF(this.job); dataOutput.writeInt(this.mgr); dataOutput.writeUTF(this.hiredate); dataOutput.writeInt(this.sal); dataOutput.writeInt(this.comm); dataOutput.writeInt(this.deptno); } @Override public void readFields(DataInput dataInput) throws IOException { //实现反序列化,从输入流中读取对象 this.empno = dataInput.readInt(); this.ename = dataInput.readUTF(); this.job = dataInput.readUTF(); this.mgr = dataInput.readInt(); this.hiredate = dataInput.readUTF(); this.sal = dataInput.readInt(); this.comm = dataInput.readInt(); this.deptno = dataInput.readInt(); } public int getEmpno() { return empno; } public void setEmpno(int empno) { this.empno = empno; } public String getEname() { return ename; } public void setEname(String ename) { this.ename = ename; } public String getJob() { return job; } public void setJob(String job) { this.job = job; } public int getMgr() { return mgr; } public void setMgr(int mgr) { this.mgr = mgr; } public String getHiredate() { return hiredate; } public void setHiredate(String hiredate) { this.hiredate = hiredate; } public int getSal() { return sal; } public void setSal(int sal) { this.sal = sal; } public int getComm() { return comm; } public void setComm(int comm) { this.comm = comm; } public int getDeptno() { return deptno; } public void setDeptno(int deptno) { this.deptno = deptno; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
EmpInforMapper.java
public class EmpInforMapper extends Mapper<LongWritable, Text, IntWritable, Emp> { @Override protected void map(LongWritable key1, Text value1, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException { //数据:7654,MARTIN,SALESMAN,7698,1998/9/29,1250,1400,30 String data = value1.toString(); String[] words = data.split(","); Emp emp = new Emp(); emp.setEmpno(Integer.parseInt(words[0])); emp.setEname(words[1]); emp.setJob(words[2]); emp.setMgr(Integer.parseInt(words[3])); emp.setHiredate(words[4]); emp.setSal(Integer.parseInt(words[5])); emp.setComm(Integer.parseInt(words[6])); emp.setDeptno(Integer.parseInt(words[7])); context.write(new IntWritable(emp.getEmpno()), emp); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
EmoInfoMain.java
public class EmpInfoMain { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { //1、创建一个任务,指定任务的入口 Job job = Job.getInstance(new Configuration()); job.setJarByClass(EmpInfoMain.class); //2、指定任务的map和map输出的数据类型 job.setMapperClass(EmpInforMapper.class); job.setMapOutputKeyClass(IntWritable.class); job.setMapOutputValueClass(Emp.class); //3、指定任务输出的数据类型 job.setOutputKeyClass(IntWritable.class); job.setOutputValueClass(IntWritable.class); //4、指定任务的输入路径、任务的输出路径 FileInputFormat.setInputPaths(job, new Path(args[0])); FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path(args[1])); //5、执行任务 job.waitForCompletion(true); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
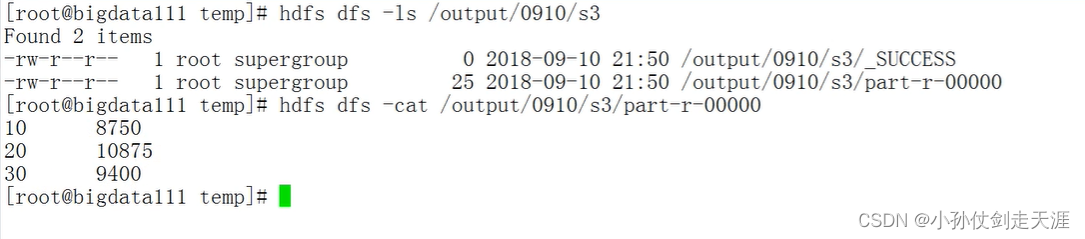
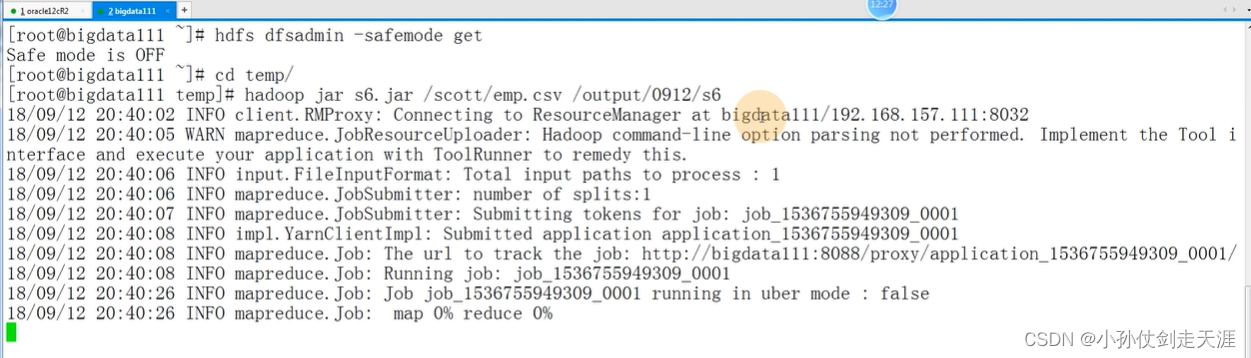
导出 jar 包,上传虚拟机,执行命令


案例2: 使用MapReduce序列化重写“求每个部门的工资总额"
SalaryTotalMapper.java
public class SalaryTotalMapper extends Mapper<LongWritable, Text, IntWritable, Emp> { @Override protected void map(LongWritable key1, Text value1, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException { //数据:7654,MARTIN,SALESMAN,7698,1998/9/29,1250,1400,30 String data = value1.toString(); String[] words = data.split(","); Emp emp = new Emp(); emp.setEmpno(Integer.parseInt(words[0])); emp.setEname(words[1]); emp.setJob(words[2]); emp.setMgr(Integer.parseInt(words[3])); emp.setHiredate(words[4]); emp.setSal(Integer.parseInt(words[5])); emp.setComm(Integer.parseInt(words[6])); emp.setDeptno(Integer.parseInt(words[7])); context.write(new IntWritable(emp.getDeptno()), emp); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
SalaryTotalReducer.java
public class SalaryTotalReducer extends Reducer<IntWritable, Emp, IntWritable, IntWritable> { @Override protected void reduce(IntWritable key3, Iterable<Emp> values3, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException { //对v3求和 int total = 0; for (Emp emp : values3) total += emp.getSal(); //输出 k4:部门 v4:部门总工资 context.write(key3, new IntWritable(total)); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
SalaryTotalMain.java
public class SalaryTotalMain { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { //1、创建一个任务,指定任务的入口 Job job = Job.getInstance(new Configuration()); job.setJarByClass(SalaryTotalMain.class); //2、指定任务的map和map输出的数据类型 job.setMapperClass(SalaryTotalMapper.class); job.setMapOutputKeyClass(IntWritable.class); job.setMapOutputValueClass(Emp.class); //3、指定任务的Reduce和reduce输出的数据类型 job.setReducerClass(SalaryTotalReducer.class); job.setOutputKeyClass(IntWritable.class); job.setOutputValueClass(IntWritable.class); //4、指定任务的输入路径、任务的输出路径 FileInputFormat.setInputPaths(job, new Path(args[0])); FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path(args[1])); //5、执行任务 job.waitForCompletion(true); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
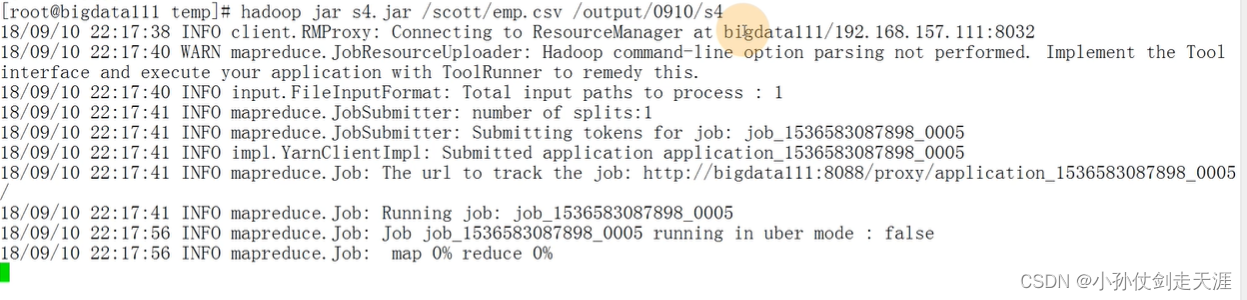
导出 jar 包,上传虚拟机,执行命令

6.2.2 排序Sort
规则:按照Key2排序
基本数据类型
- 数字
- 字符串
6.2.2.1 数字排序
默认升序。可以改变默认的排序规则(创建自己的比较器即可),以MapReduce案例2——统计每个部门的工资总额,举例如下。
其他程序不变,仅新建一个自己的比较规则类,以及修改main方法,指定自己的比较规则。
MyNumbercomparator.java
//针对是number的数据结构,定义自己的比较结构 public class MyNumbercomparator extends IntWritable.Comparator { @Override public int compare(byte[] b1, int s1, int l1, byte[] b2, int s2, int l2) { return -super.compare(b1, s1, l1, b2, s2, l2); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
SalaryTotalMain.java
public class SalaryTotalMain { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { //1、创建一个任务,指定任务的入口 Job job = Job.getInstance(new Configuration()); job.setJarByClass(SalaryTotalMain.class); //2、指定任务的map和map输出的数据类型 job.setMapperClass(SalaryTotalMapper.class); job.setMapOutputKeyClass(IntWritable.class); job.setMapOutputValueClass(Emp.class); // 指定自己的比较规则 job.setSortComparatorClass(MyNumbercomparator.class); //3、指定任务的Reduce和reduce输出的数据类型 job.setReducerClass(SalaryTotalReducer.class); job.setOutputKeyClass(IntWritable.class); job.setOutputValueClass(IntWritable.class); //4、指定任务的输入路径、任务的输出路径 FileInputFormat.setInputPaths(job, new Path(args[0])); FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path(args[1])); //5、执行任务 job.waitForCompletion(true); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27

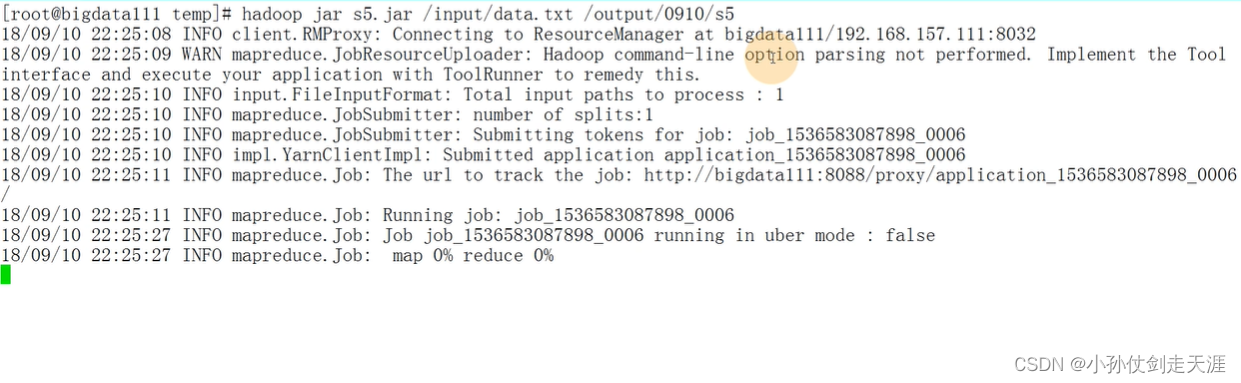
6.2.2.2 字符串排序
默认字典顺序。可以改变默认的排序规则(创建自己的比较器即可),以WordCount程序举例如下。
其他程序不变,仅新建一个自己的比较规则类,以及修改main方法,指定自己的比较规则。
MyTextComparator.java
//针对是Text的数据结构,定义自己的比较结构 public class MyTextComparator extends Text.Comparator { @Override public int compare(byte[] b1, int s1, int l1, byte[] b2, int s2, int l2) { return -super.compare(b1, s1, l1, b2, s2, l2); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
WordCountMain.java
public class WordCountMain { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, InterruptedException, ClassNotFoundException { //1、创建一个任务,指定任务的入口 Job job = Job.getInstance(new Configuration()); job.setJarByClass(WordCountMain.class); //2、指定任务的map和map输出的数据类型 job.setMapperClass(WordCountMap.class); job.setMapOutputKeyClass(Text.class); job.setMapOutputValueClass(IntWritable.class); // 指定自己的比较规则 job.setSortComparatorClass(MyTextComparator.class); //3、指定任务的Reduce job.setReducerClass(WordCountReduce.class); job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class); job.setOutputValueClass(IntWritable.class); //4、指定任务的输入路径、任务的输出路径 FileInputFormat.setInputPaths(job, new Path(args[0])); FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path(args[1])); //5、执行任务 job.waitForCompletion(true); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
6.2.1.3 对象的排序
6.2.1.3.1 复习SQL排序
order by (后面) + 列名、表达式、别名、序号
select * from emp order by sal; select empno, ename, sal, sal * 12, from emp order by sal * 12 desc; select empno, ename, sal, sal * 12 annlsal, from emp order by annlsal desc; select empno, ename, sal, sal * 12 annlsal, from emp order by 4 desc;- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
desc 只作用于最近的一列,下述语句仅对 sal 排序起作用。
select * from emp order by sal desc; select * from emp order by deptno, sal desc;- 1
- 2
- 3
补充知识:在Oracle数据库中,查询的结果不是原来的表,是Oracle创建的临时表数据
6.2.1.3.2 Java对象排序
Java 的对象排序,实现 java.lang接口 Comparable 接口
Student.java
/学生对象:按照学生的age年龄进行排序 public class Student implements Comparable<Student>{ private int stuID; private String stuName; private int age; public Student(int stuID, String stuName, int age) { this.stuID = stuID; this.stuName = stuName; this.age = age; } @Override public String toString() { return "Student{" + "stuID=" + stuID + ", stuName='" + stuName + '\'' + ", age=" + age + '}'; } @Override public int compareTo(Student o) { //定义排序规则:按照学生的age年龄进行排序 if (this.age >= o.getAge()){ return 1; }else { return -1; } } public int getStuID() { return stuID; } public void setStuID(int stuID) { this.stuID = stuID; } public String getStuName() { return stuName; } public void setStuName(String stuName) { this.stuName = stuName; } public int getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(int age) { this.age = age; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
StudentMain.java
public class StudentMain { public static void main(String[] args) { //创建几个学生对象 Student s1 = new Student(1, "Tom", 24); Student s2 = new Student(2, "Mary", 26); Student s3 = new Student(3, "Mike", 25); //创建数组排序 Student[] stuList = {s1, s2, s3}; Arrays.sort(stuList); for (Student student : stuList) System.out.println(student); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
6.2.1.3.3 MapReduce的对象排序
前提:
- 该对象必须是Key2
- 必须实现hadooop的序列化接口,Writable接口
- 对象必须是可排序的,类似 Java 的对象排序,java.lang接口 Comparable
案例1:实现员工表一个列的mr排序
Emp.java
//代表员工 //数据:7654,MARTIN,SALESMAN,7698,1998/9/29,1250,1400,30 public class Emp implements WritableComparable<Emp> { private int empno;//员工号 private String ename;//员工姓名 private String job;//职位 private int mgr;//经理的员工号 private String hiredate;//加入时间 private int sal;//月薪 private int comm;//奖金 private int deptno;//部门编号 @Override public int compareTo(Emp o) { //定义自己的排序规则:一个列的排序 //按照薪水排序 if (this.sal >= o.getSal()) return 1; else return -1; } @Override public String toString() { return "Emp{" + "empno=" + empno + ", ename='" + ename + '\'' + ", sal=" + sal + ", deptno=" + deptno + '}'; } @Override public void write(DataOutput dataOutput) throws IOException { //实现序列化,把对象输出到输出流 dataOutput.writeInt(this.empno); dataOutput.writeUTF(this.ename); dataOutput.writeUTF(this.job); dataOutput.writeInt(this.mgr); dataOutput.writeUTF(this.hiredate); dataOutput.writeInt(this.sal); dataOutput.writeInt(this.comm); dataOutput.writeInt(this.deptno); } @Override public void readFields(DataInput dataInput) throws IOException { //实现反序列化,从输入流中读取对象 this.empno = dataInput.readInt(); this.ename = dataInput.readUTF(); this.job = dataInput.readUTF(); this.mgr = dataInput.readInt(); this.hiredate = dataInput.readUTF(); this.sal = dataInput.readInt(); this.comm = dataInput.readInt(); this.deptno = dataInput.readInt(); } public int getEmpno() { return empno; } public void setEmpno(int empno) { this.empno = empno; } public String getEname() { return ename; } public void setEname(String ename) { this.ename = ename; } public String getJob() { return job; } public void setJob(String job) { this.job = job; } public int getMgr() { return mgr; } public void setMgr(int mgr) { this.mgr = mgr; } public String getHiredate() { return hiredate; } public void setHiredate(String hiredate) { this.hiredate = hiredate; } public int getSal() { return sal; } public void setSal(int sal) { this.sal = sal; } public int getComm() { return comm; } public void setComm(int comm) { this.comm = comm; } public int getDeptno() { return deptno; } public void setDeptno(int deptno) { this.deptno = deptno; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
EmpSortMapper.java
/** * 一定要把Emp作为Key2 * 没有value2,返回null值 */ public class EmpSortMapper extends Mapper<LongWritable, Text, Emp, NullWritable> { @Override protected void map(LongWritable key1, Text value1, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException { //数据:7654,MARTIN,SALESMAN,7698,1998/9/29,1250,1400,30 String data = value1.toString(); String[] words = data.split(","); Emp emp = new Emp(); emp.setEmpno(Integer.parseInt(words[0])); emp.setEname(words[1]); emp.setJob(words[2]); emp.setMgr(Integer.parseInt(words[3])); emp.setHiredate(words[4]); emp.setSal(Integer.parseInt(words[5])); emp.setComm(Integer.parseInt(words[6])); emp.setDeptno(Integer.parseInt(words[7])); context.write(emp, NullWritable.get()); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
EmpSortMain.java
public class EmpSortMain { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { //1、创建一个任务,指定任务的入口 Job job = Job.getInstance(new Configuration()); job.setJarByClass(EmpSortMain.class); //2、指定任务的map和map输出的数据类型 job.setMapperClass(EmpSortMapper.class); job.setMapOutputKeyClass(Emp.class);//k2是员工对象 job.setMapOutputValueClass(NullWritable.class);//v2是空值 //3、指定任务输出的数据类型 job.setOutputKeyClass(Emp.class); job.setOutputValueClass(NullWritable.class); //4、指定任务的输入路径、任务的输出路径 FileInputFormat.setInputPaths(job, new Path(args[0])); FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path(args[1])); //5、执行任务 job.waitForCompletion(true); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23

案例2:实现员工表多个列的mr排序
仅修改mr对象中的排序规则,规则代码对下
@Override public int compareTo(Emp o) { //定义自己的排序规则:多个列的排序 //先按照部门号进行排序,在按照薪水进行排序 if (this.deptno > o.getDeptno()) return 1; else if (this.deptno < o.getDeptno()){ return -1; } //再按照薪水排序 if (this.sal >= o.getSal()) return 1; else return -1; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16


6.2.3 分区Partition
6.2.3.1 概念
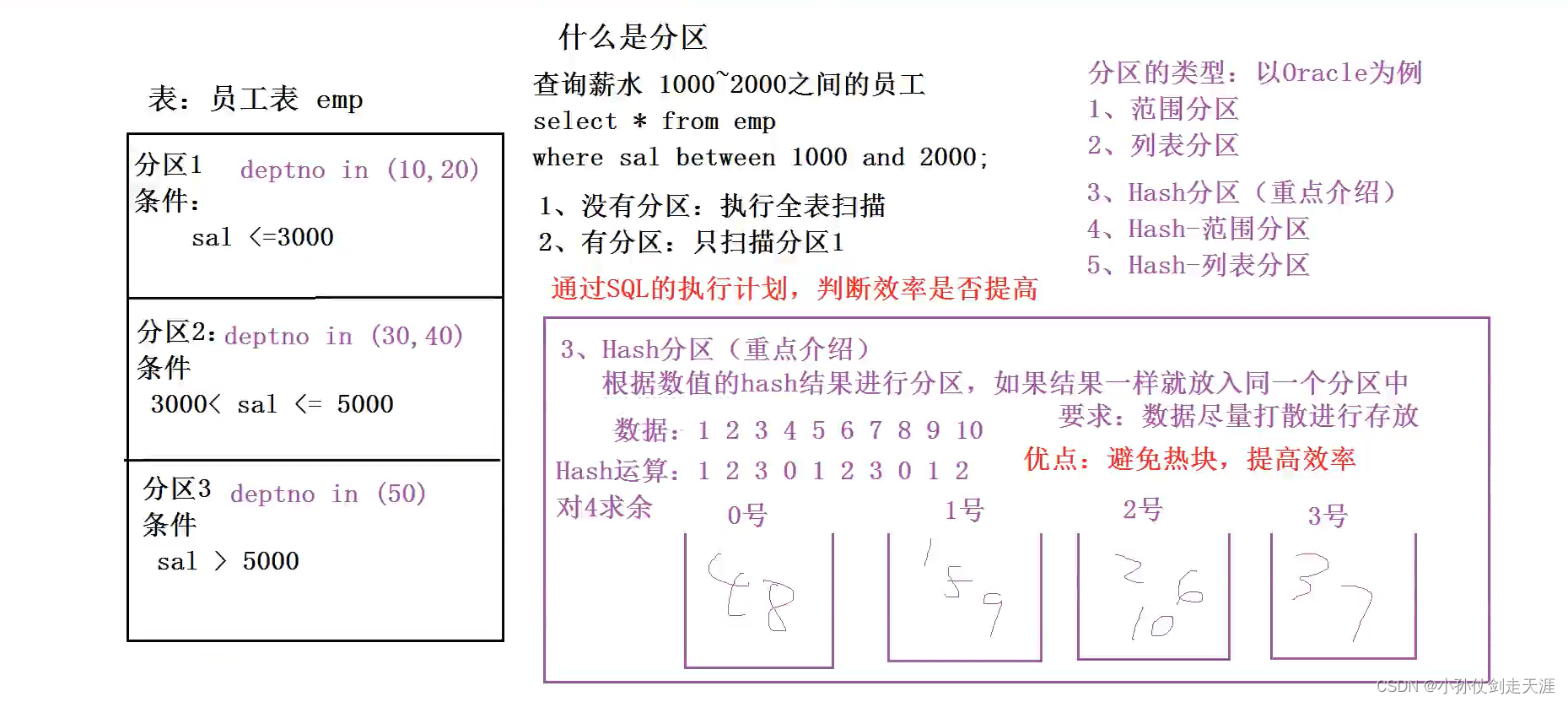
什么是分区(partition)? 结合关系型数据库Oracle说明
6.2.3.2 MapReduce的分区
1、默认情况下,MapReduce只有一个分区(只有一个输出文件)
2、MapReduce的分区根据 Map 的输出<key2, value2>进行分区
3、自定义分区:
Demo: 按照员工的部门号进行分区,相同部门号的员工输出到一个分区中
Emp.java 与 6.3.1.2 Mapreduce的序列化中的Emp对象一样
MyPartitioner.java
//自定义的分区规则:按照部门号进行分区 k2 部门号 v2 员工对象 public class MyPartitioner extends Partitioner<IntWritable, Emp> { /** * //建立我们的分区规则 * @param k2 部门号 * @param v2 员工对象 * @param numTask 分区的个数 * @return 分区号 */ @Override public int getPartition(IntWritable k2, Emp v2, int numTask) { //得到该员工的部门号 int deptno = v2.getDeptno(); if (deptno == 10){ return 1 % numTask; }else if (deptno == 20){ return 2 % numTask; }else { return 3 % numTask; } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
MyPartitionMapper.java
public class MyPartitionMapper extends Mapper<LongWritable, Text, IntWritable, Emp> { @Override protected void map(LongWritable key1, Text value1, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException { //数据:7654,MARTIN,SALESMAN,7698,1998/9/29,1250,1400,30 String data = value1.toString(); String[] words = data.split(","); Emp emp = new Emp(); emp.setEmpno(Integer.parseInt(words[0])); emp.setEname(words[1]); emp.setJob(words[2]); emp.setMgr(Integer.parseInt(words[3])); emp.setHiredate(words[4]); emp.setSal(Integer.parseInt(words[5])); emp.setComm(Integer.parseInt(words[6])); emp.setDeptno(Integer.parseInt(words[7])); //输出员工对象 k2 :部门号 context.write(new IntWritable(emp.getDeptno()), emp); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
MyPartitionReducer.java
public class MyPartitionReducer extends Reducer<IntWritable, Emp, IntWritable, Emp> { @Override protected void reduce(IntWritable key3, Iterable<Emp> values3, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException { for (Emp emp : values3){ context.write(key3, emp); } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
MyPartitionMain.java
public class MyPartitionMain { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { //1、创建一个任务,指定任务的入口 Job job = Job.getInstance(new Configuration()); job.setJarByClass(MyPartitionMain.class); //2、指定任务的map和map输出的数据类型 job.setMapperClass(MyPartitionMapper.class); job.setMapOutputKeyClass(IntWritable.class);//k2是部门号 job.setMapOutputValueClass(Emp.class);//v2输出是员工对象 //加入分区规则 job.setPartitionerClass(MyPartitioner.class); //指定分区的个数 job.setNumReduceTasks(3); //3、指定任务输出的数据类型 job.setOutputKeyClass(IntWritable.class); job.setOutputValueClass(Emp.class); //4、指定任务的输入路径、任务的输出路径 FileInputFormat.setInputPaths(job, new Path(args[0])); FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path(args[1])); //5、执行任务 job.waitForCompletion(true); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
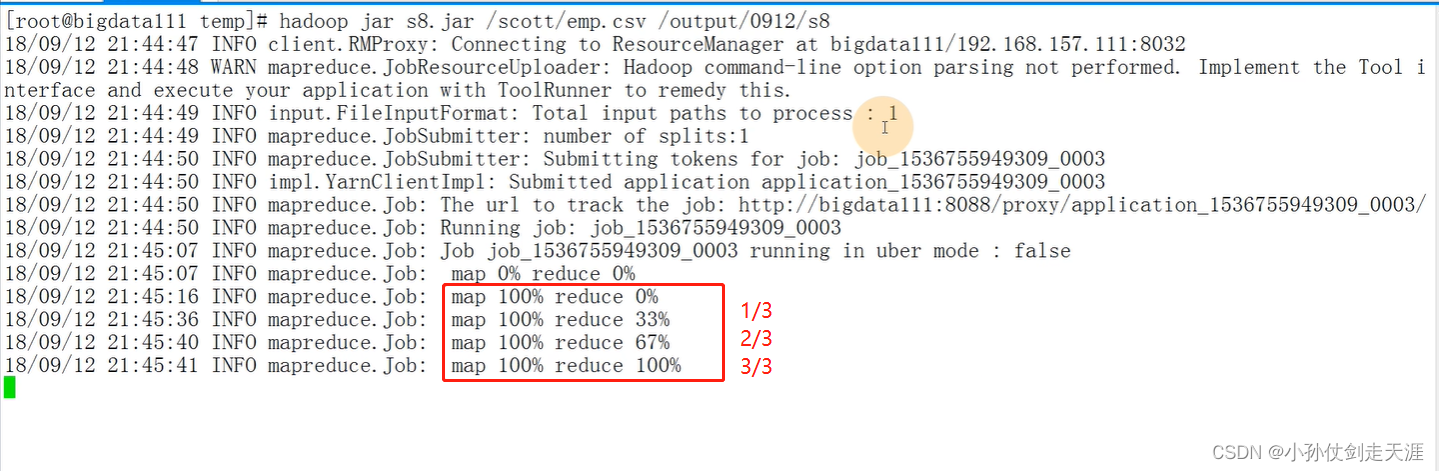
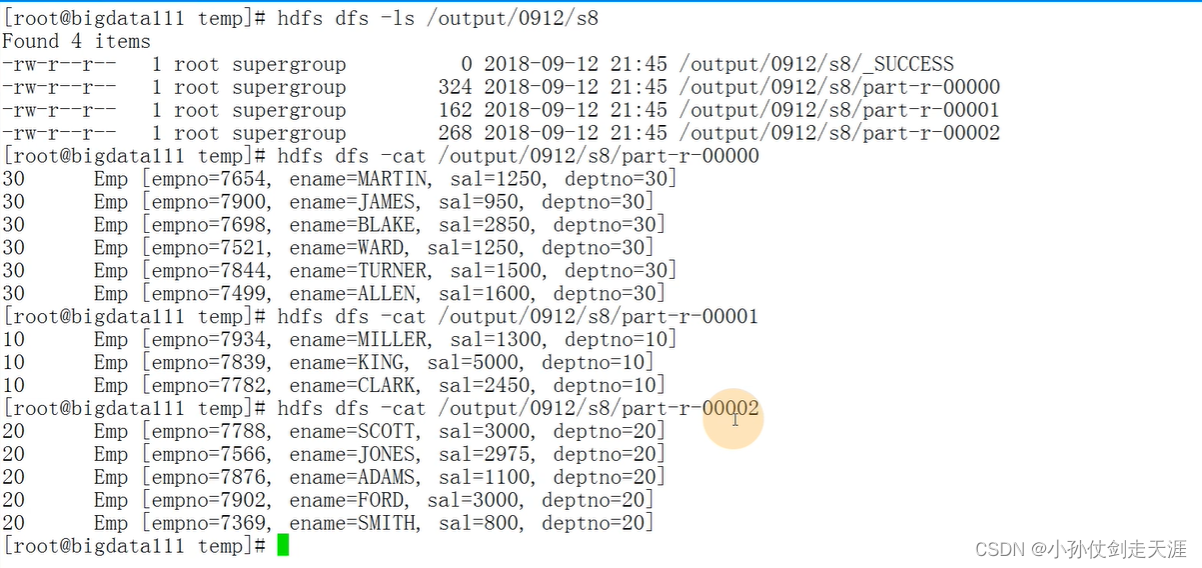
执行程序
6.2.4 合并combiner
6.2.4.1 概念
1、合并(Combiner)是一种特殊的 reducer
2、作用:合并是在 Map 端执行一次合并,用于减少 Map 输出到 Reducer 的数据量,可以提高效率。
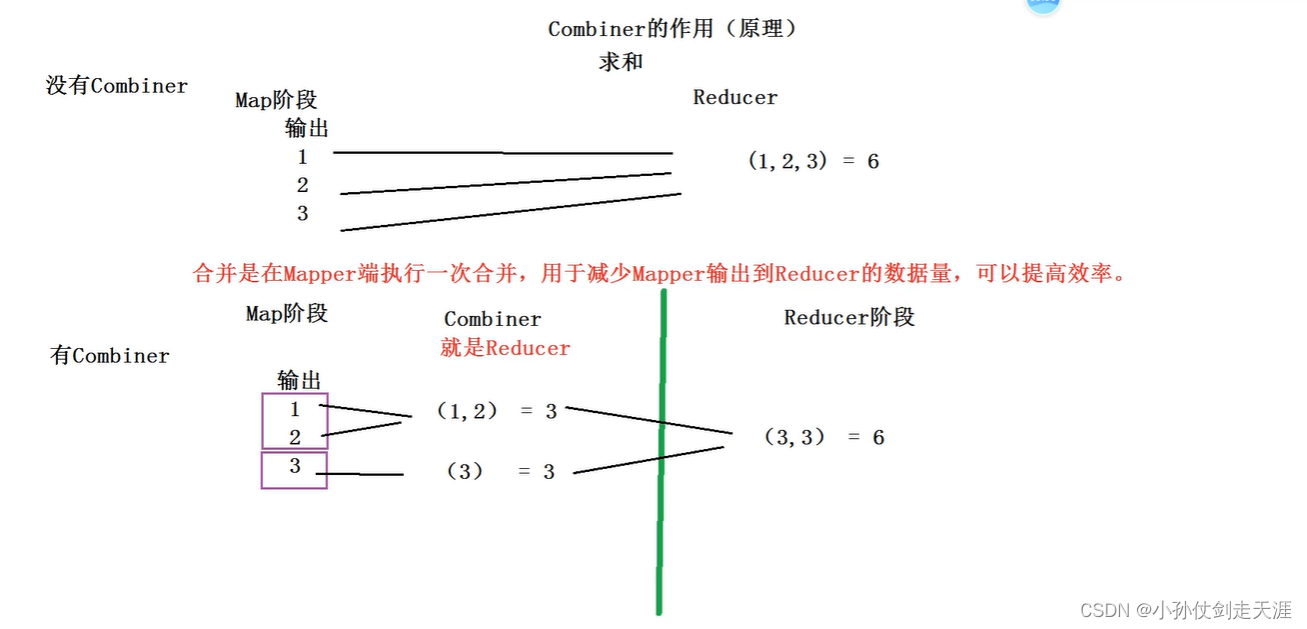
3、举例:以 WordCount 为例
仅仅在**6.1.1.2 开发程序 **小节的 WordCount.java 程序中加入 Combiner,如下
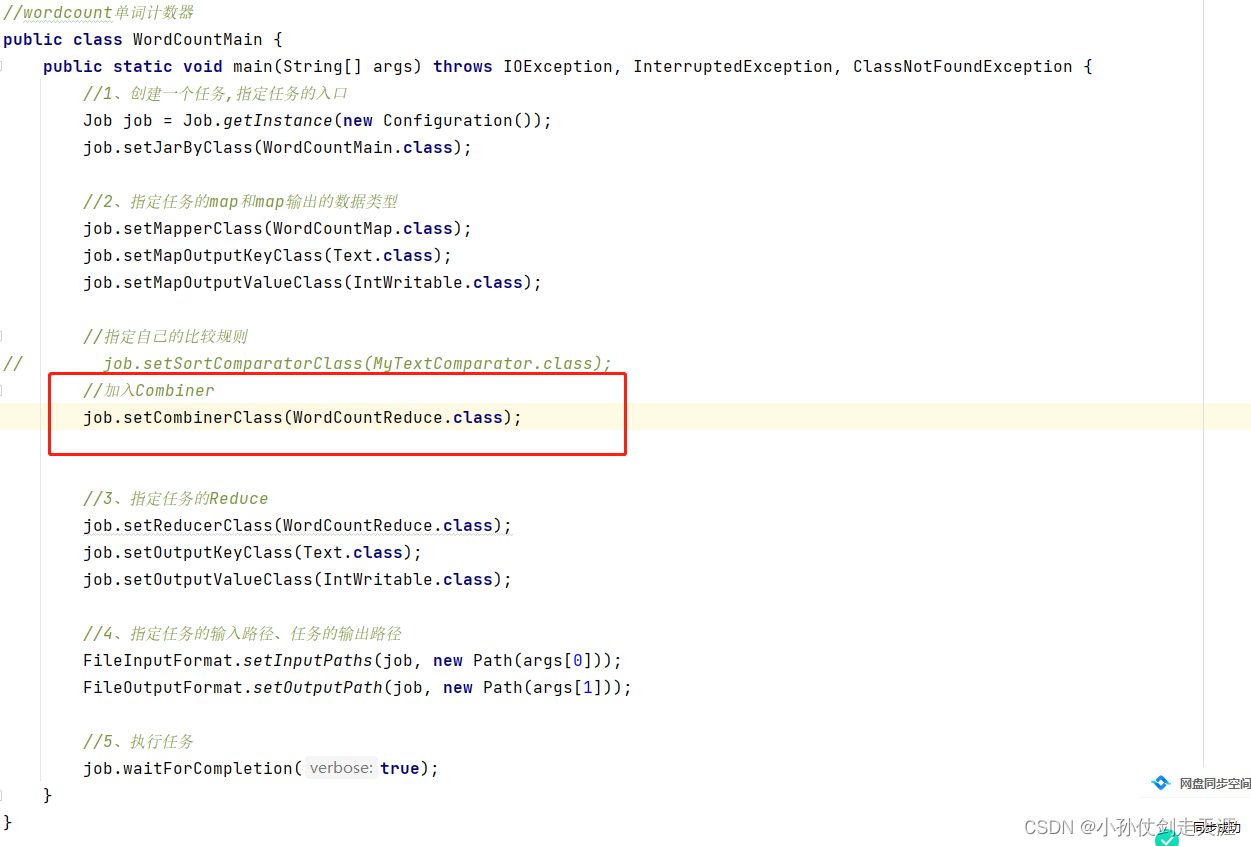
6.2.4.2 Combiner 的注意事项
使用 Combiner 的注意事项:
- 求平均值
- 不管有没有使用 combiner,都不能改变 Map 和 Reducer 对应数据的类型
正常情况:没有引入Combiner
AvgSalaryMapper.java
public class AvgSalaryMapper extends Mapper<LongWritable, Text, Text, IntWritable> { @Override protected void map(LongWritable key1, Text value1, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException { String data = value1.toString(); String[] words = data.split(","); context.write(new Text("salary"), new IntWritable(Integer.parseInt(words[5]))); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
AvgSalaryReducer.java
public class AvgSalaryReducer extends Reducer<Text, IntWritable, Text, DoubleWritable> { @Override protected void reduce(Text key3, Iterable<IntWritable> values3, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException { int total = 0; int count = 0; for (IntWritable salary : values3){ total += salary.get();//工资求和 count++;//人数加一 } context.write(new Text("The avg salary is :"), new DoubleWritable(total / count)); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
AvgSalaryMain.java
public class AvgSalaryMain { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { //1、创建一个任务,指定任务的入口 Job job = Job.getInstance(new Configuration()); job.setJarByClass(AvgSalaryMain.class); //2、指定任务的map和map输出的数据类型 job.setMapperClass(AvgSalaryMapper.class); job.setMapOutputKeyClass(Text.class);//k2是部门号 job.setMapOutputValueClass(IntWritable.class);//v2输出是员工对象 //加入combiner job.setCombinerClass(AvgSalaryReducer.class); //3、指定任务输出的数据类型 job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class); job.setOutputValueClass(DoubleWritable.class); //4、指定任务的输入路径、任务的输出路径 FileInputFormat.setInputPaths(job, new Path(args[0])); FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path(args[1])); //5、执行任务 job.waitForCompletion(true); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26

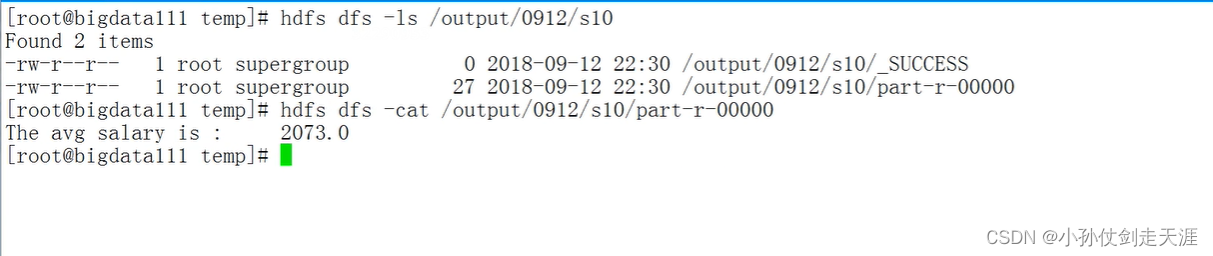
异常情况:引入Combiner
在 map 和 Reducer 的中间添加 Combiner
//2、指定任务的map和map输出的数据类型 ... //加入combiner job.setCombinerClass(AvgSalaryReducer.class); //4、指定任务的输入路径、任务的输出路径 ...- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8


6.2.5 洗牌 Shuffle
参数文件 配置参数 参考值 yarn-site.xml yarn.nodemanager.aux-services mapreduce_shuffle 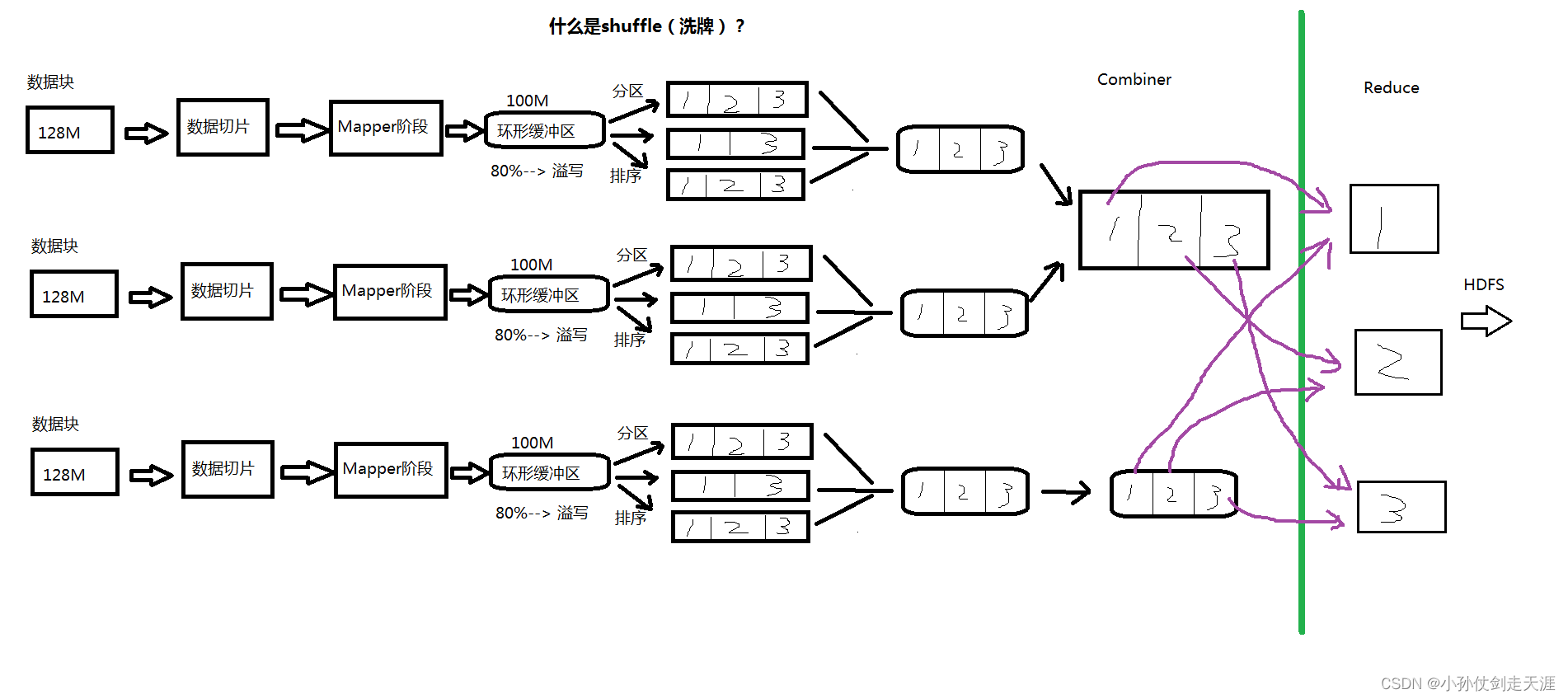
- Hadoop 3.x以前:会有数据的落地(产生I/O操作),速度会比较慢,上图会产生6次 I/O 操作(读进来、分区排序、combiner2次、map-reduce-hdfs2次)
- spark会产生两次 I/O 操作。(读进来、写进去各一次)
-
相关阅读:
人工智能基础_机器学习030_ElasticNet弹性网络_弹性回归的使用---人工智能工作笔记0070
【数学建模】2023数学建模国赛C题完整思路和代码解析
系统平台:新店如何打造爆款
P1996 约瑟夫问题 题解
在机器学习领域中,One-Hot Encoding是什么
java计算机毕业设计高校在线办公系统源程序+mysql+系统+lw文档+远程调试
【数模之数据分析-1】
RPC 框架设计 四、Netty高级应用
ctfshow 反序列化篇(下)
(附源码)ssm码农论坛 毕业设计 231126
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/m0_66345324/article/details/125600876
