-
C# 更加优质的操作MongoDB数据库
C# 更加优质的操作MongoDB数据库
之前就写过一篇C#操作MongoDB数据库的文章,直接对数据库进行操作,不是很优化,代码在实际项目中比较零散,没有一个统一的规划,所以有了这篇文章,如果要入门的化看看之前的文章也可以进行项目的开发了C# 操作Mongodb数据库
- 因为我们要进行mongodb数据库的操作,但我们业务层面不想直接跟数据库打交道,所以做了一个中间层ORM(代理映射) 下面我们开始实现这个ORM 步骤如下
- 还是使用之前的库
MongoDB.Driver
目录结构
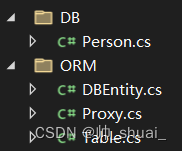
分别解释一下:- 真正的中间层是ORM文件夹下的3个文件,而DB文件夹下的Person是测试文件!
- DBEntity.cs 这是MongoDB的所有的表中的实体的基类~我们自定义的实体类都要集成于DBEntity,例如Person类
- Proxy.cs 这是一个代理类,任何一个具体的Table类都有一个对应的Proxy代理类
- Table.cs 这是一个表,说白了,我们业务层面只用接触这个Table类即可,通过Table类进行增删改查!
DBEntity.cs 完整代码
using MongoDB.Bson; using MongoDB.Bson.Serialization.Attributes; using System; namespace Common.ORM { [Serializable] [BsonIgnoreExtraElements(Inherited = true)] public abstract class DBEntity { public DBEntity() { ID = ObjectId.GenerateNewId().ToString(); } [BsonElement("_id")] [BsonRepresentation(BsonType.ObjectId)] public virtual string ID { get; set; } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
Proxy.cs 完整代码
using MongoDB.Bson.Serialization; using MongoDB.Driver; using System; namespace Common.ORM { public static class Proxy<T> { /// <summary> /// 数据库表的名字 /// </summary> private static string tableName; /// <summary> /// 数据库名字 /// </summary> private static string dataBaseName; /// <summary> /// 数据库连接配置Url /// </summary> private static string mongoUrl; /// <summary> /// 数据库单个表的引用(即mongo的单个集合) /// </summary> private static IMongoCollection<T> collection; /// <summary> /// 数据库单个表的引用(即mongo的单个集合) /// </summary> public static IMongoCollection<T> Collection { get => collection; } /// <summary> /// 静态构造函数 (注意:不允许出现访问控制符) /// </summary> static Proxy() { Init(); } /// <summary> /// 单个表的初始化函数 /// </summary> private static void Init() { dataBaseName = "TestMongoDB"; mongoUrl = "mongodb://localhost:27017"; tableName = typeof(T).Name; BsonClassMap.RegisterClassMap<T>(cm => cm.AutoMap()); collection = new MongoClient(mongoUrl).GetDatabase(dataBaseName).GetCollection<T>(tableName); } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
Table.cs 完整代码
using MongoDB.Bson; using MongoDB.Driver; using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq.Expressions; using System.Reflection; namespace Common.ORM { public class Table<T> where T : DBEntity { /// <summary> /// 对应的集合的引用 /// </summary> private IMongoCollection<T> collection = Proxy<T>.Collection; /// <summary> /// 增加一条记录 /// </summary> /// <param name="entity"></param> /// <returns></returns> public bool Add(T entity) { try { collection.InsertOne(entity); return true; } catch (Exception ex) { throw ex; } } /// <summary> /// 删除一条记录 /// </summary> /// <param name="entity"></param> /// <param name="conditions"></param> /// <returns></returns> public bool Delete(T entity, Expression<Func<T, bool>> conditions = null) { try { string _id = string.Empty; if (conditions == null) { foreach (PropertyInfo item in entity.GetType().GetProperties()) { if (item.Name == "ID" && item.GetValue(entity) != null) { _id = item.GetValue(entity).ToString(); DeleteResult result = collection.DeleteOne(new BsonDocument("_id", BsonValue.Create(new ObjectId(_id)))); return result.IsAcknowledged; } } } DeleteResult res = collection.DeleteOne(conditions); return res.IsAcknowledged; } catch (Exception ex) { throw ex; } } /// <summary> /// 更新一条记录 /// </summary> /// <param name="entity"></param> /// <param name="conditions"></param> /// <returns></returns> public bool Update(T entity, Expression<Func<T, bool>> conditions = null) { try { ObjectId _id; var options = new ReplaceOptions() { IsUpsert = true }; if (conditions == null) { foreach (var item in entity.GetType().GetProperties()) { if (item.Name == "ID" && item.GetValue(entity) != null) { _id = new ObjectId(item.GetValue(entity).ToString()); ReplaceOneResult result = collection.ReplaceOne(new BsonDocument("_id", BsonValue.Create(_id)), entity, options); return result.IsAcknowledged; } } } ReplaceOneResult res = collection.ReplaceOne(conditions, entity, options); return res.IsAcknowledged; } catch (Exception ex) { throw ex; } } /// <summary> /// 查找一条记录 /// </summary> /// <param name="conditions"></param> /// <returns></returns> public List<T> Find(Expression<Func<T, bool>> conditions = null) { try { if (conditions == null) { conditions = t => true; } return collection.Find(conditions).ToList() ?? new List<T>(); } catch (Exception ex) { throw ex; } } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
- 134
Person.cs 完整代码
using Common.ORM; using MongoDB.Bson.Serialization.Attributes; using System; using System.Collections.Generic; namespace Common.DB { [Serializable] public class Person : DBEntity { [BsonConstructor] public Person(string name, int age, string guid, GenderEnum gender) { Name = name; Age = age; Guid = guid; Gender = gender; } public override string ToString() { return "ID:" + ID + " " + "user:" + Name + " " + "age:" + Age + " " + "guid:" + Guid + " " + "Gender:" + Gender.ToString() + " " + "宠物叫" + Pet.Name + "," + Pet.Age + "岁了"; } public string Name { get; set; } public int Age { get; set; } public string Guid { get; set; } public GenderEnum Gender { get; set; } public List<Person> Students { get => students; set => students = value; } public Pet Pet { get => pet; set => pet = value; } private Pet pet; private List<Person> students; } public enum GenderEnum { 男, 女 } public class Pet { public string Name { get => name; set => name = value; } public int Age { get => age; set => age = value; } private string name; private int age; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
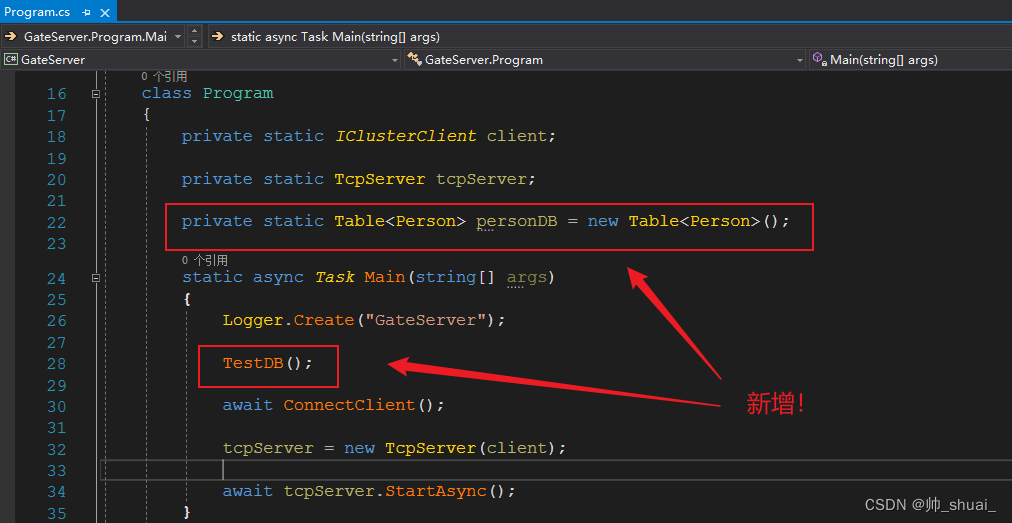
测试
ORM的框架部分以上就整理完了,下面我们来使用它!
private static void TestDB() { Person person = new Person("张三", 8, Guid.NewGuid().ToString(), GenderEnum.男); person.Students = new List<Person>() { new Person("张小三1", 8, Guid.NewGuid().ToString(), GenderEnum.男), new Person("张小三2", 8, Guid.NewGuid().ToString(), GenderEnum.男), new Person("张小三3", 8, Guid.NewGuid().ToString(), GenderEnum.男), new Person("张小三4", 8, Guid.NewGuid().ToString(), GenderEnum.男) }; person.Pet = new Pet() { Name = "旺财", Age = 3 }; personDB.Add(person); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
-
相关阅读:
20. 有效的括号-栈的应用
完整实现-通过DelayQueue实现延时任务
标记肽Bz-Pro-Phe-Arg-pNA、59188-28-2
【Rust日报】2022-09-14 使用 Rust 构建简单博客 && 华为实习生招募
DETR纯代码分享(十)matcher.py(models)匈牙利匹配算法
img图片丢失后默认图
OpenCV图像处理学习十三,图像金字塔——高斯金字塔和拉普拉斯金字塔
【Java IO模型系列教程-目录大纲】
顾客点餐系统-----操作菜品JDBC代码的编写(2)
xss跨站脚本攻击
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/zzzsss123333/article/details/125597530
