-
669. 修剪二叉搜索树 ●●
669. 修剪二叉搜索树 ●●
给你二叉搜索树的根节点 root ,同时给定最小边界 low 和最大边界 high。通过修剪二叉搜索树,使得所有节点的值在
[low, high]中。修剪树 不应该 改变保留在树中的元素的相对结构 (即,如果没有被移除,原有的父代子代关系都应当保留)。 可以证明,存在 唯一的答案 。
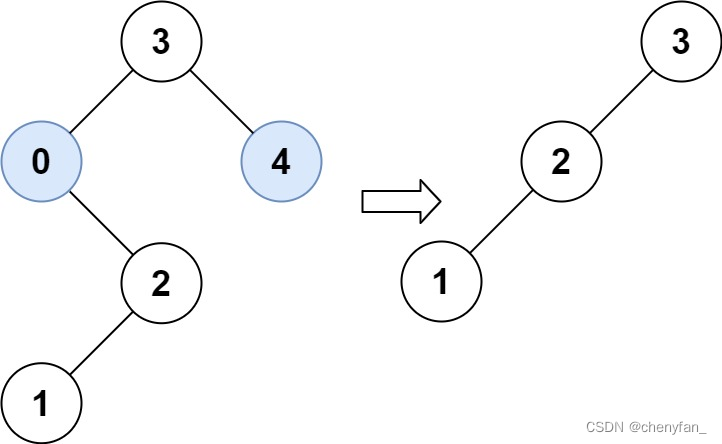
输入:root = [3,0,4,null,2,null,null,1], low = 1, high = 3
输出:[3,2,null,1]对于二叉搜索树,
如果root->val < low,那么修剪后的二叉树一定出现在根节点的右边;
如果root->val > high,那么修剪后的二叉树一定出现在根节点的左边。递归
时间复杂度:O(N),其中 N 是给定的树的全部节点。我们最多访问每个节点一次。
空间复杂度:O(N),即使我们没有明确使用任何额外的内存,在最糟糕的情况下,我们递归调用的栈可能与节点数一样大。- 从上往下遍历,在对某一节点进行修剪操作后,还需要重新再判断一次该节点(返回修剪后的子树);
class Solution { public: TreeNode* pre = nullptr; TreeNode* trimBST(TreeNode* root, int low, int high) { if(root == nullptr) return nullptr; if(root->val < low){ return trimBST(root->right, low, high); // 返回修剪后的右子树 }else if(root->val > high){ return trimBST(root->left, low, high); // 返回修剪后的左子树 } root->left = trimBST(root->left, low, high); // 修剪左子树 root->right = trimBST(root->right, low, high); // 修剪右子树 return root; } };- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 从下往上遍历,修剪子树不影响上面节点的结构,同时不需要重新判断某一节点也能遍历完成整棵树。
class Solution { public: TreeNode* pre = nullptr; TreeNode* trimBST(TreeNode* root, int low, int high) { if(root == nullptr) return nullptr; root->left = trimBST(root->left, low, high); root->right = trimBST(root->right, low, high); if(root->val < low){ // root->left = nullptr; // 删除左子树 return root->right; // 并用右子树替换该节点 }else if(root->val > high){ // root->right = nullptr; // 删除右子树 return root->left; // 并用左子树替换该节点 } return root; } };- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
迭代
由于搜索树的有序性,因此不需要用栈来模拟递归过程,处理过程为:
- 先将根节点 root 移动到区间范围内,确定新的根节点;
- 处理当前根节点左子树中不符合条件的节点;
- 处理当前根节点右子树中不符合条件的节点。
class Solution { public: TreeNode* trimBST(TreeNode* root, int low, int high) { if(root == nullptr) return nullptr; // 确定在区间内的根节点 while(root != nullptr){ if(root->val < low){ root = root->right; }else if(root->val > high){ root = root->left; }else{ break; } } // 此时root已经在[low, high] 范围内,处理左孩子元素小于low的情况 TreeNode* curr = root; while(curr != nullptr){ // 【注意此处为while循环,直到找到符合条件 > low 的左子节点进行替换】 while(curr->left != nullptr && curr->left->val < low){ curr->left = curr->left->right; } curr = curr->left; } // 此时root已经在[low, high] 范围内,处理右孩子大于high的情况 curr = root; while(curr != nullptr){ // 【注意此处为while循环】 while(curr->right != nullptr && curr->right->val > high){ curr->right = curr->right->left; } curr = curr->right; } return root; } };- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
-
相关阅读:
Java之IO流详解(二)——字节流
【DR_CAN-MPC学习笔记】1.最优化控制和MPC基本概念
阿里P7Java最全面试296题:阿里天猫、蚂蚁金服含答案文档解析,备战金九银十!
vue-插件
Shell脚本——提取目录名和文件名
Spring Boot、Spring Cloud 自定义配置文件(如何整合配置中心)
李宏毅2022机器学习HW3 Image Classification
Win11 2022 Edge浏览器解决教资报名(浏览器不兼容)问题
【Git】Git 的基本操作 -- 详解
大数据高级开发工程师——Spark学习笔记(9)
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_19887221/article/details/125596727
