-
Android退出应用后是否需要关闭数据库?
1、SQLiteOpenHelper
Android 系统为我们提供了 SQLiteOpenHelper 辅助完成 SQLiteDatabase 的创建,通过 getReadableDatabase / getWriteableDatabase 方法分别获取只读或可读/写的 SQLiteDatabase 对象;
//获得一个只读的数据库 public SQLiteDatabase getReadableDatabase() { synchronized (this) { return getDatabaseLocked(false); } } //获得一个可读写的数据库 public SQLiteDatabase getWritableDatabase() { synchronized (this) { return getDatabaseLocked(true); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
2、SQLiteDatabase
SQLiteDatabase执行open方法! private void open() { try { try { //调用onpenInner openInner(); } catch (SQLiteDatabaseCorruptException ex) { //这里回调DatabaseErrorHandler onCorruption(); openInner(); } } catch (SQLiteException ex) { Log.e(TAG, "Failed to open database '" + getLabel() + "'.", ex); close(); throw ex; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
SQLiteDatabase 的openInner方法中会执行 的数据库连接池 SQLiteConnectionPool的open方法:
//这里直接调用了 openInner 方法 private void openInner() { //mLock是ConnectionPoolLocked synchronized (mLock) { assert mConnectionPoolLocked == null; //该mConfigurationLocked就是在构造方法中创建的SQLiteDatabaseConfiguartion //打开数据库连接池,ConfigurationLocked作为参数 mConnectionPoolLocked = SQLiteConnectionPool.open(mConfigurationLocked); mCloseGuardLocked.open("close"); } synchronized (sActiveDatabases) { //缓存当前SQLiteDatabase实例 //sActiveDatabases是WeakHashMap sActiveDatabases.put(this, null); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
3、SQLiteConnectionPool 连接缓存池
SQLiteConnectionPool主要为提高数据库并发访问性能;
SQLiteDatabase 会传入配置信息 SQLiteDatabaseConfiguration ,从而创建创建 SQLiteConnectionPool 连接池,包括连接池大小、WAL 模式、空闲连接超时等。
private SQLiteConnectionPool(SQLiteDatabaseConfiguration configuration) { //copyOnWrite模式吧 mConfiguration = new SQLiteDatabaseConfiguration(configuration); //设置连接池的大小 setMaxConnectionPoolSizeLocked(); // If timeout is set, setup idle connection handler // In case of MAX_VALUE - idle connections are never closed //在Long.MAX_VALUE下永远不会关闭连接 if (mConfiguration.idleConnectionTimeoutMs != Long.MAX_VALUE) { setupIdleConnectionHandler(Looper.getMainLooper(), mConfiguration.idleConnectionTimeoutMs); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
这里的setupIdleConnectionHandler方法是为了设置闲置时间的IdleConnectionHandler;他就是普通的一个android中的Handler,会执行倒计时的任务 如果在闲置时间内没有复用SQLiteConnection,那么这个连接就会被回收释放掉
public void setupIdleConnectionHandler(Looper looper, long timeoutMs) { synchronized (mLock) { //创建IdleConnectionHandler,超时管理的Handler mIdleConnectionHandler = new IdleConnectionHandler(looper, timeoutMs); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
4、SQLiteConnection 数据库操作真实的类:
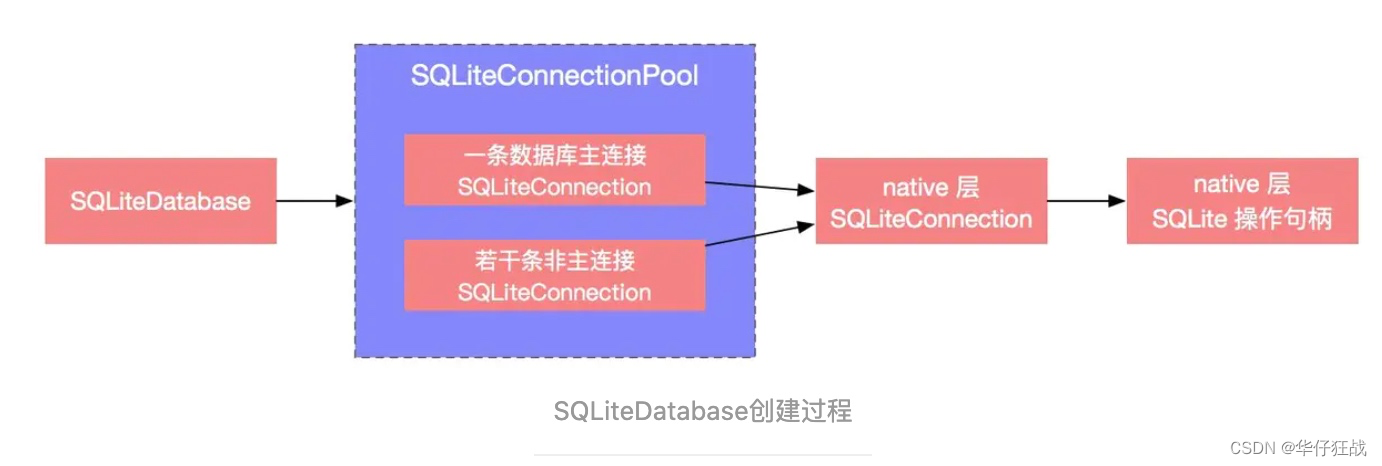
SQLiteConnectionPool 缓存所有数据库操作连接 SQLiteConnection。数据库连接池 SQLiteConnectionPool 被创建后,会默认创建一个数据库主连接 SQLiteConnection。他负责写入操作,以及其他的非主连接SQLiteConnection;非主连接会放入一个List列表里面。每个 Java 层 SQLiteConnection 对应一个 native 层 SQLiteConnection,每个 SQLiteConnection 中持有对应 native 层的匿名内存描述符 mConnectionPtr
SQLiteDatabase 的操作最后都交由 SQLiteConnection 来完成;SQLiteConnection 表示一条数据库操作连接,是真正执行数据库操作开始的地方。SQLiteConnection的open方法:
private void open() { //创建数据库操作句柄 //同一个句柄同一时间只能有同一个线程在操作 //SQLiteDatabase使用ThreadLocal解决多线程操作问题 mConnectionPtr = nativeOpen(mConfiguration.path, mConfiguration.openFlags, mConfiguration.label, SQLiteDebug.DEBUG_SQL_STATEMENTS, SQLiteDebug.DEBUG_SQL_TIME, mConfiguration.lookasideSlotSize, mConfiguration.lookasideSlotCount); //设置页缓存大小 setPageSize(); setForeignKeyModeFromConfiguration(); //根据Configuration设置WAL模式 setWalModeFromConfiguration(); //设置日志限制大小 setJournalSizeLimit(); //设置检查点信息 setAutoCheckpointInterval(); setLocaleFromConfiguration(); // Register custom functions. final int functionCount = mConfiguration.customFunctions.size(); for (int i = 0; i < functionCount; i++) { SQLiteCustomFunction function = mConfiguration.customFunctions.get(i); nativeRegisterCustomFunction(mConnectionPtr, function); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
这里通过 nativeOpen 方法获取一个数据库操作连接(native 层 SQLiteConnection),每个 Java 层 SQLiteConnection 都会对应一个 native 层 SQLiteConnection 数据库连接。每个 native 层 SQLiteConnection 都会持有一个数据库操作句柄:
static jlong nativeOpen(JNIEnv* env, jclass clazz, jstring pathStr, jint openFlags, jstring labelStr, jboolean enableTrace, jboolean enableProfile) { int sqliteFlags; if (openFlags & SQLiteConnection::CREATE_IF_NECESSARY) { sqliteFlags = SQLITE_OPEN_READWRITE | SQLITE_OPEN_CREATE; } else if (openFlags & SQLiteConnection::OPEN_READONLY) { sqliteFlags = SQLITE_OPEN_READONLY; } else { sqliteFlags = SQLITE_OPEN_READWRITE; } const char* pathChars = env->GetStringUTFChars(pathStr, NULL); String8 path(pathChars); env->ReleaseStringUTFChars(pathStr, pathChars); const char* labelChars = env->GetStringUTFChars(labelStr, NULL); String8 label(labelChars); env->ReleaseStringUTFChars(labelStr, labelChars); //数据库操作句柄 sqlite3* db; //打开一个数据库 int err = sqlite3_open_v2(path.string(), &db, sqliteFlags, NULL); if (err != SQLITE_OK) { //是否正确打开 throw_sqlite3_exception_errcode(env, err, "Could not open database"); return 0; } // Check that the database is really read/write when that is what we asked for. if ((sqliteFlags & SQLITE_OPEN_READWRITE) && sqlite3_db_readonly(db, NULL)) { //如果打开数据库模式与当前不匹配 throw_sqlite3_exception(env, db, "Could not open the database in read/write mode."); sqlite3_close(db); return 0; } // Set the default busy handler to retry automatically before returning SQLITE_BUSY. err = sqlite3_busy_timeout(db, BUSY_TIMEOUT_MS); if (err != SQLITE_OK) { //设置默认超时机制 throw_sqlite3_exception(env, db, "Could not set busy timeout"); sqlite3_close(db); return 0; } // Register custom Android functions. err = register_android_functions(db, UTF16_STORAGE); if (err) { throw_sqlite3_exception(env, db, "Could not register Android SQL functions."); sqlite3_close(db); return 0; } // Create wrapper object. //创建数据库连接,内部持有数据库操作句柄 SQLiteConnection* connection = new SQLiteConnection(db, openFlags, path, label); // Enable tracing and profiling if requested. if (enableTrace) { sqlite3_trace(db, &sqliteTraceCallback, connection); } if (enableProfile) { sqlite3_profile(db, &sqliteProfileCallback, connection); } ALOGV("Opened connection %p with label '%s'", db, label.string()); return reinterpret_cast<jlong>(connection); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
这里就是 native层 打开数据库进行的操作,这个mConnectionPtr 底层数据库的句柄 就是我们操作数据库的关键了
比如我们查询数据库 都是通过这 mConnectionPtr
public int executeForCursorWindow(String sql, Object[] bindArgs, CursorWindow window, int startPos, int requiredPos, boolean countAllRows, CancellationSignal cancellationSignal) { // ... 省略 try { //获取复用编译SQL语句后的对象 final PreparedStatement statement = acquirePreparedStatement(sql); try { try { //mConnectionPtr对应native层SQLiteConnection //mStatementPtr对应nativePrepardStatement //mWindowPtr对应native的CursorWindow,存放查询结果集 final long result = nativeExecuteForCursorWindow( mConnectionPtr, statement.mStatementPtr, window.mWindowPtr, startPos, requiredPos, countAllRows); actualPos = (int)(result >> 32); countedRows = (int)result; filledRows = window.getNumRows(); window.setStartPosition(actualPos); return countedRows; } finally { detachCancellationSignal(cancellationSignal); } } finally { releasePreparedStatement(statement); } } catch (RuntimeException ex) { mRecentOperations.failOperation(cookie, ex); throw ex; } finally { //...省略 } // ... 省略 }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
这里面的关键方法 在mConnectionPtr这个句柄了。
nativeExecuteForCursorWindow(mConnectionPtr, statement.mStatementPtr, window.mWindowPtr, startPos, requiredPos, countAllRows);- 1
- 2
5、总结:
SQLiteOpenHelper帮我们创建getReadableDatabase / getWriteableDatabase 分别获取只读或可读/写的 SQLiteDatabase 对象
而SQLiteDatabase对象创建了SQLiteConnectionPool 连接池,主要为提高数据库并发访问性能。
SQLiteConnectionPool里面缓存了很多的SQLiteConnection连接;Java层的SQLiteConnection 对应一个 native 层 SQLiteConnection,每个 SQLiteConnection 中又包含一个数据库操作句柄;通过这个native的句柄 就可以操作底层数据库了
SQLiteConnection创建的的时候设置定时器;如果使用完了但是没到时间,可以给其他的数据库操作使用!
闲置时间久没有使用,就回收这个SQLiteConnection 释放底层数据库的句柄!下次如果想使用SQLiteConnection,没办法复用的,就可以创建新的SQLiteConnection
所以如果你不关闭数据库,那么时间久了 也会自己关闭的!
-
相关阅读:
正则表达式
红与黑(bfs + dfs 解法)(算法图论基础入门)
vue的第3篇 第一个vue程序
【Java快速入门】Java语言的数组(七)
再谈函数的栈帧
79 C++ STL pair(对组)
【结构体】
谈谈数字化转型晓知识
【复杂网络】网络科学导论学习笔记-第五章节点重要性与相似性
1160 队列安排
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/huazai30000/article/details/125565411
