-
开发一个禁止删除namespace的控制器
微信公众号:运维开发故事,作者:乔克
大家好,我是乔克。
image.png
昨天收到一个朋友的信息,说不小心把集群的业务namespace干掉了,导致整个业务都停滞了,问我有没有禁止删除namespace的方案。
在我的记忆里,Kubernetes的准入里并没有这个控制器,所以我就给他说需要自己开发一个准入控制器来实现自己的目标。
作为人,何为正确!我不能只脱裤子,不放屁。所以这里也整理了一下如何自定义Kubernetes的准入控制器。理论介绍
准入控制器(Admission Controller)位于 API Server 中,在对象被持久化之前,准入控制器拦截对 API Server 的请求,一般用来做身份验证和授权。其中包含两个特殊的控制器:MutatingAdmissionWebhook 和 ValidatingAdmissionWebhook。
-
MutatingAdmissionWebhook :用于变更请求对象,比如istio为每个Pod注入sidecar,就是通过它实现。
-
ValidatingAdmissionWebhook:用于验证请求对象
整个准入控制器的流程如下:
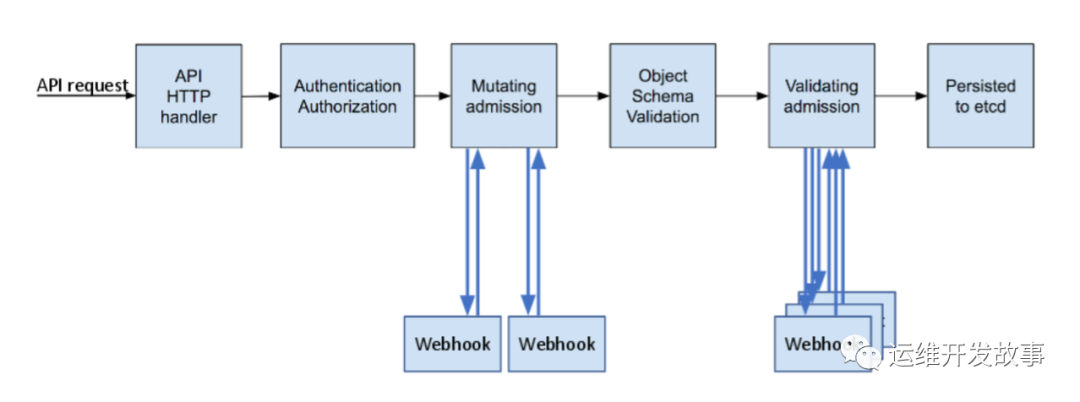
当 API 请求进入时,mutating 和 validating 控制器使用配置中的外部 webhooks 列表并发调用,规则如下:
-
如果所有的 webhooks 批准请求,准入控制链继续流转。
-
如果有任意一个 webhooks 阻止请求,那么准入控制请求终止,并返回第一个 webhook 阻止的原因。其中,多个 webhooks 阻止也只会返回第一个 webhook 阻止的原因。
-
如果在调用 webhook 过程中发生错误,那么请求会被终止或者忽略 webhook。
准入控制器是在 API Server 的启动参数中配置的。一个准入控制器可能属于以上两者中的一种,也可能两者都属于。
我们在部署 Kubernetes 集群的时候都会默认开启一系列准入控制器,如果没有设置这些准入控制器的话可以说你的 Kubernetes 集群就是在裸奔,应该叫管理员为集群添加准入控制器。
代码实现
实现逻辑
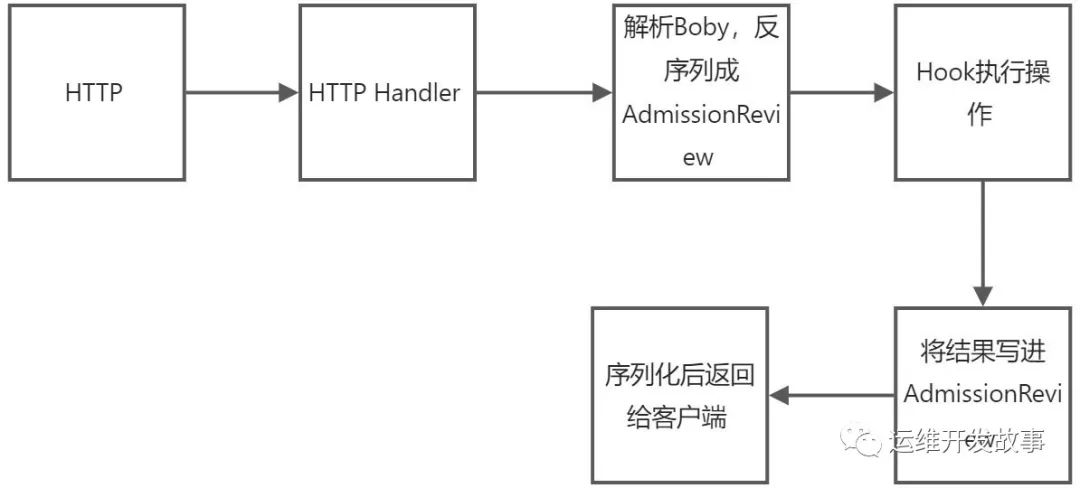
在开发之前先大致了解一下准入控制器的Webhook的大致实现逻辑:
-
Webhook是一个标准的HTTP服务,接收HTTP请求
-
接收到的请求是一个AdmissionReview对象
-
然后我们自定义的Hook会处理这个AdmissionReview对象
-
处理完过后再返回一个AdmissionReview对象,这里面会包含处理结果
AdmissionReview的结构体如下:
// AdmissionReview describes an admission review request/response. type AdmissionReview struct { metav1.TypeMeta `json:",inline"` // Request describes the attributes for the admission request. // +optional Request *AdmissionRequest `json:"request,omitempty" protobuf:"bytes,1,opt,name=request"` // Response describes the attributes for the admission response. // +optional Response *AdmissionResponse `json:"response,omitempty" protobuf:"bytes,2,opt,name=response"` }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
从代码的命名中可以很清晰的看出,在请求发送到 WebHook 时我们只需要关注内部的 AdmissionRequest(实际入参),在我们编写的 WebHook 处理完成后只需要返回包含有 AdmissionResponse(实际返回体) 的 AdmissionReview 对象即可;总的来说 AdmissionReview 对象是个套壳,请求是里面的 AdmissionRequest,响应是里面的 AdmissionResponse。
具体实现
(1)首先创建一个HTTP Server,监听端口,接收请求
package main import ( "context" "flag" "github.com/joker-bai/validate-namespace/http" log "k8s.io/klog/v2" "os" "os/signal" "syscall" ) var ( tlscert, tlskey, port string ) func main() { flag.StringVar(&tlscert, "tlscert", "/etc/certs/cert.pem", "Path to the TLS certificate") flag.StringVar(&tlskey, "tlskey", "/etc/certs/key.pem", "Path to the TLS key") flag.StringVar(&port, "port", "8443", "The port to listen") flag.Parse() server := http.NewServer(port) go func() { if err := server.ListenAndServeTLS(tlscert, tlskey); err != nil { log.Errorf("Failed to listen and serve: %v", err) } }() log.Infof("Server running in port: %s", port) // listen shutdown signal signalChan := make(chan os.Signal, 1) signal.Notify(signalChan, syscall.SIGINT, syscall.SIGTERM) <-signalChan log.Info("Shutdown gracefully...") if err := server.Shutdown(context.Background()); err != nil { log.Error(err) } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
由于准入控制器和Webhook之间需要使用TLS进行通信,所以上面监听的端口是TLS端口,通过
server.ListenAndServeTLS实现,后续在部署服务的时候需要把证书挂到相应的目录中。(2)定义Handler,将请求分发到具体的处理方法
package http import ( "fmt" "github.com/joker-bai/validate-namespace/namespace" "net/http" ) // NewServer creates and return a http.Server func NewServer(port string) *http.Server { // Instances hooks nsValidation := namespace.NewValidationHook() // Routers ah := newAdmissionHandler() mux := http.NewServeMux() mux.Handle("/healthz", healthz()) mux.Handle("/validate/delete-namespace", ah.Serve(nsValidation)) return &http.Server{ Addr: fmt.Sprintf(":%s", port), Handler: mux, } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
实现admissionHandler,主要作用是将http body的内容解析成AdmissionReview对象,然后调用具体的Hook处理,再将结果放到AdmissionReview中,返回给客户端。
package http import ( "encoding/json" "fmt" "io" "net/http" "github.com/douglasmakey/admissioncontroller" "k8s.io/api/admission/v1beta1" admission "k8s.io/api/admission/v1beta1" meta "k8s.io/apimachinery/pkg/apis/meta/v1" "k8s.io/apimachinery/pkg/runtime" "k8s.io/apimachinery/pkg/runtime/serializer" log "k8s.io/klog/v2" ) // admissionHandler represents the HTTP handler for an admission webhook type admissionHandler struct { decoder runtime.Decoder } // newAdmissionHandler returns an instance of AdmissionHandler func newAdmissionHandler() *admissionHandler { return &admissionHandler{ decoder: serializer.NewCodecFactory(runtime.NewScheme()).UniversalDeserializer(), } } // Serve returns a http.HandlerFunc for an admission webhook func (h *admissionHandler) Serve(hook admissioncontroller.Hook) http.HandlerFunc { return func(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) { w.Header().Set("Content-Type", "application/json") if r.Method != http.MethodPost { http.Error(w, fmt.Sprint("invalid method only POST requests are allowed"), http.StatusMethodNotAllowed) return } if contentType := r.Header.Get("Content-Type"); contentType != "application/json" { http.Error(w, fmt.Sprint("only content type 'application/json' is supported"), http.StatusBadRequest) return } body, err := io.ReadAll(r.Body) if err != nil { http.Error(w, fmt.Sprintf("could not read request body: %v", err), http.StatusBadRequest) return } var review admission.AdmissionReview if _, _, err := h.decoder.Decode(body, nil, &review); err != nil { http.Error(w, fmt.Sprintf("could not deserialize request: %v", err), http.StatusBadRequest) return } if review.Request == nil { http.Error(w, "malformed admission review: request is nil", http.StatusBadRequest) return } result, err := hook.Execute(review.Request) if err != nil { log.Error(err) w.WriteHeader(http.StatusInternalServerError) return } admissionResponse := v1beta1.AdmissionReview{ Response: &v1beta1.AdmissionResponse{ UID: review.Request.UID, Allowed: result.Allowed, Result: &meta.Status{Message: result.Msg}, }, } res, err := json.Marshal(admissionResponse) if err != nil { log.Error(err) http.Error(w, fmt.Sprintf("could not marshal response: %v", err), http.StatusInternalServerError) return } log.Infof("Webhook [%s - %s] - Allowed: %t", r.URL.Path, review.Request.Operation, result.Allowed) w.WriteHeader(http.StatusOK) w.Write(res) } } func healthz() http.HandlerFunc { return func(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) { w.WriteHeader(http.StatusOK) w.Write([]byte("ok")) } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
上面处理是通过
hook.Execute来处理请求,这是admissionController内部实现的一个结构体,它为每个操作定义了一个方法,如下:// AdmitFunc defines how to process an admission request type AdmitFunc func(request *admission.AdmissionRequest) (*Result, error) // Hook represents the set of functions for each operation in an admission webhook. type Hook struct { Create AdmitFunc Delete AdmitFunc Update AdmitFunc Connect AdmitFunc }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
我们就需要实现具体的AdmitFunc,并注册。
(3)将自己实现的方法注册到Hook中。
package namespace import ( "github.com/douglasmakey/admissioncontroller" ) // NewValidationHook delete namespace validation hook func NewValidationHook() admissioncontroller.Hook { return admissioncontroller.Hook{ Delete: validateDelete(), } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
(4)实现具体的AdmitFunc
package namespace import ( "github.com/douglasmakey/admissioncontroller" log "k8s.io/klog/v2" "k8s.io/api/admission/v1beta1" ) func validateDelete() admissioncontroller.AdmitFunc { return func(r *v1beta1.AdmissionRequest) (*admissioncontroller.Result, error) { if r.Kind.Kind == "Namespace" { log.Info("You cannot delete namespace: ", r.Name) return &admissioncontroller.Result{Allowed: false}, nil } else { return &admissioncontroller.Result{Allowed: true}, nil } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
这里实现很简单,如果Kind为Namespace,就拒绝操作。
部署测试
上面完成了业务逻辑开发,下面就把它部署到Kubernetes集群测试一番。
部署
(1)编写Dockerfile,将应用打包成镜像
FROM golang:1.17.5 AS build-env ENV GOPROXY https://goproxy.cn ADD . /go/src/app WORKDIR /go/src/app RUN go mod tidy RUN cd cmd && GOOS=linux GOARCH=amd64 go build -v -a -ldflags '-extldflags "-static"' -o /go/src/app/app-server /go/src/app/cmd/main.go FROM registry.cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/coolops/ubuntu:22.04 ENV TZ=Asia/Shanghai COPY --from=build-env /go/src/app/app-server /opt/app-server WORKDIR /opt EXPOSE 80 CMD [ "./app-server" ]- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
(2)创建TLS证书,使用脚本进行创建
#!/bin/bash set -e usage() { cat <<EOF Generate certificate suitable for use with an sidecar-injector webhook service. This script uses k8s' CertificateSigningRequest API to a generate a certificate signed by k8s CA suitable for use with sidecar-injector webhook services. This requires permissions to create and approve CSR. See https://kubernetes.io/docs/tasks/tls/managing-tls-in-a-cluster for detailed explantion and additional instructions. The server key/cert k8s CA cert are stored in a k8s secret. usage: ${0} [OPTIONS] The following flags are required. --service Service name of webhook. --namespace Namespace where webhook service and secret reside. --secret Secret name for CA certificate and server certificate/key pair. EOF exit 1 } while [[ $# -gt 0 ]]; do case ${1} in --service) service="$2" shift ;; --secret) secret="$2" shift ;; --namespace) namespace="$2" shift ;; *) usage ;; esac shift done [ -z ${service} ] && service=validate-delete-namespace [ -z ${secret} ] && secret=validate-delete-namespace-tls [ -z ${namespace} ] && namespace=default if [ ! -x "$(command -v openssl)" ]; then echo "openssl not found" exit 1 fi csrName=${service}.${namespace} tmpdir=$(mktemp -d) echo "creating certs in tmpdir ${tmpdir} " cat <<EOF >> ${tmpdir}/csr.conf [req] req_extensions = v3_req distinguished_name = req_distinguished_name [req_distinguished_name] [ v3_req ] basicConstraints = CA:FALSE keyUsage = nonRepudiation, digitalSignature, keyEncipherment extendedKeyUsage = serverAuth subjectAltName = @alt_names [alt_names] DNS.1 = ${service} DNS.2 = ${service}.${namespace} DNS.3 = ${service}.${namespace}.svc EOF openssl genrsa -out ${tmpdir}/server-key.pem 2048 openssl req -new -key ${tmpdir}/server-key.pem -subj "/CN=${service}.${namespace}.svc" -out ${tmpdir}/server.csr -config ${tmpdir}/csr.conf # clean-up any previously created CSR for our service. Ignore errors if not present. kubectl delete csr ${csrName} 2>/dev/null || true # create server cert/key CSR and send to k8s API cat <<EOF | kubectl create -f - apiVersion: certificates.k8s.io/v1beta1 kind: CertificateSigningRequest metadata: name: ${csrName} spec: groups: - system:authenticated request: $(cat ${tmpdir}/server.csr | base64 | tr -d '\n') usages: - digital signature - key encipherment - server auth EOF # verify CSR has been created while true; do kubectl get csr ${csrName} if [ "$?" -eq 0 ]; then break fi done # approve and fetch the signed certificate kubectl certificate approve ${csrName} # verify certificate has been signed for x in $(seq 10); do serverCert=$(kubectl get csr ${csrName} -o jsonpath='{.status.certificate}') if [[ ${serverCert} != '' ]]; then break fi sleep 1 done if [[ ${serverCert} == '' ]]; then echo "ERROR: After approving csr ${csrName}, the signed certificate did not appear on the resource. Giving up after 10 attempts." >&2 exit 1 fi echo ${serverCert} | openssl base64 -d -A -out ${tmpdir}/server-cert.pem # create the secret with CA cert and server cert/key kubectl create secret generic ${secret} \ --from-file=key.pem=${tmpdir}/server-key.pem \ --from-file=cert.pem=${tmpdir}/server-cert.pem \ --dry-run -o yaml | kubectl -n ${namespace} apply -f -- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
(3)编写Deployment部署服务
apiVersion: apps/v1 kind: Deployment metadata: name: validate-delete-namespace labels: app: validate-delete-namespace spec: replicas: 1 selector: matchLabels: app: validate-delete-namespace template: metadata: labels: app: validate-delete-namespace spec: containers: - name: server image: registry.cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/coolops/validate-delete-namespace:latest imagePullPolicy: Always livenessProbe: httpGet: path: /healthz port: 8443 scheme: HTTPS ports: - containerPort: 8443 volumeMounts: - name: tls-certs mountPath: /etc/certs readOnly: true volumes: - name: tls-certs secret: secretName: validate-delete-namespace-tls --- apiVersion: v1 kind: Service metadata: name: validate-delete-namespace spec: selector: app: validate-delete-namespace ports: - port: 443 targetPort: 8443- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
(4)部署Webhook
apiVersion: admissionregistration.k8s.io/v1beta1 kind: ValidatingWebhookConfiguration metadata: name: validate-delete-namespace webhooks: - name: validate-delete-namespace.default.svc.cluster.local clientConfig: service: namespace: default name: validate-delete-namespace path: "/validate/delete-namespace" caBundle: "${CA_BUNDLE}" rules: - operations: - DELETE apiGroups: - "" apiVersions: - "v1" resources: - namespaces failurePolicy: Ignore- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
这里有一个${CA_BUNDLE}占位符,在创建Webhook的时候要将其替换掉,使用如下命令:
cat ./validate-delete-namespace.yaml | sh ./patch-webhook-ca.sh > ./webhook.yaml- 1
- 2
然后创建webhook.yaml即可。
kubectl apply -f webhook.yaml- 1
- 2
上面的所有文件都在代码库里,可以直接使用脚本进行部署。
# sh deploy.sh creating certs in tmpdir /tmp/tmp.SvMHWcPI6x Generating RSA private key, 2048 bit long modulus ..........................................+++ .............................................................+++ e is 65537 (0x10001) certificatesigningrequest.certificates.k8s.io/validate-delete-namespace.default created NAME AGE REQUESTOR CONDITION validate-delete-namespace.default 0s kubernetes-admin Pending certificatesigningrequest.certificates.k8s.io/validate-delete-namespace.default approved secret/validate-delete-namespace-tls created Creating k8s admission deployment deployment.apps/validate-delete-namespace created service/validate-delete-namespace created validatingwebhookconfiguration.admissionregistration.k8s.io/validate-delete-namespace created- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
执行完成过后,可以查看具体的信息。
# kubectl get po NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE validate-delete-namespace-74c9b8b7bd-5g9zv 1/1 Running 0 3s # kubectl get secret NAME TYPE DATA AGE default-token-kx5wf kubernetes.io/service-account-token 3 72d validate-delete-namespace-tls Opaque 2 53s # kubectl get ValidatingWebhookConfiguration NAME CREATED AT validate-delete-namespace 2022-06-24T09:39:26Z- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
测试
(1)首先打开webhook的pod日志
# kubectl logs validate-delete-namespace-74c9b8b7bd-5g9zv -f I0624 17:39:27.858753 1 main.go:30] Server running in port: 8443- 1
- 2
- 3
(2)创建一个namespace并删除
# kubectl create ns joker # kubectl get ns | grep joker joker Active 4h5m # kubectl delete ns joker Error from server: admission webhook "validate-delete-namespace.default.svc.cluster.local" denied the request without explanation # kubectl get ns | grep joker joker Active 4h5m- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
可以发现我们的删除操作被拒绝了,并且查看namespace还存在。
我们也可以到日志中查看,如下:
# kubectl logs validate-delete-namespace-74c9b8b7bd-5g9zv -f I0624 17:39:27.858753 1 main.go:30] Server running in port: 8443 2022/06/24 17:43:34 You cannot delete namespace: joker I0624 17:43:34.664945 1 handler.go:94] Webhook [/validate/delete-namespace - DELETE] - Allowed: false 2022/06/24 17:43:34 You cannot delete namespace: joker I0624 17:43:34.667043 1 handler.go:94] Webhook [/validate/delete-namespace - DELETE] - Allowed: false- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
上面就是简单的实现了一个准入控制器,
只要思想不滑坡,办法总比困难多。感谢万能的百度,感谢牛逼的网友。参考
-
https://www.qikqiak.com/post/k8s-admission-webhook
-
https://github.com/douglasmakey/admissioncontroller
-
https://mritd.com/2020/08/19/write-a-dynamic-admission-control-webhook/
我是 乔克,《运维开发故事》公众号团队中的一员,一线运维农民工,云原生实践者,这里不仅有硬核的技术干货,还有我们对技术的思考和感悟,欢迎关注我们的公众号,期待和你一起成长!
-
-
相关阅读:
【嵌入式】STM32控制脉冲个数
7-38 掉入陷阱的数字
Effective Modern C++[实践]->理解模板类别的推导
Java练习 day1(LeetCode简单题15道)
使用HTML制作静态网站:传统文化戏剧锡剧带psd设计图(2个页面)
【Windows网络编程】一.主机相关网络信息编程
java商城免费搭建 VR全景商城 saas商城 b2b2c商城 o2o商城 积分商城 秒杀商城 拼团商城 分销商城 短视频商城
Layui快速入门之第十节 表单
【AI】实现在本地Mac,Windows和Mobile上运行Llama2模型
C语言每日一题(26)移除链表元素
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/wanger5354/article/details/125562450
