-
【C++】string笔记
string
模板:
泛型编程
函数模板
模板关键字:tmplate<calss T> //T可以随意改 template<class T> //template<typename T> 模板参数列表 - 参数类型 void Swap(T& x1, T& x2) //函数参数列表 - 参数对象 { T x = x1; x1 = x2; x2 = x; } 传入不同的类型 会调用不同的实例化函数 多个类型: template<class T1,class T2>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
模板实例化
调用Swap时 会实例化出不同类型的函数
实例化:是指在面向对象的编程中,把用类创建对象的过程称为实例化。 是将一个抽象的概念类,具体到该类实物的过程。 实例化过程中一般由类名对象名= new 类名(参数1,参数2…参数n)构成。函数模板的实例化
template<class T> T Add(const T& left, const T& right)//做返回值 和 { return left + right; } int main() { int a1 = 10, a2 = 20; double d1 = 10.1, d2 = 20.2; cout << Add(a1, a2) << endl; cout << Add(d1, d2) << endl; cout << Add((double)a1, d2) << endl; //显示实例化 cout << Add<int>(d1, d2) << endl; //指定类型 cout << Add<double>(d1, d2) << endl; return 0; } 结果: 30 30.3 30.2 30 30.3- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
如果函数模板 和 普通函数 同时存在,优先使用普通函数
类模板
一个栈类型 只能是 int 或 double 或…
定义对象只能满足 int栈 或者double栈
想要存储多个类型 则需要建多个不同类型的 类template<class T> class Stack { privvate: T* _a; int _top; int _capacity; } int main() { Stack<int> st1;//存储int Stack<double> st2;//存储double }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
STL:
S标准T模板L库
Vue - 前端贡献:尤雨溪书籍推荐
《STL源码剖析》《effcrive C++》 继承多态学完看 《高质量C++》现在看
STL 六大组件
算法、容器、迭代器、配接器、仿函数、空间配置器(内存池)
string 成员函数
c++文档:
https://cplusplus.com/
编码补充
编码 - 值 – 符号建立映射
ASCII码表 - 表示英文编码表
unicode - 表示全世界文字编码表 utf-8
gbk - 中文编码表常用的string
- 赋值
default (1) string();copy (2) string (const string& str);substring (3) string (const string& str, size_t pos, size_t len = npos);from c-string (4) string (const char* s);-
size:计算长度
Return length of string (public member function )
-
capacity:计算空间大小 不算\0 所以是15
Return size of allocated storage (public member function )
-
clear:清除string内容
Clear string (public member function )
-
Request a change in capacity (public member function )
-
operator[ ]:出错断言assert
Get character of string (public member function )
char& operator[] (size_t pos); const char& operator[] (size_t pos) const; 这里的引用返回时为了 修改返回对象- 1
- 2
- 3
读取 s1[i] = s1.operator[] 的重载- 1
- 2

修改 s1[i]+=1;- 1
- 2

-
at:获取字符串的字符,出错抛异常
Get character in string (public member function)
-
operator+=:尾插字符或字符串
Append to string (public member function)
string s1; s1 += ':'; s1 += "hello world"; cout << s1 << endl;- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
-
append:尾插字符串 不常用
Append to string (public member function)
-
push_back:尾插字符 不常用
Append character to string (public member function)
string s1; s1.push_back('a'); s1.append("bcde"); cout << s1 << endl;- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
string 迭代器
//遍历+修改 //方式1:下标+[] //返回对应位置的引用 可以直接修改s1[i] for (size_t i = 0; i < s1.size(); ++i) { s1[i] += 1; } for (size_t i = 0; i < s1.size(); ++i) { cout << s1[i] << " "; } cout << endl;- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
迭代器想象成:像指针一样的类型
end()/begin()
typedef char*iterator; typedef const char*const_iterator; iterator begin(); const_iterator begin() const; iterator end(); const_iterator end() const;- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
string s1("hello world"); //方式2:迭代器(iterator) //begin()指的是第一个元素的位置 end()是最后一个元素的【下一个】 //it像指针一样指向第一个元素 ,可以解引用,可以++ string::iterator it = s1.begin(); while (it != s1.end()) { *it -= 1; ++it; } it = s1.begin();//重置it的位置 while (it != s1.end()) { cout << *it << " "; ++it; } cout << endl;- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
iterator begin();
范围for会替换成迭代器
//方式3:范围for 语法糖用起来很爽很甜 // C++11 linux:-std=c++11 //把s1中的值取出来 赋值给e 自动++ //for (char& e : s1) for (auto& e : s1) //引用 { e += 1; } for (auto e:s1) { cout << e << " "; } cout << endl;- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
const_iterator begin() const;
const 版本只能读取 不能修改
void func(const string& s1) { string::const_iterator it = s1.begin(); //auto it = s1.cbegin(); //cbegin()和cend()代表const while (it != s1.end()) { //*it -= 1; //不能修改 cout << *it << " "; ++it; } cout << endl; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
rbegin() / rend(): 反向迭代器
reverse_iterator rbegin(); const_reverse_iterator rbegin() const;- 1
- 2
- rbegin() 最后一个字符
- rebing()的 ++ 是向前走
- rend()是第一个字符的前一个
void test_string2() { string s1("hello world"); //反向迭代器 //rbegin() 指向最后一个字符 // //反向++ 是逆向的 //string::reverse_iterator rit = s1.rbegin(); // string::reverse_iterator是类型 auto rit = s1.rbegin();//代替上面那句自动推到类型 while (rit != s1.rend()) { cout << *rit << " "; ++rit; } cout << endl; string cstr("hello world"); func(cstr); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
c++11 新增const迭代器
迭代器的意义是什么?
所有的容器都可以使用迭代器这种方式去访问修改
答:
对于string,下标和[]就足够好用,确实可以不用迭代器。
其他容器(数据结构)呢?
(list、map/set 并不支持下标,只有数组才支持[],这些是链表和二叉树并不支持下标+[])
所以迭代器才是通用的方式
string 增容
测试代码
void TestPushBack() { string s; //s.reserve(1000);//申请至少能存储10000个字符的空间 不一定是1000 要空间对其 size_t sz = s.capacity(); cout << "capacity changed: " << sz << '\n'; cout << "making s grow:\n"; for (int i = 0; i < 2000; ++i) { s.push_back('c'); if (sz != s.capacity()) { sz = s.capacity(); cout << "capacity changed: " << sz << '\n'; } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
结果
capacity changed: 15 //本质是16 但是没算\0 有效字符位置有15个 making s grow: capacity changed: 31 //本质是32 但是没算\0 有效字符位置有31个 capacity changed: 47 capacity changed: 70 capacity changed: 105 capacity changed: 157 capacity changed: 235- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
reserve:扩容,只开空间
resize:扩容+初始化
开空间,并给初始值 进行初始化
如果resize扩容比已有数据少,则会删除多余数据,不会改变空间大小
reverse也不会缩容
void test_string3() { string s1; s1.reserve(100); //开空间并初始化 string s2; //s2.resize(100); // 初始化的 \0 s2.resize(100,'x');//指定字符初始化 //resize不会把已有数据覆盖初始化,如果比已有数据小,则会除多余的数据 }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
string 查找
c_str:返回C格式字符串
const char* c_str() const;- 1
void test_string4() { string s("hello world"); cout << s << endl;//流插入 size是多少 打印多少 cout << s.c_str() << endl;//const char* 遇到\0结束 //应用场景 这里fopen的第一个参数需要const char*类型的字符串 string file("test.txt"); FILE* fout = fopen(file.c_str(), "w"); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
find:找位置
:从字符串pos位置开始往后找字符c,返回该字符在字符串中的下标
string (1) size_t find (const string& str, size_t pos = 0) const;c-string (2) size_t find (const char* s, size_t pos = 0) const;buffer (3) size_t find (const char* s, size_t pos, size_t n) const;character (4) size_t find (char c, size_t pos = 0) const;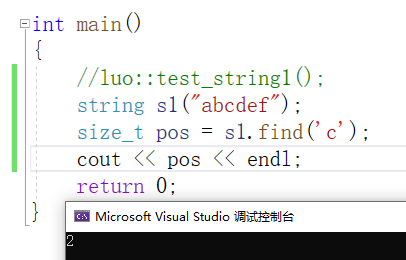
npos:-1
:size_t类型的 -1 一个很大的数
substr:查找字符串
:在str中从pos位置开始,截取n个字符,然后将其返回
string substr (size_t pos = 0, size_t len = npos) const;- 1
string file("test.txt"); FILE* fout = fopen(file.c_str(), "w"); size_t pos = file.find('.'); if (pos != string::npos)//npos是 -1 size_t全1 { //string suffix = file.substr(pos, file.size() - pos); string suffix = file.substr(pos);//直接用默认缺省值 取到最后 cout << suffix << endl; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
如果是连续后缀 ,要从右往左找
rfind:反向找
string file("test.txt.zip"); FILE* fout = fopen(file.c_str(), "w"); size_t pos = file.rfind('.');//这里用rfind if (pos != string::npos) { string suffix = file.substr(pos); cout << suffix << endl; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
-
解析URL
string url("https://www.cplusplus.com/reference/string/string/rfind/"); //取协议 size_t pos1 = url.find(':'); string protocol = url.substr(0, pos1 - 0); cout << protocol << endl; //取域名 size_t pos2 = url.find('/',pos1+3);//冒号+3是w的位置开始找/ string domain = url.substr(pos1 + 3,pos2-(pos1+3)); cout << domain << endl; //取路径 string uri = url.substr(pos2 + 1);//从域名后的/ +1 的位置找到最后 cout << uri << endl; https www.cplusplus.com reference/string/string/rfind/- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
string 插入删除
insert:插入
string (1)** string& insert (size_t pos, const string& str);substring (2) string& insert (size_t pos, const string& str, size_t subpos, size_t sublen);c-string (3) string& insert (size_t pos, const char* s);buffer (4) string& insert (size_t pos, const char* s, size_t n);fill (5)** string& insert (size_t pos, size_t n, char c); void insert (iterator p, size_t n, char c);single character (6)** iterator insert (iterator p, char c);range (7) template <class InputIterator> void insert (iterator p, InputIterator first, InputIterator last);void test_string5() { string s("hello world"); s += ' ';//尾插 s += "!!!"; cout << endl; //头插 效率低 O(N) 尽量少用 s.insert(0, 1, 'x');//在0的位置插入1个x s.insert(s.begin(), 'y');//在头部插入y s.insert(0, "test");//在0的位置插入test cout << s << endl; //中间位置插入,尽量少用 s.insert(4, "&&&&&&"); cout << s << endl; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
erase:删除
sequence (1)** string& erase (size_t pos = 0, size_t len = npos);character (2) iterator erase (iterator p);range (3) iterator erase (iterator first, iterator last);void test_string6() { string s("hello world"); //尽量少用头部和中间的删除,效率低 s.erase(0,1);//删除头上的一个字符 s.erase(s.size()-1,1);//删除尾部的一个字符 cout << s << endl; s.erase(3);//从第三个位置 后面全部删除 cout << s << endl; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
operator+:加
字符串相加,返回新的字符串
// concatenating strings #include <iostream> #include <string> main () { std::string firstlevel ("com"); std::string secondlevel ("cplusplus"); std::string scheme ("http://"); std::string hostname; std::string url; hostname = "www." + secondlevel + '.' + firstlevel; url = scheme + hostname; std::cout << url << '\n'; return 0; } 输出:http://www.cplusplus.com- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
getline:连续获取一行字符串
方法一的代码就是getline的原理,一个字符一个字符的获取!
(1) istream& getline (istream& is, string& str, char delim);(2) istream& getline (istream& is, string& str);#include <iostream> using namespace std; int main() { string s; //cin>>s;//cin读到空格或换行结束 scanf同理 //方法一:一个字符一个字符拿 // char ch = getchar(); // //char ch = cin.get(); // while(ch!='\n') // { // s+=ch; // ch = getchar(); // } //方式二: getline(cin,s); size_t pos = s.rfind(' '); if(pos == string::npos) { cout <<s.size()<<endl; } else{ cout << s.size() - pos-1; } return 0; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
string 比较大小
relational operators:比较大小
(1) bool operator== (const string& lhs, const string& rhs); bool operator== (const char* lhs, const string& rhs); bool operator== (const string& lhs, const char* rhs);(2) bool operator!= (const string& lhs, const string& rhs); bool operator!= (const char* lhs, const string& rhs); bool operator!= (const string& lhs, const char* rhs);(3) bool operator< (const string& lhs, const string& rhs); bool operator< (const char* lhs, const string& rhs); bool operator< (const string& lhs, const char* rhs);(4) bool operator<= (const string& lhs, const string& rhs); bool operator<= (const char* lhs, const string& rhs); bool operator<= (const string& lhs, const char* rhs);(5) bool operator> (const string& lhs, const string& rhs); bool operator> (const char* lhs, const string& rhs); bool operator> (const string& lhs, const char* rhs);(6) bool operator>= (const string& lhs, const string& rhs); bool operator>= (const char* lhs, const string& rhs); bool operator>= (const string& lhs, const char* rhs);void test_string7() { string s1("hello world"); string s2("string"); const char* ps = "char"; cout << (s1 < s2) << endl;//1 cout << (s1 < ps) << endl;//0 cout << ("hhh" < s2) << endl;//1 cout << (s1 < "sss") << endl;//1 }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
C++11 补充
stoi :str转int
int stoi (const string& str, size_t* idx = 0, int base = 10); int stoi (const wstring& str, size_t* idx = 0, int base = 10);- 1
- 2
int val = stoi("1234"); cout << val << endl;- 1
- 2
to_string :int 转 str
string to_string (int val); string to_string (long val); string to_string (long long val); string to_string (unsigned val); string to_string (unsigned long val); string to_string (unsigned long long val); string to_string (float val); string to_string (double val); string to_string (long double val);- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
string str = to_string(3.14); cout << str << endl;//3.140000- 1
- 2
练习题
125. 验证回文串
class Solution { public: bool isLeterOrNumber(char ch) { if(ch>='0' && ch<='9') return true; if(ch>= 'a' && ch<='z') return true; if(ch>='A' && ch<= 'Z') return true; return false; } bool isPalindrome(string s) { int begin = 0,end = s.size()-1; while(begin<end) { while(begin<end && !isLeterOrNumber(s[begin])) ++begin; while(begin<end && !isLeterOrNumber(s[end])) --end; if(tolower(s[begin]) != tolower(s[end])) return false; ++begin; --end; } return true; } };- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
415. 字符串相加

class Solution { public: string addStrings(string num1, string num2) { int end1 = num1.size()-1;int end2 = num2.size()-1; int next = 0;//计算进位 string retStr; while(end1>=0 || end2>=0) { int X1 = 0; if(end1>=0) { X1 = num1[end1]-'0'; --end1; } int X2 = 0; if(end2>=0) { X2 = num2[end2]-'0'; --end2; } int retVal = X1 + X2 + next; if(retVal > 9) { next = 1; retVal -= 10; } else { next = 0; } retStr += retVal+'0'; } if(next == 1) { retStr += '1'; } reverse(retStr.begin(),retStr.end()); return retStr; } };- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
两个swap的区别?
string::swap:string专属
void swap (string& str);- 1
std::swap:全局
适用于内置类型
template <class T> void swap ( T& a, T& b ) { T c(a); a=b; b=c; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
区别:
string::swap对于string效率高,只交换资源,改变指针的指向std::swap对于string会拷贝构造c (深拷贝1)、a=b(深拷贝2)、b=c(深拷贝3) 进行三次string的深拷贝,代价极高浅拷贝问题
1.浅拷贝会析构两次
2.期中一个对象进行修改会影响另一个
引用计数(解决浅拷贝)
如果对象不修改,则只增加了引用计数,不进行深拷贝,提高了效率
缺陷:引用计数存在线程安全问题,需要加锁,在多线程环境下要付出代价,在动态库、静态库中有些场景也会存在问题
当一块空间有多个指针指向,则会增加引用计数,例如2个指针指向 ,则引用计数是2
当指针析构的时候,引用计数不是1 则 会减减引用计数,直到只有一个指针的时候才析构
也就是说10指针指向a,前9个指着都不会析构a空间,只会减减引用计数,只有最后一个指针会析构a空间
写时拷贝
insert/+=/erase等函数中,先查看引用计数,如果引用计数不是1,要先进性深拷贝,再去修改
当引用计数不是1 ,则进行写实拷贝,因为这块空间不是一个指针维护,所以不能修改
开区间取值
0 - 9 的下标是10个有效字符
所以算有效字符是size - 0 (size是最后一个字符的下一个)
string 补充:vs下
class string { private: char _Buf[16]; //字符长度小于16,就存在这个数组_Buf中 char* _Ptr; //大于等于16,就会去堆上申请,存在_Ptr中 size_t _mySize; size_t _myRes; } sizeof() //28字节- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9


-
相关阅读:
Java版本spring cloud + spring boot企业电子招投标系统源代码
CCF CSP认证 历年题目自练Day17
函数相关概念
mysql同步数据到es
No151.精选前端面试题,享受每天的挑战和学习
ARM+Codesys runtime核心板+底板解决方案
C++类与对象初步认识
深入理解Java线程间通信
Python的计算性能优化
面向对象设计原则总结:SOLID/LKP/DRY/KISS…
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/iluo12/article/details/125555988
