-
16.linux应用实现控制led
在Linux系统中有两种操作硬件的方式sysfs文件系统和/dev下的设备节点。对于操作间单的设备例如LED、GPIO通常直接通过操作sysfs文件系统,对于复杂的设备则采用设备节点的方式,例如LCD、触摸屏等。
一、通过sysfs文件系统控制led
什么是sysfs文件系统?
什么是sys文件系统_zhubin0613的博客-CSDN博客_sys文件系统
系统中所有设备根据其功能分到了sys/class目录下,因此sys/class/leds目录便存放了所有LED类的设备。如下图所示的sys-led就是硬件设备的LED文件夹。
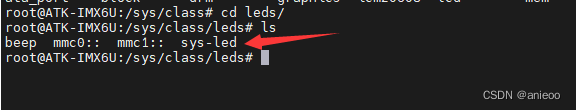
通过命令cd进入该文件夹:

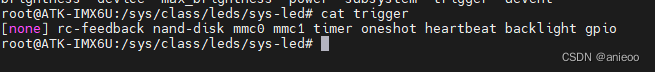
其中最重要的三个文件分别是brightness、 max_brightness 以及 trigger,分别对应亮度、最大亮度等级和触发模式。通过cat命令可以查看触发模式为none即无触发模式,通过写入高低电量led。
编写sysfsled应用程序
- #include <stdio.h>
- #include <stdlib.h>
- #include <sys/types.h>
- #include <sys/stat.h>
- #include <fcntl.h>
- #include <unistd.h>
- #include <string.h>
- #define LED_TRIGGER "/sys/class/leds/sys-led/trigger"
- #define LED_BRIGHTNESS "/sys/class/leds/sys-led/brightness"
- #define USAGE() fprintf(stderr, "usage:\n" \
- " %s <on|off>\n" \
- " %s <trigger> <type>\n", argv[0], argv[0])
- int main(int argc, char *argv[])
- {
- int fd1, fd2;
- /* 校验传参 */
- if (2 > argc) {
- USAGE();
- exit(-1);
- }
- /* 打开文件 */
- fd1 = open(LED_TRIGGER, O_RDWR);
- if (0 > fd1) {
- perror("open error");
- exit(-1);
- }
- fd2 = open(LED_BRIGHTNESS, O_RDWR);
- if (0 > fd2) {
- perror("open error");
- exit(-1);
- }
- /* 根据传参控制 LED */
- if (!strcmp(argv[1], "on")) {
- write(fd1, "none", 4); //先将触发模式设置为 none
- write(fd2, "1", 1); //点亮 LED
- }
- else if (!strcmp(argv[1], "off")) {
- write(fd1, "none", 4); //先将触发模式设置为 none
- write(fd2, "0", 1); //LED 灭
- }
- else if (!strcmp(argv[1], "trigger")) {
- if (3 != argc) {
- USAGE();
- exit(-1);
- }
- if (0 > write(fd1, argv[2], strlen(argv[2])))
- perror("write error");
- }
- else USAGE();
- exit(0);
- }
二、通过/dev设备节点控制LED
驱动的实现:Linux驱动_设备树下LED驱动_anieoo的博客-CSDN博客
在驱动中实现了底层操作硬件led的功能,对于应用层来说只需要通过系统调用传递相应的参数即可操作底层的硬件,本节编写一个应用实现底层led的控制。
代码流程
① 检验命令行参数的完整性
② 通过系统调用打开led文件:检查是否打开正确
③ 向打开led文件获得的文件描述符写入数据:检查是否写入正确数据
④ 关闭文件:检查是否正确关闭
代码
- #include "stdio.h"
- #include "unistd.h"
- #include "sys/types.h"
- #include "sys/stat.h"
- #include "stdlib.h"
- #include "string.h"
- #include "fcntl.h"
- //使用范例:
- // ./ledApp /dev/dtsled 1
- // ./ledApp /dev/dtsled 0
- int main(int argc, char *argv[])
- {
- int retval = 0; //返回值
- int fd; //保存文件描述符
- char *filename; //保存设备节点的路径
- char state[1]; //保存要操作灯的状态 1表示打开 0表示关闭
- if(argc != 3) {
- perror("Error used!\n"); //命令行元素个数不等于,打印使用错误并返回
- exit(-1);
- }
- filename = argv[1]; //保存命令行输入的设备节点路径
- //打开文件
- fd = open(filename, O_RDWR); //以读写权限打开
- if(fd < 0) {
- perror("open failed\n"); //打开失败,打印错误信息
- exit(-1);
- }
- state[0] = atoi(argv[2]);
- /* 向/dev/led文件写入数据 */
- retval = write(fd, state, sizeof(state));
- if(retval < 0){
- perror("write failed\n");
- close(fd);
- exit(-1);
- }
- retval = close(fd); /* 关闭文件 */
- if(retval < 0){
- perror("close failed\n");
- exit(-1);
- }
- exit(0);
- }
-
相关阅读:
计算机毕业设计Java电子病历系统(源码+系统+mysql数据库+lw文档)
汽车Type-C接口:特点与要求解析
自定义vue项目的雷达图组件
【Qt炫酷动画】demo02-仿苹果对话框淡入淡出的动画
前端例程20220906:霓虹灯效按钮
Java代码审计面试
iOS——weak实现原理
vue2 quill 视频上传 ,基于ruoyi vue,oss
Git仓库如何重置成新仓库或者仅留最终版本
洪荒学院 发布全球十大机器人大脑 纵然智障依然有其优劣!
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_42174306/article/details/125543493
