-
蓝旭后端第七次培训课 JDBC
一、JDBC是什么?
JDBC的全称是Java数据库连接(Java Database connect),它是一套用于执行SQL语句的Java API。应用程序可通过这套API连接到关系数据库,并使用SQL语句来完成对数据库中数据的查询、更新和删除等操作。
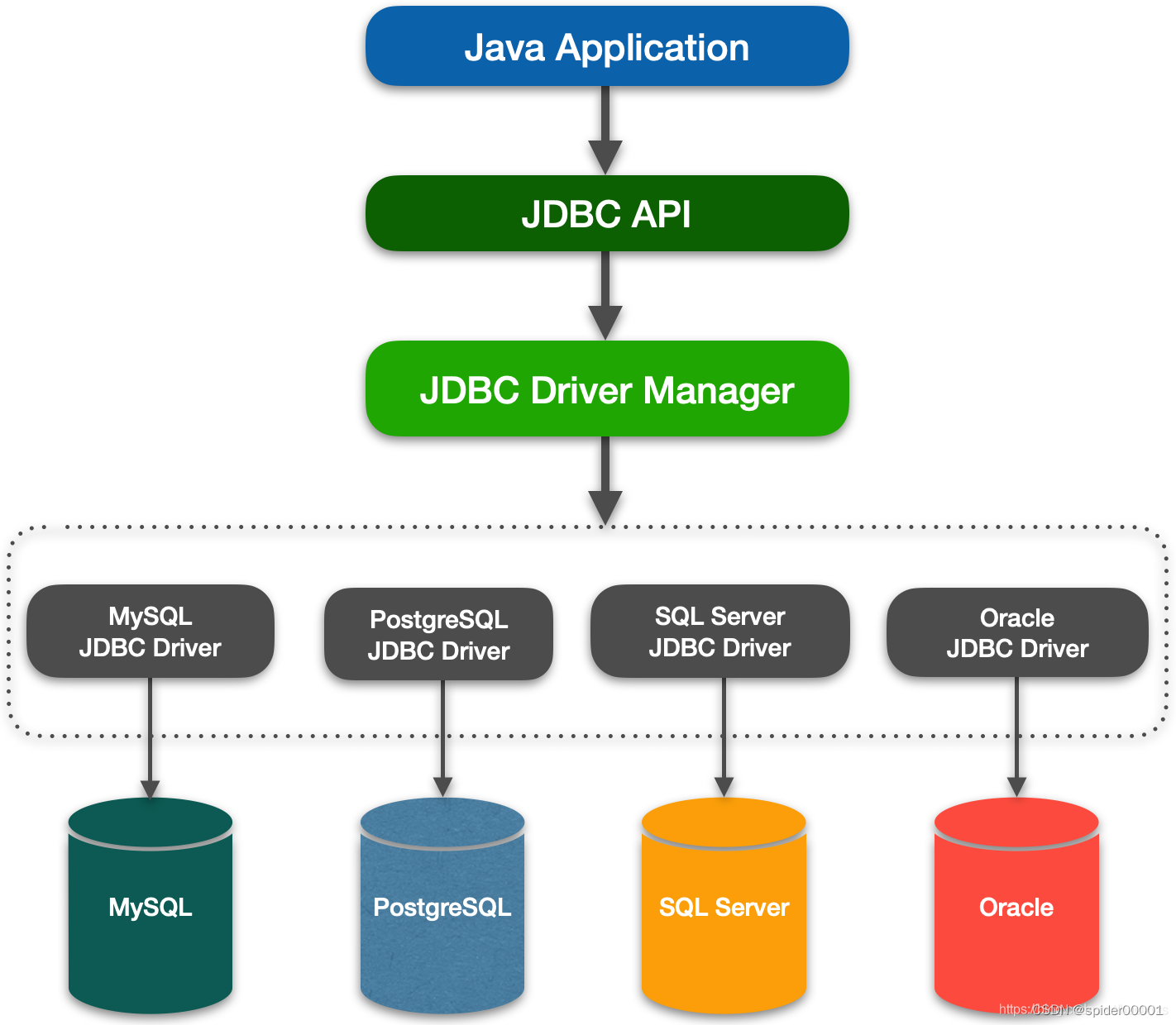
二、Hello JDBC
1.导入mysql驱动
访问MySQL数据库需要用到第三方的类,这些类都被压缩在一个Jar类型的文件里。为了代码能够使用第三方的类,需要为项目导入mysql的专用Jar包。(所需要的jar包自行去mysql官网下载)
我自己使用的是mysql-connector-java-8.0.28.jar的驱动,当然也可以使用mysql-connector-java-5.7.37.jar的驱动,但是在加载驱动的时候以及填写链接的时候会有不同之处,后面会提到。
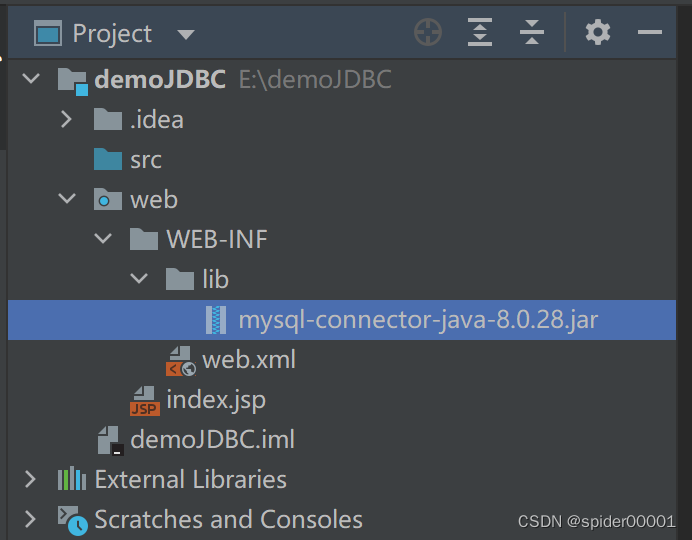
我们需要将使用到的jar包放到项目的lib目录下:
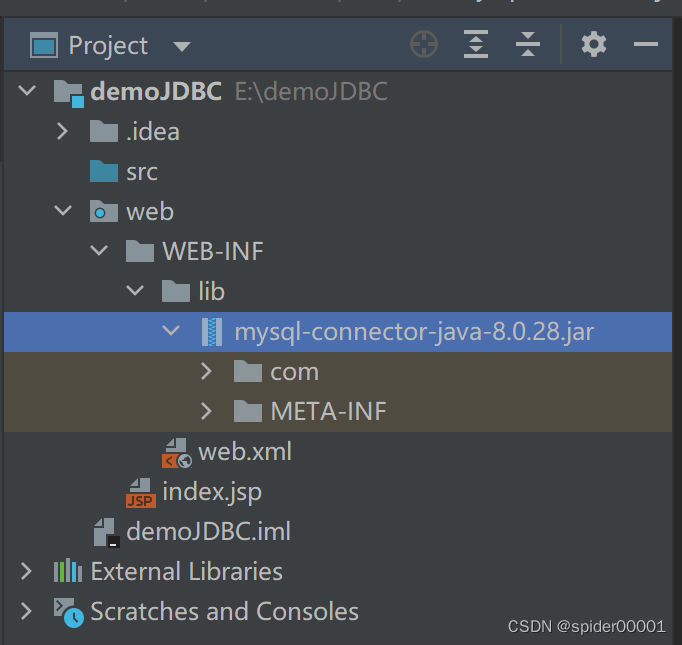
同时还需要在Project Structure中将lib文件夹添加为项目依赖,这样jar包才算是导入成功:
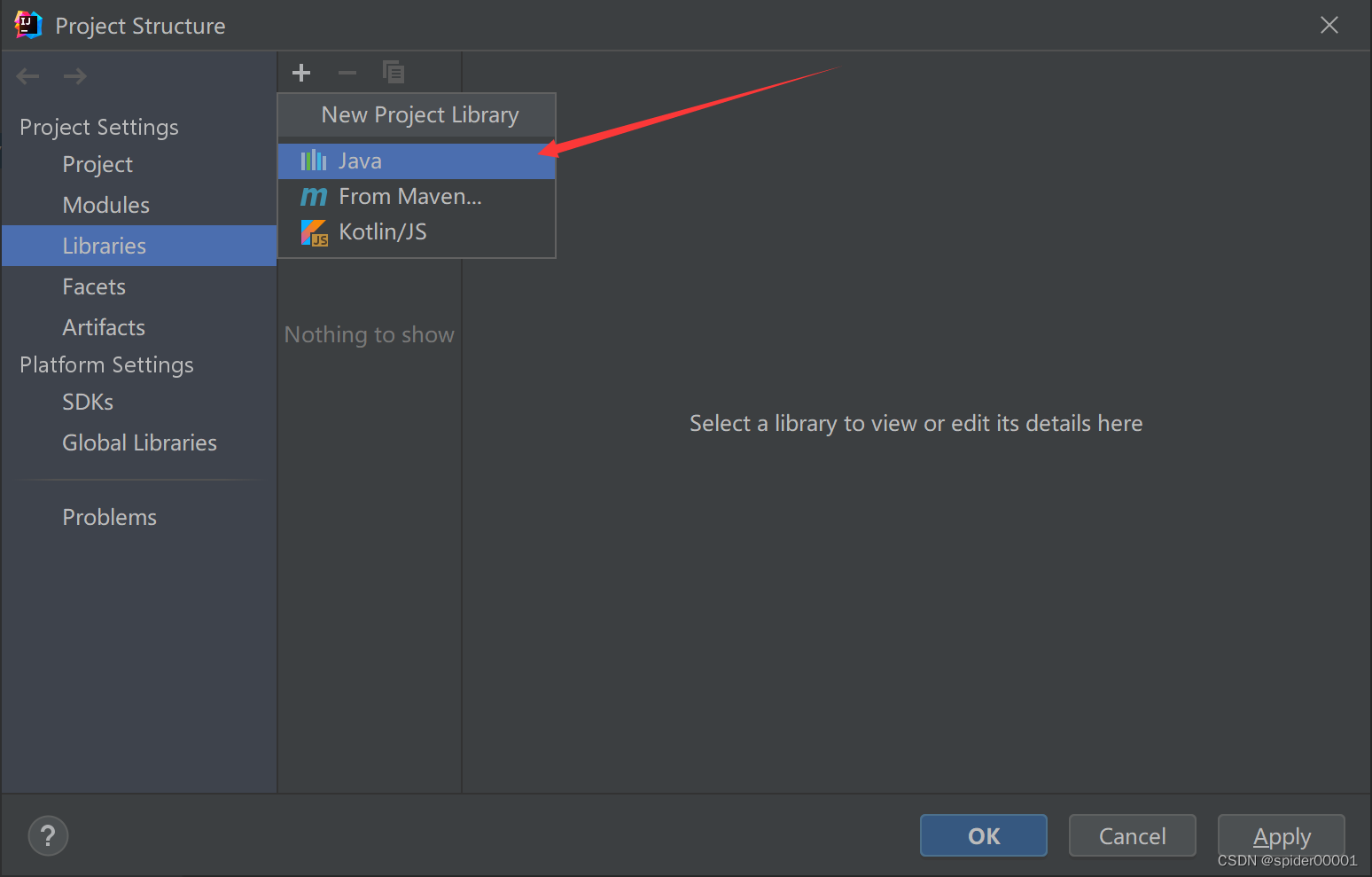
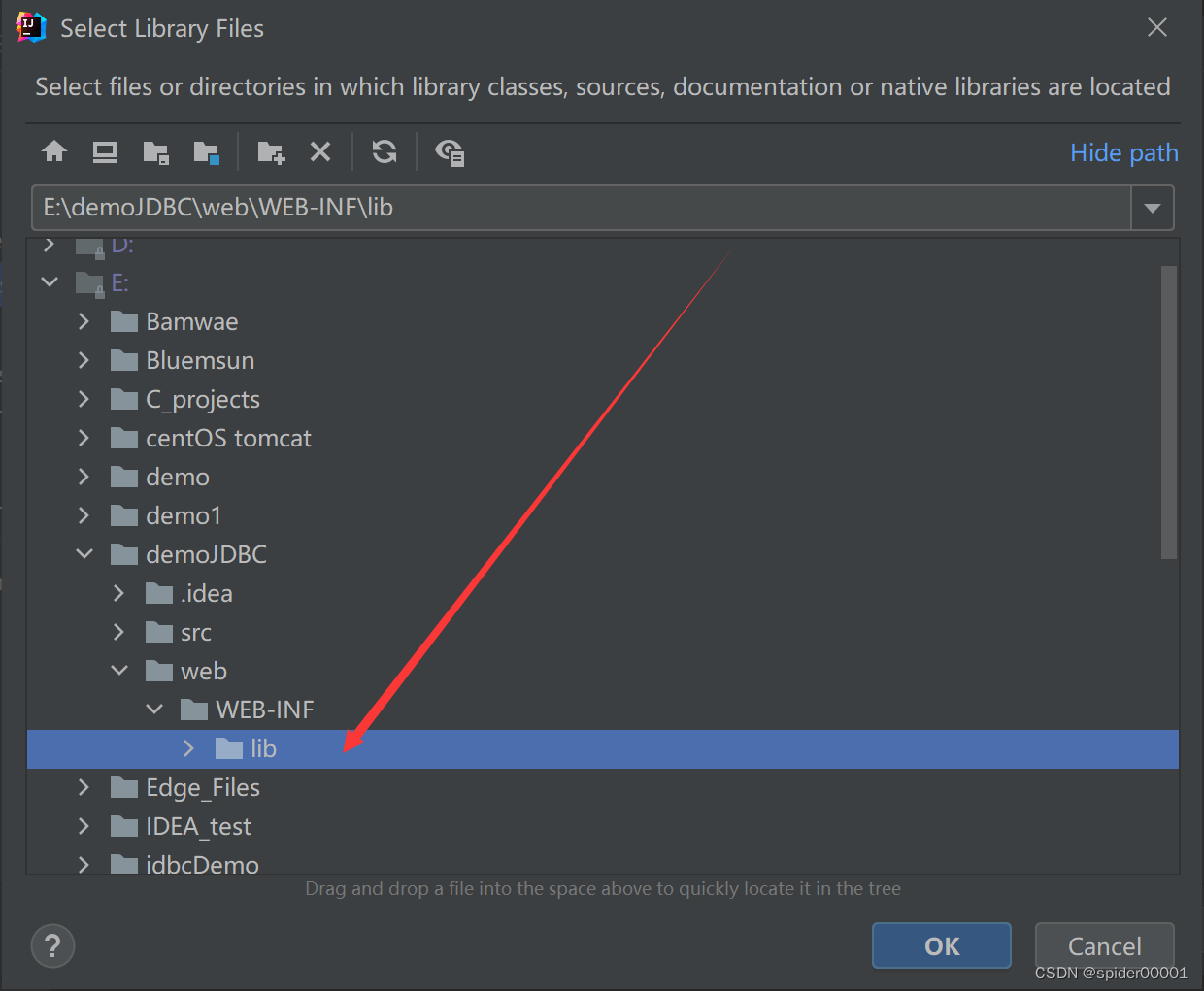

最后一路ok + apply即可。添加成功的示例:
2.使用java反射实现注册驱动(常用)
通过Class.forName(驱动类的类路径)方法来进行注册驱动:

Calss.forName:返回与具有给定字符串名称的类或接口关联的类对象。public class Demo1 { public static void main(String[] args) { try { Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver"); System.out.println("加载成功"); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
或者使用DriverManager.registerDriver()注册驱动:

DriverManager:用于管理一组 JDBC 驱动程序的基本服务。public class Demo1 { public static void main(String[] args) { try { java.sql.Driver driver = new com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver();//父类引用指向子类对象 DriverManager.registerDriver(driver); System.out.println("加载成功"); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
我们可以发现,com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver 实现了 java.sql.Driver接口。
这么做的原因是因为每一个数据库都有自己的底层原理,实现的原理也不一样。Java程序员在使用数据库时,只要实现这个的接口就可以,而接口的具体实现由各大数据库厂家来实现,我们只需要去官网下载即可。3.获取与数据库的连接
- 协议连接格式
协议名:子协议://IP地址或服务器名:端口号/数据库名?参数=参数值
例如:jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/book?characterEncoding=utf8&serverTimezone=GMT&useSSL=false
参数characterEncoding可以防止乱码出现,通常设置为utf8
参数serverTimezone用来设置时区,可以为GMT,也可以是中国标准时间Asia/Shanghai
参数useSSL用来设置是否使用ssl连接,目前学习jdbc不建议建立SSL连接,所以可设置为false。
package com.bluemsun.demo; import java.sql.Connection; import java.sql.DriverManager; public class Demo2 { public static void main(String[] args) { try { Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver"); /** * 建立与数据库的Connection连接,需要提供: * 数据库所处于的ip:127.0.0.1 或者 localhost (本机) * 数据库的端口号: 3306 (mysql专用端口号) * 数据库名称: books * 编码方式: UTF-8 * 时区: GMT (8版本的驱动要添加,5版本可以不写) * 是否使用SSL连接: false (8版本的驱动要添加,5版本可以不写) * 账号: root * 密码: root */ String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/books?characterEncoding=utf8&serverTimezone=GMT&useSSL=false"; String username = "root"; String password = "root"; Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, username, password); System.out.println("连接成功:"+connection); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
为了提高代码复用性,建议写一个JDBCUtil类方便我们操作数据库:
public class JDBCUtil { //注意:必须加上useServerPrepStmts=true才能开启mysql的预编译。 // 必须加上rewriteBatchedStatements=true才能开启mysql批处理 private static final String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/books?characterEncoding=utf8&serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai&useSSL=false&rewriteBatchedStatements=true&useServerPrepStmts=true"; private static final String username = "root"; private static final String password = "root"; //初始化驱动 static { try { Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver"); } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } //获取连接 public static Connection getConnection(){ Connection conn = null; try { conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url,username,password); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } return conn; } /** * 关闭连接 * 注意关闭顺序:ResultSet -> Statement -> Connection */ public static void close(Connection connection, Statement statement, ResultSet resultSet){ if (resultSet != null) { try { resultSet.close(); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } if (statement != null) { try { statement.close(); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } if (connection != null) { try { connection.close(); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
测试demo
public class Demo3 { public static void main(String[] args) { Connection connection = null; Statement statement = null; try { connection = JDBCUtil.getConnection(); statement = connection.createStatement(); System.out.println(connection); System.out.println(statement); JDBCUtil.close(connection,statement,null); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
三、执行SQL语句
1.SQL语句的分类
SQL语言共分为四大类:数据查询语言DQL,数据操纵语言DML,数据定义语言DDL,数据控制语言DCL。
- 数据查询语言DQL(Data Query Language):是用来进行数据库中数据的查询的,即最常用的select语句。
- 数据操纵语言DML(Data Manipulation Language):是对数据库对象运行数据访问工作的指令集,以insert、update、delete三种指令为核心,分别代表插入、更新与删除。
- 数据定义语言DDL(Data Definition Languages): 对数据库内部的对象进行创建、删除、修改等操作,例如create、drop、alter等。【这类语句我们一般不会去写,因为这类操作我们可以通过可视化界面,例如navicat完成】
- 数据控制语言DCL(Data Control Language):用于控制不同数据段直接的许可和访问级别的语句。这些语句定义了数据库、表、字段、用户的访问权限和安全级别。【这类语句我们一般不会遇到】
我们最常用的SQL语句是DQL和DML。
2.executeQuery方法
执行DQL语句使用的方法为:executeQuery(sql语句),返回值为ResultSet类型的对象。
ReusltSet常用的方法:- reusltSet.next():返回值为boolean类型,表示是否有下一个元素,若有则返回true,反之返回false。
- resultSet.getInt(数据库字段名或者字段的位置) :返回值为int类型,表示获取查询结果集中,当前元组指定字段的数据,并且转换为int类型。
- resultSet.getString(数据库字段名或者字段的位置) :返回值为String类型,表示获取查询结果集中,当前元组指定字段的数据,并且转换为String类型。
getDouble、getByte等同理
注意:字段的位置是从 1 开始的public class Demo4 { public static void main(String[] args) { Demo4 demo4 = new Demo4(); demo4.test1(); // demo4.test2(); } public void test1() { Connection connection = null; Statement statement = null; ResultSet resultSet = null; try { connection = JDBCUtil.getConnection(); statement = connection.createStatement(); String sql = "select * from books.tb_user where id = 1"; resultSet = statement.executeQuery(sql); while (resultSet.next()) { int id = resultSet.getInt("id"); String username = resultSet.getString(2); Double height = resultSet.getDouble("height"); System.out.println("id: "+id); System.out.println("username: "+username); System.out.println("height: "+height); } } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { JDBCUtil.close(connection,statement,resultSet); } } //如果查询结构集中的字段起了别名,则在获取时需要使用别名获取 public void test2() { Connection connection = null; Statement statement = null; ResultSet resultSet = null; try { connection = JDBCUtil.getConnection(); statement = connection.createStatement(); String sql = "select id, username, password, age, height as h, money from books.tb_user where id = 1"; resultSet = statement.executeQuery(sql); while (resultSet.next()) { int id = resultSet.getInt("id"); String username = resultSet.getString(2); Double height = resultSet.getDouble("h"); System.out.println("id: "+id); System.out.println("username: "+username); System.out.println("height: "+height); } } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { JDBCUtil.close(connection,statement,resultSet); } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
3.executeUpdate方法
执行DML,DDl语句使用的方法为:executeUpdate(sql语句),返回值为受影响的行数。
public class Demo5 { public static void main(String[] args) { Connection connection = null; Statement statement = null; try { connection = JDBCUtil.getConnection(); statement = connection.createStatement(); String sql = "update books.tb_user set username = '汤姆' where id = 1"; int i = statement.executeUpdate(sql); System.out.println("影响行数: "+i); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { JDBCUtil.close(connection,statement,null); } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
4.PreparedStatement
PreparedStatement 与 Statement一样都是用来执行SQL语句的,但是他们之间也有区别:
- Statement存在SQL注入问题,prepareStatement不存在
- 代码可读性高,易于维护。
- 多次执行相似SQL语句时(sql语句结构相同,但是值不同),PreparedStatement 性能比Statement更好。因为在这个过程中PreparedStatement 的sql语句只编译一次。Statement是编译一次运行一次,而prepareStatement是编译一次运行N次。
- prepareStatement会在编译阶段做类型的安全检查。
public class Demo6 { public static void main(String[] args) { Demo6 demo6 = new Demo6(); // demo6.test1(); // demo6.test2(111.11, 666, " 'aaa' or 1 = 1 "); // demo6.test3(111.11, 666, " 'aaa' or 1 = 1 "); // demo6.test4(); // demo6.test5(); // demo6.test6(); // demo6.test7(); } public void test1() { Connection connection = null; PreparedStatement preparedStatement = null; ResultSet resultSet = null; try { connection = JDBCUtil.getConnection(); String sql = "select * from books.tb_user where username = ? and age = ?"; preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql); //注意:这里的序号是从1开始的 preparedStatement.setString(1,"Tom"); preparedStatement.setInt(2,20); resultSet = preparedStatement.executeQuery(); while (resultSet.next()) { Double height = resultSet.getDouble("height"); System.out.println("height: "+height); } } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { JDBCUtil.close(connection,preparedStatement,resultSet); } } //使用Statement会有sql注入风险 public void test2(Double height, Integer age, String username) { Connection connection = null; Statement statement = null; ResultSet resultSet = null; try { connection = JDBCUtil.getConnection(); statement = connection.createStatement(); String sql = "select * from books.tb_user where height = "+ height + " and age = "+age + " and username = " + username; // "select * from books.tb_user where height = 111.11 and age = 666 and username = 'aaa' or 1 = 1" resultSet = statement.executeQuery(sql); while (resultSet.next()) { Integer id = resultSet.getInt("id"); String usernameRes = resultSet.getString("username"); String password = resultSet.getString("password"); Integer ageRes = resultSet.getInt("age"); Double heightRes = resultSet.getDouble("height"); System.out.println("id: "+id + " username: "+usernameRes + " password: "+password + " ageRes: "+ageRes + " height: "+ heightRes); } } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { JDBCUtil.close(connection,statement,resultSet); } } //使用PreparedStatement防止sql注入 public void test3(Double height, Integer age, String username) { Connection connection = null; PreparedStatement preparedStatement = null; ResultSet resultSet = null; try { connection = JDBCUtil.getConnection(); String sql = "select * from books.tb_user where height = ? and age = ? and username = ?"; preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql); // 代码可读性高,易于维护。 preparedStatement.setString(1,username); //注意:这里的序号是从1开始的 preparedStatement.setInt(2,age); preparedStatement.setDouble(3,height); resultSet = preparedStatement.executeQuery(); while (resultSet.next()) { Integer id = resultSet.getInt("id"); String usernameRes = resultSet.getString("username"); String password = resultSet.getString("password"); Integer ageRes = resultSet.getInt("age"); Double heightRes = resultSet.getDouble("height"); System.out.println("id: "+id + " username: "+usernameRes + " password: "+password + " ageRes: "+ageRes + " height: "+ heightRes); } } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { JDBCUtil.close(connection,preparedStatement,resultSet); } } /** * 测试插入10000条数据 三种方式用时比较 */ //使用Statement对象 public void test4() { Connection connection = null; Statement statement = null; try { //设置不自动提交,等到所有数据都传输完成以后,最后一块提交 connection = JDBCUtil.getConnection(); connection.setAutoCommit(false); Long beginTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); statement = connection.createStatement(); for (int i = 100000; i>0; i--) { String sql = "insert into books.tb_test(number) values(" + i + ")"; statement.executeUpdate(sql); } connection.commit(); //最后打开自动提交,避免影响其他自动提交的操作 connection.setAutoCommit(true); Long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); //计算时间 System.out.println("Statement用时:"+(endTime-beginTime)+"毫秒"); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { JDBCUtil.close(connection,statement,null); } } //使用PreparedStatement对象 public void test5() { Connection connection = null; PreparedStatement preparedStatement = null; try { //设置不自动提交,等到所有数据都传输完成以后,最后一块提交 connection = JDBCUtil.getConnection(); connection.setAutoCommit(false); Long beginTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); String sql = "insert into books.tb_test(number) values(?)"; preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql); for (int i = 100000; i > 0; i--) { preparedStatement.setInt(1, i); preparedStatement.executeUpdate(); } connection.commit(); //最后打开自动提交,避免影响其他自动提交的操作 connection.setAutoCommit(true); Long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); //计算时间 System.out.println("PreparedStatement用时:"+(endTime-beginTime)+"豪秒"); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { JDBCUtil.close(connection,preparedStatement,null); } } //PreparedStatement + 批处理 (注意: mysql服务器默认是关闭批处理的,我们需要通过一个参数让mysql开启批处理的支持: rewriteBatchedStatements=true ) /** * PreparedStatement + 批处理的使用情景:一次需要更新数据库表多条记录。 * 优点:减少和SQL引擎交互的次数,再次提高效率,相似语句只编译一次,减少编译次数。 * */ public void test6() { Connection connection = null; PreparedStatement preparedStatement = null; try { //设置不自动提交,等到所有数据都传输完成以后,最后一块提交 connection = JDBCUtil.getConnection(); connection.setAutoCommit(false); Long beginTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); String sql = "insert into books.tb_test(number) values(?)"; preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql); for (int i = 100000; i > 0; i --) { preparedStatement.setInt(1, i); //添加到同一个批处理中 preparedStatement.addBatch(); //缓存1000个sql,执行一次数据库插入的交互 if (i % 1000 == 0) { //执行batch preparedStatement.executeBatch(); //清空batch preparedStatement.clearBatch(); } } //统一提交数据 connection.commit(); //最后打开自动提交,避免影响其他自动提交的操作 connection.setAutoCommit(true); Long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); System.out.println("PreparedStatement + 批处理用时:"+(endTime-beginTime)+"豪秒");//计算时间 } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
- 134
- 135
- 136
- 137
- 138
- 139
- 140
- 141
- 142
- 143
- 144
- 145
- 146
- 147
- 148
- 149
- 150
- 151
- 152
- 153
- 154
- 155
- 156
- 157
- 158
- 159
- 160
- 161
- 162
- 163
- 164
- 165
- 166
- 167
- 168
- 169
- 170
- 171
- 172
- 173
- 174
- 175
- 176
- 177
- 178
- 179
- 180
- 181
- 182
- 183
- 184
- 185
- 186
- 187
- 188
- 189
- 190
- 191
- 192
- 193
- 194
- 195
- 196
- 197
- 198
- 199
- 200
- 201
- 202
5.execute方法,executeUpdate方法与executeQuery方法
execute方法可以执行任何SQL语句,返回类型为布尔类型,若有结果集则为true,否则为false。
executeUpdate方法只可以执行DML数据操纵语言和DDL数据定义语言,返回受影响的行数。
executeQuery方法只可以执行DQL数据查询语言,返回值为ResultSet返回结果集。四、事务
- 概念:数据库的事务(Transaction)是一种机制、一个操作序列,包含了一组数据库操作命令。事务把所有的命令作为一个整体一起向系统提交或撤销操作请求,即这一组数据库命令要么都执行,要么都不执行,因此事务是一个不可分割的工作逻辑单元。
- 事务是一个原子操作。是一个最小执行单元。可以甶一个或多个SQL语句组成。
- 在同一个事务当中,所有的SQL语句都成功执行时,整个事务成功,有一个SQL语句执行失败,整个事务都执行失败。
-
事务具有 4 个特性,即原子性、一致性、隔离性、和持久性,这 4 个特性通常简称为 ACID。
1.原子性(Atomicity)
事务是一个不可分割的单位,事务中的所有SQL等操作要么都发生,要么都不发生。
2.一致性(Consistency)
事务发生前和发生后,数据的完整性必须保持一致。
3.隔离性(Isolation)
当并发访问数据库时,一个正在执行的事务在执行完毕前,对应其他的会话是不可见的,多个并发事务之间的数据是相互隔离的。
4.持久性(Durability)
一个事务一旦被提交,它对数据库中的数据改变就是永久性的。如果出了错误,事务也不允许撤销。 -
什么情况下要使用事务?
举一个例子,假如我们去超市购物,在付款时,我们选择使用wx支付,会进行以下操作:
(1)我:账户余额 -100
(2)售货员:账户余额 +100
如果步骤(1)执行成功,而步骤(2)执行失败,那么就会出现:我的账户余额-100,而售货员的账户余额没有变化,这是一个很严重的利益问题。
所以,为了解决这样的问题,我们要用到事务。
上述情况,如果使用了事务,在事务中出现错误的时候,整个执行操作都会被自动回滚(或者也可以自己调用rollback方法进行回滚),这样就保证的数据的正确。
public class Demo7 { public static void main(String[] args) { Connection connection = null; PreparedStatement preparedStatement = null; BigDecimal money = BigDecimal.valueOf(100.00); String sql = "update books.tb_user set money = money - ? where id = ?"; try { connection = JDBCUtil.getConnection(); //关闭自动提交 connection.setAutoCommit(false); preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql); preparedStatement.setBigDecimal(1,money); preparedStatement.setInt(2,1); int i = preparedStatement.executeUpdate();//返回影响行数 if (i == 1) { preparedStatement.setBigDecimal(1,money); preparedStatement.setInt(2,2); int t = preparedStatement.executeUpdate(); if (t == 1) { System.out.println("转账成功"); } else { connection.rollback(); System.out.println("事务回滚"); throw new RuntimeException("转账失败"); } } else { connection.rollback(); System.out.println("事务回滚"); throw new RuntimeException("转账失败"); } //手动提交 connection.commit(); } catch (Exception e) { try { connection.rollback(); } catch (SQLException exception) { exception.printStackTrace(); } e.printStackTrace(); } finally { JDBCUtil.close(connection,preparedStatement,null); } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
五、ORM
对象关系映射(Object Relational Mapping,简称ORM)模式是一种为了解决面向对象与关系数据库存在的互不匹配的现象的技术。简单的说,ORM是通过使用描述对象和数据库之间映射的元数据,将程序中的对象自动持久化到关系数据库中。
可以理解为一个对象对应数据库中的一条记录。六、DAO
DAO(Data Access Object)是一个数据访问接口。数据访问:顾名思义就是与数据库打交道。夹在业务逻辑与数据库资源中间。
简单来说,就是把和数据库打交道的逻辑,都放到DAO层,进行功能的聚合。不向外暴露与数据库交互的逻辑处理,也就是实现功能解耦。
-
相关阅读:
Linux系统中配置系统设置
ES6 Proxy
uniapp 之 充值 微信支付下 之 传递输入金额参数
P10 属性分组
基于图数据库的元数据血缘关系分析技术研究与实践
WebRTC研究:audio 丢包判断
操作系统computer operate system
力扣(LeetCode)799. 香槟塔(C++)
Qt鼠标点击事件处理:按Escape键退出程序
Codeforces 802I - Fake News(hard) 后缀数组+单调栈
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_51299174/article/details/125513434
