-
Netty11-编码和解码-Protobuf
基本介绍
- 编写网络应用程序时,因为数据在网络中传输的都是二进制字节码数据,在发送数据时就需要编码,接收数据时就需要解码
- codec(编解码器) 的组成部分有两个:**decoder(解码器)**和 encoder(编码器)。encoder 负责把业务数据转换成字节码数据,decoder 负责把字节码数据转换成业务数据

Netty 本身的编码解码的机制和问题分析
-
Netty 自身提供了一些 codec(编解码器)
-
Netty 提供的编码器
• StringEncoder,对字符串数据进行编码
• ObjectEncoder,对 Java 对象进行编码 -
Netty 提供的解码器
• StringDecoder, 对字符串数据进行解码
• ObjectDecoder,对 Java 对象进行解码 -
Netty 本身自带的 ObjectDecoder 和 ObjectEncoder 可以用来实现 POJO 对象或各种业务对象的编码和解码,底层使用的仍是 Java 序列化技术 , 而Java 序列化技术本身效率就不高,存在如下问题
• 无法跨语言
• 序列化后的体积太大,是二进制编码的 5 倍多。
• 序列化性能太低
解决方案-Protobuf
Protobuf基本介绍和使用示意图
- Protobuf 是 Google 发布的开源项目,全称 Google Protocol Buffers,是一种轻便高效的结构化数据存储格式,可以用于结构化数据串行化,或者说序列化。它很适合做数据存储或 RPC[远程过程调用 remote procedure call ] 数据交换格式 。目前很多公司 http+json 逐渐转换为 tcp+protobuf
- 参考文档 : https://developers.google.com/protocol-buffers/docs/proto 语言指南
- Protobuf 是以 message 的方式来管理数据的.
- 支持跨平台、跨语言,即[客户端和服务器端可以是不同的语言编写的] (支持目前绝
大多数语言,例如 C++、C#、Java、python 等)
Protobuf基本介绍和使用示意图
- 高性能,高可靠性
- 使用 protobuf 编译器能自动生成代码,Protobuf 是将类的定义使用.proto 文件进行描述。说明,在idea 中编写 .proto 文件时,会自动提示是否下载 .ptotot 编写插件. 可以让语法高亮。
- 然后通过 protoc.exe 编译器根据.proto 自动生成.java 文件
- protobuf 使用示意图
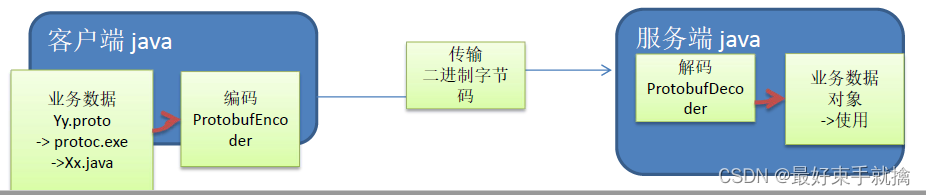
.proto Type C++ Type Java Type Go Type PHP Type double double double float64 float float float float float32 float int32 int32 int int32 integer int64 in64 long int64 integer/string uint32 uint32 int uint32 integer uint64 uint64 long uint64 integer/string sint32 int32 int int32 integer sint64 int64 long int64 integer/string fixed3 uint32 int uint32 integer fixed6 uint64 long uint64 integer/string sfixed int32 int int32 integer sfixed int64 long int64 integer/string bool bool boolean bool boolean string string String string string bytes string yteString []byte string Protobuf快速入门实例
- 客户端可以发送一个Student PoJo 对象到服务器 (通过 Protobuf 编码)
- 服务端能接收Student PoJo 对象,并显示信息(通过 Protobuf 解码)
1. 编辑 .proto文件
syntax = "proto3"; //版本 option java_outer_classname = "SpuPOJO";//生成的外部类名,同时也是文件名 //protobuf 使用message 管理数据 message SpuPOJO { //会在 StudentPOJO 外部类生成一个内部类 Student, 他是真正发送的POJO对象 int32 id = 1; // Student 类中有 一个属性 名字为 id 类型为int32(protobuf类型) 1表示属性序号,不是值 string name = 2; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
2.使用protoc.exe生成.java文件
将标编辑好的.proto文件放入主目录下
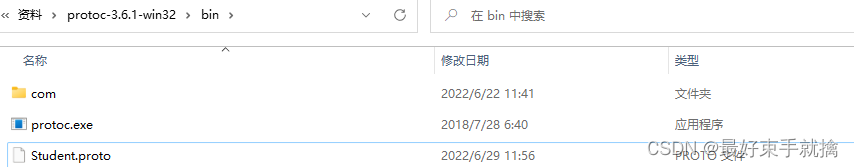
进入cmdprotoc.exe --java_out=. Student.proto- 1
生成.java
编辑客户端
1.在客户端加入Protobuf的编码器
package com.atguigu.netty.codec; import io.netty.bootstrap.Bootstrap; import io.netty.channel.ChannelFuture; import io.netty.channel.ChannelInitializer; import io.netty.channel.ChannelPipeline; import io.netty.channel.EventLoopGroup; import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup; import io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel; import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioSocketChannel; import io.netty.handler.codec.protobuf.ProtobufEncoder; public class NettyClient { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { //客户端需要一个事件循环组 EventLoopGroup group = new NioEventLoopGroup(); try { //创建客户端启动对象 //注意客户端使用的不是 ServerBootstrap 而是 Bootstrap Bootstrap bootstrap = new Bootstrap(); //设置相关参数 bootstrap.group(group) //设置线程组 .channel(NioSocketChannel.class) // 设置客户端通道的实现类(反射) .handler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() { @Override protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception { ChannelPipeline pipeline = ch.pipeline(); //在pipeline中加入 ProtoBufEncoder 编码器 pipeline.addLast("encoder", new ProtobufEncoder()); pipeline.addLast(new NettyClientHandler()); //加入自己的处理器 } }); System.out.println("客户端 ok.."); //启动客户端去连接服务器端 //关于 ChannelFuture 要分析,涉及到netty的异步模型 ChannelFuture channelFuture = bootstrap.connect("127.0.0.1", 6668).sync(); //给关闭通道进行监听 channelFuture.channel().closeFuture().sync(); }finally { group.shutdownGracefully(); } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
2.发送StudentPOJO
package com.atguigu.netty.codec; import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf; import io.netty.buffer.Unpooled; import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext; import io.netty.channel.ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter; import io.netty.util.CharsetUtil; public class NettyClientHandler extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter { //当通道就绪就会触发该方法 @Override public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception { //发生一个Student 对象到服务器 StudentPOJO.Student student = StudentPOJO.Student.newBuilder().setId(1).setName("我是StudentPOJO").build(); //Teacher , Member ,Message ctx.writeAndFlush(student); } //当通道有读取事件时,会触发 @Override public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception { ByteBuf buf = (ByteBuf) msg; System.out.println("服务器回复的消息:" + buf.toString(CharsetUtil.UTF_8)); System.out.println("服务器的地址: "+ ctx.channel().remoteAddress()); } @Override public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception { cause.printStackTrace(); ctx.close(); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
编辑服务端
加入解码器并指定对哪种对象进行解码
package com.atguigu.netty.codec; import com.google.protobuf.ByteString; import io.netty.bootstrap.ServerBootstrap; import io.netty.channel.*; import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup; import io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel; import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioServerSocketChannel; import io.netty.handler.codec.protobuf.ProtobufDecoder; public class NettyServer { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { //创建BossGroup 和 WorkerGroup //说明 //1. 创建两个线程组 bossGroup 和 workerGroup //2. bossGroup 只是处理连接请求 , 真正的和客户端业务处理,会交给 workerGroup完成 //3. 两个都是无限循环 //4. bossGroup 和 workerGroup 含有的子线程(NioEventLoop)的个数 // 默认实际 cpu核数 * 2 EventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(1); EventLoopGroup workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(); //8 try { //创建服务器端的启动对象,配置参数 ServerBootstrap bootstrap = new ServerBootstrap(); //使用链式编程来进行设置 bootstrap.group(bossGroup, workerGroup) //设置两个线程组 .channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class) //使用NioSocketChannel 作为服务器的通道实现 .option(ChannelOption.SO_BACKLOG, 128) // 设置线程队列得到连接个数 .childOption(ChannelOption.SO_KEEPALIVE, true) //设置保持活动连接状态 // .handler(null) // 该 handler对应 bossGroup , childHandler 对应 workerGroup .childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {//创建一个通道初始化对象(匿名对象) //给pipeline 设置处理器 @Override protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception { ChannelPipeline pipeline = ch.pipeline(); //在pipeline加入ProtoBufDecoder 解码器 //StudentPOJO.Student.getDefaultInstance()指定对哪种对象进行解码 pipeline.addLast("decoder", new ProtobufDecoder(StudentPOJO.Student.getDefaultInstance())); pipeline.addLast(new NettyServerHandler()); } }); // 给我们的workerGroup 的 EventLoop 对应的管道设置处理器 System.out.println(".....服务器 is ready..."); //绑定一个端口并且同步, 生成了一个 ChannelFuture 对象 //启动服务器(并绑定端口) ChannelFuture cf = bootstrap.bind(6668).sync(); //给cf 注册监听器,监控我们关心的事件 cf.addListener((ChannelFutureListener) future -> { if (cf.isSuccess()) { System.out.println("监听端口 6668 成功"); } else { System.out.println("监听端口 6668 失败"); } }); //对关闭通道进行监听 cf.channel().closeFuture().sync(); }finally { bossGroup.shutdownGracefully(); workerGroup.shutdownGracefully(); } } } `` ##### Handle ```java package com.atguigu.netty.codec; import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf; import io.netty.buffer.Unpooled; import io.netty.channel.*; import io.netty.util.CharsetUtil; /* 说明 1. 我们自定义一个Handler 需要继续netty 规定好的某个HandlerAdapter(规范) 2. 这时我们自定义一个Handler , 才能称为一个handler */ //public class NettyServerHandler extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter { public class NettyServerHandler extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler<StudentPOJO.Student> { //读取数据实际(这里我们可以读取客户端发送的消息) /* 1. ChannelHandlerContext ctx:上下文对象, 含有 管道pipeline , 通道channel, 地址 2. Object msg: 就是客户端发送的数据 默认Object */ @Override public void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, StudentPOJO.Student msg) throws Exception { //读取从客户端发送的StudentPojo.Student 继承SimpleChannelInboundHandler 可以指定对象 System.out.println("客户端发送的数据 id=" + msg.getId() + " 名字=" + msg.getName()); } // //读取数据实际(这里我们可以读取客户端发送的消息) // /* // 1. ChannelHandlerContext ctx:上下文对象, 含有 管道pipeline , 通道channel, 地址 // 2. Object msg: 就是客户端发送的数据 默认Object // */ @Override public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception { //读取从客户端发送的StudentPojo.Student 继承ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter的情况下 StudentPOJO.Student student = (StudentPOJO.Student) msg; System.out.println("客户端发送的数据 id=" + student.getId() + " 名字=" + student.getName()); } //数据读取完毕 @Override public void channelReadComplete(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception { //writeAndFlush 是 write + flush //将数据写入到缓存,并刷新 //一般讲,我们对这个发送的数据进行编码 ctx.writeAndFlush(Unpooled.copiedBuffer("hello, 客户端~(>^ω^<)喵1", CharsetUtil.UTF_8)); } //处理异常, 一般是需要关闭通道 @Override public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception { ctx.close(); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
- 134
- 135
- 136
- 137
- 138
- 139
- 140
- 141
- 142
- 143
- 144
- 145
- 146
- 147
快速入门实例2 Protobuf发送多类型
1.新建proto文件 并生成java文件
syntax = "proto3"; option optimize_for = SPEED; // 加快解析 option java_package="com.atguigu.netty.codec2"; //指定生成到哪个包下 option java_outer_classname="MyDataInfo"; // 外部类名, 文件名 //protobuf 可以使用message 管理其他的message message MyMessage { //定义一个枚举类型 enum DataType { StudentType = 0; //在proto3 要求enum的编号从0开始 WorkerType = 1; TestType = 2; } //用data_type 来标识传的是哪一个枚举类型 //1 是代表 data_type 是MyMessage里的第一个属性 DataType data_type = 1; //表示每次枚举类型最多只能出现其中的一个, 节省空间 oneof dataBody { Student student = 2; Worker worker = 3; Test test = 4; } } message Student { int32 id = 1;//Student类的属性 string name = 2; // } message Worker { string name=1; int32 age=2; } message Test { string name=1; int32 sex=2; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
Client
需要配置对哪种对象进行解析
//指定对哪种对象进行解码 pipeline.addLast("decoder", new ProtobufDecoder(MyDataInfo.MyMessage.getDefaultInstance()));- 1
- 2
package com.atguigu.netty.codec2; import com.atguigu.netty.codec.StudentPOJO; import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf; import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext; import io.netty.channel.ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter; import io.netty.util.CharsetUtil; import java.util.Random; public class NettyClientHandler extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter { //当通道就绪就会触发该方法 @Override public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception { //随机的发送Student 或者 Workder 对象 int random = new Random().nextInt(3); MyDataInfo.MyMessage myMessage = null; if(0 == random) { //发送Student 对象 myMessage = MyDataInfo.MyMessage.newBuilder().setDataType(MyDataInfo.MyMessage.DataType.StudentType).setStudent(MyDataInfo.Student.newBuilder().setId(5).setName("玉麒麟 卢俊义").build()).build(); } else { // 发送一个Worker 对象 myMessage = MyDataInfo.MyMessage.newBuilder().setDataType(MyDataInfo.MyMessage.DataType.WorkerType).setWorker(MyDataInfo.Worker.newBuilder().setAge(20).setName("老李").build()).build(); } ctx.writeAndFlush(myMessage); } //当通道有读取事件时,会触发 @Override public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception { ByteBuf buf = (ByteBuf) msg; System.out.println("服务器回复的消息:" + buf.toString(CharsetUtil.UTF_8)); System.out.println("服务器的地址: "+ ctx.channel().remoteAddress()); } @Override public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception { cause.printStackTrace(); ctx.close(); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
-
相关阅读:
chatgpt输出mysql常用语法汇总
Bean管理注解
字节一面后,我又看了一遍ThreadLocal核心原理
消除卡顿 mac MATLAB2022b m1/m2原生下载安装 教程
java计算机毕业设计员工信息管理系统源码+mysql数据库+系统+lw文档+部署
XXE漏洞详解:从基础到防御
C# 程序开机自动启动
MySQL第二弹
DEJA_VU3D - Cesium功能集 之 057-百度地图纠偏
Linux之父一语成谶:Valve拯救桌面版Linux,但新版本仍在分裂其生态
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_47409774/article/details/125489155
